RAM, Storage Devices and Peripherals
Diunggah oleh
Nomer Flores0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
21 tayangan24 halamanRAM, Storage Devices and Peripherals info
Judul Asli
3. RAM, Storage Devices and Peripherals
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniRAM, Storage Devices and Peripherals info
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
21 tayangan24 halamanRAM, Storage Devices and Peripherals
Diunggah oleh
Nomer FloresRAM, Storage Devices and Peripherals info
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 24
THE PC PARTS AND ITS FUNCTIONS
COMPUTER SYSTEM SERVICING NC II
NOMER T. FLORES
THE RAM
THE MEMORY OR RAM
• Alternatively referred to as main memory, primary memory, or
system memory, RAM (random access memory) is a hardware
device that allows information to be stored and retrieved on a
computer.
• RAM is usually associated with DRAM (Dynamic RAM), which
is a type of memory module.
• RAM is a volatile memory and requires power to keep the
data accessible. If the computer is turned off, all data
contained in RAM is lost.
• Because of its volatility, Random Access Memory can't store
permanent data.
WHY DO COMPUTERS NEED RAM?
• The purpose of RAM is to provide quick read and write access
to a storage device.
• Your computer uses RAM to load data because it's much
quicker than running that same data directly off of a hard
drive.
• A computer also works this way. If RAM fills up, the
computer's processor must repeatedly go to the hard disk to
overlay the old data in RAM with new data. This process slows
the computer's operation.
RAM COMPATIBILITY GUIDELINES
• Older-generation computers are unlikely to accommodate the
more recent types of RAM technology
• Laptop memory won’t fit in desktops (and vice versa)
• RAM is not always backward compatible
• A system generally can't mix and match different
types/generations of RAM together
TYPES OF RAM
STATIC RAM (SRAM)
• Time in Market: 1990s to present
• Popular Products Using SRAM: Digital cameras, routers, printers,
LCD screens
• The advantages of using SRAM (vs. DRAM) are lower power
consumption and faster access speeds. The disadvantages of using
SRAM (vs. DRAM) are lesser memory capacities and higher costs of
manufacturing. Because of these characteristics, SRAM is typically
used in:
• CPU cache (e.g. L1, L2, L3)
• Hard drive buffer/cache
• Digital-to-analog converters (DACs) on video cards
DYNAMIC RAM (DRAM)
• Time in Market: 1970s to mid-1990s
• Popular Products Using DRAM: Video game consoles,
networking hardware
• The advantages of using DRAM (vs. SRAM) are lower costs of
manufacturing and greater memory capacities. The disadvantages of
using DRAM (vs. SRAM) are slower access speeds and higher power
consumption. Because of these characteristics, DRAM is typically used
in:
• System memory
• Video graphics memory
SYNCHRONOUS DYNAMIC RAM (SDRAM)
• Time in Market: 1993 to present
• Popular Products Using SDRAM: Computer memory, video
game consoles
• SDRAM is a classification of DRAM that operates in sync with the CPU clock, which
means that it waits for the clock signal before responding to data input (e.g. user
interface). By contrast, DRAM is asynchronous, which means it responds
immediately to data input.
DOUBLE DATA RATE SYNCHRONOUS DYNAMIC
RAM (DDR SDRAM)
• Time in Market: 2000 to present
• Popular Products Using DDR SDRAM: Computer memory
• DDR SDRAM operates like SDRAM, only twice as fast. DDR SDRAM is capable
of processing two read and two write instructions per clock cycle (hence the
‘double’).
• DDR2 SDRAM is the evolutionary upgrade to DDR SDRAM. While still double data rate
(processing two read and two write instructions per clock cycle), DDR2 SDRAM is faster because
it can run at higher clock speeds.
• DDR3 SDRAM improves performance over DDR2 SDRAM through advanced signal processing
(reliability), greater memory capacity, lower power consumption (1.5 V), and higher standard
clock speeds (up to 800 Mhz).
• DDR4 SDRAM improves performance over DDR3 SDRAM through more advanced signal
processing (reliability), even greater memory capacity, even lower power consumption (1.2 V),
and higher standard clock speeds (up to 1600 Mhz).
GRAPHICS DOUBLE DATA RATE SYNCHRONOUS
DYNAMIC RAM (GDDR SDRAM)
• Time in Market: 2003 to present
• Popular Products Using GDDR SDRAM: Video graphics cards,
some tablets
• GDDR SDRAM is a type of DDR SDRAM that is specifically designed for video graphics
rendering, typically in conjunction with a dedicated GPU (graphics processing unit) on
a video card.
• Similar to DDR SDRAM, GDDR SDRAM has its own evolutionary line (improving performance and lowering
power consumption): GDDR2 SDRAM, GDDR3 SDRAM, GDDR4 SDRAM, and GDDR5 SDRAM.
