Lecture 03 - Amino Acids
Diunggah oleh
Helen LuHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Lecture 03 - Amino Acids
Diunggah oleh
Helen LuHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
The Amino Acids
BIOCHEM 301 SPRING 2016
Lecture 3
Monday, January 25, 2016
alpha carbon
connects to carboxylic
acid of another amino acid
connects to amine
of another amino acid
R-group
sidechain
Amino Acid Stereochemistry
L-amino acid
(normal form)
D-amino acid
Protonation States
Free amino acid:
pKa: 1.8-2.6
pKa: 9.0-10.8
Protonation States
Free amino acid:
pKa: 1.8-2.6
As part of polypeptide:
pKa: 9.0-10.8
Protonation States
As part of polypeptide:
Protonation would result in
the loss of resonance.
Deprotonation would result
in negatively charged N.
Name
Three-Letter
Code
One-Letter Code
Alanine
Ala
Arginine
Arg
Aspartate
Asp
Asparagine
Asn
Cysteine
Cys
Glycine
Gly
Glutamate
Glu
Glutamine
Gln
Histidine
His
Isoleucine
Ile
Leucine
Leu
Lysine
Lys
Methionine
Met
Phenylalanine
Phe
Proline
Pro
Serine
Ser
Threonine
Thr
Tryptophan
Trp
Tyrosine
Tyr
Valine
Val
Glycine
Alanine
Valine
Leucine
Isoleucine
Methionine
Proline
Phenylalanine
Tyrosine
Tyrosine
pKa: ~10
protonated: H-bond donor/acceptor
deprotonated: H-bond acceptor, nucleophile
Tryptophan
Tryptophan
not acidic: removing a proton
would put a negative charge
and extra lone pair on N
not basic: accepting a proton
would require disrupting
aromaticity (lone pair is in p
orbital, part of aromatic system)
Tryptophan
H-bond donor
not an H-bond acceptor:
lone pair is in p orbital and
part of aromatic system
Serine
pKa: 14-16
H-bond donor? H-bond acceptor? nucleophile?
Cysteine
pKa: ~8
Cysteine and Disulfide Bonds
Threonine
pKa: 16-18
Aspartate
pKa: ~3.6
Asparagine
Glutamate
pKa: ~4.3
Glutamine
Lysine
pKa: ~10.5
Arginine
pKa: ~12.5
unfavorable
favorable
unfavorable
favorable
favorable
favorable
Histidine
Histidine
pKa: ~6
lone pair is sp2-hybridized
and can easily gain a proton
Histidine
deprotonating this N would
result in a negatively charge
N, which is unfavorable
Histidine
neutral His has two roughly equivalent tautomers
Histidine
protonated His has two roughly equivalent resonance structures
His vs. Trp
lone pair is sp2-hybridized
(not part of aromaticity)
lone pair is in p orbital
(part of aromaticity)
Thr vs. Ser vs. Tyr vs. Cys
pKa: 16-18
pKa: 14-16
pKa: ~10
pKa: ~8
His vs. Lys vs. Arg
pKa: ~6
pKa: ~10.5
pKa: ~12.5
sp2 bonds less readily sp3 bonds readilyresonance stabilization
Asp vs. Glu
pKa: ~3.6
pKa: ~4.5
Asp, Asn, Glu, Gln
pKa: ~3.6
no sidechain
protonation
pKa: ~4.5
no sidechain
protonation
Val, Leu, Ile
Ala and Phe
Hydrophobic
Hydrophobic?
Perturbation of pKa Values
What factors could raise a sidechain pKa from
its normal value?
What factors could lower a sidechain pKa from
its normal value?
FYI: Essential Amino Acids
Essential (humans do not make, must have in
diet): Arg*, His, Ile, Leu, Lys, Met, Phe, Thr, Trp,
Val
Non-essential (humans make, not needed in
diet): Ala, Asn, Asp, Cys, Glu, Gln, Gly, Pro, Ser,
Tyr*
Other Amino Acids
4-hydroxproline is found in collagen
Ornithine and citrulline are N metabolism
intermediates.
