Chapter 3 - Consumer Behavior
Diunggah oleh
ginish12Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 3 - Consumer Behavior
Diunggah oleh
ginish12Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 4
Consumer Motivation
Consumer Behavior,
Ninth Edition
Schiffman & Kanuk
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall
Needs and Motivation
Needs are the essence of the marketing
concept. Marketers do not create
needs but can make consumers aware
of needs.
Motivation is the driving force within
individuals that impels them to action.
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4-3
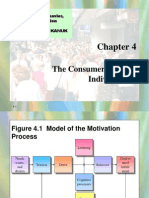
Figure 4.1 Model of the
Motivation Process
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4-4
Types of Needs
Innate Needs
Physiological (or biogenic) needs that are
considered primary needs or motives
Acquired Needs
Learned in response to our culture or
environment. Are generally psychological
and considered secondary needs
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4-5
Is a body spray
an innate or
acquired
need?
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4-6
Goals
The sought-after results of motivated
behavior
Generic goals are general categories of
goals that consumers see as a way to
fulfill their needs
Product-specific goals are specifically
branded products or services that
consumers select as their goals
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4-7
Figure 4-2c
Goals Structure for Weight Control
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 10
The Selection of Goals
The goals selected by an individual
depend on their:
Personal experiences
Physical capacity
Prevailing cultural norms and values
Goals accessibility in the physical and
social environment
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 12
Motivations and Goals
Positive Negative
Motivation Motivation
A driving force A driving force away
toward some object from some object or
or condition condition
Approach Goal Avoidance Goal
A positive goal A negative goal from
toward which which behavior is
behavior is directed directed away
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 14
Rational versus Emotional
Motives
Rationality implies that consumers
select goals based on totally objective
criteria such as size, weight, price, or
miles per gallon
Emotional motives imply the selection
of goals according to personal or
subjective criteria
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 15
The Dynamic Nature of
Motivation
Needs are never fully satisfied
New needs emerge as old needs are
satisfied
People who achieve their goals set new
and higher goals for themselves
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 17
Substitute Goals
Are used when a consumer cannot
attain a specific goal he/she anticipates
will satisfy a need
The substitute goal will dispel tension
Substitute goals may actually replace
the primary goal over time
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 18
Frustration
Failure to achieve a goal may result in
frustration.
Some adapt; others adopt defense
mechanisms to protect their ego.
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 19
Defense Mechanism
Methods by which people mentally
redefine frustrating situations to
protect their self-images and their self-
esteem
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 20
What type of
defense
mechanism is
this
spokesperson
using in this
ad?
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 21
Table 4.2
Defense Mechanisms
Aggression Projection
Rationalization Autism
Regression Identification
Withdrawal Repression
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 22
Arousal of Motives
Physiological arousal
Emotional arousal
Cognitive arousal
Environmental arousal
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 23
Philosophies Concerned with
Arousal of Motives
Behaviorist School
Behavior is response to stimulus
Elements of conscious thoughts are to be ignored
Consumer does not act, but reacts
Cognitive School
Behavior is directed at goal achievement
Needs and past experiences are reasoned,
categorized, and transformed into attitudes and
