Obligate Intracellular Parasites - Only Demonstrate Characteristics of Life While "Inside" A Host Cell: Bacteria, Animal, Plant
Diunggah oleh
Gian Andrew0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
19 tayangan24 halamanvirus
Judul Asli
virus
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inivirus
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
19 tayangan24 halamanObligate Intracellular Parasites - Only Demonstrate Characteristics of Life While "Inside" A Host Cell: Bacteria, Animal, Plant
Diunggah oleh
Gian Andrewvirus
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 24
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Obligate Intracellular Parasites – only
demonstrate characteristics of life while
“inside” a host cell: Bacteria, animal, plant
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Outside a host cell, inert, no enzyme or other activity
Inside a host cell – viral Nucleic Acid (DNA or RNA) takes over the cell and directs
the cell to produce new virus particles (replication)
Size of Viruses: See page in text 155?, very tiny (picorna) to huge (pox viruses)
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Basic virus particle is called a “virion” – intact and infective virus particle
Components: Nucleic Acid (DNA or RNA), Protein coat (capsid) made of
individual protein subunits called capsomeres. Some may have and outer
envelope, a membrane, derived from the host cell. The envelope can
have specific spikes of protein (H and N spikes of Influenza) that aid in
attachment and makes them sensitive to chemical actions of disinfectants.
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Types of viruses based on “morphology” – shape; structure
Helical (like TMV or Ebola) Polyhedral (adeno and polio) Enveloped (flu) and Complex
(bacteriophage)
Chapter 6 - Viruses
EBOLA
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Polio virions
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Influenza A: Enveloped, with spikes, RNA, multisegmented
genome (8 separate pieces of RNA)
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Bacteriophage: Complex
Chapter 6 - Viruses
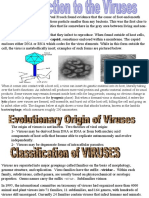
Taxonomy of viruses: complicated and “boring”; we’ll leave it
to the ones with a higher “paygrade”
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Cultivation of viruses: need living cells, living hosts
Tissue cultures, embryonated eggs, bacterial cultures
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Cultivation of viruses: need living cells, living hosts
Tissue cultures, embryonated eggs, bacterial cultures
Bacteria grown as a “lawn” – and viruses are in the clear zones, plaques
Chapter 6 – Viruses: Viral replication in bacteria – life cycle of bacterial virus
LYTIC Cycle
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Viral replication in bacteria – life cycle of bacterial virus
Lysogneic (latent) cycle, genome of virus incorporated into
host cell genome “infected with seeds of destruction”
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Animal Virus Life Cycle: Penetration, Uncoating, Biosynthesis, Assembly,
Maturation, Release Can have Latent infection also.
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Animal Virus Life Cycle: Penetration, Uncoating, Biosynthesis, Assembly,
Maturation, Release Can have Latent infection also. Latent infection is
seen in herpes type and even HIV
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Animal Virus Life Cycle: Penetration, Uncoating, Biosynthesis, Assembly,
Maturation, Release Can have Latent infection also. Latent infection is
seen in herpes type and even HIV
Hiv is a RNA virus, a “retrovirus” with an enzyme called reverse
transcriptase “ causes DNA to be synthesized from genome that is RNA