FLASH MEMORY
• Time in Market: 1984 to present
• Popular Products Using Flash Memory: Digital cameras,
smartphones/tablets, handheld gaming systems/toys
• Flash memory is a type of non-volatile storage medium that retains all data
after power has been cut off. Despite the name, flash memory is closer in form
and operation (i.e. storage and data transfer) to solid state drives than the
aforementioned types of RAM. Flash memory is most commonly used in:
• USB flash drives
• Printers
• Portable media players
• Memory cards
• Small electronics/toys
• PDAs
SYMPTOMS OF A RAM PROBLEM AND HOW TO FIX IT
SYMPTOMS OF A RAM PROBLEM
• When you first turn on your computer it runs
fine, but as you go about your business you
notice that its performance diminishes. This type
of gradual deterioration of PC performance,
especially with memory-intensive programs, may
be caused by a RAM problem.
• Your computer randomly restarts while you are
in the middle of something or freeze sporadically.
It may also reboot almost immediately upon
opening the desktop. This could be a sign of
faulty RAM.
SYMPTOMS OF A RAM PROBLEM
• A blue screen with white text flashes before restarting. Blue-
screen errors are annoying because you don't even have a chance
to read the error message. Bad RAM is one thing that cause
them.
• Files—particularly ones you frequently access and save—seem to
be inexplicably corrupted. RAM issues can lead to this problem,
which can worsen over time. The file structure of your hard drive
may slowly degenerate and you will no longer be able to boot
your machine.
• Your attempts to install a new program repeatedly fail for
unknown reasons. You try to reinstall the operating system, but
keep getting odd error messages.
WHAT CAUSES MEMORY DAMAGE?
• Power surges can damage most computer components,
including RAM.
• Before you handle any parts in your computer, make sure
you ground yourself by touching a piece of grounded metal
to discharge static electricity. Electrostatic discharge can
damage your computer.
WHAT CAUSES MEMORY DAMAGE?
• Excessive heat can cause RAM and other parts to wear out
over time. Individual components can overheat, or heat
from one component can cause damage to adjacent parts.
• If you have overclocked any part of your computer
incorrectly, it may cause damage in the form of excess
heat.
• Your memory module may have some fault that passed
through quality control and worsened over time. This is
the most likely cause behind a damaged RAM.
WHAT CAUSES MEMORY DAMAGE?
• Excessive heat can cause RAM and other parts to wear out
over time. Individual components can overheat, or heat
from one component can cause damage to adjacent parts.
• If you have overclocked any part of your computer
incorrectly, it may cause damage in the form of excess
heat.
• Your memory module may have some fault that passed
through quality control and worsened over time. This is
the most likely cause behind a damaged RAM.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- TLE11-ICT-Computer Systems Servicing-Q1 - Q2-W2-LeaPDokumen4 halamanTLE11-ICT-Computer Systems Servicing-Q1 - Q2-W2-LeaPNomer FloresBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- © UNT in Partnership With TEA 1Dokumen29 halaman© UNT in Partnership With TEA 1Nomer FloresBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Computer BasicsDokumen47 halamanComputer BasicsNomer FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- TLE11-ICT-Computer Systems Servicing-Q1 - Q2-W3-LeaPDokumen3 halamanTLE11-ICT-Computer Systems Servicing-Q1 - Q2-W3-LeaPNomer FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Types of Video CardDokumen22 halamanTypes of Video CardNomer FloresBelum ada peringkat
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Types of Video CardDokumen22 halamanTypes of Video CardNomer FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Exploring Groups Within SocietyDokumen7 halamanExploring Groups Within SocietyNomer Flores100% (3)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Intro To NetworkingDokumen29 halamanIntro To NetworkingQueniel QuezmarBelum ada peringkat
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Becoming A Member of Society PDFDokumen17 halamanBecoming A Member of Society PDFNomer FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- OHS For CSSDokumen18 halamanOHS For CSSNomer Flores100% (5)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Sukarno: Indonesia'S Founding FatherDokumen5 halamanSukarno: Indonesia'S Founding FatherNomer FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Human Cultural Variation (Understanding Culture, Society and Politics)Dokumen36 halamanHuman Cultural Variation (Understanding Culture, Society and Politics)Nomer FloresBelum ada peringkat