beliefs
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 24
Maslows Hierarchy of Needs
Figure 4.10
weblink
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 25
A Trio of Needs
Power
individuals desire to control environment
Affiliation
need for friendship, acceptance, and
belonging
Achievement
need for personal accomplishment
closely related to egoistic and self-
actualization needs
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 30
Measurement of Motives
Researchers rely on a combination of
techniques
Combination of behavioral, subjective,
and qualitative data
Construction of a measurement scale
can be complex
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 31
Motivational Research
Qualitative research designed to
uncover consumers subconscious or
hidden motivations
Attempts to discover underlying
feelings, attitudes, and emotions
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 32
Qualitative Motivational
Research
Metaphor analysis
Storytelling
Word association and sentence
completion
Thematic apperception test
Drawing pictures and photo-sorts
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 4 - 33
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Summary: “The 4 Disciplines of Execution: Achieving Your Wildly Important Goals" by Sean Covey - Discussion PromptsDari EverandSummary: “The 4 Disciplines of Execution: Achieving Your Wildly Important Goals" by Sean Covey - Discussion PromptsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Consumer Motivation: Consumer Behavior, Ninth Edition Schiffman & KanukDokumen34 halamanConsumer Motivation: Consumer Behavior, Ninth Edition Schiffman & KanukGOHAR GHAFFARBelum ada peringkat
- "Chapter 4: Consumer Motivation" Consumer BehaviorDokumen24 halaman"Chapter 4: Consumer Motivation" Consumer BehaviorBakti HasanudinBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Motivation: Consumer Behavior, Eleven EditionDokumen31 halamanConsumer Motivation: Consumer Behavior, Eleven Editionasni yunelsaBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Motivation: Consumer Behavior, Ninth Edition Schiffman & KanukDokumen31 halamanConsumer Motivation: Consumer Behavior, Ninth Edition Schiffman & KanukPRIYA SRIVASTAVABelum ada peringkat
- Perilaku Konsumen Sesi 5 - Consumer Motivation - Kelas SoreDokumen24 halamanPerilaku Konsumen Sesi 5 - Consumer Motivation - Kelas SoreNovita TriyBelum ada peringkat
- 04 MotivationDokumen30 halaman04 Motivationrizwan matloobBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer MotivationDokumen23 halamanConsumer MotivationsherazBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5: Consumer Motivation and Personality: Shah Alam Kabir PramanikDokumen42 halamanChapter 5: Consumer Motivation and Personality: Shah Alam Kabir PramanikFarhad HossainBelum ada peringkat
- The Consumer As An Individual: Consumer Behavior, Eighth EditionDokumen28 halamanThe Consumer As An Individual: Consumer Behavior, Eighth EditionJessica MahBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Motivation: Consumer Behavior, Ninth Edition Schiffman & KanukDokumen34 halamanConsumer Motivation: Consumer Behavior, Ninth Edition Schiffman & Kanukpritesh1983Belum ada peringkat
- lecture 8 (1)Dokumen24 halamanlecture 8 (1)maryam farooqBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer MotivationDokumen16 halamanConsumer MotivationOlivia TanBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Needs and MotivationDokumen37 halamanConsumer Needs and MotivationPreeti KumariBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 - PersonalityDokumen43 halamanChapter 5 - PersonalityMuhammad Munib KhanBelum ada peringkat
- MotivationDokumen5 halamanMotivationBilal MalikBelum ada peringkat
- Personality and Consumer BehaviorDokumen33 halamanPersonality and Consumer BehaviorBahram HabibiBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Motivation: Consumer Behavior, Ninth EditionDokumen20 halamanConsumer Motivation: Consumer Behavior, Ninth EditionIsrat JahanBelum ada peringkat
