Specto Poto Meter Ko: Ir Rudy Gunung Sugih
Diunggah oleh
dliyax0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
11 tayangan11 halamanSpecto Poto Rudy
Judul Asli
Specto Poto Rudy
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniSpecto Poto Rudy
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
11 tayangan11 halamanSpecto Poto Meter Ko: Ir Rudy Gunung Sugih
Diunggah oleh
dliyaxSpecto Poto Rudy
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 11
Specto poto meter ko
Ir Rudy Gunung Sugih
7.1 Using the Spectrophotometer to Detect Molecules
Molecules are too tiny to be seen.
When an indicator solution changes color, that means a
molecule of interest is present.
A VIS spectrophotometer uses white light, composed of the
visible spectrum, to detect colorful molecules.
Absorbance, Transmittance, and Reflection. A spectrophotometer measures
how light interacts with atoms or molecules in a sample.
Parts of a Spectrophotometer
• Lamp
• Prism
• Sample holder
• Display
How a Spectrophotometer Works
White light hits grating or prism
Light is split into colors of the rainbow
Wavelength knob directs different colors toward sample
Colors of Light in the Visible
Spectrum. Humans can see light
with wavelengths of about 350 to
700 nm.
How a UV Spectrophotometer Works. Similar to a
VIS spectrophotometer, the UV spec shines
ultraviolet light or visible light on a sample, and a
detector measures the amount of light that passes
through, or is absorbed by, the sample.
How Concentration Affects Absorbance. If a sample has twice as many molecules as
another, it can absorb twice as much light. This is true at any wavelength. It is important to
know a sample’s wavelength of maximum light absorbance, so that the difference in
absorbance due to concentration is obvious.
Vocabulary
• Ultraviolet light – a wavelength of light that is used to detect colorless molecules
• Spectrophotometer – an instrument that measures the amount of light that passes through (is
transmitted through) a sample
• Nanometer – 10-9 meters; the standard unit used for measuring light
• Visible light spectrum – the range of wavelengths of light that humans can see, from
approximately 350 to 700 nm; also called white light
• Transmittance – the passing of light through a sample
• Absorbance – the amount of light absorbed by a sample (the amount of light that does not pass
through or reflect off a sample)
• Tungsten lamp – a lamp, used for VIS spectrophotometers, that produces white light (350 –
700 nm)
• Deuterium lamp – a special lamp used for UV spectrophotometers that produces light in the
ultraviolet (UV light) part of the spectrum (200 – 350 nm)
• % transmittance – the manner in which a spectrophotometer reports the amount of light that
passes through a sample
• Absorbance units – (abbreviated “au”) a unit of light absorbance determined by the decrease
in the amount of light in a light beam
• Absorbance spectrum – a graph of a sample’s absorbance at different wavelengths
• Lambdamax – the wavelength that gives the highest absorbance value for a sample
A pH meter is used to adjust the pH of solutions or to watch the pH of a solution change over time. The
pH electrode is sitting in a 50-mL tube of storage solution.
