Sulphuric Acid
Diunggah oleh
HarveyKhooHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Sulphuric Acid
Diunggah oleh
HarveyKhooHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Sulphuric Acid
Presentation by:
- Harvey Khoo
- Cara Chan
- Kheng Yong Guan
- Chan Joo Yuen
- Yeong Wan Chi
- Christopher Teoh
Properties of Sulphuric Acid
Non flammable under normal conditions
Highly reactive
Release toxic and irritating fumes when heated to decomposition
Gas-tight protective suits with breathing apparatus required for
fuming acid
Short-term inhalation may result in irritation of eyes and nose
with sore throat, cough
Short-term ingestion results in burns to the mouth and throat
Short-term skin exposure can result in irritation, swelling or burns
Short-term eye exposure may cause swelling, watering and
sensitivity to light
Long term inhalation leads to inflammation of the lungs
Uses of Sulphuric Acid
Used to remove oxides from the
surface of metal (metallurgy)
One of the most important industrial
chemicals
Used in manufacturing of almost all
products
Uses of Sulphuric Acid
18%
Making
Fertilizers
1%
38%
Paints
Chemicals
Detergents
12%
Removing rust
from steel
Other Uses
18%
13%
Mainly
used in producing fertilizers
a) Superphosphate fertilizers:
Sulphuric Acid + Carbon Phosphate
2H2SO4 + Ca3(PO4)2 Ca(H2PO4)2
b) Ammonia Sulphate fertilizers:
Sulphuric Acid + Ammonia
2NH3 + H2SO4 (NH4)2SO4
Sulphonic
acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to
form a sodium alkyl sulphonate, which is
detergent.
Manufacture of Sulphuric Acid
Sulphuric
acid is made from
sulphur dioxide, SO2, by the
Contact Process.
The raw materials used are
sulphur, air and water and it
consists of 3 stages.
Contact Process Stages
Stage 1
In the furnace, sulphur is burnt in dry air at a temperature
100C to produce sulphur dioxide
Step 1: In the burner
S + O2 SO2
Stage 2
In the converter, sulphur dioxide, SO2 and excess oxygen gas,
O2 are passed over a few plates of vanadium(V)oxide, V2O5
catalyst at 450C to produce sulphur trioxide, SO3.
2SO2 + O2 2SO3
Stage 3
In the absorber, the sulphur trioxide, SO3 is first reacted with concentration sulphuric acid,
H2SO4 to form a product called oleum.
Step 3: Absorption of SO3
SO3 + H2SO4 H2S2O7
The oleum, H2S2O7 is a dilute with water to produce concentrated sulphuric acid, H2SO4 in large
quantities.
Step 4: Hydration of oleum
H2S2O7 + H20 2H2SO4
The two reactions in the 3rd stage are equivalent to adding sulphur trioxide, SO3 directly to water.
SO3 + H20 H2S04
This reaction is not carried out in the industry because it is too vigorous.
It produces a large cloud of sulphuric acid mist. This mist is corrosive and pollutes the air.
Sulphur Dioxide and Environmental Pollution
Effects
towards humans:
- Coughing
- Bronchitis
- Chest Pain
- Lung diseases
- Shortness of Breath
Can
cause acid rain
Due to reaction of SO2, with rainwater
2SO2 + O2 + 2H2O 2H2SO4
Bad Effects of Acid Rain
Air Pollutions
Cause
respiratory
problems for
humans
Corrodes
buildings and
metal
structures
especially with
carbonate and
active metals
Soil Pollutions
pH value of the
soil decreases
Salts are
leached out of
the top soil
Roots of trees
are destroyed
Plants die of
malnutrition and
diseases
Water Pollutions
Lakes and
rivers becomes
acidic
A threat to
aquatic life
because the
decrease of the
pH value of the
water
Reducing Acid Rain
Most acids causing acid rain are from:
Sulphuric Acid
SO2 + H2O H2SO4
Sulphurous Acid
SO2 + H2O H2SO3
Carbonic Acid
CO2 + H2O H2CO3
But, it can be reduced by reacting the gas with: Calcium Carbonate
CaCO3 + SO2 CaSO3 + CO2
Calcium Oxide
CaO + SO2 CaSO3
4CaO + 4SO2 + 2O2 4CaSO4
Calcium Sulphate
2CaSo3 + O2 2CaSO4
Reducing the Acidity in the Lakes, River & Soil
It
can be reduced with the following
