Link Segment Model Winter
Diunggah oleh
Hossein Najjarzade0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
84 tayangan10 halamana document about hill muscle model
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inia document about hill muscle model
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
84 tayangan10 halamanLink Segment Model Winter
Diunggah oleh
Hossein Najjarzadea document about hill muscle model
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 10
Link Segment Model
Joint Reaction Forces
Muscle Moments
Joint Power
Newtons Laws of Motion
I. Law of Inertia: A body at rest stays at rest and a
body in motion stays in motion unless acted upon
by a force or torque.
II. Law of Acceleration: The acceleration a body
experiences is directly proportional to the force or
torque, inversely proportional to the mass or
moment of inertia and occurs in the direction of the
force or torque.
III. Law of Reaction: For every action there is an
opposite reaction.
Newtons First Law: Law of Inertia
Law of Inertia: A body at rest stays at rest and a body in
motion stays in motion unless acted upon by a force or
torque.
Mass is the measure of an objects resistance to linear
change.
Moment of inertia is the measure of an objects resistance
to angular change.
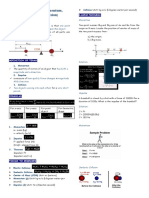
F = m a T = I
To solve for forces and torques, we need both mass
and moment of inertia.
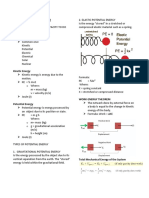
Moment of Inertia (I)
ICG= 3.5 kgm2
I CG md 2
The Moment of Inertia (I) represents
ICG= 15 kgm
2
an objects resistance to angular change
ICG= 6.5 kgm 2
about some axis.
Moment of inertia is a sum of the
product of mass times the squared
distance of the mass about the axis.
ICG= 83 kgm2 When body parts are moved closer to
the axis of rotation the moment of
inertia (resistance to spin) is reduced.
Link Segment Model Assumptions
Each segment has a fixed mass located at its center of mass
The joints are considered as hinge joints
The moment of inertia is fixed during movement
The length of each segment is constant
Input Information to Mass & moment of inertia of
Solve for Joint Forces each segment.
and Torques
Location of each segments
Center of Mass (CM).
Position, velocity, acceleration of
each segments CM (x, y, Vx, Vy,
Ax, Ay).
Angular position, velocity,
acceleration about each segments
CM (, , ).
External forces for all contact
points.
Center of pressure or location of
Center of Pressure external forces acting on the
gives the location of body.
external forces acting
on the body.
Inverse Dynamics: Finding Forces & Torques from Position Data.
[working backward to solve for forces & torques]
Anatomical Relationship
Forces & Torques Acting On Each Segment
Joint Moments
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Dark Witch Education 101Dokumen55 halamanDark Witch Education 101Wizard Luxas100% (2)
- Gce o Level Physics MatterDokumen8 halamanGce o Level Physics MatterBakhita Maryam100% (1)
- CogAT 7 PlanningImplemGd v4.1 PDFDokumen112 halamanCogAT 7 PlanningImplemGd v4.1 PDFBahrouniBelum ada peringkat
- Jake Atlas Extract 2Dokumen25 halamanJake Atlas Extract 2Walker BooksBelum ada peringkat
- Biomechanics of Shoulder Complex Part 1Dokumen62 halamanBiomechanics of Shoulder Complex Part 1Hossein NajjarzadeBelum ada peringkat
- Running Gait Analysis PDFDokumen8 halamanRunning Gait Analysis PDFHossein Najjarzade100% (1)
- Gce o Level Physics MatterDokumen9 halamanGce o Level Physics MatterirmaBelum ada peringkat
- Errol PNP Chief AzurinDokumen8 halamanErrol PNP Chief AzurinDarren Sean NavaBelum ada peringkat
- Operational Effectiveness + StrategyDokumen7 halamanOperational Effectiveness + StrategyPaulo GarcezBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrogen Peroxide DripDokumen13 halamanHydrogen Peroxide DripAya100% (1)