(backwards) The Drug AZT works on HIV by inhibiting this enzyme
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Budding of an animal virus from a host cell
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Budding of rabies viruses – electron photomicrograph
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Multi-segmented RNA genome of Influenza: higher mutation
rate, genetic shift and drift, new vaccines required
Chapter 6 - Viruses
Prions: Infectious proteins, cause scrappie in sheep, Kuru in
humans, BSE in cattle, and KJD in people (mad cow in
humans)
Watch the video “The Brain Eaters” Spoingioform
encephalopathy
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Obligate Intracellular Parasites - Only Demonstrate Characteristics of Life While "Inside" A Host Cell: Bacteria, Animal, PlantDokumen24 halamanObligate Intracellular Parasites - Only Demonstrate Characteristics of Life While "Inside" A Host Cell: Bacteria, Animal, PlantOliver Anthony HastaBelum ada peringkat
- Biology for Students: The Only Biology Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseDari EverandBiology for Students: The Only Biology Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseBelum ada peringkat
- Virus CharacteristicDokumen24 halamanVirus CharacteristicA. Nurul Virninda YusufBelum ada peringkat
- Obligate Intracellular Parasites - Only Demonstrate Characteristics of Life While "Inside" A Host Cell: Bacteria, Animal, PlantDokumen24 halamanObligate Intracellular Parasites - Only Demonstrate Characteristics of Life While "Inside" A Host Cell: Bacteria, Animal, PlantAmira VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- Obligate Intracellular Parasites - Only Demonstrate Characteristics of Life While "Inside" A Host Cell: Bacteria, Animal, PlantDokumen24 halamanObligate Intracellular Parasites - Only Demonstrate Characteristics of Life While "Inside" A Host Cell: Bacteria, Animal, PlantKrisburt Delos SantosBelum ada peringkat
- VirologyDokumen183 halamanVirologyVeronica KatigbakBelum ada peringkat
- Viruses, Viroids, and PrionsDokumen59 halamanViruses, Viroids, and Prionsjimoji7012Belum ada peringkat
- Viruses I 10Dokumen25 halamanViruses I 10priamcBelum ada peringkat
- 4 - Sub Cellular Organization Viruses, Viroids, and Prions (Compatibility Mode) (Repaired)Dokumen61 halaman4 - Sub Cellular Organization Viruses, Viroids, and Prions (Compatibility Mode) (Repaired)phiribrian468Belum ada peringkat
- Ciri-Ciri Virus: Glikoprotein: Protein Pada AmplopDokumen4 halamanCiri-Ciri Virus: Glikoprotein: Protein Pada AmplopRabila NsBelum ada peringkat
- #General Properties of Viruses 2016#Dokumen43 halaman#General Properties of Viruses 2016#Sarah PavuBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 - Micropara (Outline)Dokumen9 halamanChapter 4 - Micropara (Outline)Jezrylle BalaongBelum ada peringkat
- Viruses:: The Non-Living EntityDokumen48 halamanViruses:: The Non-Living EntityhannBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To VirusesDokumen24 halamanIntroduction To VirusesAbDul RehManBelum ada peringkat
- Viruses - GoodDokumen50 halamanViruses - GoodMohammed Faraaz MustafaBelum ada peringkat
- Microbial Diversity... Lect 5Dokumen17 halamanMicrobial Diversity... Lect 5safar akramBelum ada peringkat
- Biology 11 FederalDokumen426 halamanBiology 11 FederalAroona AkhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Viruses 2Dokumen32 halamanIntroduction To Viruses 2mega kharisma kusumawarniBelum ada peringkat
- Viruses, Viroids, and PrionsDokumen65 halamanViruses, Viroids, and PrionsIvenks EeBelum ada peringkat
- BT601 Virology 1.note On Herpes Virus?3Dokumen8 halamanBT601 Virology 1.note On Herpes Virus?3Haroon IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4Dokumen27 halamanChapter 4Blessy Martin100% (1)
