ASME Poster - Stratified - Modified
Diunggah oleh
Chris HebbesJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ASME Poster - Stratified - Modified
Diunggah oleh
Chris HebbesHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
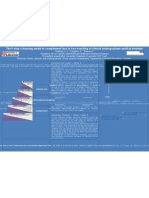
Evaluating e-learning to Teach Undergraduate Airway Management
Hebbes, C. P. Leighton, R. Kumar, N. Wright, R.
Department of Medical and Social Care Education, Leicester Medical School, University of Leicester
1. Introduction
E-learning is a tool of current interest in a wide range of spheres, carrying considerable advantages of cost and
accessibility in comparison to traditional classroom and practical techniques, such as those seen in conventional ALS and
ATLS courses.
Web based education has previously been used with success in areas of anaesthesia1 and is currently the subject of a
pilot in selected ALS centres. Pre Post P-value
In order to further evaluate this technique and provide a local context, we designed, implemented and Statement
evaluated(number)
a series Median
Anatomy
of web based e-learning tools to teach undergraduate clinical medical students about 6 ± 0.28 7.05 ± 0.21 0.003
The resource was clearairway management.
and easy to(66%)
use (78%) 3.5
• Methods Using the resource has improved my understanding of the anatomy and physiology
We used Macromedia Breeze and Blackboard VLE software Physiological
with QuestionMark Perceptions in order8.02to±design
0.22 3 modules 9.17 ± 0.19 of the 3 <0.001
airways
teaching students 1) airway anatomy and physiology, 2) management of airway obstruction and 3)(80%) advanced airway (91%)
management. Student
Clinical 4.57 ± 0.18 5.57 ±Feedback
0.08 <0.001
Students undertaking their perioperative care attachment were Using
invitedthe
to undertake the improved
resource has airway resource
my including of the principlesMean
understanding scores for
of managing aneach of the statements are
at risk 3 shown in Table 2, below. The Likert scale is used with 1 being “poor” and 4
(76%) Table(92%)
1 – Differences in assessment scores before and after using the resource. Data presented as mean ± SEM
objective assessment and a feedback questionnaire. airway being “excellent” concordance with the statements.
Total 18.60 ± 0.46 21.79 ± 0.28 <0.001
Objective assessment (74%) (87%)
Assessment scores (out of 25) relating to anatomy, clinical andIphysiological knowledge were compared before
would recommend the resource to a colleague and after 3
using the resource using Students paired t-test.
Student feedback
The feedback questionnaire comprised a 1-4 Likert scale ranking of statements relating to quality, content, usability and
change in knowledge (1 indicated dissatisfaction and 4 represented satisfaction in the outcome). Feedback data were
assessed using descriptive statistical methods.
• Results
Of 83 students within the cohort, the resource was accessed by 68. Of these, 47 completed the pre and post
assessments and the resource; the remaining 21 accessed only the pre-assessment and were excluded from analysis to
enable direct, matched comparison of pre- and post- scores. Feedback questionnaires were completed by 26 students.
Objective assessment
The mean objective assessment scores (out of 25) before and after undertaking the resource were 18.60 ± 0.46 and
21.79 ± 0.28 respectively (Mean ± SEM). There was a statistically significant improvement in the post-resource anatomy,
physiology and clinical scores (see Table 1).
Table 2 – Likert scores from the feedback questionnaire. 1 indicates disagreement with the statement, 4 indicates
concordance
Improved my understanding of the principles of
Improved my understanding of the anatomy and physiology of the airways managing an at risk airway
The resource was clear and easy to use
1. Conclusion
This e-learning resource had a positive impact on student learning, both subjective and objective. The use of e-
learning is receiving increasing interest and is a popular student method of study. This mode of learning requires
further study to refine and improve the resource.