- Ch04 SpectorDokumen19 halamanCh04 SpectorSumayya ChughtaiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Four: Consumer MotivationDokumen29 halamanChapter Four: Consumer MotivationGamachu TarikuBelum ada peringkat
- MotivationDokumen46 halamanMotivationShikha DeshpandeBelum ada peringkat
- MotivationDokumen72 halamanMotivationPrakash GotiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6 - Consumer PerceptionDokumen36 halamanChapter 6 - Consumer PerceptionAhmad ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5Dokumen29 halamanChapter 5himanshiBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Motivation: Abhideep HazariDokumen18 halamanConsumer Motivation: Abhideep HazariabhideephazariBelum ada peringkat
- Motivating Yourself and Others EffectivelyDokumen59 halamanMotivating Yourself and Others Effectively12u88elBelum ada peringkat
- Motivation As A Psychological ForceDokumen42 halamanMotivation As A Psychological ForceTia MejiaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Outline: - Model of The Motivation Process - Goals - Motives - Needs - Motivational ResearchDokumen70 halamanChapter Outline: - Model of The Motivation Process - Goals - Motives - Needs - Motivational ResearchpradeepBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 5 MotivationDokumen26 halamanTopic 5 MotivationSHI QI LEEBelum ada peringkat
- Motivation of Self and OthersDokumen26 halamanMotivation of Self and Othersnavneet260897Belum ada peringkat
- Learning and Memory: Perilaku KonsumenDokumen30 halamanLearning and Memory: Perilaku KonsumenDiah Tiffani AnnisaBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer PerceptionDokumen28 halamanConsumer PerceptionDepankan DasBelum ada peringkat
- Health Ed # 4 OnlineDokumen2 halamanHealth Ed # 4 OnlineRam AugustBelum ada peringkat
- 04 PPT To Student Perception and Individual Decision MakingDokumen29 halaman04 PPT To Student Perception and Individual Decision MakingTouleen AkoumBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 FinalDokumen33 halamanChapter 4 FinalDigesh ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Theories of Motivation: Organizational BehaviourDokumen53 halamanTheories of Motivation: Organizational BehaviourkushalkaushalBelum ada peringkat
- Organizational Behavior: An Introduction To Your Life in OrganizationsDokumen37 halamanOrganizational Behavior: An Introduction To Your Life in OrganizationsRivaldi TwentyFourBelum ada peringkat
- The Consumer As An Individual: Consumer Behavior, Eighth Edition Schiffman & KanukDokumen28 halamanThe Consumer As An Individual: Consumer Behavior, Eighth Edition Schiffman & KanukfruitfulluftBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Perception: Consumer Behavior, Ninth EditionDokumen49 halamanConsumer Perception: Consumer Behavior, Ninth EditionMuhammad MunibBelum ada peringkat
- Solomon04 (Debbie)Dokumen39 halamanSolomon04 (Debbie)Abhishek SinghalBelum ada peringkat
- Solomon MotivationDokumen36 halamanSolomon MotivationJR JRovaneshwaranBelum ada peringkat
- Module-3 INdividual Influences On Consumer BehaviourDokumen132 halamanModule-3 INdividual Influences On Consumer BehaviourAnonymous YweU6CBelum ada peringkat
- Value, Attitude: and Job SatisfactionDokumen231 halamanValue, Attitude: and Job Satisfactionmilangohil100% (1)
- Solomon Cb09 PPT 04 BDokumen58 halamanSolomon Cb09 PPT 04 BSameen JawaidBelum ada peringkat
- CB 4000Dokumen20 halamanCB 4000Bhavin MandaliyaBelum ada peringkat
- Motivation and Goal Setting: Maslow's Hierarchy and Self-ActualizationDokumen17 halamanMotivation and Goal Setting: Maslow's Hierarchy and Self-Actualizationbndgdd cncncjBelum ada peringkat
- The Consumer as an Individual: Understanding Motivation and Goal SettingDokumen31 halamanThe Consumer as an Individual: Understanding Motivation and Goal SettingSumedh BodadeBelum ada peringkat
- MotivationDokumen38 halamanMotivationAlwyn SabuBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Consumer MotivationDokumen23 halaman3 Consumer MotivationSaini JasBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 Foundations of MH Counseling CH03.pptxDokumen29 halamanUnit 1 Foundations of MH Counseling CH03.pptxNathanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Motivation and Global ValuesDokumen35 halamanChapter 5 Motivation and Global ValuesMi HạBelum ada peringkat
