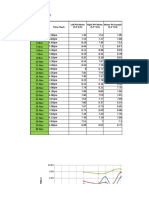
Session 4: Total Quality Management
Diunggah oleh
syamimiJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Session 4: Total Quality Management
Diunggah oleh
syamimiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Session 4:
Total Quality
Management
Total Quality Tools and
Statistical Thinking (2)
Santiago Ibarreche © 2003
Reasons for Using Tools
According to Joseph Juran:
… most people devote too much attention to
control and too little to planning and
improvement …
Santiago Ibarreche © 2003
Types of Tools
Tools for Quality Planning:
1. Quality Function deployment
2. Concurrent Engineering
3. The New Seven management and Planning Tools
Tools for Continuous Improvement:
1. Tools for data Collection and Analysis
2. The Deming Cycle
3. Poka-Yoke (Mistake Proofing)
4. Benchmarking
Creativity and Innovation
Statistical Thinking
Santiago Ibarreche © 2003
Concurrent Engineering
Objectives:
1. Distinguishing the character of the product in order to determine
appropriate design, production or operation methods, and
ensuring the rapid repair of products or solution of conflicts
2. Analyzing product and operation functions so all design
decisions can be made with full knowledge of how the item is
supposed to work and so all team members understand it well
enough to contribute.
3. Relating product function to production methods. Computer-
aided design tools allow a designer to simulate product
performance by varying assumptions within a computer model.
Santiago Ibarreche © 2003
Objectives: (Cont.)
4. Performing a design-for-manufacturability study to determine if the
design can be made easier to produce without affecting
performance.
5. Designing an assembly sequence that integrates quality control
and ensures that each part is designed so that its quality is
compatible with the assembly method.
6. Designing a factory or operation system that fully involves workers
in the production strategy, operates on minimal inventory, and is
integrated with suppliers' methods and capabilities.
Santiago Ibarreche © 2003
The Seven New Management and
Planning Tools:
1. AffinityDiagram / KJ Method
2. Interrelationship Diagraphs
3. Tree Diagrams
4. Matrix Diagrams
5. Matrix data Analysis
6. Process Decision Program Chart
7. Arrow Diagrams
Santiago Ibarreche © 2003
Affinity Diagram / KJ Method
Santiago Ibarreche © 2003
Interrelations Diagraphs
Santiago Ibarreche © 2003
Tree Diagram
Santiago Ibarreche © 2003
Matrix Diagrams
Example of Quality Function Deployment (House of Quality)
Symbols
Strong Relationship (9)
Tech. Req 1
Tech. Req 2
Tech. Req 3
Tech. Req 4
Weak Relationship(3)
Very Weak relationship(1)
Tech. Req 1
Tech. Req 2
Tech. Req 3
Tech. Req 4
Symbols
¿ Strong Relationship (9)
Company A
Tech. Req 1
Tech. Req 2
Tech. Req 3
Tech. Req 4
° Weak Relationship(3) Company B
¯ Very Weak relationship(1) Importance for
Customer Evaluation
Vice of Customer 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5
Customer Requirement 1
Customer Requirement 2
Customer Requirement 3
Customer Requirement 4
Customer Requirement 5
Customer Requirement 6
Customer Requirement 7
Customer Requirement 8
Competitive Evaluation A
B
Goals
Deployment
Santiago Ibarreche © 2003
Matrix Data Analysis
Santiago Ibarreche © 2003
Process Decision Program Chart (PDPC)
Santiago Ibarreche © 2003
Example of a CPM Chart
Santiago Ibarreche © 2003
Types of Tools
Tools for Quality Planning:
1. Quality Function deployment
2. Concurrent Engineering
