Eukaryotic Cells
Diunggah oleh
Maane Bruno0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
12 tayangan10 halamanppt
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inippt
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
12 tayangan10 halamanEukaryotic Cells
Diunggah oleh
Maane Brunoppt
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 10
1 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2009
What is a eukaryote?
A eukaryote is any organism
consisting of one or more cells that
contain DNA in a membrane-bound
nucleus, separate from the cytoplasm.
Eukaryotes include:
animals
plants
fungi
a diverse group known as the
protists (or protoctists).
All eukaryotic cells contain a large number of specialized,
membrane-bound organelles.
2 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2009
The organelles of protein synthesis
3 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2009
Mitochondria
The mitochondrion is an energy-generating organelle.
It is surrounded by two membranes. The inner layer folds
inwards to form the cristae. The cristae project into a liquid
called the matrix.
outer membrane cristae
matrix
inner membrane
The inner membrane is coated in enzymes, which catalyze
the reactions of aerobic respiration to produce ATP.
4 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2009
Microtubules and the cytoskeleton
5 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2009
Which organelle?
6 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2009
Plant cells
Plant cells share all the common features of animal cells,
but also contain some additional organelles.
Plants gain all their energy from sunlight; cells in their leaves
contain many chloroplasts to convert this into a useful form.
chloroplast
vacuole
Every plant cell is
surrounded by a cell
wall, and contains
one or more
cell wall
permanent vacuoles.
7 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2009
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts use carbon dioxide, water and light energy to
build sugars. They are present in all green plants.
The chloroplast is surrounded by a double membrane. It is
filled with a liquid called the stroma, and contains stacks
of thylakoid membranes called grana.
grana
stroma
thylakoid membrane
The thylakoid membranes are the site of photosynthesis.
8 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2009
The cell wall
The cell wall of a plant cell gives it support and structure.
It is made of the polysaccharide cellulose, and can function
as a carbohydrate store by varying the amount of cellulose
it holds.
The cell wall does not seal off a
cell completely from its
neighbors. There are pores
within the walls called
plasmodesmata. These
connect two cells together by
their cytoplasm, enabling
substances to be exchanged
and transported between them.
9 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2009
Eukaryotic organelles
10 of 10 © Boardworks Ltd 2009
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Diseases and Immunity: Defence Against MicrobesDokumen55 halamanDiseases and Immunity: Defence Against MicrobesIvan Prasetya100% (1)
- Gas ExchangeDokumen30 halamanGas ExchangeNeelam HanifBelum ada peringkat
- Circulatory System PDFDokumen40 halamanCirculatory System PDFRabia Imran100% (2)
- Decay and RecyclingDokumen46 halamanDecay and Recyclinganon_744165750Belum ada peringkat
- EquilibriumDokumen33 halamanEquilibriumGideon CavidaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell MembranesDokumen34 halamanCell MembranesayfilonBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Exchange Cystic Fibrosis & Genetic ScreeningDokumen49 halamanGas Exchange Cystic Fibrosis & Genetic Screeningmlk100% (1)
- The Halogens v1.0Dokumen37 halamanThe Halogens v1.0Supadi Rahdi100% (1)
- Making Polymers v2.0Dokumen43 halamanMaking Polymers v2.0Ricki HanBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics Part 4 - EntropyDokumen26 halamanThermodynamics Part 4 - EntropyOrangesPlzBelum ada peringkat
- Smackslidecom Exchanging Mate 5fca76fcdc9b2Dokumen23 halamanSmackslidecom Exchanging Mate 5fca76fcdc9b2Aref DahabrahBelum ada peringkat
- Halogen Oal KanesDokumen31 halamanHalogen Oal KanesEhab MuhammedBelum ada peringkat
- The Atomic ModelDokumen22 halamanThe Atomic ModelIntan CahyaningrumBelum ada peringkat
- The KidneysDokumen27 halamanThe KidneysleanneBelum ada peringkat
