Pengantar Kuliah Endodontik
Diunggah oleh
Silvia Dwi Gina0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
36 tayangan15 halamanJudul Asli
Pengantar kuliah endodontik.pptx
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
36 tayangan15 halamanPengantar Kuliah Endodontik
Diunggah oleh
Silvia Dwi GinaHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 15
Endodonti
Drg. Siti Rusdiana Puspa Dewi, M.Kes
Endodonti adalah..
The knowledge of what is inside the tooth
Endodontics: The branch of dentistry
concerned with the morphology, physiology
and pathology of the human dental pulp and
periradicular tissues
Tujuan dari perawatan endodonti
Maintain vitality of the pulp.
Preserve and restore the tooth with damaged
and necrotic pulp.
Preserve and restore the teeth which have
failed to the previous endodontic therapy, to
allow the tooth to remain functional in the
dental arch
Scope of endodontic
a. Vital pulp therapy (pulp capping, pulpotomy)
b Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of oral pain.
c. Root canal treatment of teeth with or without periradicular
pathology of pulpal origin.
d. Surgical management of pathology resulting form pulpal
pathosis.
e. Management of avulsed teeth (replantation)
f. Endodontic implants
g. Root end resections, hemisections and root resections
h. Retreatment of teeth previously treated endodontically
i. Bleaching of discolored teeth.
j. Coronal restorations of teeth using post and cores
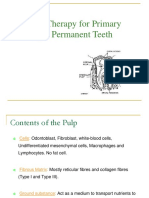
Apakah pulpa gigi itu?
Blood vessel
Nerve
Connective tissue
Jaringan pulpa berbeda dengan
jaringan lainnya di dalam tubuh
1. Surrounded by rigid walls unable to expand in response to injury
as a part of the inflammatory process.
2. There is minimal collateral blood supply to pulp tissue reduces
its capacity for repair following injury.
3. The pulp is composed almost entirely of simple connective tissue,
yet at its periphery there is a layer of highly specialized cells, the
odontoblasts.
4. The innervation of pulp tissue is both simple and complex.
Simple in that there are only free nerve endings and
consequently the pulp lacks proprioception.
Complex because of innervation of the odontoblast processes
which produces a high level of sensitivity to thermal and chemical
change
Apa yang menyebabkan jaringan pulpa
rusak?
Deep tooth decay (cavity)
A cracked tooth
Traumatic dental injury
Elective (for added retention of a crown)
Tanda umum terjadi kerusakan pulpa
1.Pain
2.Prolonged sensitivity to heat, cold or biting
3.Discoloration of the tooth
4.Swelling and tenderness in the gums
DIAGNOSA
The basic steps in diagnosis are:
1.Chief complaint
2.History: medical and dental
3.Oral examination: extra-oral and intra-oral
4.Special tests; ex. vitality test, percussion,
palpation
5.Radiographic examination
6.Data analysis: differential diagnosis
7.Treatment plan
Considerations Prior to Endodontic
Therapy
1. Is the tooth needed or important? Does it have
an opponent? Could it some day serve as an
abutment for prosthesis?
2. Is the tooth salvageable, or is it so badly
destroyed that it cannot be restored?
3. Is the entire dentition so completely broken
down that it would be virtually impossible to
restore?
Considerations Prior to Endodontic
Therapy
4. Is the tooth serving esthetically, or would the
patient be better served by its extraction and a
more cosmetic replacement?
5. Is the tooth so severely involved periodontally
that it would be lost soon for this reason?
6. Is the practitioner capable of performing the
needed endodontic procedures?
Prognosis Perawatan Saluran Akar
Success rate is high, around 90-100 % for vital
teeth
Vital teeth have better prognosis than necrotic
ones.