chemicals
Calcium Oxide
CaO + 2H+ Ca2+ + H2O
Calcium Hydroxide
Ca(OH)2 + 2H+ Ca2+ + 2H2O
Calcium Carbonate
CaCO3 + 2H Ca2+ + H2O + CO2
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
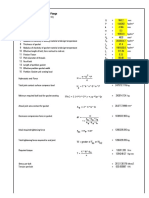
- Bolt Torque Calculation For Girth Flange (Ref.: Dennis Moss Procedure 2-10)Dokumen2 halamanBolt Torque Calculation For Girth Flange (Ref.: Dennis Moss Procedure 2-10)Manoj MulikBelum ada peringkat
- Unit - II Process in Organic Chemical manufacture-II HydrogenationDokumen15 halamanUnit - II Process in Organic Chemical manufacture-II HydrogenationMaahir AppBelum ada peringkat
- UreaDokumen86 halamanUreaAdi Ahmad100% (1)
- OSHAD-SF - TG - Occupational Air Quality Management v3.0 EnglishDokumen12 halamanOSHAD-SF - TG - Occupational Air Quality Management v3.0 EnglishNiel Brian VillarazoBelum ada peringkat
- Heat and Mass Transfer - E. R. G. Eckert and R. M. Drake PDFDokumen46 halamanHeat and Mass Transfer - E. R. G. Eckert and R. M. Drake PDFAnaQatarina50% (4)
- The Double Contact Process For Sulfuric Acid ProductionDokumen3 halamanThe Double Contact Process For Sulfuric Acid Productionshahira anuarBelum ada peringkat
- Sulfuric AcidDokumen14 halamanSulfuric AcidAkh KreshnaBelum ada peringkat
- Graduation-Project - Sulfuric AcidDokumen195 halamanGraduation-Project - Sulfuric AcidMuntazer QasimBelum ada peringkat
- Elements and Compounds PowerPointDokumen19 halamanElements and Compounds PowerPointRelayer 66Belum ada peringkat
- Clarus500 580UserGuideDokumen442 halamanClarus500 580UserGuideSelvaraj VenkatesanBelum ada peringkat
- Sulfuric AcidDokumen3 halamanSulfuric AcidSyed HashmiBelum ada peringkat
- Packing FactorDokumen80 halamanPacking FactorRabya Sana100% (1)
- Chapter 2: Sulfur & Sulfuric Acid Chapter 2: Sulfur & Sulfuric AcidDokumen20 halamanChapter 2: Sulfur & Sulfuric Acid Chapter 2: Sulfur & Sulfuric AcidabichedBelum ada peringkat
- Material and Energy BalanceDokumen28 halamanMaterial and Energy Balancemuhammad arslan100% (1)
- Steam To Carbon Ratio Calculations: InstructionsDokumen8 halamanSteam To Carbon Ratio Calculations: InstructionsSuresh Ramakrishnan100% (1)
- Industrial Preparation of Sulphuric AcidDokumen20 halamanIndustrial Preparation of Sulphuric Acidvishnu_c_singhBelum ada peringkat
- Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nox: Kushagra AbhishekDokumen21 halamanSelective Catalytic Reduction of Nox: Kushagra AbhishekKushagra AbhishekBelum ada peringkat
- What Are The Uses of Sulphuric Acid in Daily LifeDokumen18 halamanWhat Are The Uses of Sulphuric Acid in Daily LifeAi Syah50% (2)
- Contact Process: Manufacture of Sulphuric AcidDokumen3 halamanContact Process: Manufacture of Sulphuric AcidfatahleeBelum ada peringkat
- Msds Molten SulphurDokumen9 halamanMsds Molten SulphurLily DianaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1 - Sulfur and Sulfuric AcidDokumen9 halamanLecture 1 - Sulfur and Sulfuric AcidNayan HalderBelum ada peringkat
- Nitric AcidDokumen14 halamanNitric Acidmalini2201Belum ada peringkat
- Modeling and Simulation of Methanation Catalytic Reactor in Ammonia UnitDokumen8 halamanModeling and Simulation of Methanation Catalytic Reactor in Ammonia UnitMartin NizBelum ada peringkat
- The Industrial Manufacture of Sulphuric Acid (H SO) : Contact ProcessDokumen7 halamanThe Industrial Manufacture of Sulphuric Acid (H SO) : Contact Processprinc123Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture 20 Sodium Thiosulfate PDFDokumen5 halamanLecture 20 Sodium Thiosulfate PDFPutri AzzahraBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Group 13: Sodium Hydroxide Production: CH 1060 Process Engineering FundamentalsDokumen61 halamanAssignment Group 13: Sodium Hydroxide Production: CH 1060 Process Engineering FundamentalsHarshil JainBelum ada peringkat
- NitrationDokumen40 halamanNitrationM Fahad Shahid Ali100% (1)
- Alum Manufacturing ProcessDokumen13 halamanAlum Manufacturing ProcessKishor JalanBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Exchanger DesignDokumen74 halamanHeat Exchanger DesignChisom ChubaBelum ada peringkat
- Amine Gas TreatingDokumen3 halamanAmine Gas Treatinghmudassir_1Belum ada peringkat
- Plant Design Process SimulationDokumen20 halamanPlant Design Process SimulationABRAR ABDULLAHBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Statement: To Design A UREA PLANT of Capacity 1000 Ton/day Using Ammonia and Carbon Di-Oxide As Raw MaterialDokumen24 halamanProblem Statement: To Design A UREA PLANT of Capacity 1000 Ton/day Using Ammonia and Carbon Di-Oxide As Raw MaterialaamliagarBelum ada peringkat
- Sulfuric Acid - Wikipedia PDFDokumen94 halamanSulfuric Acid - Wikipedia PDFrajesh indukuriBelum ada peringkat
- Peroxo Compounds, InorganicDokumen32 halamanPeroxo Compounds, InorganicKilsys AlvaradoBelum ada peringkat
- Process Development For Metal SoapsDokumen98 halamanProcess Development For Metal SoapsAlex RichardBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4: Energy Balance: I Ki PiDokumen63 halamanChapter 4: Energy Balance: I Ki PiAhmed Qutb Akmal100% (1)
- Catalytic Hydrogenation of Organic Polymers by Mixed Transition Metal OxidesDokumen8 halamanCatalytic Hydrogenation of Organic Polymers by Mixed Transition Metal OxidesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 3: Comprehensive Report: Manyoni NDokumen5 halamanExperiment 3: Comprehensive Report: Manyoni NMpilo ManyoniBelum ada peringkat
- Arc Discharge ApplicationDokumen15 halamanArc Discharge ApplicationHong Chun LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Mass Transfer OperationsDokumen77 halamanMass Transfer OperationsNhã UyênBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal Denitration of Ammonium Nitrate Solution in A Fluidized-Bed ReactorDokumen10 halamanThermal Denitration of Ammonium Nitrate Solution in A Fluidized-Bed ReactorgauravBelum ada peringkat
- SulfonationDokumen48 halamanSulfonationArsal MaqboolBelum ada peringkat
- Oxidation of Sulfur Dioxide Heterogeneous CatalystDokumen13 halamanOxidation of Sulfur Dioxide Heterogeneous Catalysthafidz maBelum ada peringkat
- Phosphoric Acid PDFDokumen24 halamanPhosphoric Acid PDFabderrahimnBelum ada peringkat
- Overview of The ProcessDokumen10 halamanOverview of The ProcessChaitanya PottiBelum ada peringkat
- Nowak 1966Dokumen9 halamanNowak 1966adedwi utamaBelum ada peringkat
- Ethylene 2520oxide Methods 2520of 2520productionDokumen25 halamanEthylene 2520oxide Methods 2520of 2520productionmartin_2104Belum ada peringkat
- Determination of Iron in Pharmaceutical PreparationsDokumen3 halamanDetermination of Iron in Pharmaceutical PreparationsVycBelum ada peringkat
- SulfonationDokumen29 halamanSulfonationamona2020100% (1)
- 10.2.2 PCS Phosphate's New 4500 STPD Sulfuric Acid Plant in AuroraDokumen20 halaman10.2.2 PCS Phosphate's New 4500 STPD Sulfuric Acid Plant in AuroraCarlosBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Absorption ReportDokumen15 halamanGas Absorption ReportdaabgchiBelum ada peringkat
- Production of Urea Formaldehyde UF85-947312 - 2Dokumen66 halamanProduction of Urea Formaldehyde UF85-947312 - 2Sanzar Rahman 1621555030Belum ada peringkat
- Chlorine: International Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid StateDari EverandChlorine: International Thermodynamic Tables of the Fluid StateBelum ada peringkat