Reference
1. D. W. Wheeler, K. D. Whittlestone, H. L. Smith, A. K. Gupta, D. K. Menon, A web-based system for teaching, assessment and examination of the undergraduate peri-operative medicine curriculum Anaesthesia 2003; 58 (11): 1079–1086
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Surgical Patient Care - Improving Safety, Quality and ValueDokumen926 halamanSurgical Patient Care - Improving Safety, Quality and ValueYen Ngo100% (2)
- Building J Renovation-PlansDokumen83 halamanBuilding J Renovation-PlansBala Hemanth KumarBelum ada peringkat
- TCS NQT Preparation MaterialDokumen299 halamanTCS NQT Preparation Materialvizier67% (3)
- AET Assignment C Kate ThomsonDokumen12 halamanAET Assignment C Kate ThomsonaymenmoatazBelum ada peringkat
- A Karl Abraham - A Short Study of The Development of The Libido (1924)Dokumen86 halamanA Karl Abraham - A Short Study of The Development of The Libido (1924)vanpec100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPderic83% (6)
- Artificial Intelligence For Quality Assurance in Radi - 2021 - Cancer Radioth RaDokumen4 halamanArtificial Intelligence For Quality Assurance in Radi - 2021 - Cancer Radioth RaAns BarrungBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of Intent Quality Indicator (Qi) Criteria For Data MeasurementDokumen4 halamanSummary of Intent Quality Indicator (Qi) Criteria For Data Measurementapi-349641525Belum ada peringkat
- Intro To Data Science Lecture 5Dokumen7 halamanIntro To Data Science Lecture 5engmjod.88Belum ada peringkat
- Knowledge Discovery in Medical DatabasesDokumen12 halamanKnowledge Discovery in Medical DatabasesOlanrewaju AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 1-Hu2016Dokumen55 halamanPaper 1-Hu2016Sekar Inggar RBelum ada peringkat
- Errors Using Observational Methods For Ergonomics Assessment in Real Practice-1Dokumen15 halamanErrors Using Observational Methods For Ergonomics Assessment in Real Practice-1Doctora de confianza Centro MèdicoBelum ada peringkat
- Student Placement PredictionDokumen4 halamanStudent Placement PredictionshreyasBelum ada peringkat
- Ttench PosterDokumen1 halamanTtench Posterapi-371944008Belum ada peringkat
- Predicting Anxiety and Depression Using Machine Learning: A Comparative StudyDokumen1 halamanPredicting Anxiety and Depression Using Machine Learning: A Comparative StudySaeed KhalilazarBelum ada peringkat
- Expert System Predicts Customer Churn Using Improved Random ForestsDokumen5 halamanExpert System Predicts Customer Churn Using Improved Random ForestsKaran TibdewalBelum ada peringkat
- 2019 Schwartz Intra Rater and Inter Rater Reliability of The Rapid Entire Body Assessment (REBA) ToolDokumen6 halaman2019 Schwartz Intra Rater and Inter Rater Reliability of The Rapid Entire Body Assessment (REBA) ToolJohannes SchützBelum ada peringkat
- SVM KernalsDokumen7 halamanSVM KernalsursbestfriendBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 NewDokumen6 halamanChapter 3 NewDENMARKBelum ada peringkat
- Advances in Uncertainty Representation and Management For Particle Filtering Applied To PrognosticsDokumen6 halamanAdvances in Uncertainty Representation and Management For Particle Filtering Applied To PrognosticsIvan JourdanBelum ada peringkat
- Improve OR teamwork and communication with crew resource managementDokumen17 halamanImprove OR teamwork and communication with crew resource managementKovács TamásBelum ada peringkat
- Plagiarism Scan Report: Date Words CharactersDokumen1 halamanPlagiarism Scan Report: Date Words CharactersElizer DacanayBelum ada peringkat
- Using RRC Algorithm Classify The Proteins and Visualize in Biological DatabasesDokumen6 halamanUsing RRC Algorithm Classify The Proteins and Visualize in Biological DatabasesRahul SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Analytical Chemistry Numericals SolutionsDokumen41 halamanAnalytical Chemistry Numericals SolutionsNewage ScienceBelum ada peringkat
