Adsorbate
Diunggah oleh
alok sahu0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
83 tayangan25 halamanadsorbatte and its types
Judul Asli
adsorbate ppt
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Iniadsorbatte and its types
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
83 tayangan25 halamanAdsorbate
Diunggah oleh
alok sahuadsorbatte and its types
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 25
CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
Overview of plant
Properties of UREA
Uses of UREA
UREA MANUFACTURING PLANT
2.1 Description of UREA production process
2.2 Flow sheet of UREA plant
2.3 SYNTHESIS SECTION
2.4 DECOMPOSITION SECTION
2.5 RECOVERY SECTION
2.6 FINISHING SECTION
INTRODUCTION
OVERVIEW OF PLANT
KANPUR FERTILIZERS & CEMENT LTD. a unit of JAYPEE
GROUP known as DUNCANS INDUSTRIAL LTD. JAYPEE
GROUP is an infrastructure industrial conglamorates of Rs.
18000 crore turnover.
KFCL is subsidizing of JAYPEE GROUP. The fertilizer plant
of KFCL is based on TOYO TECHNOLOGY OF JAPAN &
three units of each plant & capacity of 730 ton per day.
The three ammonia production plants are natural gas
plant based on ICI TECHNOLOGY, each plant capacity of
415 ton per day.
KFCL sell the product by brand name “CHAND
CHHAP” UREA. This well known brand still in the
memories of satisfied farmers of Northern, Central &
Eastern India. UREA produced by “TOTAL RECYCLE
CIRCULATION PROCESS”.
The learning opportunities and industrial exposure at
the KFCL made not just possible to relate the book
knowledge to field application but also in developing a
through understanding of industrial practice and
operating concepts.
KFCL is a leading manufacturer & supplier of fertilizer
from KANPUR, UTTAR PRADESH. From safety point
of view, the industry is listed under “MAJOR
ACCIDENTAL HAZARD INDUSTRY”.
THERE ARE FOUR SECTION IN PLANT
OFF SITES (Water treatment, air station, cooling
tower, inert gas plant, ammonia storage)
AMMONIA PLANT
UREA PLANT
CPP ( Captive power plant)
PROPERTIES OF UREA
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
White in color
Odorless
Non corrosive
Crystalline Substance
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Chemical Formula = NH2CONH2
IUPAC Name = UREA
Molecular Weight = 60.05
Maximum Nitrogen Content = 46.6%
Specific Gravity = 1.335
Solubility in Water = 1080 g/L (20 0C )
Melting Point = 132 0C
USES OF UREA
UREA is major used as a solid fertilizer.
UREA is used to manufacture synthetic RESINS .
UREA is used in the production of PHARMACEUTICAL products.
RAW MATERIALS
BASIS; 1 Ton of urea
LIQUID AMMONIA(0.59 ton)
Supplied Conditions;
Pressure = 18 kg/cm2
Temperature = 15 to 40 0C
Composition(mole%) = 99.7%
Oil = 50 ppm
CARBON DIOXIDE(0.786 ton)
Pressure = 0.45 kg/cm2
Temperature = 40 0C
Composition(volume%) = 93.37%
UTILITIES
STEAM(1.53 ton)
Pressure = 13kg/cm2
Temperature = Saturated temperature
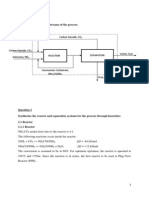
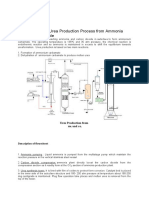
PROCESS DESCRIPTION
UREA is synthesised from CO2 gas , liquid ammonia and
recycle carbamate solution under high pressure 210 kg/cm2
and temperature 195 degree centigrade.
The reaction takes place in two stages, the first stage where
CO2 and NH3 to form AMMONIUM CARBAMATE is fast
and highly exothermic. Then in second stage AMMONIUM
CARBAMATE decomposes into UREA & WATER at slowly
and reaction is endothermic but OVERALL REACTION IS
EXOTHERMIC.
2 NH3 + CO2 = NH4COONH2 + 117 KJ
NH4COONH2 = NH2CONH2 + H2O - 15.5 KJ
The plant is designed to produce 730 ton of PRILLED
UREA per stream day single unit , using MITSUI TOTAL
RECYCLE “C” PROCESS.
