Presentation DNA Cryptography
Diunggah oleh
cool_duke88Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Presentation DNA Cryptography
Diunggah oleh
cool_duke88Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
DNA Computers Applications:
Cryptography
Constanza Lampasona
Innovative Computer Architectures and Concepts
Computer Architecture Department - University of Stuttgart
Motivation
• Silicon technologies have limits
• Research intends to deal with “silicon” disadvantages
• DNA computing -> inherent parallelism
• Cryptographic problem requires vast parallelism
Let’s solve the cryptographic problem using a molecular computer!!!
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 2
yptography
Outline
1. Introduction
2. Cryptography
3. DNA Computing
4. Breaking DES using a molecular computer
5. Conclusions
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 3
yptography
Introduction
Encoding data “as in nature”
Input Recombination Output
algorithm
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 4
yptography
Introduction
Cryptography
Secret writing
Gjoejoh uif lfz Shift by one Finding the key
Data Encryptation Standard: approved cryptographic algorithm as
required by FIPS 140-1 (Federal Information Processing Standards)
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 5
yptography
Outline
1. Introduction
2. Cryptography
3. DNA Computing
4. Breaking DES using a molecular computer
5. Conclusions
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 6
yptography
Cryptography
From the Greek: crypto-, hidden + -graphy,
-graphy writing
“The art of writing with a secret key or in an enigmatic way”
Let’s look at history...
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 7
yptography
Cryptography
Encryption
Protecting information
Data Transformation Unreadable form
Ensure privacy
Keep the information hidden
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 8
yptography
Cryptography
Decryption
Reverse of Encryption
Encrypted data Transformation Intelligible form
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 9
yptography
Cryptography
Encryption Decryption
Secret KEY
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 10
yptography
Cryptography
Encrypted data (cipher-text): Khoor zruog
Secret KEY: shift by 3
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z a b c
Decrypted data (plain-text): Hello world
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 11
yptography
Cryptography
Data Encryption Standard (DES)
• Crytographic algorithm (National Bureau of Standards).
• Enciphering and Deciphering.
Deciphering
• 64-bit key.
• Data depends on key’s security.
• Unique key for encryting and decryting.
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 12
yptography
Cryptography
DES’ Data Encryption Algorithm
Enciphering
Initial Inverse initial
Input Computation Output
permutation permutation
IP IP -1
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 13
yptography
Cryptography
Initial Inverse initial
Input Computation Output
permutation permutation
IP IP -1
IP
58 50 42 34 26 18 10 2
60 52 44 36 28 20 12 4
62 54 46 38 30 22 14 6
64 56 48 40 32 24 16 8
57 49 41 33 25 17 9 1
59 51 43 35 27 19 11 3
61 53 45 37 29 21 13 5
63 55 47 39 31 23 15 7
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 14
yptography
Cryptography
Initial Inverse initial
Input Computation Output
permutation permutation
IP IP -1
• Uses the permuted input block as input.
• Produces a pre-output block.
• 16 iterations.
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 15
yptography
Cryptography
Initial Inverse initial
Input Computation Output
permutation permutation
IP IP -1
IP-1
40 8 48 16 56 24 64 32
39 7 47 15 55 23 63 31
Plain-text
38 6 46 14 54 22 Cipher-text
62 30
37 5 45 13 53 21 61 29
36 4 44 12
Key 52 20 60 28
35 3 43 11 51 19 59 27
34 2 42 10 50 18 58 26
33 1 41 9 49 17 57 25
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 16
yptography
Outline
1. Introduction
2. Cryptography
3. DNA Computing
4. Breaking DES using a molecular computer
5. Conclusions
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 17
yptography
DNA Computing
DNA
DNA Genetic information “memory”
(Deoxyribonucleic acid)
Nucleotides strung into
polymer chains (DNA Strands)
Four classes of nucleotides:
Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine (A,C,G,T)
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 18
yptography
DNA Computing
• The Structure of DNA
The double helix structure discovered by Watson and Crick
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 19
yptography
DNA Computing
DNA
DNA
Computer:
Computer:
• Based on Adleman’s work (1994) DNAStrands
Strands
DNA
• Solve huge problems by parallel search
++
• Much faster than a conventional computer Combinations
Combinations
• More hardware vs. more DNA
==
“Solution”
“Solution”
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 20
yptography
Outline
1. Introduction
2. Cryptography
3. DNA Computing
4. Breaking DES using a molecular computer
5. Conclusions
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 21
yptography
Breaking DES
• The Idea
Finding a key given one pair (plain-text, cipher-text).