- 25 Negative Effects of TechnologyDokumen9 halaman25 Negative Effects of TechnologyNomer FloresBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Computer BasicsDokumen47 halamanComputer BasicsNomer FloresBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Workshop Layout PlanDokumen1 halamanWorkshop Layout PlanNomer FloresBelum ada peringkat
- The Economic Problem: Scarcity and Choice: Prepared By: Fernando Quijano and Yvonn QuijanoDokumen40 halamanThe Economic Problem: Scarcity and Choice: Prepared By: Fernando Quijano and Yvonn QuijanoTika GusmawarniBelum ada peringkat
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
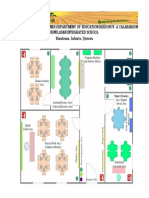
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Iv-A Calabarzon Binulasan Integrated School Binulasan, Infanta, QuezonDokumen2 halamanRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Iv-A Calabarzon Binulasan Integrated School Binulasan, Infanta, QuezonNomer FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Blade Service ManualDokumen185 halamanBlade Service ManualDiego Alejandro Gomez80% (5)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Terberg Network Structure-3661600586101635Dokumen14 halamanTerberg Network Structure-3661600586101635yousufBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Engineering Sciences 151. Electromagnetic Communication LaboratoryDokumen5 halamanEngineering Sciences 151. Electromagnetic Communication LaboratorybaymanBelum ada peringkat
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Smart Control For Home Water Heater Saving PDFDokumen111 halamanSmart Control For Home Water Heater Saving PDFPrashant JagadaleBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance NotesDokumen3 halamanMaintenance NotesHaafizee FizBelum ada peringkat
- Real-Time Environment Monitoring System Using ESP8266 and ThingSpeak On Internet of Things PlatformDokumen5 halamanReal-Time Environment Monitoring System Using ESP8266 and ThingSpeak On Internet of Things PlatformMichelle LlamatumbiBelum ada peringkat
- A Ele Spe 800 30021 0Dokumen29 halamanA Ele Spe 800 30021 0ZaidiBelum ada peringkat
- Brosur PDFDokumen3 halamanBrosur PDFEndangRatriSBelum ada peringkat
- SickDokumen4 halamanSickpredic1Belum ada peringkat
- Series: Output Power S1500 S2000 S3000 S4000 S6000 S3004 S4004 S4044 S6004 S6044 Weight DepthDokumen2 halamanSeries: Output Power S1500 S2000 S3000 S4000 S6000 S3004 S4004 S4044 S6004 S6044 Weight DepthАлексей АндрияшBelum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (120)
- Bridgewater HallDokumen4 halamanBridgewater HallHuzaifa J AhmedabadwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Plexi SE PCB VJ Conversion Parts List v2Dokumen1 halamanPlexi SE PCB VJ Conversion Parts List v2Yann RossiBelum ada peringkat
- Amted310010en WebDokumen120 halamanAmted310010en WebMemo TipBelum ada peringkat
- Maytag Neptune Motor TestDokumen1 halamanMaytag Neptune Motor TestSamurai Appliance Repair ManBelum ada peringkat
- Iia Module Iii PDFDokumen13 halamanIia Module Iii PDFgayathri vishnuBelum ada peringkat
- TO Miniasic MPW EUROPRACTICE v1 191121 PRELIMINARYDokumen3 halamanTO Miniasic MPW EUROPRACTICE v1 191121 PRELIMINARYdalbarBelum ada peringkat
- Homework 1 Solution PDFDokumen5 halamanHomework 1 Solution PDFRemon Hanna Wadie YoussefBelum ada peringkat
- Micno Ke300a 01 Solar Pump Inverter CatalogDokumen8 halamanMicno Ke300a 01 Solar Pump Inverter CatalogIbrahima DialloBelum ada peringkat
- Isa Cba 1000Dokumen137 halamanIsa Cba 1000MilosBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Field Sensor MB60-8GM50-E2: DimensionsDokumen3 halamanMagnetic Field Sensor MB60-8GM50-E2: DimensionsEric MontesBelum ada peringkat
- NexSys Charger Operations ManualDokumen47 halamanNexSys Charger Operations ManualDavid Vargas VBelum ada peringkat
- IEEE STD 404-2012Dokumen46 halamanIEEE STD 404-2012anonimoefra100% (1)
- Has 111dg Data Sheet 4921240144 UkDokumen8 halamanHas 111dg Data Sheet 4921240144 UkGullu BhargavaBelum ada peringkat
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Ds Lifebook A556 A556gDokumen6 halamanDs Lifebook A556 A556gbhaavan22Belum ada peringkat
- Project Report of Laser Security Alarm System 2.3Dokumen25 halamanProject Report of Laser Security Alarm System 2.3B LIKHITH KUMAR100% (1)
- Minecraft Franchise Fact Sheet - Updated - 1 19 18 1Dokumen3 halamanMinecraft Franchise Fact Sheet - Updated - 1 19 18 1Johnny ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Uppcl Je Ee 27 Nov 2019 Evening Shift: Useful LinksDokumen53 halamanUppcl Je Ee 27 Nov 2019 Evening Shift: Useful LinkspriyansBelum ada peringkat
- Sepeaker Aktif POLYTRON PAS 67 - 68Dokumen3 halamanSepeaker Aktif POLYTRON PAS 67 - 68Waton Rinekso0% (1)
- Mastering Stm32 SampleDokumen119 halamanMastering Stm32 SampleRached Mairchi100% (1)
- MURS320T3G, SURS8320T3G, MURS340T3G, SURS8340T3G, MURS360T3G, SURS8360T3G Surface Mount Ultrafast Power RectifiersDokumen6 halamanMURS320T3G, SURS8320T3G, MURS340T3G, SURS8340T3G, MURS360T3G, SURS8360T3G Surface Mount Ultrafast Power RectifiersBaskoro SutrisnoBelum ada peringkat