SYNTHESIS SECTION
Equipment in this section are given below-
CO2 COMPRESSOR(GB-101)
NH3 INJECTOR(GA-101)
RECYCLE FEED PUMP OR EBARA(GA-102)
NH3 PRE- HEATER(EA-101)
REACTOR(DC-101)
CO2 gas , liquid NH3 and recycle solutions are compressed
and fed separately to the base of the REACTOR which is
operates at about at 195 degree centigrade temperature and
210 kg/cm2 pressure. Ammonium carbamate is formed first
and then breaks down to give urea and water. The reaction
products are UREA , WATER, NH3 and CO2, whether free or
combined as carbamate are expanded through a let down
valve into HIGH PRESSURE DECOMPOSER(DA-201) in the
decomposition section.
CO2 COMPRESSOR
The compressor is a six crank, five stage enclosed forced
lubricated machine. The FIRST, SECOND and THIRD
stages are double acting, FOURTH & FIFTH stages are
single acting.
The compressor is capable of delivering 12,530 M3/Hr of
CO2 gas measured dry at 760 mmHg and 0 degree
centigrade.
The suction condition of the CO2 gas is 0.45 kg/cm2 and 40
degree centigrade.
The delivery condition of the CO2 gas is 230 kg/cm2
measured at the outlet from the FIFTH stage delivery
damper.
The compressor is driven by 11 KV (4090 HP), 300 RPM
brushless SYNCHRONOUS ELECTRIC MOTOR.
LIQUID AMMONIA FEED PUMP
These pumps are vertical machines having FIVE
SINGLE ACTING RAMS running at a fixed speed of
220 RPM and delivering 34.6 m3/Hr of LIQUID NH3.
There are two pumps per stream together with a
common spare.
Each pump is driven by 3.3 KV (350KW), 50 Hz, 750
RPM electric motor with a gear box to achieve the
necessary speed reduction between motor and pump.
The suction pressure of pump is at 21 kg/cm2 by
ammonia booster pump and delivery pressure is 230
kg/cm2.
RECYCLE FEED PUMP OR EBARA
This is high speed centrifugal pump and running with
7451 RPM.
EBARA PUMP has 8 stages.
The suction pressure of EBARA PUMP is 24 kg/cm2
and delivery pressure is 230 kg/cm2.
Ebara handles recycle carbamate solution to the
reactor.
REACTOR
In this plant PLUG FLOW TYPE REACTOR are used for
reaction.
Compressed CO2 gas, Compressed liquid NH3 and
compressed recycle solution are fed separately to the base
of the REACTOR, Ammonium carbamate is formed first &
this then break down to give UREA & water.
The operating pressure of reactor is 210 kg/cm2 and
temperature is 195 0C
The RESIDENCE TIME is 21 minutes and Height of
REACTOR is 27 meter.
The reaction to form urea takes place in two stages. NH3 &
CO2 first react to form ammonium carbamate & reaction is
fast , highly exothermic. After that ammonium carbamate
undergoes a slower endothermic breakdown to form urea
and water.
2NH3 + CO2 ---- NH4COONH2 ----- NH2CONH2 + H2O
DECOMPOSITION SECTION
Equipment in this section are given below-
HIGH PRESSURE DECOMPOSER with REBOILER
LOW PRESSURE DECOMPOSER with REBOILER
GAS SEPARATOR & OXIDIZER(upper & bottom)
In this section, the product mixture from the reactor is
processed to remove NH3 and CO2 and leave an
aqueous UREA solution. This is achieved by
application of heat and stepwise reduction in pressure
as solution passes through HPD , LPD ,GAS
SEPARATOR & OXIDIZER.
RECOVERY SECTION
Equipment in this section are given below-
High Pressure Absorber Cooler (HPAC)
Low Pressure Absorber (LPA)
Gas Condenser (GC)
Off Gas Condenser (OGC)
Off Gas Absorber (OGA)
Off Gas Absorber Cooler
High Pressure Absorber (HPA)
Mist Separator
NH3 Reservoir
FINISHING SECTION
Equipment in this section are given below-
FILTER
VACUUM EVAPORATER
CRYSTALLIZER
DRYER (Pneumatic type)
CYCLONE
MELTER
GRANULATORS/DISTRIBUTORS
FLUIDISING COOLER
TROMMEL & BELT CONVEYER
Urea solution from oxidizer passes through filter into vacuum
evaporator, where water flashes off. The solution than flows
down into crystallizer, part of the heat required to evaporator
water is obtained from HPAC by means of a slurry circulation
from crystallizer through HPAC to vacuum evaporator.