- Classifying Organisms: 1 of 33 © Boardworks LTD 2011Dokumen25 halamanClassifying Organisms: 1 of 33 © Boardworks LTD 2011huzaifa mobusherBelum ada peringkat
- GCSE Active TransportDokumen10 halamanGCSE Active TransportNoel Johansen-BergBelum ada peringkat
- Guide For Lead TeachersDokumen14 halamanGuide For Lead Teachersjoseph oukoBelum ada peringkat
- 1 of 41 © Boardworks LTD 2008Dokumen41 halaman1 of 41 © Boardworks LTD 2008Hanifa Uly AmrinaBelum ada peringkat
- Application of Redox ChemistryDokumen30 halamanApplication of Redox ChemistryMurugan.Subramani100% (1)
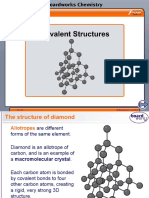
- Covalent StructuresDokumen11 halamanCovalent StructuresjtBelum ada peringkat
- Materials Part 2 - PressureDokumen26 halamanMaterials Part 2 - Pressurepeter liBelum ada peringkat
- Coastal ProcessesDokumen15 halamanCoastal Processesapi-258813608Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson 1-Introduction To Redox Reactions: Redox Chemistry and ElectrochemistryDokumen100 halamanLesson 1-Introduction To Redox Reactions: Redox Chemistry and ElectrochemistryZheng JoeyBelum ada peringkat
- DynamicsDokumen28 halamanDynamicsChaiseBelum ada peringkat
- Feeding Relationships: 1 of 38 © Boardworks LTD 2008Dokumen124 halamanFeeding Relationships: 1 of 38 © Boardworks LTD 2008jspfoiguw89Belum ada peringkat
- Digestive SystemDokumen56 halamanDigestive SystemNimas PutriBelum ada peringkat
- AstrophysicsDokumen39 halamanAstrophysicsKev Watts100% (1)
- 1 of 43 © Boardworks LTD 2009Dokumen42 halaman1 of 43 © Boardworks LTD 2009Justin HadinataBelum ada peringkat
- Nerves and ReflexesDokumen14 halamanNerves and ReflexesjtBelum ada peringkat
- Inorganic Chem 2Dokumen68 halamanInorganic Chem 2yvg95100% (1)
- Electrical Signals v2.0Dokumen42 halamanElectrical Signals v2.0jt100% (1)
- Trends in Period 3Dokumen34 halamanTrends in Period 3Fildzah AdanyBelum ada peringkat
- Reaction Kinetics 2Dokumen8 halamanReaction Kinetics 2yvg95Belum ada peringkat
- Classification - 2015Dokumen22 halamanClassification - 2015randyhmthsBelum ada peringkat
- Thermoregulation: Biology Bilingual Education 2013Dokumen32 halamanThermoregulation: Biology Bilingual Education 2013rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- Equilibrium BWDokumen54 halamanEquilibrium BWMichael EllisBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 10 SCIENCE: © Boardworks LTD 2004Dokumen20 halamanGrade 10 SCIENCE: © Boardworks LTD 2004Modesto Valdriz100% (1)
- Kinetics 1Dokumen35 halamanKinetics 1Alex BoumanBelum ada peringkat
- Reversible ReactionsDokumen39 halamanReversible ReactionsUsmaanBelum ada peringkat
- Are Very Large Molecules Made When Hundreds of Join Together To Form Long ChainsDokumen23 halamanAre Very Large Molecules Made When Hundreds of Join Together To Form Long ChainsAlaa Al HamedBelum ada peringkat
- Boardworks A2 Biology ContentsDokumen16 halamanBoardworks A2 Biology ContentsStudent 365Belum ada peringkat
- Analytical ChemistryDokumen30 halamanAnalytical ChemistrySakib AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- KS4 Biology: Defence Against DiseaseDokumen44 halamanKS4 Biology: Defence Against DiseaseKelvin Requena100% (1)
- Thermodynamics Part 1 - Enthalpy ChangesDokumen6 halamanThermodynamics Part 1 - Enthalpy ChangesYacineBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Holiday Homework on Pollution Types, Causes, Effects and ControlDokumen13 halamanChemistry Holiday Homework on Pollution Types, Causes, Effects and ControlKhushmeetBelum ada peringkat
- DAV PUBLIC SCHOOL'S GUIDE TO COORDINATION COMPOUNDSDokumen36 halamanDAV PUBLIC SCHOOL'S GUIDE TO COORDINATION COMPOUNDSAnindya BhattacharyaBelum ada peringkat
- Space (Part 1)Dokumen33 halamanSpace (Part 1)Murugan.SubramaniBelum ada peringkat
- Finishing ProcessesDokumen16 halamanFinishing ProcessesAjay P AntonyBelum ada peringkat
- Polymers IDokumen28 halamanPolymers IMichael Angelo FilomenoBelum ada peringkat
- © Boardworks LTD 2006 1 of 37Dokumen37 halaman© Boardworks LTD 2006 1 of 37Kate ParanaBelum ada peringkat
- Mce Igcse Chemistry PPT c05Dokumen30 halamanMce Igcse Chemistry PPT c05Aysha Minhas100% (1)
- 2.7 The Periodic Table - Groups 2 and 7Dokumen84 halaman2.7 The Periodic Table - Groups 2 and 7Listiyaning TiasBelum ada peringkat
- 1 of 33 © Boardworks LTD 2009Dokumen33 halaman1 of 33 © Boardworks LTD 2009gabbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbBelum ada peringkat