- Bayesian Methods With Application in Risk Analysis: Dongyang DING Xiyang LIUDokumen4 halamanBayesian Methods With Application in Risk Analysis: Dongyang DING Xiyang LIUluli_kbreraBelum ada peringkat
- Geng DengDokumen248 halamanGeng DengRaoniBelum ada peringkat
- Making On-Line Adaptive Radiotherapy Possible Using Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning For Efficient Daily Re-PlanningDokumen10 halamanMaking On-Line Adaptive Radiotherapy Possible Using Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning For Efficient Daily Re-Planningzhen yongjieBelum ada peringkat
- 0rder 269 DNP-830A-Assessment DescriptionDokumen11 halaman0rder 269 DNP-830A-Assessment Descriptionjoshua chegeBelum ada peringkat
- Introduce CCCDokumen21 halamanIntroduce CCCSuki HanantoBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal Week 8 - Usability EvaluationDokumen7 halamanJurnal Week 8 - Usability EvaluationHaris FirmansyahBelum ada peringkat
- The State of Pharmacoeconomic Evaluation Studies in Kenya and An Analysis of Their Influence On Medicine Selection and Utilisation: A ReviewDokumen20 halamanThe State of Pharmacoeconomic Evaluation Studies in Kenya and An Analysis of Their Influence On Medicine Selection and Utilisation: A Reviewesbon gakuuBelum ada peringkat
- 2018 - Song - A Sparsity-Based Stochastic Pooling Mechanism For Deep Convolutional Neural NetworksDokumen6 halaman2018 - Song - A Sparsity-Based Stochastic Pooling Mechanism For Deep Convolutional Neural NetworksDaniel Prado de CamposBelum ada peringkat
- Paper On Sensitivity Analysis of CPTs PDFDokumen48 halamanPaper On Sensitivity Analysis of CPTs PDFGovind M.PBelum ada peringkat
- Estimation of Students' Graduation Using Multiple Linear Regression MethodDokumen8 halamanEstimation of Students' Graduation Using Multiple Linear Regression MethodLaras FirdausBelum ada peringkat
- Quantitative MethodsDokumen2 halamanQuantitative MethodsWc-mark ChuvachucHuBelum ada peringkat
- Nebosh Hse Award in Managing Risks and Risk Assessment at WorkDokumen7 halamanNebosh Hse Award in Managing Risks and Risk Assessment at Workolaogun100% (1)
- Investigating Machine Learning Techniques For Predicting Risk of Asthma Exacerbations: A Systematic ReviewDokumen22 halamanInvestigating Machine Learning Techniques For Predicting Risk of Asthma Exacerbations: A Systematic ReviewHoudaBenharBelum ada peringkat
- Sarrouti Mourad PosterDokumen1 halamanSarrouti Mourad PosterMourad SarroutiBelum ada peringkat
- The Methodology For Knowledge Base Compression and Robust Diagnosis: Application To A Steam Boiler PlantDokumen12 halamanThe Methodology For Knowledge Base Compression and Robust Diagnosis: Application To A Steam Boiler PlantsuderBelum ada peringkat
- Guidance Manual For Optimizing Water Quality Monitoring Program DesignDokumen88 halamanGuidance Manual For Optimizing Water Quality Monitoring Program DesignJavier Arturo Gaspar PrialéBelum ada peringkat
- Use of Recovery and Bias Information in Analytical Chemistry and Estimation of Its Uncertainty ContributionDokumen9 halamanUse of Recovery and Bias Information in Analytical Chemistry and Estimation of Its Uncertainty ContributionRodney SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- Neurocomputing: Chengming Yang, Jian HouDokumen7 halamanNeurocomputing: Chengming Yang, Jian HouFelipePuentesCantorBelum ada peringkat
- 5.Evaluation of Analytical Data-đã chuyển đổiDokumen25 halaman5.Evaluation of Analytical Data-đã chuyển đổiVạn LingBelum ada peringkat
- Brooks 2015Dokumen12 halamanBrooks 2015Daniel PatiñoBelum ada peringkat
- Experimenta LdesignDokumen13 halamanExperimenta LdesignHardin Aaron Jn PierreBelum ada peringkat
- National General Certificate in Occupational Health and Safety Unit NG2: Risk AssessmentDokumen17 halamanNational General Certificate in Occupational Health and Safety Unit NG2: Risk AssessmentdeycallmebudBelum ada peringkat
- The Correlation Between Transcultural Nursing Competencies and Hospital-Based Nursing Therapeutic Communication in Jember, IndonesiaDokumen9 halamanThe Correlation Between Transcultural Nursing Competencies and Hospital-Based Nursing Therapeutic Communication in Jember, IndonesiaKrisna Putri WidayatiBelum ada peringkat