Urea crystal are separated from mother liquor by means of
centrifuge than dried & moisture content of crystals is reduced
up to 0.5%. & conveyed to the top of Prilling tower to a hot air
stream. Most of mother liquor returned to crystallizer, a small
part is sent to LPA, as a purge to reduce BI-URET content of
product. The BI-URET reaction is represented as-
2 NH2CONH2 ---------------- NH2CONHCONH2 + NH3
The biuret in the final product is around 0.5%. At the top of
prilling tower, urea crystals are separated from air stream in
cyclones & then melted at 140 0C. Molten urea flows to the prills
head/ distributor, from which it forms into spherical drops
which solidify and cool as they fall down the tower further
cooling is done in a fluidizing cooler sited in the tower base &
prills then overflow into a trammel where the oversize material
after dissolving is sent back to the process, while the product
goes forward to packing plant.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Cumene Manufacturing ProcedureDokumen74 halamanCumene Manufacturing ProcedureTan JieSheng78% (9)
- The Next 20 Billion Digital MarketDokumen4 halamanThe Next 20 Billion Digital MarketakuabataBelum ada peringkat
- Cumene ManufactringDokumen74 halamanCumene ManufactringTan JieSheng100% (1)
- Data Visualization Q&A With Dona Wong, Author of The Wall Street Journal Guide To Information Graphics - Content Science ReviewDokumen14 halamanData Visualization Q&A With Dona Wong, Author of The Wall Street Journal Guide To Information Graphics - Content Science ReviewSara GuimarãesBelum ada peringkat
- Process Design and Economic Evaluation of Urea ProductionDokumen11 halamanProcess Design and Economic Evaluation of Urea ProductionSean Suraj JeremiahBelum ada peringkat
- KRIBHCO SHYAM FERTILISERS LTD AMMONIA PROCESS OVERVIEWDokumen51 halamanKRIBHCO SHYAM FERTILISERS LTD AMMONIA PROCESS OVERVIEWSaad Khan89% (9)
- Controlling the evaporator in urea productionDokumen15 halamanControlling the evaporator in urea productiontariq fareedBelum ada peringkat
- Co2 StripperDokumen5 halamanCo2 StripperOkta Ochan Chandra100% (1)
- Builder's Greywater Guide Branched DrainDokumen4 halamanBuilder's Greywater Guide Branched DrainGreen Action Sustainable Technology GroupBelum ada peringkat
- Mid-Term Training EvaluationDokumen26 halamanMid-Term Training EvaluationVishalSharmaBelum ada peringkat
- UREA PROCESSDokumen8 halamanUREA PROCESSIshan HaiderBelum ada peringkat
- NFL PPTDokumen46 halamanNFL PPTvipin6kumar-718654Belum ada peringkat
- Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Limited Mini Ratna CompanyDokumen20 halamanRashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Limited Mini Ratna CompanyRana KeyurBelum ada peringkat
- Process Description of Ammonia PlantDokumen12 halamanProcess Description of Ammonia PlantSridharBelum ada peringkat
- Urea Plant National Fertilizers LimitedDokumen22 halamanUrea Plant National Fertilizers LimitedSatya Narayan SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- An Industrialreport ON Urea Plant atDokumen17 halamanAn Industrialreport ON Urea Plant atDeep GajjarBelum ada peringkat
- Abhishek's TrainingDokumen26 halamanAbhishek's TrainingVishalSharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Urea-1 PlantDokumen34 halamanUrea-1 PlantAjeet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Description of Various Urea Manufacturing ProcessDokumen5 halamanDescription of Various Urea Manufacturing ProcessSameer Pandey100% (1)
- Urea Plant TrainingDokumen34 halamanUrea Plant TrainingUtkarsh Sharma100% (1)
- Process DescriptionDokumen4 halamanProcess DescriptionJoshua ArrojoBelum ada peringkat
- KRIBHCO SHYAM FERTILISERS LTD AMMONIA PLANT PROCESS OVERVIEWDokumen51 halamanKRIBHCO SHYAM FERTILISERS LTD AMMONIA PLANT PROCESS OVERVIEWSabeeh Faruqui100% (1)