- Perspective Son Consumer BehaviorDokumen42 halamanPerspective Son Consumer Behaviordiep nhyBelum ada peringkat
- Schiffman CB10 PPT 04Dokumen42 halamanSchiffman CB10 PPT 04Sonali TazrinBelum ada peringkat
- Day 2Dokumen46 halamanDay 2thelowngeBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer LearningDokumen30 halamanConsumer Learningdevendrasaradhana5Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing Theories 2Dokumen41 halamanNursing Theories 2Earl TanBelum ada peringkat
- 04-Motivatian and ValuesDokumen40 halaman04-Motivatian and Valuesarya_85Belum ada peringkat
- 8th Lec Updated Determinants of Learning Ch. 4Dokumen42 halaman8th Lec Updated Determinants of Learning Ch. 4Nica Marie LumbaBelum ada peringkat
- Solomon - cb09 - PPT - 04 (Me)Dokumen41 halamanSolomon - cb09 - PPT - 04 (Me)MuratBelum ada peringkat
- China Southern Internet Check-In Boarding Pass2Dokumen2 halamanChina Southern Internet Check-In Boarding Pass2ginish12Belum ada peringkat
- ScholarDokumen1 halamanScholarginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 8 Ethics and Fair Treatment in Human Resources ManagementDokumen56 halamanUnit 8 Ethics and Fair Treatment in Human Resources Managementginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 Personnel Planning and RecruitmentDokumen70 halamanUnit 2 Personnel Planning and Recruitmentginish12Belum ada peringkat
- 1 CoverpageDokumen4 halaman1 CoverpagePiyal HossainBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3 Employee SelectionDokumen68 halamanUnit 3 Employee Selectionginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 9 Employee Safety and HealthDokumen28 halamanUnit 9 Employee Safety and Healthginish12Belum ada peringkat
- ScholarDokumen1 halamanScholarginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Presentation On Application Software and Software IssuesDokumen23 halamanPresentation On Application Software and Software Issuesginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 7 Labor Relations and Collective BargainingDokumen79 halamanUnit 7 Labor Relations and Collective Bargainingginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 5 Performance Management and AppraisalDokumen63 halamanUnit 5 Performance Management and Appraisalginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 6 Employee CompensationDokumen48 halamanUnit 6 Employee Compensationginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 Overview of The FieldDokumen46 halamanUnit 1 Overview of The Fieldginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 4 Employee Training and DevelopmentDokumen50 halamanUnit 4 Employee Training and Developmentginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Potato ChipsDokumen11 halamanPotato Chipsginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Measurement Scale SelectionDokumen40 halamanMeasurement Scale Selectionginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Potato ChipsDokumen11 halamanPotato Chipsginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Dhankuta RESDokumen18 halamanDhankuta RESginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Path - Goal TheoryDokumen10 halamanPath - Goal Theoryginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 2Dokumen4 halamanAssignment 2ginish12Belum ada peringkat
- MBO DeviationDokumen1 halamanMBO Deviationginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Case Analysis FormatDokumen1 halamanCase Analysis Formatginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Validated Lean Canvas for UR StoreDokumen1 halamanValidated Lean Canvas for UR Storeginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Buddha Air CaseDokumen3 halamanBuddha Air Caseginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment - 1Dokumen4 halamanAssignment - 1ginish12Belum ada peringkat
- WP IHR PerformanceManagement 0319Dokumen7 halamanWP IHR PerformanceManagement 0319Archana PooniaBelum ada peringkat