- Configuration Steps - Settlement Management in S - 4 HANA - SAP BlogsDokumen30 halamanConfiguration Steps - Settlement Management in S - 4 HANA - SAP Blogsenza100% (4)
- Planar Kinetics of A Rigid Body: Force and AccelerationDokumen25 halamanPlanar Kinetics of A Rigid Body: Force and Accelerationzahraa BahjatBelum ada peringkat
- RIVERAMOIDokumen2 halamanRIVERAMOIcarlo riveraBelum ada peringkat
- Center of MassDokumen2 halamanCenter of MassAnn Margarette MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics PortionDokumen55 halamanMechanics PortionRupak MandalBelum ada peringkat
- Linear MomentumDokumen30 halamanLinear Momentumyuxing lieBelum ada peringkat
- 018 Moment of InertiaDokumen17 halaman018 Moment of InertiaDasaka BrahmendraBelum ada peringkat
- Moment of InertiaDokumen6 halamanMoment of InertiaAngelo SaysonBelum ada peringkat
- Physics ReviewerDokumen5 halamanPhysics ReviewerJohnny TestBelum ada peringkat
- Rotation of A Rigid Body About A Fixed AxisDokumen14 halamanRotation of A Rigid Body About A Fixed AxisFebrina RahayuBelum ada peringkat
- Ch17 PDFDokumen73 halamanCh17 PDFمحمد علي عمرانBelum ada peringkat
- Biomechanics & Ergonomics-Ii SHS.306.Lec-22: Saba RiazDokumen40 halamanBiomechanics & Ergonomics-Ii SHS.306.Lec-22: Saba RiazsidrazBelum ada peringkat
- Hibb 11e Dynamics Lecture Section 17-01 RDokumen17 halamanHibb 11e Dynamics Lecture Section 17-01 RMichael Danny AndersonBelum ada peringkat
- PHY 001 (Physics I) : Instructor: Dr. Mohamed Fouad SalemDokumen26 halamanPHY 001 (Physics I) : Instructor: Dr. Mohamed Fouad SalemJiyan LitohonBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics of Rigid BodyDokumen21 halamanMechanics of Rigid Bodyhenzel espinaBelum ada peringkat
- Physics NotesDokumen161 halamanPhysics NotesNtendraniaBelum ada peringkat
- Mass Moment of InertiaDokumen13 halamanMass Moment of InertiaDavid LumaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture No 17Dokumen12 halamanLecture No 17Informative ChannelBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics PortionDokumen6 halamanMechanics PortionRupak MandalBelum ada peringkat
- Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsDokumen8 halamanRotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsNathalie SerafinBelum ada peringkat
- Work, Energy, and PowerDokumen41 halamanWork, Energy, and PowerDebayanbasu.juBelum ada peringkat
- 13 Rotational Movement PDFDokumen24 halaman13 Rotational Movement PDFDiego A. MezaBelum ada peringkat
- 106 AngularMomentum ENGDokumen14 halaman106 AngularMomentum ENGKristy LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Class 11 Physics Notes Chapter 5 Studyguide360Dokumen29 halamanClass 11 Physics Notes Chapter 5 Studyguide360Astrid RedBelum ada peringkat
- Applications in Linear and Angular KineticsDokumen30 halamanApplications in Linear and Angular Kineticsafifah temiziBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Rotational MotionDokumen33 halaman1 - Rotational Motionvasudha sriramBelum ada peringkat
- 7 Systems of Particles & Rot. MotionDokumen10 halaman7 Systems of Particles & Rot. MotionLalitha GorantlaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 30 - Chapter 11Dokumen15 halamanLecture 30 - Chapter 11Mircea PanteaBelum ada peringkat
- Momen InersiaDokumen19 halamanMomen InersiaAgus SetyawanBelum ada peringkat
- Gce o Level Physics MatterDokumen8 halamanGce o Level Physics MatterJonas Tianyou KhooBelum ada peringkat
- Moment of InertiaDokumen28 halamanMoment of InertiadskymaximusBelum ada peringkat
- SCIA5202Dokumen67 halamanSCIA52022BA19CV059 Rakshita SarangmathBelum ada peringkat