Pre-processing + one day of work = recover the key.
First example of a real problem solved using DNA.
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 22
yptography
Breaking DES
• Massive parallel DNA computing approach:
• Generate all possible solutions in parallel
• Remove wrong solutions
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 23
yptography
Breaking DES
Representing binary strings
Plan of DES attack
Prepare the DNA solution
Extract desired patterns
Read the result
Break DES!!!
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 24
yptography
Breaking DES
• Summary of the experiment
DES(M0,k) encoding plain-text with all possible 256 keys
4 months
Extract DES(M0,k)=E0, (plaintext, cipher-text)
Read k
1 day
DNAComputer:
DNA Computer:
DNAStrands
DNA Strands
++
Combinations
Combinations
==
“Solution”
“Solution”
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 25
yptography
Outline
1. Introduction
2. Cryptography
3. DNA Computing
4. Breaking DES using a molecular computer
5. Conclusions
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 26
yptography
Conclusions
DNA computing with a concrete application,
Cryptography
Very general attack on DES, using 64-bit key
Cryptosystems with 64-bit key are insecure
Future of molecular computers: Unclear
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 27
yptography
Summary
Cryptography
DES
DNA Computing >>> Parallelism
Breaking DES
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 28
yptography
http://www.ra.informatik.uni-stuttgart.de/~virazela/Seminar/Material/Presentation8/
June 2002 DNA Computers Applications: Cr 29
yptography
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- PPL Complete Notes JntuhDokumen125 halamanPPL Complete Notes JntuhAngel SweetyBelum ada peringkat
- Network Management System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDari EverandNetwork Management System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Theory QBankDokumen7 halamanTheory QBankPrashant RautBelum ada peringkat
- Deep Learning R18 Jntuh Lab ManualDokumen21 halamanDeep Learning R18 Jntuh Lab Manualnphotographer99Belum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Data Science Lab Manual New1Dokumen32 halamanFundamentals of Data Science Lab Manual New1Shamilie MBelum ada peringkat
- Cse Lab Manual NetworksDokumen40 halamanCse Lab Manual NetworksLoganathan RmBelum ada peringkat
- DL Lab Manual A.Y 2022-23-1Dokumen67 halamanDL Lab Manual A.Y 2022-23-1sivaswaroopsarma rockstar100% (1)
- PPS Lab File With SolutionDokumen70 halamanPPS Lab File With SolutionSomesh ShuklaBelum ada peringkat
- Cs8591 - CN Unit 4Dokumen33 halamanCs8591 - CN Unit 4Vidhya RajBelum ada peringkat
- VB Net Unit IDokumen25 halamanVB Net Unit Ishamalu2011100% (1)
- An Introduction of Web Engineering: Windu Gata, MkomDokumen173 halamanAn Introduction of Web Engineering: Windu Gata, MkomWindu Gata100% (1)
- GATE Compiler Design 93-2009Dokumen12 halamanGATE Compiler Design 93-2009singhmanish1997100% (2)
- Ccs335 Cloud Computing L T P C 2 0 2 3Dokumen3 halamanCcs335 Cloud Computing L T P C 2 0 2 3gtrajasekaran1Belum ada peringkat
- DCN Lab ManualDokumen34 halamanDCN Lab ManualUmang Thakkar100% (1)
- Instruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle Memory Reference Instructions Input-Output and Interrupt Complete Computer DescriptionDokumen38 halamanInstruction Codes Computer Registers Computer Instructions Timing and Control Instruction Cycle Memory Reference Instructions Input-Output and Interrupt Complete Computer DescriptionYash Gupta MauryaBelum ada peringkat
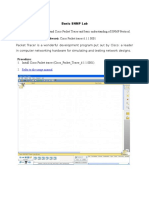
- Basic SNMP LabsDokumen10 halamanBasic SNMP LabsSyed Imran Ali Kazmi0% (1)
- CS3591 Computer Networks Unit-01 NotesDokumen87 halamanCS3591 Computer Networks Unit-01 Notescse241085Belum ada peringkat
- Augmented Reality and Mixed RealityDokumen44 halamanAugmented Reality and Mixed RealityDevesh KankariyaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 5Dokumen4 halamanUnit 5imm100% (1)
- Agents and CommunitiesDokumen53 halamanAgents and CommunitiesManoj PuliBelum ada peringkat
- Secrecy Preserving Discovery of Subtle Statistic ContentsDokumen5 halamanSecrecy Preserving Discovery of Subtle Statistic ContentsIJSTEBelum ada peringkat