- Current Issues In Selection: Broadly Defined and Team-Based JobsDokumen13 halamanCurrent Issues In Selection: Broadly Defined and Team-Based Jobsginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Slide 4Dokumen15 halamanSlide 4ginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Demand Conditions Factor Conditions Related and Supporting Industries Firm Strategy, Structure, and RivalryDokumen5 halamanDemand Conditions Factor Conditions Related and Supporting Industries Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalryginish12Belum ada peringkat
- How Stressful Is Your LifeDokumen1 halamanHow Stressful Is Your Lifeginish12Belum ada peringkat
- Edu 223 - Lesson Plan 1Dokumen3 halamanEdu 223 - Lesson Plan 1api-438638989Belum ada peringkat
- JSF - Chapter 1 - Language and Culture Overview PDFDokumen3 halamanJSF - Chapter 1 - Language and Culture Overview PDFJudith FetalverBelum ada peringkat
- Sally Mann - Immediate FamilyDokumen82 halamanSally Mann - Immediate FamilyIon Popescu68% (25)
- Communication Is A Process of Transmitting Information From Origin Recipients Where The Information Is Required To Be UnderstoodDokumen10 halamanCommunication Is A Process of Transmitting Information From Origin Recipients Where The Information Is Required To Be Understoodal_najmi83Belum ada peringkat
- Project CalendarDokumen2 halamanProject Calendarapi-246393723Belum ada peringkat
- We Are Living FasterDokumen4 halamanWe Are Living Fasteraeryll1305Belum ada peringkat
- Mcclellan DDokumen5 halamanMcclellan DDhruvi GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- HWT - Transcripts With Notes 1.1 (Tripp)Dokumen33 halamanHWT - Transcripts With Notes 1.1 (Tripp)hypnos2011100% (3)
- OB Perceptions.19134329Dokumen66 halamanOB Perceptions.19134329hansdeep479Belum ada peringkat
- Principles of Teaching - Part 2Dokumen25 halamanPrinciples of Teaching - Part 2Jomar M. TeofiloBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding the rare and idealistic INFP personality typeDokumen5 halamanUnderstanding the rare and idealistic INFP personality typeLuthfi HakimBelum ada peringkat
- Coaching & EmpowermentDokumen15 halamanCoaching & EmpowermentXavier ContrerasBelum ada peringkat
- Art Martin LectureDokumen13 halamanArt Martin LecturesoguetaBelum ada peringkat
- Discourse Analysis: Language Beyond SentencesDokumen30 halamanDiscourse Analysis: Language Beyond SentencesVirginia HelzainkaBelum ada peringkat
- Remarks on Colour by WittgensteinDokumen17 halamanRemarks on Colour by Wittgensteinতারিক মোর্শেদ0% (1)
- Clifford 1988 Intro Pure ProductsDokumen17 halamanClifford 1988 Intro Pure ProductsUlrich DemmerBelum ada peringkat
- CSI - The Deer at Providencia.Dokumen2 halamanCSI - The Deer at Providencia.RodrigoTaipe93Belum ada peringkat
- Landscape WellbeingDokumen12 halamanLandscape WellbeingFathima IbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Pycho For A People To ComeDokumen20 halamanPycho For A People To ComeRed Deleuze & Guattari LatinoaméricaBelum ada peringkat
- Translating Prose and Drama ChallengesDokumen3 halamanTranslating Prose and Drama ChallengesDimas Farayndra Pranidhana0% (1)
- 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleDokumen38 halaman7 Habits of Highly Effective PeoplePayal Malik100% (1)
- Lesson Plan EspDokumen2 halamanLesson Plan EspIcha NisaBelum ada peringkat
- 7habits of Highly Effective PeopleDokumen30 halaman7habits of Highly Effective PeopleumaBelum ada peringkat
- Asri Samrotul Hilmiah - 182122090 - UTSDokumen2 halamanAsri Samrotul Hilmiah - 182122090 - UTSAsri Samrotul HilmiahBelum ada peringkat
- Let Review On MotivationDokumen20 halamanLet Review On MotivationAnonymous st4mP4C4Belum ada peringkat
- 10 Strategies for Eliciting Change TalkDokumen2 halaman10 Strategies for Eliciting Change Talkandrew dwyerBelum ada peringkat
- NSTP 2.3.2-Information Sheet TeamBuildingDokumen2 halamanNSTP 2.3.2-Information Sheet TeamBuildingVeraniceBelum ada peringkat
- Ian Jeffreys PDFDokumen27 halamanIan Jeffreys PDFJuan Andres Guzman WongBelum ada peringkat
- GilgameshDokumen2 halamanGilgameshTJ VandelBelum ada peringkat
- Developed by George Homans, Advocates That Group Development IsDokumen4 halamanDeveloped by George Homans, Advocates That Group Development Isshamini binoyBelum ada peringkat