Surgical wound dressing techniques and principles
Diunggah oleh
Babita Dhruw0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
54 tayangan18 halamanh
Judul Asli
Wound Dressing
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inih
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
54 tayangan18 halamanSurgical wound dressing techniques and principles
Diunggah oleh
Babita Dhruwh
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 18
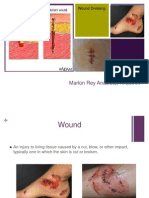
Surgical wound are caused due to the surgical
incision in any part of the body. surgical
wound ‘s edges are usually clean and occur
under aseptic conditions.
According to TNAI
-It is a sterile protective surgical covering,
applied to a wound /incision with aseptic
technique, with or without medication.
According to Annamma Jacob
Cleansing a wound or incision and applying
sterile protective covering using aseptic
technique.
To promote wound healing.
To prevent micro organism from entering the
wound.
To decrease the presence of purulent wound
drainage.
To absorb fluid and apply medication .
To immobilize and support the wound.
To assist in removal of necrotic tissue.
To apply medication to the wound
To provide comfort.
To support or splint the wound site.
Sterile dressing tray containing
Artery forceps-1
Thumb forceps-1
Cotton swabs.
Gauze pieces.
Surgical pads
Kidney tray-1
Sterile scissor-1
Suture cutting scissor-1
Small bowl-1
Dressing towels
A clean tray containing
Sterile gloves
Normal saline
Ordered medication
Adhesive plaster
Bandage scissors
Plastic bag
Mackintosh
Culture tube(optional)
Maintain a strict aseptic technique to prevent cross
infection ,to and from the wound .all materials
touching the wound should be sterile.
All articles should be disinfected thoroughly.
Wash hands thoroughly before and after the
procedure.
One set of instruments should be used for one
dressing.
Use masks,sterile gloves and gown to minimise
wound contamination.
Dressing should not be done immediately after
sweeping and dusting wait atleast for 15-20 mins.
Use individually wrapped sterile dressing and
equipment for the wound.
Maintain a sterile field around the wound by spreading
sterile towels.
Avoid talking coughing sneezing once the area is
opened.
If the dressing is adherent to the wound due to dry
secreations or blood wet it with sterile saline before it is
removed.
Observe the discharge from the wound accurately for
colour odour amount and consistency
Avoid meal timings for doing dressings .it should be
done either half an hour before or after the meal.
Identify the patient and position him comfortably.
Explain the procedure and provide privacy
Drape the patient.
Close the doors and windows. put off the fan to
prevent draughts.
Keep one assistant for dressing of the large wounds.
Protect the bed with a mackintosh and a treatment
towel.
Expose the part as necessary.
Untie the bandage or adhesive and remove only after
hand washing.
Turn the patient’s head to one side to prevent anxiety.
Remove the mackintosh and treatment towel.
Take all articles to the treatment room
Discard the soiled dressing in the covered container and send it
for incineration.
Remove the instruments and other articles from the infectant
solution and clean them thoroughly.
Dry them and reset the tray and send it for autoclaving.
Replace all articles at the proper place.
Help the patient to dress up and make him comfortable.
Replace the bed linen.
Wash hands.
Record the procedure in nurses record ,condition of wound type
and amount of discharge ,condition of the suture etc.if any
abnormality is found report to the surgeon keep the unit tidy and
clean
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
Superficial wounds pierce only the skin.deeper wound
involve connective tissue ,fascia ,muscles,blood vessels
and nerves.
Nerves are close to the surface ,so superficial wounds
are very painful.
The skin is richly supplied with blood and blood
supply is essential for healing.
Healing is rapid if there is no infection in the wound.
Healing is rapid if there is no infection in the wound.
Healing is faster in the young and more slowly in aged.
Healing is slow due to dehydration,hypoproteinemia
and deficiency of vitamin c
MICROBIOLOGY
Wash hands thouroughly before and after the
procedure to avoid cross infection
Maintain aseptic technique during dressing.
Anything that touches a wound should be sterile .the
dressing ,instruments ,solutions etc.
All dressing material,instruments,should be sterilized
by autoclaving.
Never touch the wound itself ,the skin surrounding the
wound or the inner dressing to avoid infection.
Disinfect the contaminated articles before reuse.
Collect soiled dressings and burn it to prevent spread
of infection.
Use gloves ,gown,mask for dressing.
Keep all the sterile articles covered until it is time for use.
As bacteria travel along with the dust particles, avoid
flapping of the bed cloths and dresses to prevent dust
particles entering the wound.
Open wound provide a ready culture medium for bacteria
so open wounds must be sealed as early as possible.