- C Programming Source Code For CRCDokumen7 halamanC Programming Source Code For CRCSathiyapriya ShanmugasundaramBelum ada peringkat
- Os Lab ManualDokumen107 halamanOs Lab ManualYuva PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Practical-2: 2IT702: Artificial Intelligence Practical-2Dokumen5 halamanPractical-2: 2IT702: Artificial Intelligence Practical-2DEVANSHI PAREJIYABelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Problems For OsDokumen4 halamanAssignment Problems For Osmanishbhavesh0% (1)
- Co-Po Big Data AnalyticsDokumen41 halamanCo-Po Big Data AnalyticssuniBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-4 Question BankDokumen3 halamanUnit-4 Question BankDeepakBelum ada peringkat
- Arp and Rarp Chap 08Dokumen18 halamanArp and Rarp Chap 08Hanu Pratap SinghBelum ada peringkat
- CG Monitors WorkstationDokumen14 halamanCG Monitors WorkstationAmbika JaiswalBelum ada peringkat
- Prototyping The Physical Design For IoT DevicesDokumen4 halamanPrototyping The Physical Design For IoT DevicesZia AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- DLP Practicals 1 To 7Dokumen24 halamanDLP Practicals 1 To 7Mit PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Example of Des Algorithm PDFDokumen2 halamanExample of Des Algorithm PDFGary0% (1)
- Computer Graphics - PPTDokumen22 halamanComputer Graphics - PPTrjBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Graphics: Geometry and Line GenerationDokumen5 halamanComputer Graphics: Geometry and Line GenerationVuggam VenkateshBelum ada peringkat
- CCS374 Web Application SecurityDokumen18 halamanCCS374 Web Application Securitybarathkumar00001Belum ada peringkat
- CN Lab Record FinalDokumen77 halamanCN Lab Record Finalsham kevinBelum ada peringkat
- Programming in C++ Term Project Assignment: General InstructionsDokumen2 halamanProgramming in C++ Term Project Assignment: General InstructionsBENBelum ada peringkat
- Graphics Functions in CDokumen9 halamanGraphics Functions in CKedar KulkarniBelum ada peringkat
- Bca-Vi Sem-Pc HW and Network-SylDokumen6 halamanBca-Vi Sem-Pc HW and Network-Syllo leeeBelum ada peringkat
- CCS341-Data Warehousing Notes-Unit IDokumen30 halamanCCS341-Data Warehousing Notes-Unit INISHANTH MBelum ada peringkat
- C&NS Lab Manual 2021Dokumen64 halamanC&NS Lab Manual 2021nawal 109Belum ada peringkat
- DM Mod3 PDFDokumen96 halamanDM Mod3 PDFshilpa veeruBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT 2 Virtualization CCDokumen73 halamanUNIT 2 Virtualization CCjetowi8867Belum ada peringkat
- Network Programming ImpDokumen5 halamanNetwork Programming Impsharath_rakkiBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz Application in C#Dokumen9 halamanQuiz Application in C#Shreya100% (1)
- Computer Science and Engineering - 2019 Scheme s4 Syllabus - Ktustudents - inDokumen153 halamanComputer Science and Engineering - 2019 Scheme s4 Syllabus - Ktustudents - inAswin AyyappadasBelum ada peringkat
- AD3251 Data Structures Design Question Bank 1Dokumen1 halamanAD3251 Data Structures Design Question Bank 1bbook6930Belum ada peringkat
- 2017-CE-008 Lab 04Dokumen12 halaman2017-CE-008 Lab 04kamran khanBelum ada peringkat
- Amity University Haryana: Digital Image Processing Lab Practical FileDokumen20 halamanAmity University Haryana: Digital Image Processing Lab Practical FileRamakrishna MaligeyBelum ada peringkat
- Os Practical FileDokumen50 halamanOs Practical FileKunal MathurBelum ada peringkat
- Lab ManualDokumen48 halamanLab ManualVIDYA PBelum ada peringkat
- Selected Topics in Computer Science CHDokumen24 halamanSelected Topics in Computer Science CHMehari TemesgenBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Graphics Practical FileDokumen30 halamanComputer Graphics Practical FileFotavo JugilanBelum ada peringkat
- OOPs in C++ UNIT-IDokumen135 halamanOOPs in C++ UNIT-IAnanya Gupta0% (1)
- Topic 1 - Introduction To C# ProgrammingDokumen42 halamanTopic 1 - Introduction To C# ProgrammingKhalid Mehboob100% (1)
- Computer Graphics - Unit 1 ABG Notes PPT Part IDokumen63 halamanComputer Graphics - Unit 1 ABG Notes PPT Part IAshwini Gavali100% (2)
- DWDM Lab Manual FinalDokumen153 halamanDWDM Lab Manual FinalVaahnikaBelum ada peringkat
- 5d-MC Final ReportDokumen26 halaman5d-MC Final ReportsurvivalofthepolyBelum ada peringkat