Vocabulary
• Acid – a solution that has a pH less than 7
• Base – a solution that has a pH greater than 7
• Hydrogen – a hydrogen atom which has lost an electron (H+)
• Neutral – uncharged
• Pepsin – an enzyme, found in gastric juice, that works to break down food (protein) in
the stomach
• pH paper – a piece of paper that has one or more chemical indicators on it and that
changes colors depending on the amount of H+ ions in a solution
• pH meter – an instrument that uses an electrode to detect the pH of a solution
• Buffer standards – solutions, each of specific pH, used to calibrate a pH meter
7.3 Buffers
Buffer solution resists changes in pH.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersDokumen48 halamanSafety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersRaza Muhammad Soomro60% (5)
- Ophthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneDari EverandOphthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OnePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (3)
- Inoxpran Coffee MakerDokumen4 halamanInoxpran Coffee MakerelvisandmickBelum ada peringkat
- Exam 3 Review Sheet Chem 1601 F17Dokumen1 halamanExam 3 Review Sheet Chem 1601 F17RossBelum ada peringkat
- Civil Engineering Interview QuestionsDokumen123 halamanCivil Engineering Interview QuestionsSoni Mishra Tiwari89% (9)
- Bol Filter ManualDokumen7 halamanBol Filter ManualAmster Limatog100% (2)
- Yokohama Conveyor BeltsDokumen87 halamanYokohama Conveyor BeltsU Thaung Myint100% (12)
- Introduction To SpectrophotometryDokumen26 halamanIntroduction To Spectrophotometryiryasti2yudistiaBelum ada peringkat
- Analytical Equipment IDokumen17 halamanAnalytical Equipment IHry WkBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To SpectrophotometryDokumen26 halamanIntroduction To SpectrophotometryhardmanpersonBelum ada peringkat
- Uv-Vis SpecrtosDokumen23 halamanUv-Vis SpecrtosAttia YameenBelum ada peringkat
- Spectrophotometry and ColorimetryDokumen29 halamanSpectrophotometry and ColorimetryLea Ann Sembrano Fandida100% (2)
- 2 LI Apr 2019 SpectrophotometerDokumen45 halaman2 LI Apr 2019 SpectrophotometerVisaNathanBelum ada peringkat
- Instrument, Principles & UsageDokumen28 halamanInstrument, Principles & UsageNida RidzuanBelum ada peringkat
- Ultraviolet Visible SpectrophotometerDokumen11 halamanUltraviolet Visible Spectrophotometerapi-246263792Belum ada peringkat
- Final Colorimeter SpectrophotometerDokumen19 halamanFinal Colorimeter SpectrophotometerDr Izza AyubBelum ada peringkat
- LBT110Using The Spectrophotometer For Protein AssaysDokumen4 halamanLBT110Using The Spectrophotometer For Protein AssaysBrian LimBelum ada peringkat
- Uv VisDokumen6 halamanUv VisTannecia BenjaminBelum ada peringkat
- ComponentsPrincipleandApplicationsofUVVis Spectophotometer DRSJDokumen20 halamanComponentsPrincipleandApplicationsofUVVis Spectophotometer DRSJgigigiBelum ada peringkat
- ComponentsPrincipleandApplicationsofUVVis Spectophotometer DRSJDokumen20 halamanComponentsPrincipleandApplicationsofUVVis Spectophotometer DRSJAnurak OnnnoomBelum ada peringkat
- UV Visible SpectrosDokumen6 halamanUV Visible SpectrosNagarakshita V KBelum ada peringkat
- Equipments 2Dokumen24 halamanEquipments 2Khushi KumariBelum ada peringkat
- Photo MeterDokumen4 halamanPhoto MeterRKMBelum ada peringkat
- Detecting and Quantifying Biological Molecules Using SpectrophotometryDokumen12 halamanDetecting and Quantifying Biological Molecules Using SpectrophotometryAGBelum ada peringkat
- Theory of Color Physics 05 SlideDokumen20 halamanTheory of Color Physics 05 SlideRikta IslamBelum ada peringkat