4-hydroxyproline
ornithine
citrulline
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1091)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Experiment Instructions TM150 Universal PDFDokumen73 halamanExperiment Instructions TM150 Universal PDFAli A. Ismaeel50% (2)
- Steel BS 5950Dokumen26 halamanSteel BS 5950Rodain NajjarBelum ada peringkat
- Structural Optimization Procedure of A Composite Wind Turbine Blade For Reducing Both Material Cost and Blade WeightDokumen20 halamanStructural Optimization Procedure of A Composite Wind Turbine Blade For Reducing Both Material Cost and Blade WeightNasser ShelilBelum ada peringkat
- Stevin, Simon PDFDokumen3 halamanStevin, Simon PDFcreeshaBelum ada peringkat
- Finite DifferencesDokumen25 halamanFinite Differencesshobhit63062Belum ada peringkat
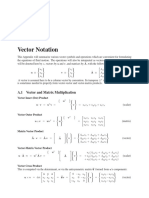
- Vector NotationDokumen2 halamanVector NotationAmmar BegenBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge International A Level: Mathematics 9709/31 May/June 2020Dokumen13 halamanCambridge International A Level: Mathematics 9709/31 May/June 2020Mubashir AsifBelum ada peringkat
- Pressure Vessel, Asme CodeDokumen10 halamanPressure Vessel, Asme Codeabhi_mohit2005100% (1)
- Viscosimetro OfiteDokumen20 halamanViscosimetro OfitejomarlucaBelum ada peringkat
- StructuralMechanicsModuleUsersGuide PDFDokumen420 halamanStructuralMechanicsModuleUsersGuide PDFFrancisco RibeiroBelum ada peringkat
- THERMOREGULATIONDokumen8 halamanTHERMOREGULATIONDewiSartikaBelum ada peringkat
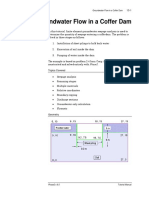
- Tutorial 13 Cofferdam SeepageDokumen15 halamanTutorial 13 Cofferdam Seepagemed Amine100% (1)
- Evosta Ts EngDokumen3 halamanEvosta Ts Engmky_roBelum ada peringkat
- Hazard and Safety Investigations For LNG Tanks PDFDokumen2 halamanHazard and Safety Investigations For LNG Tanks PDFcisco100% (1)
- Steam TurbineDokumen28 halamanSteam Turbineakusuper88% (8)
- Metric System Hand OutDokumen3 halamanMetric System Hand OutKenny TothBelum ada peringkat
- Lessons For The Young Economist Robert P MurphyDokumen422 halamanLessons For The Young Economist Robert P Murphysleepyninjitsu100% (1)
- 3rd ICAMPN Circular Rev 1Dokumen10 halaman3rd ICAMPN Circular Rev 1Nashrullah Fathullah PrawiraWinataBelum ada peringkat
- Scia Engineer 2014 - Advanced Concept Training - FEM PDFDokumen102 halamanScia Engineer 2014 - Advanced Concept Training - FEM PDFericfgBelum ada peringkat
- 2017 H2 Chemistry Paper 3 Suggested SolutionsDokumen19 halaman2017 H2 Chemistry Paper 3 Suggested SolutionsLee Jun Hui78% (9)
- Nucl - Phys.B v.646Dokumen538 halamanNucl - Phys.B v.646buddy72Belum ada peringkat
- Monofocal and Progrssive LensDokumen2 halamanMonofocal and Progrssive LensPablo Ramirez CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 RoboticsDokumen30 halamanUnit 1 RoboticsVishnu PriyanBelum ada peringkat
- Index of ApplicationDokumen6 halamanIndex of ApplicationNeil Erwin A. RoselloBelum ada peringkat
- LRV 175-1 / 350-1 / 700-1 Lift Control Valve: NTA-1 Power Supply Unit and Delta Controller DELCONDokumen44 halamanLRV 175-1 / 350-1 / 700-1 Lift Control Valve: NTA-1 Power Supply Unit and Delta Controller DELCONraymon janszenBelum ada peringkat
- PVElite ManualDokumen691 halamanPVElite Manuals.mladin75% (4)
- Investigation of Chloro Pentaammine Cobalt (III) Chloride - Polyvinyl Alcohol CompositesDokumen5 halamanInvestigation of Chloro Pentaammine Cobalt (III) Chloride - Polyvinyl Alcohol CompositesAlexander DeckerBelum ada peringkat
- Experimental Investigation of Load Deflection Characteristics of Beam With Various End Conditions of Different MaterialsDokumen5 halamanExperimental Investigation of Load Deflection Characteristics of Beam With Various End Conditions of Different MaterialsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (2)
- Review ChapterDokumen13 halamanReview ChaptermirosehBelum ada peringkat