- Intact Stability: Session 1 Forces and Moments Centroids Gravitational StabilityDokumen56 halamanIntact Stability: Session 1 Forces and Moments Centroids Gravitational Stabilityレックス ハボネテBelum ada peringkat
- "Don't Be A Normie, I Guess": Invisible MechanicsDokumen30 halaman"Don't Be A Normie, I Guess": Invisible Mechanicssameeryad72Belum ada peringkat
- CursED Laborator Lab1Dokumen6 halamanCursED Laborator Lab1Prica AdrianBelum ada peringkat
- CH-7 System of Particles and Rotaional MotionDokumen9 halamanCH-7 System of Particles and Rotaional MotionMithul VPBelum ada peringkat
- Biruk. A: Static and Dynamic Analysis of Muscle and Joint LoadsDokumen26 halamanBiruk. A: Static and Dynamic Analysis of Muscle and Joint Loadssamrawit zerihunBelum ada peringkat
- General Physics 1 Q2 Module 1Dokumen31 halamanGeneral Physics 1 Q2 Module 1Angel CendañaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 13 Angular ImpulseDokumen15 halamanChapter 13 Angular ImpulseRoger MelkoBelum ada peringkat
- 1 IntroductionDokumen19 halaman1 Introductionmsi appleBelum ada peringkat
- L15 PDFDokumen15 halamanL15 PDFlesBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Vibration Lab: Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDokumen64 halamanMechanical Vibration Lab: Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DepartmentMuhammad Haris KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Numerical SDokumen82 halamanNumerical Smuhammad adilBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamics of Rotational MotionDokumen2 halamanDynamics of Rotational MotionDEEPAK TBelum ada peringkat
- Rotational MechanicsDokumen25 halamanRotational MechanicsUjib DamianBelum ada peringkat
- Chap2 CIV305Dokumen29 halamanChap2 CIV305Gable SmithBelum ada peringkat
- Moment of InertiaDokumen3 halamanMoment of Inertiakarnati saidireddyBelum ada peringkat
- Powerpoint PHY01 CO5Dokumen51 halamanPowerpoint PHY01 CO5HURHURBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 & 4Dokumen30 halamanChapter 3 & 4Junyi JiBelum ada peringkat
- System of Particles & Rotational MotionDokumen40 halamanSystem of Particles & Rotational MotionDebayanbasu.juBelum ada peringkat
- Moment of Inertia - WikipediaDokumen108 halamanMoment of Inertia - Wikipediayan naingBelum ada peringkat
- Rotational Dynamics: Angular Velocity and Angular AccelerationDokumen5 halamanRotational Dynamics: Angular Velocity and Angular AccelerationFoster TadiwanasheBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamics of Rigid BodyDokumen14 halamanDynamics of Rigid BodyAnbarin ParisaBelum ada peringkat
- Impulse and Momentum For KALAMDokumen15 halamanImpulse and Momentum For KALAMNordin fatihahBelum ada peringkat
- Tos - Research Magno (Bs-Arch 22e2)Dokumen5 halamanTos - Research Magno (Bs-Arch 22e2)mlyceee1298Belum ada peringkat
- Moment of Inertia Slides-1Dokumen20 halamanMoment of Inertia Slides-1Thato TumeloBelum ada peringkat
- COE 2001 Statics - Lecture 1 - IntroductionDokumen22 halamanCOE 2001 Statics - Lecture 1 - Introductionremino1Belum ada peringkat
- Static Stretches: Forward Flexion: Facing Forward, Move Your Head ForwardDokumen21 halamanStatic Stretches: Forward Flexion: Facing Forward, Move Your Head ForwardHossein NajjarzadeBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance Systems 2Dokumen32 halamanMaintenance Systems 2Hossein NajjarzadeBelum ada peringkat
- FEA 12 Three-DimensionDokumen31 halamanFEA 12 Three-DimensionHossein NajjarzadeBelum ada peringkat
- Finite Element Method: Main Applications: Field ProblemsDokumen29 halamanFinite Element Method: Main Applications: Field ProblemsHossein NajjarzadeBelum ada peringkat
- RunningDokumen21 halamanRunningHossein NajjarzadeBelum ada peringkat