- KS4 Reversible ReactionsDokumen25 halamanKS4 Reversible ReactionsAisha KhanBelum ada peringkat
- NutrientsDokumen50 halamanNutrientsThomas YeBelum ada peringkat
- The Halogens ANORGANIKDokumen13 halamanThe Halogens ANORGANIKghinaputriauliaBelum ada peringkat
- Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions: © Boardworks LTD 2005Dokumen19 halamanEndothermic & Exothermic Reactions: © Boardworks LTD 2005Shelby Mikayla KosimaBelum ada peringkat
- Biological Molecules Proteins Lipids Part 2 - LipidsDokumen7 halamanBiological Molecules Proteins Lipids Part 2 - Lipidsjt100% (1)
- Cell StructureDokumen37 halamanCell StructureayfilonBelum ada peringkat
- Cell StructureDokumen37 halamanCell Structurechantellelim100% (1)
- TRUKE C20-33(35)L CLARK ENGINE PARTS LISTDokumen2 halamanTRUKE C20-33(35)L CLARK ENGINE PARTS LISTРоман ПетровBelum ada peringkat
- General Biology 2: Quarter 3, Module 1 Genetic EngineeringDokumen20 halamanGeneral Biology 2: Quarter 3, Module 1 Genetic EngineeringRonalyn AndaganBelum ada peringkat
- Đánh giá chế độ ăn kiêng: Nhịn ăn gián đoạn để giảm cân- wed HarvardDokumen14 halamanĐánh giá chế độ ăn kiêng: Nhịn ăn gián đoạn để giảm cân- wed HarvardNam NguyenHoangBelum ada peringkat
- Lock Out Tag Out ProceduresDokumen9 halamanLock Out Tag Out ProceduresyawarhassanBelum ada peringkat
- EC6702-Optical Communication and NetworksDokumen18 halamanEC6702-Optical Communication and Networkskasim_1983Belum ada peringkat
- General Science EnvironmentDokumen28 halamanGeneral Science EnvironmentHamza MujahidBelum ada peringkat
- WIP CaseStudyDokumen3 halamanWIP CaseStudypaul porrasBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Exchanger Design and Drawing FundamentalsDokumen11 halamanHeat Exchanger Design and Drawing Fundamentalsjeevanantham 5846Belum ada peringkat
- Wire Rope: - Bright - 6 X 19 - Fibre CoreDokumen8 halamanWire Rope: - Bright - 6 X 19 - Fibre CoreQuynh NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Orpheus' Tragic Love and Quest to Save EurydiceDokumen3 halamanOrpheus' Tragic Love and Quest to Save EurydiceShiedrose Allaina ArangorinBelum ada peringkat
- Ammonia Tech Manual 2002Dokumen28 halamanAmmonia Tech Manual 2002Talha Bin Zubair0% (1)
- Real Possibility of Future ConditionDokumen3 halamanReal Possibility of Future ConditionHusBelum ada peringkat
- Vectors FoundationDokumen8 halamanVectors FoundationNaning RarasBelum ada peringkat
- On The Problem of The External World in The Ch'Eng Wei Shih LunDokumen64 halamanOn The Problem of The External World in The Ch'Eng Wei Shih LunGuhyaprajñāmitra3100% (1)
- Caterpillar 360 KWDokumen6 halamanCaterpillar 360 KWAde WawanBelum ada peringkat
- St. John of The Cross - UnknownDokumen19 halamanSt. John of The Cross - UnknownthepillquillBelum ada peringkat
- HYKDDokumen15 halamanHYKDAri RamadhanBelum ada peringkat
- Colistimethate Sodium 1 Million I.U. Powder For Solution For Injection - Colistin - (Emc)Dokumen8 halamanColistimethate Sodium 1 Million I.U. Powder For Solution For Injection - Colistin - (Emc)hakim shaikhBelum ada peringkat
- Painting, DrawingDokumen22 halamanPainting, DrawingMithilesh_Kuma_7083Belum ada peringkat
- AkzoNobel-Trigonox 239Dokumen6 halamanAkzoNobel-Trigonox 239Wafa AjiliBelum ada peringkat
- Traxonecue Catalogue 2011 Revise 2 Low Res Eng (4!5!2011)Dokumen62 halamanTraxonecue Catalogue 2011 Revise 2 Low Res Eng (4!5!2011)Wilson ChimBelum ada peringkat
- Preparation and Evaluation of Orthodontic Setup PDFDokumen20 halamanPreparation and Evaluation of Orthodontic Setup PDFLiezty VioLen'sBelum ada peringkat
- How To Use Dr. Foster's Essentials: Essential Oils and BlendsDokumen5 halamanHow To Use Dr. Foster's Essentials: Essential Oils and BlendsemanvitoriaBelum ada peringkat
- Dasar Eksitasi Pada GeneratorDokumen8 halamanDasar Eksitasi Pada GeneratorTeknisi Abal AbalBelum ada peringkat
- Msds PentaneDokumen6 halamanMsds PentaneMuhammad FikriansyahBelum ada peringkat
- ABB Price Book 714Dokumen1 halamanABB Price Book 714EliasBelum ada peringkat
- Etabloc Technical DataDokumen108 halamanEtabloc Technical Dataedward ksbBelum ada peringkat
- Study Plan NCEPU PDFDokumen2 halamanStudy Plan NCEPU PDFAhsan100% (1)
- Your Song RitaDokumen1 halamanYour Song Ritacalysta felix wBelum ada peringkat
- EAPP w2Dokumen13 halamanEAPP w2Elijah AquinoBelum ada peringkat