- Ultra-Violate Spectrophotometry: ,,Aversi-Rational'' LTDDokumen12 halamanUltra-Violate Spectrophotometry: ,,Aversi-Rational'' LTDNoor AliBelum ada peringkat
- Org ChemDokumen8 halamanOrg ChemAnam MustafaBelum ada peringkat
- Spectro Photo Me TryDokumen5 halamanSpectro Photo Me TrySaravanapriya KarthikBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 1 (Lab Period 1) Spectrophotometry: Absorption Spectra and The Use of Light Absorption To Measure ConcentrationDokumen7 halamanExperiment 1 (Lab Period 1) Spectrophotometry: Absorption Spectra and The Use of Light Absorption To Measure ConcentrationSharifah Zulaikha BenYahyaBelum ada peringkat
- Spctrophtometer 4Dokumen12 halamanSpctrophtometer 4Abdalkaher AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 3Dokumen9 halamanLab 3hussemadl41Belum ada peringkat
- CH 4 2023Dokumen34 halamanCH 4 2023Kaleb AshikoBelum ada peringkat
- Colorimeter NewDokumen22 halamanColorimeter NewKarthik RajaBelum ada peringkat
- Analytic Techniques and Instrumentation Lecture FormatDokumen15 halamanAnalytic Techniques and Instrumentation Lecture FormatMandy A. DelfinBelum ada peringkat
- SPECTROPHOTOMETERDokumen5 halamanSPECTROPHOTOMETERKokab KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Spectrophotometer: - Class: 1ADokumen12 halamanSpectrophotometer: - Class: 1Aniken larasatiBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation Uv SpectrophotometerDokumen14 halamanPresentation Uv SpectrophotometerKrishna DabgarBelum ada peringkat
- PHR312 UV Vis Spectroscopy NSU ABPDokumen59 halamanPHR312 UV Vis Spectroscopy NSU ABPMeem Abdullah Azeem 1813455049Belum ada peringkat
- Lab Instrumentation 4Dokumen2 halamanLab Instrumentation 4rlatjorlukBelum ada peringkat
- Spectrophotometry04 1Dokumen9 halamanSpectrophotometry04 1prakush_prakushBelum ada peringkat
- IntroductionDokumen1 halamanIntroductionSherlyn cheahBelum ada peringkat
- The Spectrophotometry: by Ain & TiniDokumen9 halamanThe Spectrophotometry: by Ain & TiniNur Ain BorhanBelum ada peringkat
- SPECTROPHOTOMETRYDokumen3 halamanSPECTROPHOTOMETRYMelkamu ZazaBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Task 5 - SPECTROPHOTOMETRYDokumen2 halamanPerformance Task 5 - SPECTROPHOTOMETRYKeith BagangBelum ada peringkat
- Technology For Spectroscopic Techniques (UV-Vis Spectrophotometry)Dokumen6 halamanTechnology For Spectroscopic Techniques (UV-Vis Spectrophotometry)Sosuke AizenBelum ada peringkat
- SpectrophotometryDokumen7 halamanSpectrophotometrySantanah Daxene DayloBelum ada peringkat
- 11 Chapter 11Dokumen8 halaman11 Chapter 11Smita SahooBelum ada peringkat
- SpectrophotometryDokumen40 halamanSpectrophotometryMUKESH SUNDARARAJANBelum ada peringkat
- ColorimetryDokumen15 halamanColorimetrydeepika kanojiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Colorimetri TheoryDokumen1 halamanColorimetri TheoryronapriBelum ada peringkat
- NepheloturbidimetryDokumen4 halamanNepheloturbidimetrypranav.joshi2020Belum ada peringkat
- Spectrophotometers Lecture 2Dokumen6 halamanSpectrophotometers Lecture 2Sabah MajzoubBelum ada peringkat
- Jove Protocol 10204 Ultraviolet Visible Uv Vis SpectrosDokumen4 halamanJove Protocol 10204 Ultraviolet Visible Uv Vis Spectrosloah_123Belum ada peringkat
- NephelometryDokumen22 halamanNephelometryBassem AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- SpektrofotometriDokumen13 halamanSpektrofotometriBayu RagilBelum ada peringkat
- Spectro Photo Me TryDokumen81 halamanSpectro Photo Me TrySunil100% (1)