- Running Biomech VideoDokumen20 halamanRunning Biomech VideoHossein NajjarzadeBelum ada peringkat
- Example Sheet 2 SolutionsDokumen8 halamanExample Sheet 2 SolutionsHossein NajjarzadeBelum ada peringkat
- Example Sheet 6 SolutionsDokumen7 halamanExample Sheet 6 SolutionsHossein NajjarzadeBelum ada peringkat
- Modeling of Tool-Tissue Interactions For ComputerDokumen30 halamanModeling of Tool-Tissue Interactions For ComputerHossein NajjarzadeBelum ada peringkat
- Supporting References in Release 12 SLA PDFDokumen8 halamanSupporting References in Release 12 SLA PDFsoireeBelum ada peringkat
- HIS Unit COMBINES Two Birthdays:: George Washington's BirthdayDokumen9 halamanHIS Unit COMBINES Two Birthdays:: George Washington's BirthdayOscar Panez LizargaBelum ada peringkat
- Directions: Choose The Best Answer For Each Multiple Choice Question. Write The Best Answer On The BlankDokumen2 halamanDirections: Choose The Best Answer For Each Multiple Choice Question. Write The Best Answer On The BlankRanulfo MayolBelum ada peringkat
- Artemis - Star+Wars+VolatilityDokumen7 halamanArtemis - Star+Wars+VolatilityjacekBelum ada peringkat
- CSEC Eng A Summary ExerciseDokumen1 halamanCSEC Eng A Summary ExerciseArisha NicholsBelum ada peringkat
- RWE Algebra 12 ProbStat Discrete Math Trigo Geom 2017 DVO PDFDokumen4 halamanRWE Algebra 12 ProbStat Discrete Math Trigo Geom 2017 DVO PDFハンター ジェイソンBelum ada peringkat
- TOPIC I: Moral and Non-Moral ProblemsDokumen6 halamanTOPIC I: Moral and Non-Moral ProblemsHaydee Christine SisonBelum ada peringkat
- Saxonville CaseDokumen2 halamanSaxonville Casel103m393Belum ada peringkat
- A Lei Do Sucesso Napoleon Hill Download 2024 Full ChapterDokumen23 halamanA Lei Do Sucesso Napoleon Hill Download 2024 Full Chapterdavid.brown752100% (12)
- Instructions: Reflect On The Topics That Were Previously Discussed. Write at Least Three (3) Things Per TopicDokumen2 halamanInstructions: Reflect On The Topics That Were Previously Discussed. Write at Least Three (3) Things Per TopicGuevarra KeithBelum ada peringkat
- Copper Reaction: Guillermo, Charles Hondonero, Christine Ilao, Ellaine Kim, Yumi Lambrinto, Arl JoshuaDokumen6 halamanCopper Reaction: Guillermo, Charles Hondonero, Christine Ilao, Ellaine Kim, Yumi Lambrinto, Arl JoshuaCharles GuillermoBelum ada peringkat
- Em 1.4 RMDokumen18 halamanEm 1.4 RMMangam RajkumarBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics Trial SPM 2015 P2 Bahagian BDokumen2 halamanMathematics Trial SPM 2015 P2 Bahagian BPauling ChiaBelum ada peringkat
- WPhO (Singapore) - World Physics Olympiad (WPhO) - 2011Dokumen20 halamanWPhO (Singapore) - World Physics Olympiad (WPhO) - 2011GXGGXG50% (2)
- Hygiene and HealthDokumen2 halamanHygiene and HealthMoodaw SoeBelum ada peringkat
- HG G5 Q1 Mod1 RTP PDFDokumen11 halamanHG G5 Q1 Mod1 RTP PDFKimberly Abilon-Carlos100% (1)
- WHAT - IS - SOCIOLOGY (1) (Repaired)Dokumen23 halamanWHAT - IS - SOCIOLOGY (1) (Repaired)Sarthika Singhal Sarthika SinghalBelum ada peringkat
- History of Drugs (Autosaved)Dokumen68 halamanHistory of Drugs (Autosaved)Juan TowTowBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - HandBook CBBR4106Dokumen29 halaman1 - HandBook CBBR4106mkkhusairiBelum ada peringkat
- Preliminaries Qualitative PDFDokumen9 halamanPreliminaries Qualitative PDFMae NamocBelum ada peringkat
- Prime White Cement vs. Iac Assigned CaseDokumen6 halamanPrime White Cement vs. Iac Assigned CaseStephanie Reyes GoBelum ada peringkat
- Some Problems in Determining The Origin of The Philippine Word Mutya' or Mutia'Dokumen34 halamanSome Problems in Determining The Origin of The Philippine Word Mutya' or Mutia'Irma ramosBelum ada peringkat
- Tan vs. Macapagal, 43 SCRADokumen6 halamanTan vs. Macapagal, 43 SCRANikkaDoriaBelum ada peringkat