The skin is cleaned as well as possible around the wound
with alcohol to prevent the bacteria on the skin from
infecting the wound.
Contaminated dressing must be destroyed by burning.
Maintain resistance of the patient by giving adequate diet
rich in proteins vit B and C.
PHYSICS AND CHEMISTRY
Gauze absorbs drainage by capillary attraction and keeps
the wound dry.
Fluids move downwards asa a result of gravitational pull so
drainage tubes are put at the lower edge of the wound.
Alcohol is most efficient in a 70% solution because its action
is slow and diffuses throughout the entire bacterium before
proteins coagulate .when coagulation occurs the diffusion is
complete and the organism is dead.
A solution greater than 80% hardens the bacteria and does
not penetrate them therefore not killing them
Strong chemical destroy tissues as well as micro organisms
and healing is destroyed.
PHARMACOLOGY
Spirit ,iodine ,dettol etc are used as skin antiseptics.
Silver nitrate is germicidal and helps in healing .
Antibiotics are used as a solutions or ointments directly
against many types of bacteria.
PSYCHOLOGY
Explain the procedure to the patient .how much pain is
involved .this will reduce the fear and anxiety.
Screen the patient while dressing
Divert his mind by talking with the patient .
Do not expose the wound in front of the patient.
Turn his head to one side to avoid unpleasant sight.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Survival Skills: How to Survive Anything and Anywhere in the World (A Comprehensive Guide to Preparing for and Overcoming Challenges of Earthquakes)Dari EverandSurvival Skills: How to Survive Anything and Anywhere in the World (A Comprehensive Guide to Preparing for and Overcoming Challenges of Earthquakes)Belum ada peringkat
- Diphtheria how to recognize the disease, how to keep from catching it, how to treat those who do catch itDari EverandDiphtheria how to recognize the disease, how to keep from catching it, how to treat those who do catch itBelum ada peringkat
- First Aid For Wounds On The SkinDokumen2 halamanFirst Aid For Wounds On The SkinJetha Nica CaabBelum ada peringkat
- or ConceptsDokumen65 halamanor ConceptsAzehr CommzBelum ada peringkat
- Care of WoundsDokumen6 halamanCare of WoundsKimpoy Tu-osBelum ada peringkat
- Medical and Surgical AsepsisDokumen5 halamanMedical and Surgical AsepsisRae Marie AquinoBelum ada peringkat
- DressingDokumen17 halamanDressingSushmaBelum ada peringkat
- Kle U Institute of Nursing Sciences, BelgaumDokumen8 halamanKle U Institute of Nursing Sciences, BelgaumShivraj DandgiBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertonic SolutionsDokumen4 halamanHypertonic SolutionsVanessa PaguiriganBelum ada peringkat
- Or DR Report Tumbaga and CumlatDokumen3 halamanOr DR Report Tumbaga and CumlatDanica CumlatBelum ada peringkat
- By: Mary Angelie M. Atienza: Infection Control Nurse Bicol Regional Training and Teaching HospitalDokumen70 halamanBy: Mary Angelie M. Atienza: Infection Control Nurse Bicol Regional Training and Teaching HospitalCiao AtienzaBelum ada peringkat
- Woundppt1 180620135508Dokumen34 halamanWoundppt1 180620135508Smriti GroverBelum ada peringkat
- Wound Care Procedure GuideDokumen5 halamanWound Care Procedure GuideAbegyl Nicole FiguraBelum ada peringkat
- Wound Dressing TechniquesDokumen5 halamanWound Dressing TechniquesSandeep Maan60% (5)
- Nicole - DBE and Wound DressingDokumen4 halamanNicole - DBE and Wound DressingnicolemellaBelum ada peringkat
- Wound Care: Types of DressingDokumen5 halamanWound Care: Types of DressingAmit MartinBelum ada peringkat
- Aseptic Techniques (2022)Dokumen65 halamanAseptic Techniques (2022)Usama SeleimBelum ada peringkat
- 4) Wound DebridementDokumen48 halaman4) Wound DebridementTaha HasanBelum ada peringkat