- Color Wavelength NM Violet Blue Cyan Green Yellow Orange RedDokumen4 halamanColor Wavelength NM Violet Blue Cyan Green Yellow Orange RedJhenard John Lansangan BeltranBelum ada peringkat
- Lab1 SpectrophotometryDokumen25 halamanLab1 SpectrophotometrynqwrgnbzhqBelum ada peringkat
- UV-Vis Spectroscopy - Principle, Strengths and Limitations and ApplicationsDokumen19 halamanUV-Vis Spectroscopy - Principle, Strengths and Limitations and ApplicationsSajjad AliBelum ada peringkat
- FluorescenceDokumen40 halamanFluorescencefatemaBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Concept of Instrument Analysis PDFDokumen4 halamanBasic Concept of Instrument Analysis PDF1910 65 Vrushali PotdarBelum ada peringkat
- Spectrophotometer Mls 3rdDokumen14 halamanSpectrophotometer Mls 3rdRuhulla AbbassBelum ada peringkat
- Lab #4 SpectrophotometryDokumen10 halamanLab #4 Spectrophotometrythamizh555Belum ada peringkat
- Application of Spectral Studies in Pharmaceutical Product development: (Basic Approach with Illustrated Examples) First Revised EditionDari EverandApplication of Spectral Studies in Pharmaceutical Product development: (Basic Approach with Illustrated Examples) First Revised EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Ultraviolet Lamps Made Easy: The "RIGHT-WAY" Guide to Using Gem Identification ToolsDari EverandUltraviolet Lamps Made Easy: The "RIGHT-WAY" Guide to Using Gem Identification ToolsBelum ada peringkat
- Cohrence in CinemaDokumen8 halamanCohrence in CinemadliyaxBelum ada peringkat
- Why Magnetic JossDokumen2 halamanWhy Magnetic JossdliyaxBelum ada peringkat
- US Patent Motor Control Inverter Converter Pinter PDFDokumen9 halamanUS Patent Motor Control Inverter Converter Pinter PDFdliyaxBelum ada peringkat
- Safety Explosion MaintenanceDokumen2 halamanSafety Explosion MaintenancedliyaxBelum ada peringkat
- Why Quantum PositionDokumen10 halamanWhy Quantum PositiondliyaxBelum ada peringkat
- Vilometer IntroductionDokumen15 halamanVilometer IntroductiondliyaxBelum ada peringkat
- Level Measurement: - Some of The Most Commonly Used Liquid-Level Measurement Methods AreDokumen27 halamanLevel Measurement: - Some of The Most Commonly Used Liquid-Level Measurement Methods AredliyaxBelum ada peringkat
- Distrbuted Introduction ControlDokumen20 halamanDistrbuted Introduction ControldliyaxBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrantana Tic DraulicDokumen69 halamanHydrantana Tic DraulicdliyaxBelum ada peringkat
- Agenda: o Current Task Group Actions o Overview of API 6D 24 Edition o Future Task Group ActionsDokumen29 halamanAgenda: o Current Task Group Actions o Overview of API 6D 24 Edition o Future Task Group ActionsdliyaxBelum ada peringkat
- User'S Guide: FX - 4Ad-Tc Special Function BlockDokumen8 halamanUser'S Guide: FX - 4Ad-Tc Special Function BlockdliyaxBelum ada peringkat
- C Curve PDFDokumen2 halamanC Curve PDFdliyax100% (1)
- Picostrain Digital LoadCell PDFDokumen48 halamanPicostrain Digital LoadCell PDFdliyaxBelum ada peringkat
- Isobar 4 Outgoers Miniature Circuit Breakers 1 - 63A: InstallationDokumen2 halamanIsobar 4 Outgoers Miniature Circuit Breakers 1 - 63A: InstallationdliyaxBelum ada peringkat
- Magenta RS Engineering TrainingDokumen1 halamanMagenta RS Engineering TrainingdliyaxBelum ada peringkat
- Schneider 12005Dokumen2 halamanSchneider 12005Mạnh ĐạtBelum ada peringkat
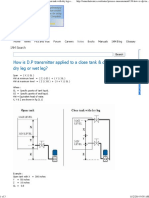
- How Is D.P Transmitter Applied To A Close Tank & Open Tank With Dry Leg or Wet Leg?Dokumen3 halamanHow Is D.P Transmitter Applied To A Close Tank & Open Tank With Dry Leg or Wet Leg?dliyaxBelum ada peringkat