- AAEF Viruses, Viroids, and PrionsDokumen56 halamanAAEF Viruses, Viroids, and Prionschinseuchisomo11Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction To VirusesDokumen10 halamanIntroduction To VirusesWhite RoseBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5: VIRUS 18 - Lacap, Dixie Mae N. Lacap 02. .15Dokumen10 halamanChapter 5: VIRUS 18 - Lacap, Dixie Mae N. Lacap 02. .15Dixie LacapBelum ada peringkat
- Virus StructureDokumen2 halamanVirus Structurewakadur RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Virology IntroductionDokumen31 halamanVirology IntroductionEsther WanjukiBelum ada peringkat
- English Short SemesterDokumen9 halamanEnglish Short SemesterSelestin NisfuBelum ada peringkat
- General Properties of VirusesDokumen93 halamanGeneral Properties of VirusesSeena SamBelum ada peringkat
- Virology Course 1Dokumen33 halamanVirology Course 1Uyisabye VénusteBelum ada peringkat
- Viruses: Why Are We Learning About Them?Dokumen50 halamanViruses: Why Are We Learning About Them?Nurul 'AdilahBelum ada peringkat
- BIO320 2 0 VirusesDokumen28 halamanBIO320 2 0 VirusesnabilahdaudBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction of VirusesDokumen6 halamanAn Introduction of VirusesMisha WilliamsBelum ada peringkat
- Mirando Essential QuestionDokumen7 halamanMirando Essential QuestionJustin MirandoBelum ada peringkat
- VIRUSDokumen26 halamanVIRUSCrystal Ann TadiamonBelum ada peringkat
- MCB211 Structure, General Characteristics and Reproduction of VirusesDokumen7 halamanMCB211 Structure, General Characteristics and Reproduction of VirusesElohorBelum ada peringkat
- Myco Assignment VIRUSDokumen1 halamanMyco Assignment VIRUSMarjorie BaquialBelum ada peringkat
- Viruses Morphology and Ultrastructure. Viruses Cultivation in Chicken Embryo and Laboratory Animals Organism!Dokumen21 halamanViruses Morphology and Ultrastructure. Viruses Cultivation in Chicken Embryo and Laboratory Animals Organism!Amirs AmjadBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 4 - Protozoa, Virus and Prion: Dyke Gita Wirasisya, S.Farm., MSC., AptDokumen50 halamanLecture 4 - Protozoa, Virus and Prion: Dyke Gita Wirasisya, S.Farm., MSC., AptDyke Gita WirasisyaBelum ada peringkat
- Viruses and Other Acellular Microorganisms: Kristina C. Erasmo, M.DDokumen28 halamanViruses and Other Acellular Microorganisms: Kristina C. Erasmo, M.DcabralmdBelum ada peringkat
- 2018 Virologi 1 Introduction To Medical Virology PDFDokumen48 halaman2018 Virologi 1 Introduction To Medical Virology PDFDave JhonsonBelum ada peringkat
- Ch. 6 Viruses ELCDokumen54 halamanCh. 6 Viruses ELCBobBelum ada peringkat
- Virus-PrionDokumen28 halamanVirus-PrionHaikal FahreziBelum ada peringkat
- CH 13 Objectives SummaryDokumen10 halamanCH 13 Objectives SummaryKhawla MustafaBelum ada peringkat
- H2 Biology - Notes On Genetics of VirusesDokumen10 halamanH2 Biology - Notes On Genetics of VirusesSefLRhoBelum ada peringkat
- Cytolog Viruses (Stud)Dokumen5 halamanCytolog Viruses (Stud)OnSolomonBelum ada peringkat
- VirusesDokumen40 halamanVirusesRimayaniBelum ada peringkat
- DR - Husni Samadin Mikrobiologi FK - UnsriDokumen55 halamanDR - Husni Samadin Mikrobiologi FK - UnsriIlham Akbar Ilaker'ErumbiaBelum ada peringkat
- Viral ReplicationDokumen26 halamanViral ReplicationJhann100% (1)
- VirusesDokumen17 halamanVirusesSara SantiagoBelum ada peringkat
- Viruses Viroids and Prions 18 2Dokumen59 halamanViruses Viroids and Prions 18 2learn bioBelum ada peringkat
- ZOOL 143 Topic 4Dokumen10 halamanZOOL 143 Topic 4nattydreadfathelahBelum ada peringkat
- Lec09 PDFDokumen10 halamanLec09 PDFSofi Mehraj100% (1)
- Virus StructureDokumen28 halamanVirus StructureMeilana Sapta D67% (3)
- