Audit Principles
Diunggah oleh
Jhayanti Nithyananda Kalyani0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
37 tayangan34 halamanShareholders should have the right to participate in key corporate governance decisions. An annual audit should be conducted by an independent, competent and qualified, auditor. External auditors should be accountable to the shareholders and exercise due professional care.
Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniShareholders should have the right to participate in key corporate governance decisions. An annual audit should be conducted by an independent, competent and qualified, auditor. External auditors should be accountable to the shareholders and exercise due professional care.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
37 tayangan34 halamanAudit Principles
Diunggah oleh
Jhayanti Nithyananda KalyaniShareholders should have the right to participate in key corporate governance decisions. An annual audit should be conducted by an independent, competent and qualified, auditor. External auditors should be accountable to the shareholders and exercise due professional care.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 34
Perusahaan Indonesia berskala nasional yang termotivasi
untuk mengembangkan bisnisnya di tingkat ASEAN
hendak melakukan IPO. Perusahaan saat ini sedang
mempertimbangkan restrukturisasi organisasi terkait
dengan fungsi audit internal agar fungsinya efektif dan
efektif sekaligus sesuai dengan kriteria ASEAN Corporate
Governance Scorecard. Terdapat tiga pilihan yang
dipikirkan, yaitu:
A. Fungsi audit internal di bawah CFO (chief financial
officer)
B. Fungsi audit internal di bawah masing-masing manajer
di kantor cabang dan kantor perwakilan.
C. Fungsi audit internal di bawah komite audit.
Pilihan manakah yang Anda, sebagai konsultan CG,
rekomendasikan untuk digunakan. Jelaskan kelebihan dari
pilihan Anda, dan jelaskan kekurangan-kekurangan dari
dua pilihan lainnya yang tidak Anda rekomendasikan.
(2) Shareholders should have the
opportunity to ask questions to the
board, including questions relating to
the annual external audit, to place
items on the agenda of general
meetings, and to propose
resolutions, subject to reasonable
limitations.
OECD Principle II (C)
Shareholders should have the
right to participate in key
corporate governance decisions,
such as the right to nominate,
appoint and remove directors in
an individual basis and also the
right to appoint external auditor.
ICGN 8.3.2 Shareholder
participation in governance
An annual audit should be conducted
by an independent, competent and
qualified, auditor in order to provide an
external and objective assurance to the
board and shareholders that the
financial statements fairly represent
the financial position and performance
of the company in all material respects.
OECD Principle V (C)
External auditors should be
accountable to the shareholders
and owe a duty to the company
to exercise due professional care
in the conduct of the audit.
OECD Principle V (D)
The auditors should observe highquality auditing and ethical standards.
To limit the possible risk of possible
conflicts of interest, non-audit services
and fees paid to auditors for non-audit
services should be both approved in
advance by the audit committee and
disclosed in the Annual Report.
ICGN 6.5 Ethical standards
(Audit)
(D) The board should fulfill certain key
functions, including:
7. Ensuring the integrity of the corporations
accounting and financial reporting systems,
including the independent audit, and that
appropriate systems of control are in place,
in particular, systems for risk management,
financial and operational control, and
compliance with the law and relevant
standards.
OECD PRINCIPLE VI: The
Responsibilities of the Board
(2) When committees of the board are established, their mandate,
composition and working procedures should be well defined and disclosed
by the board.
While the use of committees may improve the work of the board they may
also raise questions about the collective responsibility of the board and of
individual board members. In order to evaluate the merits of board
committees it is therefore important that the market receives a full and
clear picture of their purpose, duties and composition. Such information is
particularly important in an increasing number of jurisdictions where boards
are establishing independent Audit Committees with powers to oversee the
relationship with the external auditor and to act in many cases
independently. Other such
committees include those dealing with nomination and compensation. The
accountability of the rest of the board and the board as a whole should be
clear. Disclosure should not extend to committees set up to deal with, for
example, confidential commercial transactions
OECD PRINCIPLE VI (E)
C.3.1. The board should satisfy
itself that at least one member of
the Audit Committee has recent
and relevant financial experience.
UK CODE (JUNE 2010)
As many of the key responsibilities of the
Audit Committee are accounting-related,
such as oversight of financial reporting and
audits, it is important to have someone
specifically with accounting expertise, not
just general financial expertise.
UK CODE (JUNE 2010)
C.3.6 The Audit Committee should have primary
responsibility for making a recommendation on
the appointment, reappointment and removal of
the external auditor. If the board does not accept
the Audit Committees recommendation, it should
include in the Annual Report, and in any papers
recommending appointment or re- appointment, a
statement from the Audit Committee explaining
the recommendation and should set out reasons
why the board has taken a different position.
UK CODE (JUNE 2010)
(F) In order to fulfill their responsibilities, board members should
have access to accurate, relevant and timely information.
Board members require relevant information on a timely basis in
order to support their decision-making. Non-executive board
members do not typically have the same access to information
as key managers within the company. The contributions of nonexecutive board members to the company can be enhanced by
providing access to certain key managers within the company
such as, for example, the company secretary and the internal
auditor, and recourse to independent external advice at the
expense of the company. In order to fulfil their responsibilities,
board members should ensure that they obtain
accurate, relevant and timely information.
OECD PRINCIPLE VI
Ensuring the integrity of the essential reporting
and monitoring systems will require the board
to set and enforce clear lines of responsibility
and accountability throughout the
organization. The board will also need to
ensure that there is appropriate oversight by
senior management. One way of doing this is
through an internal audit system directly
reporting to the board.
OECD PRINCIPLE VI (D)
Companies often disclose that they have an internal audit
but, in practice, it is not uncommon for it to exist more in
form than in substance. For example, the in-house internal
audit may be assigned to someone with other operational
responsibilities. As internal audit is unregulated, unlike
external audit, there are firms providing outsourced
internal audit services which are not properly qualified to
do so. Making the identity of the head of internal audit or
the external service provider public would provide some
level of safeguard that the internal audit is substantive.
OECD PRINCIPLE VI (D)
In some jurisdictions it is considered
good practice for the internal auditors to
report to an independent Audit
Committee of the board or an equivalent
body which is also responsible for
managing the relationship with the
external auditor, thereby allowing a
coordinated response by the board.
OECD PRINCIPLE VI (D)
(7)
(VI.D.7.9) Does the internal
auditors have direct and
unfettered access to the board of
directors and its independent
Audit Committee?
WORLDBANK PRINCIPLE 6
companies should consider a second
reporting line from the internal audit function to
the board or relevant committee. Under the
ASX Principles it is also recommended that the
Audit Committee have access to internal audit
without the presence of management, and that
the audit committee should recommend to the
board the appointment and dismissal of a chief
internal audit executive."
ASX Principles on CG
The members of these key board committees
should be solely non-executive directors, and
in the case of the audit and remuneration
committees, solely independent directors. All
members of the nominations committee
should be independent from management
and at least a majority should be independent
from dominant owners.
ICGN 2.4.4 Composition
of board committees
Did the chairman of the Audit
Committee attend the most
recent AGM?
A.3.12
Are the auditors seeking
appointment/re-appointment
clearly identified?
B.2.4
Where the same audit firm is
engaged for both audit and non-audit
services
Are the non-audit fees disclosed?
D.5.2
Where the same audit firm is
engaged for both audit and non-audit
services
Does the non-audit fee exceed the
audit fees?
D.5.3
Does the Audit Committee comprise
entirely of non-executive directors/
commissioners with a majority of
independent
directors/commissioners?
E.2.22
Is the chairman of the Audit
Committee an independent
director/commissioner?
E.2.23 (default)
Does the company disclose the
terms of reference/governance
structure/charter of the Audit
Committee?
E.2.24
Does the Annual Report
disclose the profile or
qualifications of the Audit
Committee members?
E.2.25
Does at least one of the
independent directors/
commissioners of the (audit)
committee have accounting
expertise (accounting
qualification or experience)?
E.2.26
Did the Audit Committee
meet at least four times
during the year?
E.2.27
Is the attendance of members
at Audit Committee meetings
disclosed?
E.2.28
Does the Audit Committee
have primary responsibility
for recommendation on the
appointment, and removal of
the external auditor?
E.2.29
Does the company have a
separate internal audit
function?
E.3.16
Is the head of internal audit
identified or, if outsourced, is
the name of the external firm
disclosed?
E.3.17
Does the appointment and
removal of the internal
auditor require the approval
of the Audit Committee?