3. The New Seven management and Planning Tools
Tools for Continuous Improvement:
1. Tools for data Collection and Analysis
2. The Deming Cycle
3. Poka-Yoke (Mistake Proofing)
4. Benchmarking
Creativity and Innovation
Statistical Thinking
Santiago Ibarreche © 2003
The Deming Cycle
Plan Do
Act Study
Santiago Ibarreche © 2003
Ishikawa (Fishbone or Cause Effect)
Santiago Ibarreche © 2003
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Ieq S-22Dokumen20 halamanIeq S-22alextushar140Belum ada peringkat
- The Importance of Software TestingDokumen19 halamanThe Importance of Software TestingSky DeskBelum ada peringkat
- Important Instructions To Examiners:: 4M Diagram 2 Marks, Explanation 2 MarksDokumen29 halamanImportant Instructions To Examiners:: 4M Diagram 2 Marks, Explanation 2 MarksRushikesh KadamBelum ada peringkat
- Ta Assignments: Problem Question From TA1 (q1 and q4)Dokumen38 halamanTa Assignments: Problem Question From TA1 (q1 and q4)Iam anonymousBelum ada peringkat
- All PPTs MergedDokumen264 halamanAll PPTs Mergedabhishek0% (1)
- Project Proposal Development of A Dynamic Website Name: Ariyo Olukayode Olawale Candidate Number: B13/990307119Dokumen5 halamanProject Proposal Development of A Dynamic Website Name: Ariyo Olukayode Olawale Candidate Number: B13/990307119Ariyo Olawale SamuelBelum ada peringkat
- Mirpur University of Science and Technology: Deparment Software EngineeringDokumen22 halamanMirpur University of Science and Technology: Deparment Software EngineeringahsanBelum ada peringkat
- A Brief Overview of Software Testing MetricsDokumen9 halamanA Brief Overview of Software Testing MetricsarbanBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Iii - TQM - QBDokumen11 halamanUnit Iii - TQM - QBNambi RajanBelum ada peringkat
- Ba Re SyllabusDokumen18 halamanBa Re Syllabuschee pin wongBelum ada peringkat
- OOTB Reports - SemiconductorDokumen25 halamanOOTB Reports - SemiconductorDeepak GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Project Management WorkbookDokumen36 halamanProject Management WorkbookDenimfajita100% (2)
- Computing Science: University of Newcastle Upon TyneDokumen8 halamanComputing Science: University of Newcastle Upon Tyneremir mirandaBelum ada peringkat
- University of Mauritius Faculty of EngineeringDokumen5 halamanUniversity of Mauritius Faculty of Engineeringmy pcBelum ada peringkat
- Software Quality Metrics MethodologyDokumen17 halamanSoftware Quality Metrics MethodologySumit RajputBelum ada peringkat
- Irjet V7i6159Dokumen6 halamanIrjet V7i6159SanketBelum ada peringkat
- Madhu FinalDokumen80 halamanMadhu FinalANU GRAPHICSBelum ada peringkat
- Software Development Life CycleDokumen9 halamanSoftware Development Life CycleNehal AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Technology Acquisition Group ProjectDokumen12 halamanTechnology Acquisition Group Projectapi-727051109Belum ada peringkat
- Lean Six Sigma: DR Simmy MarwaDokumen27 halamanLean Six Sigma: DR Simmy MarwabcitilciBelum ada peringkat
- Ictict517 Ae Pro 2of3Dokumen19 halamanIctict517 Ae Pro 2of3Ashutosh MaharajBelum ada peringkat
- Requirements Based TestingDokumen4 halamanRequirements Based TestingVick'y A'AdemiBelum ada peringkat
- SPMP & SRS Online Banking System PDFDokumen10 halamanSPMP & SRS Online Banking System PDFDimo OfficialBelum ada peringkat
- Abhishek VishwkarmaDokumen42 halamanAbhishek Vishwkarmasai projectBelum ada peringkat
- PartII PracticeExams TOGAF9 Cert v9 2Dokumen15 halamanPartII PracticeExams TOGAF9 Cert v9 2somkumar1Belum ada peringkat