- Proceeding of The 3rd Annul National Conference On Agriculture and Environmental Management For Sustainable Development From June 17-18, 2016Dokumen277 halamanProceeding of The 3rd Annul National Conference On Agriculture and Environmental Management For Sustainable Development From June 17-18, 2016Tolasa RegasaBelum ada peringkat
- Spin Your Self Talk: A Guide To Breaking Out of A Self-Talk RutDokumen11 halamanSpin Your Self Talk: A Guide To Breaking Out of A Self-Talk RutAmelia HandayaniBelum ada peringkat
- A869-6-44-0005 PMS For RevampDokumen950 halamanA869-6-44-0005 PMS For RevampMastram HatheshBelum ada peringkat
- EN 10168 - 2004 - Steel Products - Inspection Documents PDFDokumen12 halamanEN 10168 - 2004 - Steel Products - Inspection Documents PDFBogdanBelum ada peringkat
- Week 13 & 14 - LecturesDokumen46 halamanWeek 13 & 14 - LecturesAmyHuiBelum ada peringkat
- Structural Geolgy MCQs With AnswerDokumen11 halamanStructural Geolgy MCQs With Answerkumar Harsh100% (4)
- 03Dokumen34 halaman03Gagan JainBelum ada peringkat
- Efectele SimulatieiDokumen84 halamanEfectele SimulatieimihaelaBelum ada peringkat
- DLL Mathematics 6 Whole YearDokumen241 halamanDLL Mathematics 6 Whole YearHazel Jane Fabrigas - BaguioBelum ada peringkat
- Read Each Question Carefully. Mark Only One Answer. Solve Your Diagnostic Test On Time. Do HandwritingDokumen3 halamanRead Each Question Carefully. Mark Only One Answer. Solve Your Diagnostic Test On Time. Do HandwritingJhoanna ToroBelum ada peringkat
- Description: V / S - r250dDokumen4 halamanDescription: V / S - r250dAli OsmanBelum ada peringkat
- How To Write The Introduction of Your Research Paper?: Marjurie Lourince E. Zanoria, CPADokumen22 halamanHow To Write The Introduction of Your Research Paper?: Marjurie Lourince E. Zanoria, CPAulquira grimamajowBelum ada peringkat
- CBO9780511530159A007Dokumen3 halamanCBO9780511530159A007Ali AzariunBelum ada peringkat
- PD GadDokumen45 halamanPD GadB I N SBelum ada peringkat
- Issue 01 PDFDokumen98 halamanIssue 01 PDFUmmeBelum ada peringkat
- Issues in MathematicsDokumen7 halamanIssues in MathematicsPavitra KannadassBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Bahasa Inggris KLS IxDokumen5 halamanSoal Bahasa Inggris KLS IxIrvan RiandiBelum ada peringkat
- Research Foundation For Science Technology and Natural Resource Policy V Union of India OthersDokumen6 halamanResearch Foundation For Science Technology and Natural Resource Policy V Union of India OthersKartik BhargavaBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 7 CBC Business Studies Schemes of Work Term 1Dokumen14 halamanGrade 7 CBC Business Studies Schemes of Work Term 1GEOFRY KIRUIBelum ada peringkat
- Chapters 2-4Dokumen72 halamanChapters 2-4WondmageneUrgessaBelum ada peringkat
- MEEN 20052 - Week 4 - Salamat, Andre Agassi D.Dokumen4 halamanMEEN 20052 - Week 4 - Salamat, Andre Agassi D.andreagassiBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Full Book TestDokumen3 halamanPhysics Full Book TestLearnEnglish WithAriBelum ada peringkat
- Uise Turgeon: and TechniqueDokumen456 halamanUise Turgeon: and TechniqueybiernasdonBelum ada peringkat
- ICP-OES - ICP Chemistry, ICP-OES Analysis, Strengths and LimitationsDokumen11 halamanICP-OES - ICP Chemistry, ICP-OES Analysis, Strengths and LimitationsMuhammad NadeemBelum ada peringkat
- Instructor: Dipanjan Basu: Civil & Environmental Engineering University of Waterloo Waterloo, ON, CanadaDokumen29 halamanInstructor: Dipanjan Basu: Civil & Environmental Engineering University of Waterloo Waterloo, ON, CanadaDamilare OlaniyanBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 7 Computer Workstation ErgonomicsDokumen17 halamanLesson 7 Computer Workstation ErgonomicsRonaldo PalomaBelum ada peringkat
- Research and Writing For Undergraduates: What You Need To Know For Survival and SuccessDokumen46 halamanResearch and Writing For Undergraduates: What You Need To Know For Survival and SuccessAlynsa ErynBelum ada peringkat
- Consumers Health and ResponsibilitiesDokumen6 halamanConsumers Health and Responsibilitiesmary rose ombrogBelum ada peringkat
- Soal B. Inggris Kelas X Semester 2Dokumen5 halamanSoal B. Inggris Kelas X Semester 2Aliyah Al-IhsaniyahBelum ada peringkat
- Mi CepDokumen9 halamanMi CepSaad khanBelum ada peringkat
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsDari EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (722)