Teeth without periradicualrradiolucency have
better prognosis than teeth with
periradicularradiolucency
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Fixed Partial Dentures PPT For StudentsDokumen151 halamanFixed Partial Dentures PPT For Studentsduracell1950% (4)
- Focusing Instruction ManualDokumen15 halamanFocusing Instruction Manualplan2222100% (1)
- Foot and Ankle ArthrokinematicsDokumen6 halamanFoot and Ankle ArthrokinematicsCraig StewartBelum ada peringkat
- Six Elements and Chinese MedicineDokumen182 halamanSix Elements and Chinese MedicinePedro Maia67% (3)
- Pediatric ProsthodonticsDokumen84 halamanPediatric Prosthodonticsnihu100% (2)
- Pedodontic EndodonticDokumen141 halamanPedodontic EndodonticMihaela TuculinaBelum ada peringkat
- Wound CareDokumen14 halamanWound CareKirsten Padilla Chua100% (4)
- Endodontic Surgery: Bilog Falloran Ferrer Delos Reyes Palor Quinones'Dokumen42 halamanEndodontic Surgery: Bilog Falloran Ferrer Delos Reyes Palor Quinones'Michael Francis MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Pulp Therapy in Pediatric Dentistry ReviewDokumen47 halamanPulp Therapy in Pediatric Dentistry Reviewfirginaa100% (1)
- Lecture Notes On Prosthetics DentistryDokumen45 halamanLecture Notes On Prosthetics DentistryvelangniBelum ada peringkat
- Orthodontic Handbook for Dental AssistantsDari EverandOrthodontic Handbook for Dental AssistantsPenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- Fruit and Vegetable Diseases PDFDokumen563 halamanFruit and Vegetable Diseases PDFgrigorasalexandru100% (1)
- Introduction To Fixed ProsthodonticsDokumen15 halamanIntroduction To Fixed ProsthodonticsSyamilBunyamin100% (1)
- Acquired Diseases of Teeth, Dental Materials and Dental Radiography in Small AnimalsDokumen97 halamanAcquired Diseases of Teeth, Dental Materials and Dental Radiography in Small AnimalsgangaBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZDari EverandOral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (9)
- Prostho Rehabilitation - HypodontiaDokumen24 halamanProstho Rehabilitation - HypodontiaAmniAzmiBelum ada peringkat
- Non Vital Pulp TherapyDokumen23 halamanNon Vital Pulp TherapyAmit GaurBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar 6 Preventive Prosthodontics in CD WordDokumen29 halamanSeminar 6 Preventive Prosthodontics in CD Wordketaki kunteBelum ada peringkat
- Pulp Therapy in ChildrenDokumen4 halamanPulp Therapy in ChildrenshahinshamshiriBelum ada peringkat
- Muscles of Mastication Functions and Clinical SignificanceDokumen130 halamanMuscles of Mastication Functions and Clinical SignificanceDevanand GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Restoration of Endodontically Treated Teeth: Post and Core SystemDokumen59 halamanRestoration of Endodontically Treated Teeth: Post and Core SystemBishoy MaherBelum ada peringkat
- Endo & RestorativeDokumen59 halamanEndo & RestorativeLoredana RaduBelum ada peringkat
- Pulp Therapy in Pediatric Dentistry RevisedDokumen47 halamanPulp Therapy in Pediatric Dentistry RevisedShahid Shaikh100% (2)
- Implantology in General Dental PracticeDari EverandImplantology in General Dental PracticePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- 8-Treatment of Deep Caries, Vital Pulp Exposure, Pulpless TeethDokumen8 halaman8-Treatment of Deep Caries, Vital Pulp Exposure, Pulpless TeethAhmed AbdBelum ada peringkat
- Paed Endodontics 1Dokumen8 halamanPaed Endodontics 1Wen Shu GohBelum ada peringkat
- Scope of Endodontics: DefinitionDokumen5 halamanScope of Endodontics: DefinitionRana SayedBelum ada peringkat
- Tooth Extraction Bahasa InggrisDokumen3 halamanTooth Extraction Bahasa InggrisNoviyana Idrus DgmapatoBelum ada peringkat
- Non-Vital Pulp Therapy in Pediatric Dentistry: Lec.3 / Stage: 5 Dr. Huda Hussein Radhi Al-Manara Dentistry CollegeDokumen25 halamanNon-Vital Pulp Therapy in Pediatric Dentistry: Lec.3 / Stage: 5 Dr. Huda Hussein Radhi Al-Manara Dentistry CollegeDark DarkBelum ada peringkat
