What is an Image Sensor
Diunggah oleh
Ihuhwa Marta TauDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
What is an Image Sensor
Diunggah oleh
Ihuhwa Marta TauHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
What is an Image Sensor?
• An Image Sensor is a photosensitive device that converts light signals into digital signals
(colours). It uses film to capture and store an image.
• Image sensors contain millions of photosensitive diodes known as photosites.
• When you take a picture, the camera's shutter opens briefly and each photo site on the
image sensor records the brightness of the light that falls on it by accumulating photons.
The more light that hits a photo site, the more photons it records.
• The brightness recorded by each photosite is then stored as a set of numbers (digital
numbers) that can then be used to set the color and brightness of a single pixel on the
screen or ink on the printed page to reconstruct the image.
An image sensor is typically of two types:
1. Charged Coupled Device (CCD)
2. Complementary Metal Oxide
Semiconductor (CMOS)
What is CCD?
• Charge-coupled devices (CCDs) are silicon-based integrated
circuits consisting of a dense matrix of photodiodes that
operate by converting light energy in the form of photons into
an electronic charge.
• Electrons generated by the interaction of photons with silicon
atoms are stored in a potential well and can subsequently be
transferred across the chip through registers and output to an
amplifier.
What is CMOS?
• “CMOS" refers to both a particular style of digital circuitry design, and the
family of processes used to implement that circuitry on integrated circuits
(chips).
• CMOS circuitry dissipates less power when static, and is denser than other
implementations having the same functionality.
• CMOS circuits use a combination of p-type and n-type metal–oxide–
semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) to implement logic gates and
other digital circuits found in computers, telecommunications equipment, and
signal processing equipment.
CCD vs CMOS
• CMOS image sensors can incorporate other circuits on the same chip, eliminating
the many separate chips required for a CCD.
• This also allows additional on-chip features to be added at little extra cost. These
features include image stabilization and image compression.
• Not only does this make the camera smaller, lighter, and cheaper; it also requires
less power so batteries last longer.
• CMOS image sensors can switch modes on the fly between still photography and
video.
• CMOS sensors excel in the capture of outdoor pictures on sunny days, they suffer
in low light conditions.
• Their sensitivity to light is decreased because part of each photosite is covered
with circuitry that filters out noise and performs other functions.
• The percentage of a pixel devoted to collecting light is called the pixel’s fill factor.
CCDs have a 100% fill factor but CMOS cameras have much less.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- CVP The Fundamentals of Camera and Image Sensor Technology Jon ChouinardDokumen157 halamanCVP The Fundamentals of Camera and Image Sensor Technology Jon ChouinardJopher Fernandez NazarioBelum ada peringkat
- Diy #506 Cable HomemadeDokumen2 halamanDiy #506 Cable Homemadewexler100% (1)
- R01an0239ej sh7125Dokumen35 halamanR01an0239ej sh7125ArmanBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar ON Image SensorDokumen22 halamanSeminar ON Image SensorBE CAREFULBelum ada peringkat
- CCTV and Image SensorsDokumen15 halamanCCTV and Image SensorsmjmanishBelum ada peringkat
- Image Sensors: Unit 5Dokumen14 halamanImage Sensors: Unit 5laka singhBelum ada peringkat
- Charge Coupled DevicesDokumen11 halamanCharge Coupled DevicesSucrose FructoseBelum ada peringkat
- Diff in Cmos and CCDDokumen1 halamanDiff in Cmos and CCDAanya BansalBelum ada peringkat
- Image Sensor Performance MetricsDokumen29 halamanImage Sensor Performance Metricsmarshal robertBelum ada peringkat
- Difference Between CCD and CMOSDokumen4 halamanDifference Between CCD and CMOSVikas LakhmaniBelum ada peringkat
- CCD & CMOS Image SensorsDokumen17 halamanCCD & CMOS Image SensorsJc Mtge0% (1)
- Image SensorDokumen15 halamanImage SensorPianist AliBelum ada peringkat
- Image Sensor - CMOS VS CCDDokumen21 halamanImage Sensor - CMOS VS CCDbkrebtelBelum ada peringkat