- Biologically Inspired Cognitive Architectures: Hadjer Boubenna, Dohoon Lee TDokumen7 halamanBiologically Inspired Cognitive Architectures: Hadjer Boubenna, Dohoon Lee TSabha NayaghamBelum ada peringkat
- Nixon, Measuring Calibration in Deep LearningDokumen14 halamanNixon, Measuring Calibration in Deep LearningJosé-Manuel Martin CoronadoBelum ada peringkat
- Book 2.0 - PythonDokumen143 halamanBook 2.0 - PythonShiva YadandlaBelum ada peringkat
- Upskilling Health and Care Workers With AugmentedDokumen10 halamanUpskilling Health and Care Workers With AugmentedShinde Chaitanya Sharad C-DOT 5688Belum ada peringkat
- Neale Final Assessment ProjectDokumen13 halamanNeale Final Assessment Projectapi-726948535Belum ada peringkat
- Ritonga 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1460 012107Dokumen7 halamanRitonga 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1460 012107Soleh RitongaBelum ada peringkat
- IjrsrfinalDokumen5 halamanIjrsrfinalKritharth PendyalaBelum ada peringkat
- Astuti 2018 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 971 012003Dokumen8 halamanAstuti 2018 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 971 012003fauzieahmad526Belum ada peringkat
- Exer8-Indigo-1Dokumen2 halamanExer8-Indigo-1Karl SorianoBelum ada peringkat
- Entropy Balancing For Causal Effects: A Multivariate Reweighting Method To Produce Balanced Samples in Observational StudiesDokumen22 halamanEntropy Balancing For Causal Effects: A Multivariate Reweighting Method To Produce Balanced Samples in Observational Studiesmarting91Belum ada peringkat
- Customer Churn Prediction Using Improved Balanced Random ForestsDokumen5 halamanCustomer Churn Prediction Using Improved Balanced Random ForestsGuillermo González RubilarBelum ada peringkat
- Implementation of Decision Tree and Naïve Bayes Classification Method For Predicting Study PeriodDokumen7 halamanImplementation of Decision Tree and Naïve Bayes Classification Method For Predicting Study PeriodFenny RahmayaniBelum ada peringkat
- Hybrid Approach For Conducting Segmentation of Retinal Images From DRIVE and STARE DatasetsDokumen20 halamanHybrid Approach For Conducting Segmentation of Retinal Images From DRIVE and STARE DatasetsSukh SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Ati RN 2016 Proctor PedsDokumen6 halamanAti RN 2016 Proctor PedsStan Tan50% (2)
- Comparison of Two Probabilistic Fatigue Damage Assessment Approaches Using Prognostic Performance MetricsDokumen11 halamanComparison of Two Probabilistic Fatigue Damage Assessment Approaches Using Prognostic Performance Metricsnacer zidiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3Dokumen7 halamanChapter 3Dee Bonah DearBelum ada peringkat
- RLE assessment proposes DEU modelDokumen17 halamanRLE assessment proposes DEU modelChristian Angelo LeonorBelum ada peringkat
- Thought Organizers: Learning Delivery Modalities Course 1 Module 6A (School Heads)Dokumen3 halamanThought Organizers: Learning Delivery Modalities Course 1 Module 6A (School Heads)Rodnel Moncera100% (1)
- ASME 2009 ElearningDokumen1 halamanASME 2009 ElearningChris HebbesBelum ada peringkat
- ASME 2008 ElearningDokumen1 halamanASME 2008 ElearningChris HebbesBelum ada peringkat
- Ottawa 2010 ErrorsDokumen16 halamanOttawa 2010 ErrorsChris HebbesBelum ada peringkat
- Asme FinalDokumen1 halamanAsme FinalChris HebbesBelum ada peringkat
- Student Detection of Errors in ExaminationsDokumen16 halamanStudent Detection of Errors in ExaminationsChris HebbesBelum ada peringkat
- Asme FinalDokumen1 halamanAsme FinalChris HebbesBelum ada peringkat
- Elearning ConferenceDokumen1 halamanElearning ConferenceChris HebbesBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of COVID 19 On The Mental HealthDokumen17 halamanEffect of COVID 19 On The Mental HealthlokBelum ada peringkat