- Controlling Side Reactions in Ammonium Carbamate ProductionDokumen3 halamanControlling Side Reactions in Ammonium Carbamate ProductionMichael Taylor WarrenBelum ada peringkat
- 2021 01 Baboo Snamprogetti Urea ProcessDokumen24 halaman2021 01 Baboo Snamprogetti Urea ProcessusmanalihaashmiBelum ada peringkat
- Urea Synthesis With Pool CondenserDokumen1 halamanUrea Synthesis With Pool Condensersite commissing teamBelum ada peringkat
- UREA MANUFACTURING PROCESSDokumen5 halamanUREA MANUFACTURING PROCESSIVAN SAMCRUZBelum ada peringkat
- Manufacture of UreaDokumen36 halamanManufacture of UreaNandadulal GhoshBelum ada peringkat
- International Process Plants: 1,100 Metric Tons/Day U PLT Urea PlantDokumen17 halamanInternational Process Plants: 1,100 Metric Tons/Day U PLT Urea PlantRawagBelum ada peringkat
- By - Hari - Om - Pandey - Roll - No. - 210003005 - B.Tech - (Final - Year) (Intern)Dokumen31 halamanBy - Hari - Om - Pandey - Roll - No. - 210003005 - B.Tech - (Final - Year) (Intern)hariompandey27051Belum ada peringkat
- The Urea Manufacturing ProcessDokumen5 halamanThe Urea Manufacturing ProcessJhonny Huanca ChampiriBelum ada peringkat
- 6200 Area - Urea Plant: Process OverviewDokumen8 halaman6200 Area - Urea Plant: Process OverviewtreyzzztylerBelum ada peringkat
- KRIBHCO Urea Plant OverviewDokumen25 halamanKRIBHCO Urea Plant OverviewHarsh DholakiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Urea ProjectDokumen17 halamanUrea ProjectAbdo Shaaban100% (2)
- Crude Distillation Unit & Vacuum Distillation UnitDokumen10 halamanCrude Distillation Unit & Vacuum Distillation Unitsenthilkumarbt100% (1)
- Urea Production Flow DiagramDokumen8 halamanUrea Production Flow DiagramAyatBelum ada peringkat
- Ajeet Singh Iffco PDFDokumen38 halamanAjeet Singh Iffco PDFAjeet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Stamicarbon (Holland)Dokumen3 halamanStamicarbon (Holland)Mohd Hakimie100% (2)
- Aniline Process DescriptionDokumen13 halamanAniline Process Descriptionkeyur1109100% (3)
- Chemical Reaction Engineering: INTRODUCTION TO COMPANY (Pak American Fertilizers LTD.)Dokumen24 halamanChemical Reaction Engineering: INTRODUCTION TO COMPANY (Pak American Fertilizers LTD.)Badar RasheedBelum ada peringkat
- Refinery Overview FinalDokumen65 halamanRefinery Overview FinalasifBelum ada peringkat
- Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited Kalol - unit urea plant processDokumen12 halamanIndian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited Kalol - unit urea plant processYogeshPooniaBelum ada peringkat
- Process Descp. Start-Up OperationDokumen24 halamanProcess Descp. Start-Up OperationManoj KumarBelum ada peringkat
- SNAMPROGETTI UREA PROCESS STEPSDokumen23 halamanSNAMPROGETTI UREA PROCESS STEPSTu Hai50% (2)
- W VishDokumen52 halamanW VishVikram Kumar VishBelum ada peringkat
- National Fertilizer LimitedDokumen22 halamanNational Fertilizer LimitedJayesh RaghuwanshiBelum ada peringkat
- Urea Manufacturing Process: BY Ashvani Shukla C&I RelianceDokumen18 halamanUrea Manufacturing Process: BY Ashvani Shukla C&I RelianceAdam RizkyBelum ada peringkat
- Refinery ReportDokumen21 halamanRefinery ReportUsama MajeedBelum ada peringkat
- IOCL Paradip Refinery UnitsDokumen8 halamanIOCL Paradip Refinery UnitsAkankshya MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2Dokumen45 halamanChapter 2Haiqal AzizBelum ada peringkat
- NFL NANGAL Urea Plant Process & SpecsDokumen35 halamanNFL NANGAL Urea Plant Process & SpecsAkhil AklBelum ada peringkat
- Nirbhay Urea Final PDFDokumen99 halamanNirbhay Urea Final PDFHimanshu vikram100% (1)
- Control of Evaporator in The Production of UreaDokumen15 halamanControl of Evaporator in The Production of Ureatariq fareedBelum ada peringkat