- Differences between CMOS and CCD image sensorsDokumen37 halamanDifferences between CMOS and CCD image sensorsmehta_kpBelum ada peringkat
- Reading Material-1st ClassDokumen5 halamanReading Material-1st ClassMansi GaurBelum ada peringkat
- CCD and Cmos SensorsDokumen16 halamanCCD and Cmos SensorsVijay Ravi100% (1)
- Charge Coupled Device (CCD) : Prepared By: Sagar Reddy DOEACC B Level (Sagarred@yahoo - Co.in)Dokumen43 halamanCharge Coupled Device (CCD) : Prepared By: Sagar Reddy DOEACC B Level (Sagarred@yahoo - Co.in)BE CAREFULBelum ada peringkat
- What Is The Difference Between CCD and Cmos Image Sensors in A Digital CameraDokumen2 halamanWhat Is The Difference Between CCD and Cmos Image Sensors in A Digital Cameraapi-281488866Belum ada peringkat
- Flow Measurement Via Via: Digital Image AnalysisDokumen27 halamanFlow Measurement Via Via: Digital Image Analysis400KVBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Cameras 061401 Siddharth ChauhanDokumen30 halamanDigital Cameras 061401 Siddharth ChauhanSiddharth ChauhanBelum ada peringkat
- Charge-Coupled Device: Integrated Circuit Capacitors Electric Charge Digital ImagingDokumen4 halamanCharge-Coupled Device: Integrated Circuit Capacitors Electric Charge Digital ImagingGaurav TewatiaBelum ada peringkat
- Key Technologies and Research Development of CMOS Image Sensors - SEMINARDokumen19 halamanKey Technologies and Research Development of CMOS Image Sensors - SEMINARSurajRNBelum ada peringkat
- High Speed Sensor: Pratyush ParimalDokumen5 halamanHigh Speed Sensor: Pratyush ParimalAnonymous mlYYLRe7HBelum ada peringkat
- Mechatronics: Module - ViDokumen53 halamanMechatronics: Module - ViNazeema TTBelum ada peringkat
- CCD Camera Basics: Pixels, Sensors and Digital ImagingDokumen18 halamanCCD Camera Basics: Pixels, Sensors and Digital ImagingSoif AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Sensor TechnologyDokumen9 halamanSensor TechnologyMudasir MirBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To The Digital Still CamDokumen9 halamanAn Introduction To The Digital Still CamZlatko OžanićBelum ada peringkat
- CCD Imaging Process ExplainedDokumen23 halamanCCD Imaging Process ExplainedTAIEBA TAHER 19METE011PBelum ada peringkat
- A Seminar On Digital Photography: Ashish Kulkarni (04ec18)Dokumen14 halamanA Seminar On Digital Photography: Ashish Kulkarni (04ec18)dannyzarBelum ada peringkat
- EnglishDokumen12 halamanEnglishDinno Noody BobicBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Cameras How THEY WORK ?Dokumen14 halamanDigital Cameras How THEY WORK ?Ruve Baba100% (2)
- What Is CMOS SensorDokumen2 halamanWhat Is CMOS SensorndaputBelum ada peringkat
- Notes On Digital Camera 1Dokumen5 halamanNotes On Digital Camera 1Ashoka VanjareBelum ada peringkat
- How Digital Cameras WorkDokumen17 halamanHow Digital Cameras WorkAnusha DandayBelum ada peringkat
- Active Pixel Sensors Seminar Report: Harikumar.K. E7B, 16Dokumen12 halamanActive Pixel Sensors Seminar Report: Harikumar.K. E7B, 16Hari KumarBelum ada peringkat
- CCDs Convert Light to Digital ImagesDokumen13 halamanCCDs Convert Light to Digital ImagesSourodeep BasuBelum ada peringkat
- Perfomrance Analysis - Image QualityDokumen22 halamanPerfomrance Analysis - Image QualityYousef ElganzouryBelum ada peringkat
- Perfomrance Analysis - Image QualityDokumen11 halamanPerfomrance Analysis - Image QualityYousef ElganzouryBelum ada peringkat
- Dip1 IntroductionDokumen46 halamanDip1 IntroductionmadumacBelum ada peringkat
- CCD Imaging Sensor Wins Nobel PrizeDokumen6 halamanCCD Imaging Sensor Wins Nobel PrizeBE CAREFULBelum ada peringkat
- Active pixel sensor technology explainedDokumen2 halamanActive pixel sensor technology explainedSumeet Nagpal RahiBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar ON: Guru Nanak Institute of TechnologyDokumen11 halamanSeminar ON: Guru Nanak Institute of TechnologyAritra RoyBelum ada peringkat
- CMOS Vs CCDDokumen5 halamanCMOS Vs CCDTad FerreiraBelum ada peringkat
- CCD TheoryDokumen4 halamanCCD Theoryajmalhussain7676Belum ada peringkat
- Cmos Image SensorsDokumen10 halamanCmos Image Sensorsaleksandar.haBelum ada peringkat
- How The Camera " Sees" The Image: A Presentation OnDokumen22 halamanHow The Camera " Sees" The Image: A Presentation OnhelpresearchBelum ada peringkat
