The Dispute Settlement Mechanism
Diunggah oleh
Kiran G0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
53 tayangan6 halamanHak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
53 tayangan6 halamanThe Dispute Settlement Mechanism
Diunggah oleh
Kiran GHak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 6
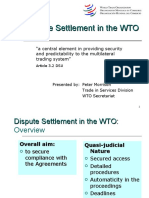
The Dispute Settlement Mechanism
An overview of the WTO Dispute Settlement Process
Introduction
The DSB is, in effect, a session of the General Council of the
WTO: that is, all of the representatives of the WTO member
governments, usually at ambassadorial level, meeting
together.
It decides the outcome of a trade dispute on the
recommendation of a Dispute Panel and (possibly) on a report
from the Appellate Body of WTO, which may have amended
the Panel recommendation if a party chose to appeal.
Only the DSB can make these decisions: Panels and the
Appellate Body are limited to making recommendations.
Reverse Consensus :
Contributions
Dispute settlement is the central pillar of the
multilateral trading system, and the WTO’s unique
contribution to the stability of the global economy.
The system is based on clearly-defined rules, with
timetables for completing a case. 339 cases settled as
on 2007
First rulings are made by a panel and endorsed (or
rejected) by the WTO’s full membership.
Appeals based on points of law are possible.
The priority is to settle disputes, through consultations
if possible.
Principles
Proper balance between rights and obligations of members, Article
3.3 Annex 2
Security and predictability to multilateral trading system,
US – Section 301 Trade Act, clarify existing provisions of WTO
covered agreements according to customary rules of interpretation
of public international law, Article 3.2 of DSU
Settlement of disputes through multilateral procedures, and not
through unilateral actions, Article 23.1 of DSU, US-certain EC
products
Members should not unilaterally determine the violation of WTO
law and should not take unilateral retaliation
Settlement of disputes through consultations, Article 3.7 positive
solution which is mutually acceptable.
Principles continued..
Article 19.2 of the DSU , the Appellate Body cannot add to or
diminish the rights and obligations provided in the covered
agreements.
This flows from Article IX: 2 of the WTO Agreement, “The
Ministerial Conference and the General Council shall have the
exclusive authority to adopt interpretations of this Agreement and of
the Multilateral Trade Agreements”
This principle was clearly laid out in US- Certain EC Products
DSU cannot take the role of a legislator or judicial activism
Article 3.10 ,Settlement of Disputes in Good Faith,
US – Offset Act (Byrd Amendment) , two conditions,
(a) Member failed to act in good faith
(b) there should be something more than mere violation.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- WTO Dispute Settlement SystemDokumen13 halamanWTO Dispute Settlement SystemRasel AhammedBelum ada peringkat
- Dispute Settlement Under Wto: Anushtha SaxenaDokumen26 halamanDispute Settlement Under Wto: Anushtha SaxenaDrishti TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- Unilateral Measures of Enforcement of WTO LawDokumen23 halamanUnilateral Measures of Enforcement of WTO Lawnishant kumarBelum ada peringkat
- ResearchDokumen3 halamanResearchWilmore Tendai Hasan ChisiiwaBelum ada peringkat
- WTO Detailed Brief On Dispute SettlementDokumen38 halamanWTO Detailed Brief On Dispute SettlementHafizSajidBelum ada peringkat
- WTO Dispute SettlementDokumen9 halamanWTO Dispute SettlementSakshi JhaBelum ada peringkat
- 6-MoinuddinDokumen12 halaman6-MoinuddinAnisha PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- ITL PrezDokumen3 halamanITL Prezxokog31418Belum ada peringkat
- Int Trade Law Unit 3Dokumen35 halamanInt Trade Law Unit 3s8pcq8qjmpBelum ada peringkat