- MOnth1 ReportDokumen12 halamanMOnth1 ReportXheikhKaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Treatment of Ethane-Propane in A Petrochemical Complex: Apoorva Vinayak RudraDokumen5 halamanTreatment of Ethane-Propane in A Petrochemical Complex: Apoorva Vinayak RudraEditorijer IjerBelum ada peringkat
- Steam Generation System OverviewDokumen35 halamanSteam Generation System OverviewNevermoreBelum ada peringkat
- Failure of LP Flash Drum Packing Bed Support: Geoff BlewettDokumen10 halamanFailure of LP Flash Drum Packing Bed Support: Geoff BlewettDheeraj DheeruBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation On: Sulphur BlockDokumen58 halamanPresentation On: Sulphur Blockvinkan_chemBelum ada peringkat
- Urea 2Dokumen16 halamanUrea 2ginga716Belum ada peringkat
- Nitric Acid Design Project: Shivam PandyaDokumen15 halamanNitric Acid Design Project: Shivam PandyaShivam PandyaBelum ada peringkat
- Sustainable Energy Conversion for Electricity and Coproducts: Principles, Technologies, and EquipmentDari EverandSustainable Energy Conversion for Electricity and Coproducts: Principles, Technologies, and EquipmentBelum ada peringkat
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersDari EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersBelum ada peringkat
- 10 1016@j Ijbiomac 2019 01 202Dokumen12 halaman10 1016@j Ijbiomac 2019 01 202alok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S2452223620300250 MainDokumen7 halaman1 s2.0 S2452223620300250 Mainalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- AM CNF Films MS Carb Polym Revision2 UnmarkedDokumen44 halamanAM CNF Films MS Carb Polym Revision2 Unmarkedalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- Hemicelluloses Extraction From Giant BamDokumen8 halamanHemicelluloses Extraction From Giant Bamalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S0926669020304386 MainDokumen9 halaman1 s2.0 S0926669020304386 Mainalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- Beroual2021 Article PhysicochemicalPropertiesAndThDokumen13 halamanBeroual2021 Article PhysicochemicalPropertiesAndThalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S0167732215303561 MainDokumen6 halaman1 s2.0 S0167732215303561 Mainalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S0959652621012026 MainDokumen11 halaman1 s2.0 S0959652621012026 Mainalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- Liu2019 Article CholineChloride-lacticAcidDeepDokumen16 halamanLiu2019 Article CholineChloride-lacticAcidDeepalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S0014305715000968 MainDokumen11 halaman1 s2.0 S0014305715000968 Mainalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- PROCESS FLOW DIAGRAMDokumen1 halamanPROCESS FLOW DIAGRAMalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- Presented By:: Simerpreet Kaur Prachi Pandey Kumari Priya Shubham GuptaDokumen12 halamanPresented By:: Simerpreet Kaur Prachi Pandey Kumari Priya Shubham Guptaalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- Documentary ON Fashion CapitalDokumen15 halamanDocumentary ON Fashion Capitalalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- Urea Reactor Designing: Chemical EngineeringDokumen15 halamanUrea Reactor Designing: Chemical Engineeringalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- Drilling Fluid Functions and PropertiesDokumen33 halamanDrilling Fluid Functions and Propertiesalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- Iffco PresentationDokumen16 halamanIffco Presentationalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- Shivam Report 2Dokumen30 halamanShivam Report 2alok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- Diesel Hydrodesulphurization (DHDS) / Hydrotreating (DHDT) TechnologyDokumen10 halamanDiesel Hydrodesulphurization (DHDS) / Hydrotreating (DHDT) Technologyalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- Bio ColorantDokumen7 halamanBio Colorantalok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- AIR Pollution: Jelly C. Daroy Bea May P. DuranteDokumen12 halamanAIR Pollution: Jelly C. Daroy Bea May P. Durantealok sahuBelum ada peringkat