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewDari EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Chaos Monkeys: Obscene Fortune and Random Failure in Silicon ValleyDari EverandChaos Monkeys: Obscene Fortune and Random Failure in Silicon ValleyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (111)
- Cyber War: The Next Threat to National Security and What to Do About ItDari EverandCyber War: The Next Threat to National Security and What to Do About ItPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (66)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveDari EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveBelum ada peringkat
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyDari EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (228)
- Scary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldDari EverandScary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (55)
- Learn Python Programming for Beginners: Best Step-by-Step Guide for Coding with Python, Great for Kids and Adults. Includes Practical Exercises on Data Analysis, Machine Learning and More.Dari EverandLearn Python Programming for Beginners: Best Step-by-Step Guide for Coding with Python, Great for Kids and Adults. Includes Practical Exercises on Data Analysis, Machine Learning and More.Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (34)
- Alibaba: The House That Jack Ma BuiltDari EverandAlibaba: The House That Jack Ma BuiltPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (29)
- CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Ninth EditionDari EverandCISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, Ninth EditionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Excel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceDari EverandExcel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceBelum ada peringkat
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindDari EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindBelum ada peringkat
- Four Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceDari EverandFour Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligencePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Solutions Architect's Handbook: Kick-start your career as a solutions architect by learning architecture design principles and strategiesDari EverandSolutions Architect's Handbook: Kick-start your career as a solutions architect by learning architecture design principles and strategiesBelum ada peringkat
- The Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldDari EverandThe Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (107)
- Understanding Software: Max Kanat-Alexander on simplicity, coding, and how to suck less as a programmerDari EverandUnderstanding Software: Max Kanat-Alexander on simplicity, coding, and how to suck less as a programmerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (44)
- Python for Beginners: A Crash Course Guide to Learn Python in 1 WeekDari EverandPython for Beginners: A Crash Course Guide to Learn Python in 1 WeekPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (7)
- 100M Offers Made Easy: Create Your Own Irresistible Offers by Turning ChatGPT into Alex HormoziDari Everand100M Offers Made Easy: Create Your Own Irresistible Offers by Turning ChatGPT into Alex HormoziBelum ada peringkat
- The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationDari EverandThe Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (6)
- CompTIA Security+ Get Certified Get Ahead: SY0-701 Study GuideDari EverandCompTIA Security+ Get Certified Get Ahead: SY0-701 Study GuidePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewDari EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (104)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeDari EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (69)
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessDari EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessBelum ada peringkat
- The Staff Engineer's Path: A Guide for Individual Contributors Navigating Growth and ChangeDari EverandThe Staff Engineer's Path: A Guide for Individual Contributors Navigating Growth and ChangePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (6)