E.3.18 (default)
TERIMAKASIH
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- GCU CHP Flowchart PDFDokumen1 halamanGCU CHP Flowchart PDFJhayanti Nithyananda KalyaniBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Audit Chapter 7-13Dokumen6 halamanSoal Audit Chapter 7-13Jhayanti Nithyananda KalyaniBelum ada peringkat
- Sas 110Dokumen23 halamanSas 110Jhayanti Nithyananda KalyaniBelum ada peringkat
- DCUBS Research Paper Series 13Dokumen33 halamanDCUBS Research Paper Series 13Jhayanti Nithyananda KalyaniBelum ada peringkat
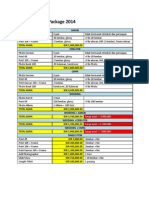
- Vphotography Package 2014: Harga Awal - 3.900.000 Harga Awal - 5.700.000 Harga Awal - 7.400.000Dokumen1 halamanVphotography Package 2014: Harga Awal - 3.900.000 Harga Awal - 5.700.000 Harga Awal - 7.400.000Jhayanti Nithyananda KalyaniBelum ada peringkat
- Branch Node City Node City Distance NodeDokumen3 halamanBranch Node City Node City Distance NodeJhayanti Nithyananda KalyaniBelum ada peringkat
- Sony: Betting It All On Blu-Ray SynopsisDokumen4 halamanSony: Betting It All On Blu-Ray SynopsisJhayanti Nithyananda KalyaniBelum ada peringkat
- Objective Function Z X + X + X + X + X + X + X + X + X: Branch Node City Node City Distance Node Network FlowDokumen3 halamanObjective Function Z X + X + X + X + X + X + X + X + X: Branch Node City Node City Distance Node Network FlowJhayanti Nithyananda KalyaniBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan 7Dokumen2 halamanPertemuan 7Jhayanti Nithyananda KalyaniBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Nyamango Site Meeting 9 ReportDokumen18 halamanNyamango Site Meeting 9 ReportMbayo David GodfreyBelum ada peringkat
- HPCL CSR Social Audit ReportDokumen56 halamanHPCL CSR Social Audit Reportllr_ka_happaBelum ada peringkat
- 2001 Ford F150 ManualDokumen296 halaman2001 Ford F150 Manualerjenkins1100% (2)
- For ClosureDokumen18 halamanFor Closuremau_cajipeBelum ada peringkat
- Household: Ucsp11/12Hsoiii-20Dokumen2 halamanHousehold: Ucsp11/12Hsoiii-20Igorota SheanneBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Interview Questions For Planning EngineersDokumen16 halamanSample Interview Questions For Planning EngineersPooja PawarBelum ada peringkat
- Jota - EtchDokumen3 halamanJota - EtchRidwan BaharumBelum ada peringkat
- ProspDokumen146 halamanProspRajdeep BharatiBelum ada peringkat
- Pontevedra 1 Ok Action PlanDokumen5 halamanPontevedra 1 Ok Action PlanGemma Carnecer Mongcal50% (2)
- Work Site Inspection Checklist 1Dokumen13 halamanWork Site Inspection Checklist 1syed hassanBelum ada peringkat
- MPT EnglishDokumen5 halamanMPT Englishkhadijaamir435Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 4Dokumen76 halamanChapter 1 4Sean Suing100% (1)
- Ariba Collaborative Sourcing ProfessionalDokumen2 halamanAriba Collaborative Sourcing Professionalericofx530Belum ada peringkat
- Contigency Plan On Class SuspensionDokumen4 halamanContigency Plan On Class SuspensionAnjaneth Balingit-PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Beamng DxdiagDokumen22 halamanBeamng Dxdiagsilvioluismoraes1Belum ada peringkat
- Mindray PM 9000 User ID10240 PDFDokumen378 halamanMindray PM 9000 User ID10240 PDFJuan FernandoBelum ada peringkat
- Uh 60 ManualDokumen241 halamanUh 60 ManualAnonymous ddjwf1dqpBelum ada peringkat
- Nse 2Dokumen5 halamanNse 2dhaval gohelBelum ada peringkat
- Chestionar 2Dokumen5 halamanChestionar 2Alex AndruBelum ada peringkat
- ASHRAE Elearning Course List - Order FormDokumen4 halamanASHRAE Elearning Course List - Order Formsaquib715Belum ada peringkat
- Induction Motor Steady-State Model (Squirrel Cage) : MEP 1422 Electric DrivesDokumen21 halamanInduction Motor Steady-State Model (Squirrel Cage) : MEP 1422 Electric DrivesSpoiala DragosBelum ada peringkat
- Ose Sample QuotationDokumen37 halamanOse Sample Quotationrj medelBelum ada peringkat
- Interbond 2340UPC: Universal Pipe CoatingDokumen4 halamanInterbond 2340UPC: Universal Pipe Coatingnoto.sugiartoBelum ada peringkat
- Trading Journal TDA Branded.v3.5 - W - Total - Transaction - Cost - BlankDokumen49 halamanTrading Journal TDA Branded.v3.5 - W - Total - Transaction - Cost - BlankChristyann LojaBelum ada peringkat
- USDA List of Active Licensees and RegistrantsDokumen972 halamanUSDA List of Active Licensees and Registrantswamu885Belum ada peringkat
- KiSoft Sort & Pack Work Station (User Manual)Dokumen41 halamanKiSoft Sort & Pack Work Station (User Manual)Matthew RookeBelum ada peringkat
- MOS - Steel StructureDokumen15 halamanMOS - Steel StructuredennisBelum ada peringkat
- Pautas Anatómicas para La Inserción de Minitornillos: Sitios PalatinosDokumen11 halamanPautas Anatómicas para La Inserción de Minitornillos: Sitios PalatinosValery V JaureguiBelum ada peringkat
- Yarn HairinessDokumen9 halamanYarn HairinessGhandi AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Ice 3101: Modern Control THEORY (3 1 0 4) : State Space AnalysisDokumen15 halamanIce 3101: Modern Control THEORY (3 1 0 4) : State Space AnalysisBipin KrishnaBelum ada peringkat