- Paint Color Comparison ChartDokumen132 halamanPaint Color Comparison ChartCarlos Rubiños AlonsoBelum ada peringkat
- Oracle SCM TrainingDokumen9 halamanOracle SCM TrainingVishnu SajaiBelum ada peringkat
- Player Alex's SEO-Optimized Character Sheet for Antero VipunenDokumen2 halamanPlayer Alex's SEO-Optimized Character Sheet for Antero VipunenAlex AntiaBelum ada peringkat
- Ref Paper 2Dokumen4 halamanRef Paper 2Subhanjali MyneniBelum ada peringkat
- NETWORK ANALYSIS Chap.8 TWO PORT NETWORK & NETWORK FUNCTIONS PDFDokumen34 halamanNETWORK ANALYSIS Chap.8 TWO PORT NETWORK & NETWORK FUNCTIONS PDFsudarshan poojaryBelum ada peringkat
- Duotone GuideDokumen1 halamanDuotone Guideapi-648378651Belum ada peringkat
- V 2172 0020 0031 - Rev - 6 (3458748) PDFDokumen262 halamanV 2172 0020 0031 - Rev - 6 (3458748) PDFLG Milton LuisBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Engineer Resume - Digambar BhangeDokumen3 halamanMechanical Engineer Resume - Digambar BhangeTOP DHAMAKABelum ada peringkat
- Ficha Tecnica 750 GPMDokumen156 halamanFicha Tecnica 750 GPMByron Chele0% (2)
- MyPower S3220&S3320-INSTALLATIONDokumen83 halamanMyPower S3220&S3320-INSTALLATIONJorge GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- X-Span & Setting ToolsDokumen18 halamanX-Span & Setting ToolsDenier RubianoBelum ada peringkat
- # 6030 PEN OIL: Grade: Industrial Grade Heavy Duty Penetrating OilDokumen3 halaman# 6030 PEN OIL: Grade: Industrial Grade Heavy Duty Penetrating OilPrakash KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Method Statement For Cable & TerminationDokumen6 halamanMethod Statement For Cable & TerminationRajuBelum ada peringkat
- FlowCon General InstructionDokumen4 halamanFlowCon General InstructionGabriel Arriagada UsachBelum ada peringkat
- Model Railroad Plans and DrawingsDokumen7 halamanModel Railroad Plans and DrawingsBán ZoltánBelum ada peringkat
- PLCDokumen16 halamanPLCMohit Kinger100% (1)
- G12gasa Group5 PR2Dokumen7 halamanG12gasa Group5 PR2Lizley CordovaBelum ada peringkat
- Associating Numbers With Sets Having 51 Up To 100 Objects or ThingsDokumen4 halamanAssociating Numbers With Sets Having 51 Up To 100 Objects or ThingssweetienasexypaBelum ada peringkat
- Vantio CacheServe 7.2.0 Administrators Manual 20161208 PDFDokumen577 halamanVantio CacheServe 7.2.0 Administrators Manual 20161208 PDFPaulette Servin100% (1)
- BS 5896 2010Dokumen33 halamanBS 5896 2010shashiresh50% (2)
- Roof Slab of Guard RoomDokumen3 halamanRoof Slab of Guard RoomAditya KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Transient and Random VibrationDokumen19 halamanTransient and Random VibrationAman SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- AMG ActuatorsDokumen12 halamanAMG ActuatorsMohan ArumugavallalBelum ada peringkat
- Fortumo Mobile Payments API GuideDokumen8 halamanFortumo Mobile Payments API GuideVladimir UtješinovićBelum ada peringkat
- 38.11 Cum Total Qty of 4 Nos. Culvests 38.11x4 152.43 CumDokumen14 halaman38.11 Cum Total Qty of 4 Nos. Culvests 38.11x4 152.43 CumMandeep SinghBelum ada peringkat
- SEO ProposalDokumen5 halamanSEO ProposalShivdev SaiBelum ada peringkat
- India's Growing Social Media Landscape and Future TrendsDokumen5 halamanIndia's Growing Social Media Landscape and Future Trendspriyaa2688Belum ada peringkat