- Dispute Settlement Machanism of WtoDokumen17 halamanDispute Settlement Machanism of WtoShikha Gupta100% (1)
- Dispute Settlement MechnaismDokumen62 halamanDispute Settlement Mechnaismnishant kumarBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Câu Preclass Bài 3 ĐầuDokumen2 halaman4 Câu Preclass Bài 3 ĐầuHiếu Vũ MinhBelum ada peringkat
- 1.4Dokumen4 halaman1.4Ayush ThakurBelum ada peringkat
- Intro Wto Disput SettleDokumen25 halamanIntro Wto Disput SettleHemant PantBelum ada peringkat
- Business Communication Text BookDokumen25 halamanBusiness Communication Text BookJayantBelum ada peringkat
- DissertationDokumen27 halamanDissertationWilmore Tendai Hasan ChisiiwaBelum ada peringkat
- Ii. Wto Over Gatt: 3Rd Semester, Ilinew DelhiDokumen22 halamanIi. Wto Over Gatt: 3Rd Semester, Ilinew DelhiSyed Imran AdvBelum ada peringkat
- Dispute SettlementDokumen10 halamanDispute SettlementdebasishroutBelum ada peringkat
- Dispute Settlement Mechanisms in International TradeDokumen55 halamanDispute Settlement Mechanisms in International TradeTamrika TyagiBelum ada peringkat
- Differences between WTO and GATT 1947 dispute settlement systemsDokumen7 halamanDifferences between WTO and GATT 1947 dispute settlement systemsLaVieBelum ada peringkat
- WtoDispute Settlent Mechanism WTODokumen12 halamanWtoDispute Settlent Mechanism WTOKshamaa Kshamaa0% (1)
- Dispute Resolution in WTO: Figure 1structure of WTODokumen3 halamanDispute Resolution in WTO: Figure 1structure of WTOHimanshu BhatiaBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar - ITDS - WTO Dispute Settlement SystemDokumen47 halamanSeminar - ITDS - WTO Dispute Settlement SystemThanh HuynhBelum ada peringkat
- Gpit Ca 3 1629Dokumen9 halamanGpit Ca 3 1629prdyumnBelum ada peringkat
- Dispute Resolution Under GATTDokumen33 halamanDispute Resolution Under GATTrishiBelum ada peringkat
- The World Trade Organization: Legal Basis For Dispute SettlementDokumen7 halamanThe World Trade Organization: Legal Basis For Dispute SettlementAppukuttannairBelum ada peringkat
- 2 16DisputeSettlementDokumen31 halaman2 16DisputeSettlementFATIMA ZAHRA TOUABIBelum ada peringkat
- WTO Dispute Settlement Mechanism: A Critical Analysis: (Type The Document Subtitle)Dokumen18 halamanWTO Dispute Settlement Mechanism: A Critical Analysis: (Type The Document Subtitle)siddharth pandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Source: World Trade OrganisationDokumen4 halamanSource: World Trade OrganisationSakshee SahayBelum ada peringkat
- Himachal Pradesh National Law University Structure of the Dispute Settlement Process under WTODokumen17 halamanHimachal Pradesh National Law University Structure of the Dispute Settlement Process under WTOMrīgendra Narayan UpadhyayBelum ada peringkat
- Name: Shivam Singh Roll Number: 1522 (Fifteen Hundred Twenty-Two) Semester: Ug Sem Vi Subject: General Principles of International Trade Law CA - 1Dokumen9 halamanName: Shivam Singh Roll Number: 1522 (Fifteen Hundred Twenty-Two) Semester: Ug Sem Vi Subject: General Principles of International Trade Law CA - 1Shivam SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Dispute Settlement in WtoDokumen23 halamanDispute Settlement in Wtorishabhsingh261Belum ada peringkat
- WTO Dispute Settlement Procedures and RemediesDokumen11 halamanWTO Dispute Settlement Procedures and RemediesArsalan AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- WTO Dispute Settlement System Fails Developing CountriesDokumen23 halamanWTO Dispute Settlement System Fails Developing CountriesMoud KhalfaniBelum ada peringkat
- INTERNATIONAL TRADE LAW Lecture 2Dokumen8 halamanINTERNATIONAL TRADE LAW Lecture 2Bless King-LumorBelum ada peringkat
- WTO Law and The "Fragmentation" of International Law: Specificity, Integration, ConflictsDokumen22 halamanWTO Law and The "Fragmentation" of International Law: Specificity, Integration, ConflictsJonah Mark AvilaBelum ada peringkat