- Endo Instruments and MaterialsDokumen131 halamanEndo Instruments and MaterialsIndrani DasBelum ada peringkat
- Why Do We Need Root Canal TreatmentDokumen1 halamanWhy Do We Need Root Canal Treatmentethicaldental careBelum ada peringkat
- Journal ClubDokumen25 halamanJournal ClubAnonymous Val05Blj100% (1)
- Pulp Therapy For ChildrenDokumen5 halamanPulp Therapy For ChildrenathenaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Indications For Removal of TeethDokumen7 halaman1 - Indications For Removal of TeethLama NahedBelum ada peringkat
- DentoalveolarAbscess in Children LectureDokumen22 halamanDentoalveolarAbscess in Children LectureARNOLD OBIBelum ada peringkat
- Endodontics 1: PrelimsDokumen30 halamanEndodontics 1: PrelimsDaymon, Ma. TeresaBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDokumen13 halamanMakalah Bahasa InggrisNurmadinah Jamila YusriBelum ada peringkat
- An Adult OrthodonticsDokumen16 halamanAn Adult OrthodonticsDrAla MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Indirect Restoration That Covered On or More Cusp and It Is Located Between Oclusal Surfaces of The Posterior Tooth Too Damage The Basics FillingDokumen4 halamanIndirect Restoration That Covered On or More Cusp and It Is Located Between Oclusal Surfaces of The Posterior Tooth Too Damage The Basics FillingBagas Luthfi AlfatBelum ada peringkat
- Root Canal Treatment Consent FormDokumen2 halamanRoot Canal Treatment Consent FormMartina HodgsonBelum ada peringkat
- Pedo Pulp Therapy Y4Dokumen49 halamanPedo Pulp Therapy Y4Noor MaxeemBelum ada peringkat
- Preventive and InterseptiveDokumen90 halamanPreventive and InterseptivemuhammadBelum ada peringkat
- Pedodontic Lect 17Dokumen10 halamanPedodontic Lect 17Mustafa AmmarBelum ada peringkat
- Endodontics HandoutDokumen5 halamanEndodontics HandoutKristoffer JaraBelum ada peringkat
- Dental Trauma Presentation Group 1Dokumen29 halamanDental Trauma Presentation Group 1Nadya YoselinBelum ada peringkat
- What is a Root Canal TreatmentDokumen5 halamanWhat is a Root Canal TreatmentjjahaddinBelum ada peringkat
- Single DentureDokumen18 halamanSingle DentureKamugisha MosesBelum ada peringkat
- Overdentures for Tooth RetentionDokumen51 halamanOverdentures for Tooth Retentionsneha palBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnosis & Treatment PlanningDokumen46 halamanDiagnosis & Treatment PlanningNeha ChughBelum ada peringkat
- Anomalies DentinDokumen19 halamanAnomalies DentinHaffie HafiziBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar 6 Preventive Prosthodontics in CD WordDokumen29 halamanSeminar 6 Preventive Prosthodontics in CD Wordketaki kunteBelum ada peringkat
- 3-Mouth PreparationDokumen55 halaman3-Mouth Preparationyahia salahBelum ada peringkat
- 00 Intro Department of ProsthodonticsDokumen31 halaman00 Intro Department of ProsthodonticsLalit KumarBelum ada peringkat
- TUTORIAL IN ENGLISH Blok 12Dokumen7 halamanTUTORIAL IN ENGLISH Blok 12Ifata RDBelum ada peringkat
- IFDEA Dental Anatomy Educational Teaching ResourceDokumen38 halamanIFDEA Dental Anatomy Educational Teaching ResourceaerowongBelum ada peringkat
- Kuliah Gigi Dan MulutDokumen75 halamanKuliah Gigi Dan MulutWendz BouvierBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 4Dokumen4 halamanLec 4Pakistan Dental SocietyBelum ada peringkat
- StomatoDokumen22 halamanStomatoLuna sweetBelum ada peringkat
- Document (Denture Over Denture)Dokumen39 halamanDocument (Denture Over Denture)Saifurahman TarakiBelum ada peringkat
- CU-Sil Dentures - A Novel Approach To ConserveDokumen27 halamanCU-Sil Dentures - A Novel Approach To Conservereshma shaikBelum ada peringkat
- Ajman University of Science and TechnoloddgyDokumen10 halamanAjman University of Science and TechnoloddgyZainab Al-ObaidiBelum ada peringkat
- Overdenture 4th Year 15-3-2020Dokumen52 halamanOverdenture 4th Year 15-3-2020Ahmed AliBelum ada peringkat
- Teeth Root Canal TreatmentDokumen3 halamanTeeth Root Canal TreatmentAdit Wendy YRBelum ada peringkat
- Dental ImplantDokumen28 halamanDental Implantemanmoawia32Belum ada peringkat