- Utilidad de La Puntuación de Boey Y Portsmouth-Possum Fisiológico en Pacientes Con Úlcera Péptica PerforadaDokumen8 halamanUtilidad de La Puntuación de Boey Y Portsmouth-Possum Fisiológico en Pacientes Con Úlcera Péptica PerforadaEdgarOrtaBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Bahasa Inggris TKJ SEMESTER GENAP 2020-2021: PoinDokumen18 halamanSoal Bahasa Inggris TKJ SEMESTER GENAP 2020-2021: PoinRauf AthilaBelum ada peringkat
- Salter 2018 - Changes in Temperature Management of Cardiac Arrest Patients Following Publication of The Target Temperature Management TrialDokumen9 halamanSalter 2018 - Changes in Temperature Management of Cardiac Arrest Patients Following Publication of The Target Temperature Management TrialSteven BrownBelum ada peringkat
- Fenugreek Benefits PDFDokumen10 halamanFenugreek Benefits PDFrecianzubyBelum ada peringkat
- Emergency Response Plan TemplateDokumen4 halamanEmergency Response Plan TemplateDilkhaz HSEBelum ada peringkat
- Evidence Based Practice in Postgraduate Healthcare EducationDokumen29 halamanEvidence Based Practice in Postgraduate Healthcare EducationGab FgilzcheBelum ada peringkat
- Reflection Writing For LogbookDokumen4 halamanReflection Writing For Logbookkio josephBelum ada peringkat
- Health Protocol - Diskwento Caravan - As of Oct 22, 2020Dokumen2 halamanHealth Protocol - Diskwento Caravan - As of Oct 22, 2020Randell ManjarresBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Education: Region Vi-Western Visayas Schools Division of SipalayDokumen3 halamanDepartment of Education: Region Vi-Western Visayas Schools Division of SipalayRoseo BatillerBelum ada peringkat
- Pelvic Organ Prolapse and Urinary Incontinence in Women After Bariatric Surgery: 5-Year Follow-UpDokumen6 halamanPelvic Organ Prolapse and Urinary Incontinence in Women After Bariatric Surgery: 5-Year Follow-UpsusiBelum ada peringkat
- Production of OrganicDokumen6 halamanProduction of OrganicbackseeBelum ada peringkat
- Admission Criteria in A Pediat Ric Intensive Therapy Unit: Presentation of An Evaluation InstrumentDokumen8 halamanAdmission Criteria in A Pediat Ric Intensive Therapy Unit: Presentation of An Evaluation InstrumentrupaliBelum ada peringkat
- The Brown Economy Is Killing UsDokumen3 halamanThe Brown Economy Is Killing UsGeorge BusuiocBelum ada peringkat
- Report More Pe Activity Programs Needed in SchoolsDokumen2 halamanReport More Pe Activity Programs Needed in Schoolsapi-237341571Belum ada peringkat
- Explore The Role of The HCA in The Promotion of Positive AgeingDokumen9 halamanExplore The Role of The HCA in The Promotion of Positive Ageing1chirciu1976floBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of The Neuromuscular Taping (NMT) Towards Flexibility Muscle Functions at The Lower Back and HamstringsDokumen3 halamanEffect of The Neuromuscular Taping (NMT) Towards Flexibility Muscle Functions at The Lower Back and HamstringsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyBelum ada peringkat
- Faktor-Faktor Yang Memengaruhi Kegagalan Inisiasi Menyusui Dini Pada Ibu Post Sectio Caesarea Di Rumah Sakit Tentara Binjai Tahun 2018Dokumen14 halamanFaktor-Faktor Yang Memengaruhi Kegagalan Inisiasi Menyusui Dini Pada Ibu Post Sectio Caesarea Di Rumah Sakit Tentara Binjai Tahun 2018Salma AzzahraBelum ada peringkat
- Occupational Hazards in DentistryDokumen7 halamanOccupational Hazards in DentistryTejas KulkarniBelum ada peringkat
- 1948 Staff Listing for PREPPO HospitalDokumen481 halaman1948 Staff Listing for PREPPO Hospitalpriya selvarajBelum ada peringkat
- Stihl Ts 410 420 Owners Instruction ManualDokumen112 halamanStihl Ts 410 420 Owners Instruction ManualLucyan IonescuBelum ada peringkat
- Herd Health Management For Dairy Sheep PDFDokumen10 halamanHerd Health Management For Dairy Sheep PDFkhouchaymiBelum ada peringkat
- Instagram Dentistry: Hui Lynn Ooi, Martin G.D. KelleherDokumen7 halamanInstagram Dentistry: Hui Lynn Ooi, Martin G.D. KelleherJustin Ong KywenBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Handling and ManagementDokumen22 halamanChemical Handling and Managementrizwan chBelum ada peringkat