- Ecommerce Workshop 1a v1 0Dokumen60 halamanEcommerce Workshop 1a v1 0Pablo Fernández-CastanysBelum ada peringkat
- 2-1 2003 Dec QDokumen5 halaman2-1 2003 Dec QpossibleaungkyawzawBelum ada peringkat
- Msbte Model Answer Paper of Software EngineeringDokumen27 halamanMsbte Model Answer Paper of Software EngineeringParam Kamble67% (3)
- Sheet1: Questiontext Ans1Text Ans2TextDokumen4 halamanSheet1: Questiontext Ans1Text Ans2TextVinay KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Sheet1: Questiontext Ans1Text Ans2TextDokumen4 halamanSheet1: Questiontext Ans1Text Ans2TextVinay KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Measurement IT InvestmentDokumen5 halamanMeasurement IT Investmentizal005Belum ada peringkat
- PART A-Plan Format of Micro Project Proposal For 1 To4 SemesterDokumen6 halamanPART A-Plan Format of Micro Project Proposal For 1 To4 SemesterNabil PevekarBelum ada peringkat
- CS3430 Project Instructions 2023Dokumen7 halamanCS3430 Project Instructions 2023Bokang LerataBelum ada peringkat
- Presale & Project Management: The Life Cycle of A Large System Integration ProjectDokumen29 halamanPresale & Project Management: The Life Cycle of A Large System Integration ProjectTiborGašparacBelum ada peringkat
- PA Project Management Plan TemplateDokumen11 halamanPA Project Management Plan TemplateAndre ReinaldyBelum ada peringkat
- Causal Analysis and Resolution - Case StudyDokumen8 halamanCausal Analysis and Resolution - Case StudypriyankaroraBelum ada peringkat
- Bhupathi ELM Mirtech Teamlease DigitalDokumen4 halamanBhupathi ELM Mirtech Teamlease DigitalHaseeb KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Lect M HDokumen10 halamanLect M Hdeepakarora201188Belum ada peringkat
- QFD Acc O8Dokumen48 halamanQFD Acc O8Vishal MeenaBelum ada peringkat
- Sample ReportDokumen45 halamanSample ReportSaurabh MauryaBelum ada peringkat
- Spreadsheet Risk Optimization QuestionnaireDokumen3 halamanSpreadsheet Risk Optimization QuestionnaireAdegbola OluwaseunBelum ada peringkat
- Project ReportDokumen53 halamanProject ReportstARBelum ada peringkat
- Se Exp 1Dokumen5 halamanSe Exp 1Alok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- DIG 3521 Module 02.1Dokumen35 halamanDIG 3521 Module 02.1BamBelum ada peringkat
- CSE 314 Principles of Software Engineering Assignment No 3Dokumen7 halamanCSE 314 Principles of Software Engineering Assignment No 3Nishant KaundalBelum ada peringkat
- Researchpaper Improving Customers Service at IKEA Using Six Sigma MethodologyDokumen9 halamanResearchpaper Improving Customers Service at IKEA Using Six Sigma MethodologyM Nadeem Baig100% (1)
- Chapter 3, Requirement Engineering (Part 1) + Requirement Process (Part 2)Dokumen10 halamanChapter 3, Requirement Engineering (Part 1) + Requirement Process (Part 2)nadiahraisBelum ada peringkat
- A Brief Overview of Software Testing MetricsDokumen8 halamanA Brief Overview of Software Testing MetricsPrasad DannapaneniBelum ada peringkat
- K I TB G/ Itp (MKTG) / P-11 Procedure For D Esig N and DevelopmentDokumen5 halamanK I TB G/ Itp (MKTG) / P-11 Procedure For D Esig N and DevelopmentinspireBelum ada peringkat
- University of Mauritius Faculty of EngineeringDokumen9 halamanUniversity of Mauritius Faculty of Engineeringmy pcBelum ada peringkat
- Software Project ManagementDokumen4 halamanSoftware Project ManagementImranBelum ada peringkat
- 15,16 2 Mark SEQADokumen32 halaman15,16 2 Mark SEQAbhuvi2312Belum ada peringkat