- CCD Cameras - How They Work: and How To Correct For The Errors They Make Along The WayDokumen31 halamanCCD Cameras - How They Work: and How To Correct For The Errors They Make Along The WayClinton NyachieoBelum ada peringkat
- Https Myguru - Upsi.edu - My Documents 2021 Courses MRM3015 Material K03448 20211015113951 MRM3015 Week 7Dokumen21 halamanHttps Myguru - Upsi.edu - My Documents 2021 Courses MRM3015 Material K03448 20211015113951 MRM3015 Week 7farah naziraBelum ada peringkat
- Cmos Image Sensors - Electronic Camera On A ChipDokumen9 halamanCmos Image Sensors - Electronic Camera On A Chipziko23Belum ada peringkat
- What Is CCD Camera?: Infrared Astronomy CmosDokumen4 halamanWhat Is CCD Camera?: Infrared Astronomy CmosSamaresh RoyBelum ada peringkat
- Webcams:: How Does A Webcam Work?Dokumen4 halamanWebcams:: How Does A Webcam Work?Kiran Kumar Athirala0% (1)
- Detectors: Ccds For Life-Science ApplicationsDokumen6 halamanDetectors: Ccds For Life-Science ApplicationsgastromonoBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Charge Coupled Devices: Steve B. Howell NoaoDokumen27 halamanBasics of Charge Coupled Devices: Steve B. Howell Noaoucing_33Belum ada peringkat
- Active Pixel Sensor / CMOS: HistoryDokumen7 halamanActive Pixel Sensor / CMOS: HistoryMoji PiyapongBelum ada peringkat
- Artificial Intelligence: Chapter# 03 Computer VisionDokumen33 halamanArtificial Intelligence: Chapter# 03 Computer Visionzabih niazaiBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To How Camcorders WorkDokumen15 halamanIntroduction To How Camcorders Worksaravvanon_murthyBelum ada peringkat
- CMOS Image Sensors - IntroductionDokumen15 halamanCMOS Image Sensors - IntroductionthikgaidepBelum ada peringkat
- CCD CMOS WhitePaperDokumen28 halamanCCD CMOS WhitePaperVictor CiprianBelum ada peringkat
- Single Lens Reflex Camera (SLR) : Presentation by Hemanathan. GDokumen17 halamanSingle Lens Reflex Camera (SLR) : Presentation by Hemanathan. GsathyasonyBelum ada peringkat
- Selecting Video Monitors For The Home Features Of The Best Video MonitorDari EverandSelecting Video Monitors For The Home Features Of The Best Video MonitorBelum ada peringkat
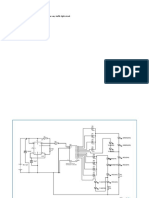
- 12v Practicaldual CircuitDokumen3 halaman12v Practicaldual CircuitIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- 4way Traffic IghtsDokumen2 halaman4way Traffic IghtsIhuhwa Marta Tau100% (1)
- Revision Notes: By: Marta Ihuhwa PeeeDokumen21 halamanRevision Notes: By: Marta Ihuhwa PeeeIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- Capacitors PDFDokumen44 halamanCapacitors PDFIhuhwa Marta Tau100% (1)
- Power System OverviewDokumen2 halamanPower System OverviewIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- 7 Counters PDFDokumen23 halaman7 Counters PDFIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Treatment of MetalsDokumen3 halamanHeat Treatment of MetalsIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- SemiconductorsDokumen23 halamanSemiconductorsabcBelum ada peringkat
- Earthing SystemDokumen31 halamanEarthing Systemssamonas0% (1)
- Summary of Iso 90091Dokumen3 halamanSummary of Iso 90091Ihuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- Power System OverviewDokumen29 halamanPower System OverviewIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- Solar SystemsDokumen15 halamanSolar SystemsIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- Basically Engineering Materials Can Be Classified Into Two CategoriesDokumen4 halamanBasically Engineering Materials Can Be Classified Into Two CategoriesIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- Amplifiers FirstyearDokumen28 halamanAmplifiers FirstyearIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- ICSlide 2Dokumen16 halamanICSlide 2Ihuhwa Marta Tau0% (1)
- Information Network and InternetDokumen24 halamanInformation Network and InternetIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To ComputersDokumen14 halamanIntroduction To ComputersIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- CorrosionDokumen4 halamanCorrosionIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- Maintain Oil Quality with Purification MethodsDokumen1 halamanMaintain Oil Quality with Purification MethodsIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Gaseous Breakdown in Uniform and NonDokumen3 halamanIntroduction To Gaseous Breakdown in Uniform and NonIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- Brief History of CADDokumen2 halamanBrief History of CADIhuhwa Marta Tau100% (2)