- Best Easy Flowmeter HydrogenDokumen2 halamanBest Easy Flowmeter HydrogendliyaxBelum ada peringkat
- Ver 3.0 - Test Series - NEET - Schedule (XII & RM) - Code-A - BDokumen3 halamanVer 3.0 - Test Series - NEET - Schedule (XII & RM) - Code-A - BCorona virusBelum ada peringkat
- Modes of Occurrence and Provenance of Gemstones of Sri Lanka (Mineralium Deposita, Vol. 15, Issue 1) (1980)Dokumen6 halamanModes of Occurrence and Provenance of Gemstones of Sri Lanka (Mineralium Deposita, Vol. 15, Issue 1) (1980)StarScourgeBelum ada peringkat
- Multiple Choice LachingDokumen3 halamanMultiple Choice Lachingraghu_iict100% (1)
- Experiment 2 - ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLSDokumen5 halamanExperiment 2 - ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLSFroz ChickenBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Enhancing Substances and TechniquesDokumen2 halamanPerformance Enhancing Substances and Techniquesapi-391714949Belum ada peringkat
- Compact First - EnglishDokumen45 halamanCompact First - EnglishLilianaOliveiraBelum ada peringkat
- Dhulian FinalDokumen50 halamanDhulian FinalShams Sardar100% (1)
- Resin Screening To Optimize Chromatographic SeparaDokumen5 halamanResin Screening To Optimize Chromatographic SeparamohanBelum ada peringkat
- Landfill-Gas-Engine-Oil AnalysisDokumen2 halamanLandfill-Gas-Engine-Oil AnalysisKeith ChengBelum ada peringkat
- Interactive Textbook 1 PDF 4 1Dokumen8 halamanInteractive Textbook 1 PDF 4 1api-240094705100% (2)
- Prelab No. 1 - Determination-of-Noise-Level-Using-Sound-Level-Meter-Final - Group No. 7Dokumen2 halamanPrelab No. 1 - Determination-of-Noise-Level-Using-Sound-Level-Meter-Final - Group No. 7louryBelum ada peringkat
- Autoclave Aerated ConcreteDokumen3 halamanAutoclave Aerated ConcreteFireSwarmBelum ada peringkat
- SISTO - Maintenance-Free Diaphragm Valves With and Without LiningDokumen2 halamanSISTO - Maintenance-Free Diaphragm Valves With and Without LiningsharemwBelum ada peringkat
- Salitex Expansion Joint Filler BoardDokumen2 halamanSalitex Expansion Joint Filler BoardSandipBelum ada peringkat
- Colloid Chemistry and Phase Rule 4022146-1: (Essentials of Physical Chemistry - Arun Bahl & B.S. Bahl) Chapter 19 and 22Dokumen51 halamanColloid Chemistry and Phase Rule 4022146-1: (Essentials of Physical Chemistry - Arun Bahl & B.S. Bahl) Chapter 19 and 22Razan khalidBelum ada peringkat
- 5031 Acid Base WorksheetDokumen5 halaman5031 Acid Base WorksheetSaima Usman/TCHR/MGBBelum ada peringkat
- The Efficiency of Powdered Ceramic Tiles As A Fire Resisting Component Mixed With Wall PaintDokumen5 halamanThe Efficiency of Powdered Ceramic Tiles As A Fire Resisting Component Mixed With Wall Paintnorman del rosarioBelum ada peringkat
- 2004 - JMS - Jain & GuptaDokumen17 halaman2004 - JMS - Jain & GuptasemantBelum ada peringkat
- Determine PH by PH Indicator and Universal IndicatorDokumen3 halamanDetermine PH by PH Indicator and Universal IndicatorhaleelBelum ada peringkat
- CertificateDokumen28 halamanCertificateKhaldi KaisBelum ada peringkat
- Post Weld Heat TreatmentDokumen3 halamanPost Weld Heat TreatmentpvdrameshBelum ada peringkat
- Safety Data Sheet - Perfect Coat Flea & Tick Dog Shampoo PDFDokumen7 halamanSafety Data Sheet - Perfect Coat Flea & Tick Dog Shampoo PDFhoneybelBelum ada peringkat
- History of Organic Chemistry 2Dokumen2 halamanHistory of Organic Chemistry 2MiaBelum ada peringkat
- Pollutants and Its MeasurementDokumen70 halamanPollutants and Its MeasurementECRDBelum ada peringkat