- OrthodonticsDokumen18 halamanOrthodonticsSorinBelum ada peringkat
- Pengantar Kuliah EndodontikDokumen15 halamanPengantar Kuliah EndodontikSilvia Dwi GinaBelum ada peringkat
- Cyst of The JawDokumen61 halamanCyst of The JawSilvia Dwi GinaBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal Asli RKG 4Dokumen6 halamanJurnal Asli RKG 4Silvia Dwi GinaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S0012160608010221 MainDokumen10 halaman1 s2.0 S0012160608010221 MainSilvia Dwi GinaBelum ada peringkat
- Radiographic Interpretation of Periodontal Disease Part 1Dokumen25 halamanRadiographic Interpretation of Periodontal Disease Part 1Silvia Dwi GinaBelum ada peringkat
- Vit CDokumen10 halamanVit C3/2 no.34 สรัญญากร สีหาราชBelum ada peringkat
- Overview of Complications Occurring in The Post-Anesthesia Care UnitDokumen14 halamanOverview of Complications Occurring in The Post-Anesthesia Care UnitShahabuddin ShaikhBelum ada peringkat
- Gastro-Intestinal System Diagnostic TestsDokumen11 halamanGastro-Intestinal System Diagnostic TestsFev BanataoBelum ada peringkat
- CH4106 Formulation Module GuideDokumen29 halamanCH4106 Formulation Module GuideWeimingTanBelum ada peringkat
- POLYGRAPHY: THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD OF DETECTING DECEPTIONDokumen15 halamanPOLYGRAPHY: THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD OF DETECTING DECEPTIONEino DuldulaoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4Dokumen7 halamanChapter 4R LashBelum ada peringkat
- Comparative Study The Effect of Induction of General Anesthesia With Propofol Versus Thiopentone in Pediatric Age Group On Cardiovascular SystemDokumen8 halamanComparative Study The Effect of Induction of General Anesthesia With Propofol Versus Thiopentone in Pediatric Age Group On Cardiovascular SystemCentral Asian StudiesBelum ada peringkat
- Thalassemia: SymptomsDokumen3 halamanThalassemia: SymptomsAndi BandotBelum ada peringkat
- CorneaDokumen41 halamanCorneaNikhil KorripatiBelum ada peringkat
- Pengaruh Faktor-Faktor Psikososial Dan Insomnia Terhadap Depresi Pada Lansia Di Kota YogyakartaDokumen5 halamanPengaruh Faktor-Faktor Psikososial Dan Insomnia Terhadap Depresi Pada Lansia Di Kota YogyakartaKristina Puji LestariBelum ada peringkat
- Lim Et Al 2017 PDFDokumen37 halamanLim Et Al 2017 PDFkirshBelum ada peringkat
- Bacillus lipopeptides: versatile weapons against plant diseasesDokumen11 halamanBacillus lipopeptides: versatile weapons against plant diseasesjazminBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology-REVIEWER-Practical ExamDokumen12 halamanAnatomy and Physiology-REVIEWER-Practical ExamDeity Ann ReuterezBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER SUMMARY-opiod AnalgesicDokumen9 halamanCHAPTER SUMMARY-opiod AnalgesicNuttiya WerawattanachaiBelum ada peringkat
- Journal Reading Radiologi EllaDokumen44 halamanJournal Reading Radiologi EllaElla Putri SaptariBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanisms of Cardiac Arrhythmias From Automatici+Dokumen24 halamanMechanisms of Cardiac Arrhythmias From Automatici+Malar MannanBelum ada peringkat
- Metabolism of DisaccharidesDokumen15 halamanMetabolism of DisaccharidesminaBelum ada peringkat
- Comprehensive Review of Temporal Lobe EpilepsyDokumen36 halamanComprehensive Review of Temporal Lobe Epilepsyyohanes0gadiBelum ada peringkat
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputDokumen4 halamanRisk For Decreased Cardiac Outputapi-283482759Belum ada peringkat
- 3 PBDokumen12 halaman3 PBDumitruBelum ada peringkat
- 201305283en Capsurefix 5076Dokumen2 halaman201305283en Capsurefix 5076Bian PurwaBelum ada peringkat
- Anxiety: What Are Some Symptoms of Anxiety?Dokumen3 halamanAnxiety: What Are Some Symptoms of Anxiety?Khairil AshrafBelum ada peringkat
- Form4 NOTES-Nervous SystemDokumen9 halamanForm4 NOTES-Nervous SystemCaroline H DavidBelum ada peringkat
- SGD Physiology Endocrine and MetabolismDokumen7 halamanSGD Physiology Endocrine and MetabolismTinesh RajahBelum ada peringkat