- CSR - The WTO's Appellate Body Loses Its QuorumDokumen4 halamanCSR - The WTO's Appellate Body Loses Its QuorumWilliam WulffBelum ada peringkat
- Gatt & Wto - DSBDokumen39 halamanGatt & Wto - DSBnavneet_sahota05Belum ada peringkat
- WTO Dispute Settlement Mechanism: A Critical AnalysisDokumen19 halamanWTO Dispute Settlement Mechanism: A Critical AnalysisBalaji P Nadar100% (5)
- WTO Dispute Settlement and Application of Public International LawDokumen5 halamanWTO Dispute Settlement and Application of Public International Lawgiang nguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Structure of The WTODokumen3 halamanStructure of The WTOjjkjjrBelum ada peringkat
- Dispute Settlement in The WTODokumen25 halamanDispute Settlement in The WTODe Dios JVBelum ada peringkat
- Definition:: Scope of The WTODokumen10 halamanDefinition:: Scope of The WTOaskmeeBelum ada peringkat
- NotesDokumen26 halamanNotespranjal meshramBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6 TradeDokumen11 halamanChapter 6 TradeSaabbaa ManBelum ada peringkat
- International Trade LawDokumen16 halamanInternational Trade LawAmit Vikram100% (2)
- ACC E R4 PrintDokumen124 halamanACC E R4 PrintPrem KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Wto Dispute SettlementDokumen18 halamanWto Dispute SettlementMohammad ArishBelum ada peringkat
- Recommendations and suggestions under WTO dispute settlementDokumen2 halamanRecommendations and suggestions under WTO dispute settlementSapna RajmaniBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of WtoDokumen8 halamanPrinciples of WtoDurgesh 136Belum ada peringkat
- Wto Agree Art9 JurDokumen7 halamanWto Agree Art9 JurasdfBelum ada peringkat
- Could the MPIA Replace the WTO Appellate Body? Problems and Solutions ExplainedDokumen6 halamanCould the MPIA Replace the WTO Appellate Body? Problems and Solutions ExplainedBaseer HaqqieBelum ada peringkat
- Notes On Basic MaterialsDokumen6 halamanNotes On Basic MaterialsSteven AveBelum ada peringkat
- Apuntes International Trade LawDokumen13 halamanApuntes International Trade LawEstefanía RodríguezBelum ada peringkat
- International Trading SystemDokumen16 halamanInternational Trading SystemAshish NambiarBelum ada peringkat
- The Wto Dispute Settlement BodyDokumen12 halamanThe Wto Dispute Settlement BodyShivani ChoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Objectives of WTODokumen6 halamanObjectives of WTOanusha1d1bhatBelum ada peringkat
- Dispute Settlement BodyDokumen10 halamanDispute Settlement BodyVida Hanum SalzabillaBelum ada peringkat
- Dispute Settlement in WtoDokumen4 halamanDispute Settlement in WtoRaghavendra RaoBelum ada peringkat
- Consolidated version of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU, 2007)Dari EverandConsolidated version of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU, 2007)Belum ada peringkat
- Hamad Bin Khalifa University - PHD in Islamic Finance and Economy - 2019-04-09Dokumen4 halamanHamad Bin Khalifa University - PHD in Islamic Finance and Economy - 2019-04-09Kiran GBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Protection Act-1986: A Shield for ConsumersDokumen32 halamanConsumer Protection Act-1986: A Shield for ConsumershimanshusangaBelum ada peringkat
- The Problem of Kompetenz-KompetenzDokumen24 halamanThe Problem of Kompetenz-KompetenzKiran GBelum ada peringkat
- Dua BookDokumen19 halamanDua Bookazee100% (14)
- Practical Training Paper I: Professional Ethics and Contempt of Court LawDokumen23 halamanPractical Training Paper I: Professional Ethics and Contempt of Court LawrupaliBelum ada peringkat
- 2022 Legal Opinion Online SabongDokumen2 halaman2022 Legal Opinion Online SabongDem SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- Managing Your Hazards in The WorkplaceDokumen8 halamanManaging Your Hazards in The WorkplaceDaniel TudorBelum ada peringkat
- Position Essay 1Dokumen7 halamanPosition Essay 1api-664569333Belum ada peringkat