- Requirements Quality Metrics Paper With Addendum PPA 005330 9 140710Dokumen8 halamanRequirements Quality Metrics Paper With Addendum PPA 005330 9 140710Mehwish rafiqueBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 Software RequirementsDokumen120 halamanChapter 3 Software RequirementsPrabhat SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Project - Templates WBSDokumen68 halamanProject - Templates WBSjay-ar MaravillaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 11: Software Metrics: Ð Lord Kelvin (Physicist) Ð Tom Demarco (Software Engineer)Dokumen10 halamanUnit 11: Software Metrics: Ð Lord Kelvin (Physicist) Ð Tom Demarco (Software Engineer)Krishna GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- TBI Overview Slides v3Dokumen13 halamanTBI Overview Slides v3Jorge GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- MomoDokumen1 halamanMomosyamimiBelum ada peringkat
- Chemlite Industries SDN BHD: SPC Implementation PlanDokumen14 halamanChemlite Industries SDN BHD: SPC Implementation PlansyamimiBelum ada peringkat
- QA-89!06!071 - RoHS TemplateDokumen2 halamanQA-89!06!071 - RoHS TemplatesyamimiBelum ada peringkat
- Air Gun Safety Procedure: Ear Plugs IsDokumen1 halamanAir Gun Safety Procedure: Ear Plugs IssyamimiBelum ada peringkat
- IETSDokumen360 halamanIETSsyamimiBelum ada peringkat
- Level: Ref. Number: APEL: (Office Use Only)Dokumen12 halamanLevel: Ref. Number: APEL: (Office Use Only)syamimiBelum ada peringkat
- Chemlite: Audit ChecklistDokumen34 halamanChemlite: Audit ChecklistsyamimiBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial Training ReportDokumen32 halamanIndustrial Training ReportsyamimiBelum ada peringkat
- Aluminium AnodDokumen1 halamanAluminium AnodsyamimiBelum ada peringkat
- Audit On Antibiotics Prescribing For Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Primary Healthcare Facilities in Kedah (NMRR ID: NMRR-16-315-29590)Dokumen34 halamanAudit On Antibiotics Prescribing For Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Primary Healthcare Facilities in Kedah (NMRR ID: NMRR-16-315-29590)syamimiBelum ada peringkat
- VIVA PresentationDokumen5 halamanVIVA PresentationsyamimiBelum ada peringkat
- Analgesics: Safety Considerations and Patient FactorsDokumen10 halamanAnalgesics: Safety Considerations and Patient FactorssyamimiBelum ada peringkat
- Compressed Airgun Information SheetDokumen2 halamanCompressed Airgun Information SheetsyamimiBelum ada peringkat
- Name: Ili Syamimi Binti Mohamad Saad Matric No.: 151342440 Course: RY20 (Industrial Chemical Process)Dokumen2 halamanName: Ili Syamimi Binti Mohamad Saad Matric No.: 151342440 Course: RY20 (Industrial Chemical Process)syamimiBelum ada peringkat
- Universiti Malaysia Perlis (Unimap) : Fakulti Teknologi KejuruteraanDokumen2 halamanUniversiti Malaysia Perlis (Unimap) : Fakulti Teknologi KejuruteraansyamimiBelum ada peringkat
- HA Assignment 9005Dokumen3 halamanHA Assignment 9005syamimiBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1 PCDDokumen1 halamanAssignment 1 PCDsyamimiBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Plan Ekt120-Sem1 2014 - 2015Dokumen6 halamanTeaching Plan Ekt120-Sem1 2014 - 2015syamimiBelum ada peringkat
- Extraction and Concentration of Pesticide ResidueDokumen13 halamanExtraction and Concentration of Pesticide ResiduesyamimiBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Engineering Drawing Coordinate Systems in AutoCADDokumen38 halamanFundamentals of Engineering Drawing Coordinate Systems in AutoCADthorBelum ada peringkat