- 5.5 Class B Power AmplifiersDokumen3 halaman5.5 Class B Power AmplifiersIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- Fem-19 UgDokumen6 halamanFem-19 UgGoogle DocsBelum ada peringkat
- Operational Amplifier ApplicationsDokumen1 halamanOperational Amplifier ApplicationsIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- Fem-19 UgDokumen6 halamanFem-19 UgGoogle DocsBelum ada peringkat
- Risk AssessmentDokumen22 halamanRisk AssessmentIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- 12v Practical Dual CircuitDokumen2 halaman12v Practical Dual CircuitIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- Fem-19 UgDokumen6 halamanFem-19 UgGoogle DocsBelum ada peringkat
- List of Important CAD Software Applicable in EEE EngineeringDokumen3 halamanList of Important CAD Software Applicable in EEE EngineeringIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- In Induction Motors TheDokumen3 halamanIn Induction Motors TheIhuhwa Marta TauBelum ada peringkat
- Ram and Its Types: Multiplexing DemultiplexingDokumen3 halamanRam and Its Types: Multiplexing Demultiplexingusman100% (1)
- SP1ML-868 and 915MHz RF SubGHz ModulesDokumen15 halamanSP1ML-868 and 915MHz RF SubGHz ModulesEugenio LyseiBelum ada peringkat
- MM Module2 Cse Notes PDFDokumen54 halamanMM Module2 Cse Notes PDFVishnu prasadBelum ada peringkat
- C: T.E. S: Tcs Q B T - I: (Academic Year 2018-19 Odd Sem)Dokumen3 halamanC: T.E. S: Tcs Q B T - I: (Academic Year 2018-19 Odd Sem)jayabaBelum ada peringkat
- Moving message display: Embedded C and hardware requirementsDokumen45 halamanMoving message display: Embedded C and hardware requirementsMuraliKrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Xapp386, Coolrunner-Ii Serial Peripheral Interface MasterDokumen21 halamanXapp386, Coolrunner-Ii Serial Peripheral Interface MasterMagendran PKBelum ada peringkat
- How To Avoid Lock Out ConditionDokumen3 halamanHow To Avoid Lock Out ConditionSiva Guru100% (1)
- CSE231 - Lecture 3Dokumen31 halamanCSE231 - Lecture 3Rayhan Amin 2212830042Belum ada peringkat
- DP55WBDokumen4 halamanDP55WBputamadre_3000Belum ada peringkat
- MPC5604BCRMDokumen929 halamanMPC5604BCRMEdgar MenezesBelum ada peringkat
- 8086 Lab ManualDokumen154 halaman8086 Lab ManualM A Hossain Joe100% (3)
- CMOS Schmitt Trigger Test Circuit Simplifies Threshold MeasurementDokumen21 halamanCMOS Schmitt Trigger Test Circuit Simplifies Threshold MeasurementRavi VermaBelum ada peringkat
- Converting PIC To Freescale Motorola HC08Dokumen9 halamanConverting PIC To Freescale Motorola HC08hc_ieBelum ada peringkat
- NIT Rourkela B.Tech Computer Organization Exam QuestionsDokumen2 halamanNIT Rourkela B.Tech Computer Organization Exam QuestionsSatya DasBelum ada peringkat
- Example: Modulo-4 CounterDokumen15 halamanExample: Modulo-4 CounterMuh Arul SyahrullahBelum ada peringkat
- Mobile Charging On Coin InsertionDokumen5 halamanMobile Charging On Coin InsertionVenkatram PrabhuBelum ada peringkat
- An 10587Dokumen11 halamanAn 10587estraj1954Belum ada peringkat
- Roll Number: R-OSDokumen2 halamanRoll Number: R-OStarun singlaBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Hardware 101 Lesson Plan 8-27-13Dokumen5 halamanComputer Hardware 101 Lesson Plan 8-27-13Cathynen Grace VegaBelum ada peringkat
- 3500 Software Datasheet 141527e PDFDokumen3 halaman3500 Software Datasheet 141527e PDFSoumen PaulBelum ada peringkat
- DE Quiz SnehDokumen8 halamanDE Quiz Snehavnesh joshiBelum ada peringkat
- Intel Core I5-9600k Processor Product SpecificationsDokumen6 halamanIntel Core I5-9600k Processor Product SpecificationshellbentBelum ada peringkat
- DE1-SoC User Manual RefDokumen117 halamanDE1-SoC User Manual RefabcBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical and Electronic DevicesDokumen406 halamanElectrical and Electronic DevicesAl KBelum ada peringkat
- Logic Families: Designed By: Asadullah JamalovDokumen6 halamanLogic Families: Designed By: Asadullah JamalovAsadullah JamalovBelum ada peringkat
- Lec07 DS 2018Dokumen76 halamanLec07 DS 2018Hưng PhạmBelum ada peringkat
- Low Power Clock Gates Optimization For Clock Tree DistributionDokumen5 halamanLow Power Clock Gates Optimization For Clock Tree DistributionNguyen Van ToanBelum ada peringkat
- IRPS Spacer Q&ADokumen2 halamanIRPS Spacer Q&ASnehaBelum ada peringkat