- AcctngEd 03 True or False AssignmentDokumen9 halamanAcctngEd 03 True or False AssignmentAudrey Gayle Castelo GervacioBelum ada peringkat
- Seaview Subd., Silay City, Negros Occidental Hda. Mariano D., Brgy. E. Lopez, Silay City, Negros OccidentalDokumen1 halamanSeaview Subd., Silay City, Negros Occidental Hda. Mariano D., Brgy. E. Lopez, Silay City, Negros OccidentalCarlo Frances CaballeroBelum ada peringkat
- APPENDIX 6 - OMAS Contractor Pre-Qualification Questionnaire - 2.0Dokumen20 halamanAPPENDIX 6 - OMAS Contractor Pre-Qualification Questionnaire - 2.0Timuçin ÖztürkBelum ada peringkat
- Heirs of Frisca Dianito dispute ownership of two lots in AklanDokumen19 halamanHeirs of Frisca Dianito dispute ownership of two lots in AklanNet WeightBelum ada peringkat
- Hindu College Gazette - August September Issue-1Dokumen91 halamanHindu College Gazette - August September Issue-1Abhinandan KhajuriaBelum ada peringkat
- Biorisk ManagementDokumen4 halamanBiorisk ManagementcsfcfssfBelum ada peringkat
- Long Ross LawsuitDokumen13 halamanLong Ross LawsuitDan LehrBelum ada peringkat
- 2020/21 LMT in Legal EthicsDokumen5 halaman2020/21 LMT in Legal EthicsKiko OralloBelum ada peringkat
- Ownership by Estoppel Under Transfer of Property ActDokumen6 halamanOwnership by Estoppel Under Transfer of Property ActAashish GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- First Division: J. REYES, JR., J.Dokumen9 halamanFirst Division: J. REYES, JR., J.CJBelum ada peringkat
- LCP4805-environmental Law Norms and PrinciplesDokumen6 halamanLCP4805-environmental Law Norms and Principlestech hutBelum ada peringkat
- Updated Court Email AddressesDokumen36 halamanUpdated Court Email AddressesAmicus CuriaeBelum ada peringkat
- Explaining the Doctrine of Lis PendensDokumen4 halamanExplaining the Doctrine of Lis PendensANTHE MENTORBelum ada peringkat
- Belize Registered Land Act SummaryDokumen91 halamanBelize Registered Land Act SummaryJose MejiaBelum ada peringkat
- Criminal Liability Course WorkDokumen7 halamanCriminal Liability Course Workblessing bBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Safety TrainingDokumen1 halamanBasic Safety TrainingMade HartawanBelum ada peringkat
- Rajasthan State Judicial Academy - Note On Judicial Approach Towards Child Sexual Abuse With Reference To Provisions of POCSO Act, 2012Dokumen20 halamanRajasthan State Judicial Academy - Note On Judicial Approach Towards Child Sexual Abuse With Reference To Provisions of POCSO Act, 2012Chetna GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- 2013 Legal and Ethical Issues in Nursing 6th Edition Test BankDokumen14 halaman2013 Legal and Ethical Issues in Nursing 6th Edition Test BankEricaPhillipsaszpc100% (29)
- Background Material - Cross Border - EU - enDokumen7 halamanBackground Material - Cross Border - EU - enjovanaBelum ada peringkat
- Continuous Assessment Task-I Competition Law Assignment-IDokumen6 halamanContinuous Assessment Task-I Competition Law Assignment-IJyoti MehmiBelum ada peringkat
- Plate 2Dokumen5 halamanPlate 2Josie JugalbotBelum ada peringkat
- Bananotes Civpro MidtermsDokumen288 halamanBananotes Civpro MidtermsCharlene MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- RULE 114 Bail Sec. 1. Bail Defined Almeda v. Villaluz: Criminal Procedure - Atty. Soleng - A.Y. 2020-2021Dokumen28 halamanRULE 114 Bail Sec. 1. Bail Defined Almeda v. Villaluz: Criminal Procedure - Atty. Soleng - A.Y. 2020-2021Harold Saldy CasalemBelum ada peringkat
- VR Hackers - Risk Assesment Hacking-2Dokumen3 halamanVR Hackers - Risk Assesment Hacking-2Vikas RameshBelum ada peringkat
- Michigan Law Review Article Analyzes Heartbalm Statutes and Deceit ActionsDokumen29 halamanMichigan Law Review Article Analyzes Heartbalm Statutes and Deceit Actionsangelica poBelum ada peringkat
- Law of TortsDokumen19 halamanLaw of Tortsguru pratapBelum ada peringkat