- 220kV RRVPNL Cable SpecificationDokumen22 halaman220kV RRVPNL Cable Specificationanurag_pugaliaaBelum ada peringkat
- Final Thesis - With AppendicesDokumen103 halamanFinal Thesis - With AppendicesAzkalzstriker Den100% (1)
- Eng Bouwali Amine CVDokumen1 halamanEng Bouwali Amine CVAmine BOUWALIBelum ada peringkat
- 83 Kashif NaveedDokumen2 halaman83 Kashif NaveedSajid HanifBelum ada peringkat
- CA - AML - 1 & 2 - Genap 2018-2019Dokumen18 halamanCA - AML - 1 & 2 - Genap 2018-2019ImeldaBelum ada peringkat
- Week2 - Lesson 2. Basics of Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)Dokumen11 halamanWeek2 - Lesson 2. Basics of Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)manorajcvBelum ada peringkat
- RVSDX Instruction Manual 23.09.2012Dokumen60 halamanRVSDX Instruction Manual 23.09.2012edgarcooBelum ada peringkat
- Biomedical Engineering Trends Research and TechnologiesDokumen656 halamanBiomedical Engineering Trends Research and TechnologiesVictor Melo MuñozBelum ada peringkat
- Design Basis TelecommunicationsDokumen36 halamanDesign Basis Telecommunicationsnknfive100% (6)
- Plate 6Dokumen3 halamanPlate 6XDXDXDBelum ada peringkat
- LT299 Microcracking CTBDokumen2 halamanLT299 Microcracking CTBArturo TotolhuaBelum ada peringkat
- Prestressing Thread Steel BarDokumen3 halamanPrestressing Thread Steel BarIsmantoTaufikBelum ada peringkat
- B7 VarunDokumen19 halamanB7 Varunridhima senBelum ada peringkat
- Aircraft Electric Secondary Power PDFDokumen195 halamanAircraft Electric Secondary Power PDFMuhammedNayeemBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 89672Dokumen16 halamanPaper 89672RUDHRA DHANASEKARBelum ada peringkat
- Alexander Elder Como Se Transformar em Um Operador e Investidor de Sucesso PDFDokumen18 halamanAlexander Elder Como Se Transformar em Um Operador e Investidor de Sucesso PDFGustavo Vasconcellos0% (1)
- File 4Dokumen60 halamanFile 4AVADHESH CHAMOLABelum ada peringkat
- Demag KBK Light Crane System: Overhead Transport, Exact Positioning, Ergonomic HandlingDokumen36 halamanDemag KBK Light Crane System: Overhead Transport, Exact Positioning, Ergonomic HandlingVijay PapriwalBelum ada peringkat
- Napier NT1 BrochureDokumen16 halamanNapier NT1 Brochureairtupas100% (2)
- Substructure Taking OffDokumen4 halamanSubstructure Taking Offlutos2100% (5)
- Anna University Chennai:: Chennai - 600025. Office of The Controller of Examinations Rank List April / May 2022 ExaminationsDokumen74 halamanAnna University Chennai:: Chennai - 600025. Office of The Controller of Examinations Rank List April / May 2022 ExaminationsJoseph DurairajBelum ada peringkat
- Chance Reichel Templ TaskID WBS 05 12 00Dokumen12 halamanChance Reichel Templ TaskID WBS 05 12 00smshaidrBelum ada peringkat
- RSBDokumen2 halamanRSBJohn Aries Almelor SarzaBelum ada peringkat
- RoboTek Curriculum Guide (2019)Dokumen32 halamanRoboTek Curriculum Guide (2019)tonet enteaBelum ada peringkat
- DO 117 s2017Dokumen24 halamanDO 117 s2017EFLORENDO25Belum ada peringkat
- Sisbang Lotte PDFDokumen17 halamanSisbang Lotte PDFadityaCS3Belum ada peringkat
- ChemistryDokumen22 halamanChemistrySanketh R GowdaBelum ada peringkat
- Stress Analysis of Mast Structure For Water-Well Drilling MachineDokumen8 halamanStress Analysis of Mast Structure For Water-Well Drilling MachineBruno Santos100% (1)
- Good Practices For Requirements EngineeringDokumen4 halamanGood Practices For Requirements EngineeringJessicaBelum ada peringkat