- Halogen ChemistryDari EverandHalogen ChemistryViktor GutmannPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Oxidation of Organic Compounds: Medium Effects in Radical ReactionsDari EverandOxidation of Organic Compounds: Medium Effects in Radical ReactionsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Recent Advances in the Science and Technology of Zeolites and Related Materials: Proceedings of the 14th International Zeolite Conference, Cape Town, South Africa, 25-30th April 2004Dari EverandRecent Advances in the Science and Technology of Zeolites and Related Materials: Proceedings of the 14th International Zeolite Conference, Cape Town, South Africa, 25-30th April 2004Belum ada peringkat
- Electronic Configuration: By: Cyra Eunicer. TanaelDokumen17 halamanElectronic Configuration: By: Cyra Eunicer. TanaelDegala, Jan Marlou V.Belum ada peringkat
- Behavior DS MM247LC (Bae2001)Dokumen6 halamanBehavior DS MM247LC (Bae2001)Alex CostaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 2Dokumen65 halaman1 2AQEESHA NUWAIRA BINTI USMAN BN21110154Belum ada peringkat
- Sarmica 2Dokumen5 halamanSarmica 2Akash RughaniBelum ada peringkat
- Shell Gadus S3 Wirerope: Performance, Features & Benefits Main ApplicationsDokumen2 halamanShell Gadus S3 Wirerope: Performance, Features & Benefits Main ApplicationsptscmscBelum ada peringkat
- ANALYSIS AND DENATURATION OF PROTEINS AnswersDokumen5 halamanANALYSIS AND DENATURATION OF PROTEINS AnswersdgfdgsdfgsdsdgBelum ada peringkat
- Nippon Muki Catalogue (Seperator Type, J-Model)Dokumen20 halamanNippon Muki Catalogue (Seperator Type, J-Model)Hou HonBelum ada peringkat
- Efficascy of Fly Ash & Stone Dust Stabilizing Clayey Soil 1Dokumen77 halamanEfficascy of Fly Ash & Stone Dust Stabilizing Clayey Soil 1KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Focuse Ion BeamDokumen34 halamanFocuse Ion BeamAhsan SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Safety Data Sheet Dated 27/11/2012, Version 1Dokumen9 halamanSafety Data Sheet Dated 27/11/2012, Version 1Radu JuneBelum ada peringkat
- Carbon Enrichment in Mo SteelDokumen50 halamanCarbon Enrichment in Mo SteelDhananjay ShimpiBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 4th Edition Rizzo Test BankDokumen14 halamanFundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 4th Edition Rizzo Test BankGeorgeCobbjgbcs100% (16)
- Marine Adhesives Product CatalogueDokumen35 halamanMarine Adhesives Product CatalogueDaniela TomovaBelum ada peringkat
- Bpharm 5 Sem Industrial Pharmacy 1 bp502t 2020Dokumen1 halamanBpharm 5 Sem Industrial Pharmacy 1 bp502t 2020Amol TupeBelum ada peringkat
- Ishrae PPT On RefrigerantDokumen9 halamanIshrae PPT On RefrigerantJigar ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Calcium-Magnesium by EDTA TitrationDokumen5 halamanCalcium-Magnesium by EDTA TitrationnisscriBelum ada peringkat
- Sadhu Forging Limite1 - 2Dokumen4 halamanSadhu Forging Limite1 - 2Priya KaleBelum ada peringkat
- Lett 2c03388Dokumen5 halamanLett 2c03388Vũ LưuBelum ada peringkat
- CreepDokumen25 halamanCreepORANG BiasaBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis Synthesis and Design of Chemical Processes 3rd Edition Turton Solutions ManualDokumen21 halamanAnalysis Synthesis and Design of Chemical Processes 3rd Edition Turton Solutions ManualdarrenrichncogbpizjkBelum ada peringkat
- Acid BaseDokumen5 halamanAcid Bases5mcfdr7ztBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 12-Coagulation & FlocculationDokumen29 halamanLec 12-Coagulation & FlocculationYaseen YousafBelum ada peringkat
- Reactions of Acids Homework Worksheet HADokumen3 halamanReactions of Acids Homework Worksheet HASarah KKCBelum ada peringkat
- Bahareh Tavakoli - A Review of Preparation Methods For Supported Metal CatalystsDokumen37 halamanBahareh Tavakoli - A Review of Preparation Methods For Supported Metal CatalystsAarón NavarreteBelum ada peringkat
- Auto 4sem MSEMDokumen214 halamanAuto 4sem MSEMkhairnarsayali257Belum ada peringkat