- Asepsis and Antisepsis, Disinfectans and Sterilization: DR Wahyu Purnam PutraDokumen52 halamanAsepsis and Antisepsis, Disinfectans and Sterilization: DR Wahyu Purnam PutraHanifan NugrahaBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Asepsis TechniquesDokumen6 halamanMedical Asepsis TechniquesChetan KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Content: Normal Wound HealingDokumen4 halamanLearning Content: Normal Wound HealingJovele BenitoBelum ada peringkat
- Dressing and Bandaging in First Aid: A Complete GuideDokumen8 halamanDressing and Bandaging in First Aid: A Complete GuideRosalouise P. UngabBelum ada peringkat
- © 2021 Lippincott Advisor - Treatments - DebridementDokumen5 halaman© 2021 Lippincott Advisor - Treatments - DebridementJoyJoy Tabada CalunsagBelum ada peringkat
- Infection Control and Standard Safety MeasuresDokumen25 halamanInfection Control and Standard Safety MeasuresManisha Thakur100% (1)
- Dressing and Bandaging WoundsDokumen28 halamanDressing and Bandaging WoundsGemma Mondero ColladoBelum ada peringkat
- Marlon Rey Anacleto, RN, MAN: Wound DressingDokumen7 halamanMarlon Rey Anacleto, RN, MAN: Wound DressingMarlon Rey AnacletoBelum ada peringkat
- Handwashing, Gowning, & GlovingDokumen25 halamanHandwashing, Gowning, & GlovingRiteka SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Infection Control Part IDokumen3 halamanInfection Control Part IFadz HadjiriBelum ada peringkat
- A SepsisDokumen5 halamanA SepsisAi KogaBelum ada peringkat
- Performing a Surgical ScrubDokumen15 halamanPerforming a Surgical ScrubSavita HanamsagarBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 100 Skills Updated VersionnnnDokumen29 halamanNCM 100 Skills Updated VersionnnnDhie Jhay InigoBelum ada peringkat
- Wound and Wound Dressing Dressing: Presentedby Mrs - Sylvia Ranjan Mathew Principal MGM College of NursingDokumen21 halamanWound and Wound Dressing Dressing: Presentedby Mrs - Sylvia Ranjan Mathew Principal MGM College of Nursingjyoti singhBelum ada peringkat
- Skills of The 2nd WeekDokumen22 halamanSkills of The 2nd Weekalharbimanar20Belum ada peringkat
- AssignmentDokumen9 halamanAssignmentTenzin Norzom NegiBelum ada peringkat
- Wound DressingDokumen3 halamanWound DressingJane BelvisBelum ada peringkat
- For VisualDokumen35 halamanFor VisualPsykotik RozBelum ada peringkat
- Eye Care NewDokumen20 halamanEye Care NewlinilBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Changing A Dry Sterile DressingDokumen3 halaman2 Changing A Dry Sterile DressingAnn Jalover PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Asepsis and antisepsis techniques for infection preventionDokumen22 halamanAsepsis and antisepsis techniques for infection preventionNdor BariboloBelum ada peringkat
- Standard Measures of Management of Infected WoundDokumen11 halamanStandard Measures of Management of Infected WoundMohamed FarahatBelum ada peringkat
- Wound CareDokumen3 halamanWound CareLian James MataBelum ada peringkat
- HIV/AIDS Precautions - Correctional Institutions: What Precautions Should I Take When Employed in Correctional Services?Dokumen35 halamanHIV/AIDS Precautions - Correctional Institutions: What Precautions Should I Take When Employed in Correctional Services?ditaagustinaBelum ada peringkat
- Performing a sterile dressing changeDokumen14 halamanPerforming a sterile dressing changeHannaBelum ada peringkat
- Surgery delays as ER cases surge at Launceston hospitalDokumen5 halamanSurgery delays as ER cases surge at Launceston hospitalRosalie Valdez EspirituBelum ada peringkat
- Sutureworkshop Handout PDFDokumen8 halamanSutureworkshop Handout PDFViharaDewiMahendraBelum ada peringkat
- PERIOPERATIVE NURSING BASICS: STERILE TECHNIQUEDokumen10 halamanPERIOPERATIVE NURSING BASICS: STERILE TECHNIQUEIris MambuayBelum ada peringkat
- Aseptic TechniqueDokumen10 halamanAseptic TechniqueIan Carlo Padama MosesBelum ada peringkat
- P3infection Control PracticesDokumen7 halamanP3infection Control Practicesprivate3wardBelum ada peringkat
- Pereneal CareDokumen2 halamanPereneal CareindumathiBelum ada peringkat
- Attire, Surgical Scrub, Gowning and GlovingDokumen23 halamanAttire, Surgical Scrub, Gowning and GlovingRumelle ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Isolation and Hand Hygienepresentation1Dokumen37 halamanIsolation and Hand Hygienepresentation1Nirmal Cricket UniverseBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation DEEPTHIDokumen17 halamanPresentation DEEPTHIsarathchandran deepthiBelum ada peringkat
- Surgical Principles From MbbsBasicDokumen47 halamanSurgical Principles From MbbsBasicbasic100% (5)
- Wound Dressing Procedure WPS OfficeDokumen8 halamanWound Dressing Procedure WPS OfficeAbhishek VermaBelum ada peringkat
- Surgical AsepsisDokumen29 halamanSurgical AsepsisRyan Llanto100% (1)
- Surgical DressingDokumen2 halamanSurgical Dressinggao1989Belum ada peringkat
- Ob Bag DemoDokumen3 halamanOb Bag DemoARJAY DAPILAGABelum ada peringkat
- Infection Control inDokumen45 halamanInfection Control inmohdmaghyreh100% (2)
- Survival Medicine Kit: A Complete Medical Handbook For All First Kit NeedsDari EverandSurvival Medicine Kit: A Complete Medical Handbook For All First Kit NeedsBelum ada peringkat
- PEDIATRIC FIRST AID: How to respond quickly when your child is in dangerDari EverandPEDIATRIC FIRST AID: How to respond quickly when your child is in dangerBelum ada peringkat
- CHC - 2Dokumen15 halamanCHC - 2Babita Dhruw75% (4)
- Occupational HazardsDokumen22 halamanOccupational HazardsBabita DhruwBelum ada peringkat
- National Rural Health Mission AssignmentDokumen12 halamanNational Rural Health Mission AssignmentFaceless BubbiesBelum ada peringkat
- M.sc. Nursing SyllabusDokumen145 halamanM.sc. Nursing SyllabusSathish Rajamani100% (4)
- Primary Health Center Survey and FunctionsDokumen4 halamanPrimary Health Center Survey and FunctionsBabita Dhruw100% (3)
- Community Health Nursing Socio-Cultural FactorsDokumen8 halamanCommunity Health Nursing Socio-Cultural FactorsBabita DhruwBelum ada peringkat
- NVDCPDokumen10 halamanNVDCPBabita DhruwBelum ada peringkat
- Types and Prevention of Food Adulteration and Substance AbuseDokumen22 halamanTypes and Prevention of Food Adulteration and Substance AbuseBabita Dhruw100% (1)
- Five Yr PlanDokumen40 halamanFive Yr PlanBabita Dhruw100% (3)
- Training rural health workersDokumen23 halamanTraining rural health workersBabita DhruwBelum ada peringkat
- OHS - Unit-6 - Course Content - OHS Legislation in India PDFDokumen46 halamanOHS - Unit-6 - Course Content - OHS Legislation in India PDFVikas NaagarBelum ada peringkat
- Family Folder FormateDokumen10 halamanFamily Folder FormateBabita Dhruw86% (7)
- Scope College of Nursing Clinical Rotation PlansDokumen4 halamanScope College of Nursing Clinical Rotation PlansBabita DhruwBelum ada peringkat
- Community Health NursingDokumen26 halamanCommunity Health NursingBabita Dhruw100% (2)
- Smaple Case Study - Virginia's Henderson Need Theory PDFDokumen8 halamanSmaple Case Study - Virginia's Henderson Need Theory PDFEduardo AnerdezBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Rotation Plan BSCDokumen10 halamanClinical Rotation Plan BSCBabita DhruwBelum ada peringkat
- Virginia HendersonDokumen21 halamanVirginia HendersonBabita Dhruw100% (2)
- My Master Rotation PlanDokumen1 halamanMy Master Rotation PlanBabita DhruwBelum ada peringkat
- Presented by Babita Dhrue Ankita Panigrahi MSC Nursing Previous YearDokumen15 halamanPresented by Babita Dhrue Ankita Panigrahi MSC Nursing Previous YearBabita DhruwBelum ada peringkat
- Virginia Henderson All DtailDokumen9 halamanVirginia Henderson All DtailBabita DhruwBelum ada peringkat
- NRHM InitiativeDokumen7 halamanNRHM InitiativeBabita DhruwBelum ada peringkat
- PT of Endotrachealt Tube IntubationDokumen28 halamanPT of Endotrachealt Tube IntubationBabita DhruwBelum ada peringkat
- Ngo With LiaisonDokumen7 halamanNgo With LiaisonBabita Dhruw100% (1)
- HAND OUT Food HygieneDokumen2 halamanHAND OUT Food HygieneBabita DhruwBelum ada peringkat
- Purposes of Home VisitDokumen4 halamanPurposes of Home VisitBabita Dhruw100% (8)
- CHN TextbookDokumen313 halamanCHN TextbookCynfully SweetBelum ada peringkat
- P T of Comm NSGDokumen27 halamanP T of Comm NSGBabita DhruwBelum ada peringkat
- Geriatric Consideration in NursingDokumen31 halamanGeriatric Consideration in NursingBabita Dhruw100% (5)
- Govt College of Nursing, Jagdalpur (C.G) : Visit Report OnDokumen7 halamanGovt College of Nursing, Jagdalpur (C.G) : Visit Report OnBabita DhruwBelum ada peringkat
- Guidance and Councelling For RehabilitationDokumen10 halamanGuidance and Councelling For RehabilitationBabita Dhruw100% (3)
- An Organization Study OnDokumen39 halamanAn Organization Study Onvelmuthusamy100% (2)
- Sketchy Pharm RuntimesDokumen5 halamanSketchy Pharm RuntimesAmin ValenciaBelum ada peringkat
- EGA Factsheet 01Dokumen1 halamanEGA Factsheet 01Rajeeb Chandra ShahaBelum ada peringkat
- NM ObtDokumen22 halamanNM ObtIlyan NastiBelum ada peringkat
- Threshold Reiki Reiki Ryoho HikkeiDokumen27 halamanThreshold Reiki Reiki Ryoho HikkeiHarrison KoehliBelum ada peringkat
- Nurs 205 Concept MapDokumen1 halamanNurs 205 Concept MapJami SpearsBelum ada peringkat
- Ethical PrinciplesDokumen2 halamanEthical PrinciplesyoonjessBelum ada peringkat
- Pleural EffusionDokumen3 halamanPleural EffusionEjie Boy IsagaBelum ada peringkat
- Patient Contract SummaryDokumen2 halamanPatient Contract SummaryFaten SalahBelum ada peringkat
- Wound Healing SchwartzDokumen37 halamanWound Healing SchwartzCarla Putri Chandra100% (1)
- Atomoxetine in ADHD in Children With and Without Comorbid Mood DisordersDokumen10 halamanAtomoxetine in ADHD in Children With and Without Comorbid Mood DisordersNeuro GYMBelum ada peringkat
- AgeLOC R Squared Product and Science PresentationDokumen27 halamanAgeLOC R Squared Product and Science PresentationSiaw Sing OngBelum ada peringkat
- Gastrointestinal System Ppt.-NewDokumen117 halamanGastrointestinal System Ppt.-NewFatima Syed100% (3)
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)Dokumen53 halamanContinuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)indiamahesh100% (1)
- Client Intake FormsDokumen5 halamanClient Intake FormsGuillaume VingtcentBelum ada peringkat
- Puyer Asthma and Diare Medication DosagesDokumen1 halamanPuyer Asthma and Diare Medication DosagesAlbert SudharsonoBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Diseases and Life-Threatening Conditions: Assistant Professor Kenan KaravdićDokumen33 halamanAcute Diseases and Life-Threatening Conditions: Assistant Professor Kenan KaravdićGoran MaliBelum ada peringkat
- Psychotherapy Assessment FormatDokumen10 halamanPsychotherapy Assessment Formatshivani singh100% (1)
- Food Procces Engineering. Vol 3 PDFDokumen726 halamanFood Procces Engineering. Vol 3 PDFNelson MorbanBelum ada peringkat
- Fear of IntimacyDokumen9 halamanFear of IntimacyHelsi MayaBelum ada peringkat
- HemorrhageDokumen15 halamanHemorrhageMariegreat Piscos BisnarBelum ada peringkat
- Phils NC Address (Responses) - Update Jan22Dokumen149 halamanPhils NC Address (Responses) - Update Jan22RoroRichardsBelum ada peringkat
- RN Fundamentals of Nursing PDFDokumen325 halamanRN Fundamentals of Nursing PDFDonnabell DayudayBelum ada peringkat
- Third Molar Impaction-A Review: Divya.T, Themozhi M.SDokumen5 halamanThird Molar Impaction-A Review: Divya.T, Themozhi M.SCiutac ŞtefanBelum ada peringkat
- Formulation and Evaluation of Antiseptic Polyherbal OintmentDokumen11 halamanFormulation and Evaluation of Antiseptic Polyherbal OintmentandrapradeshsseBelum ada peringkat
- Sclar 2004Dokumen16 halamanSclar 2004Kelly N100% (1)
- Piis0167814014005246 PDFDokumen8 halamanPiis0167814014005246 PDFDiana MitreaBelum ada peringkat
- Types of PsychologyDokumen62 halamanTypes of PsychologyParamjit SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Sociology Final ProjectDokumen16 halamanSociology Final Projectabt09Belum ada peringkat
- Research ArticleDokumen4 halamanResearch ArticleBharathi RagavanBelum ada peringkat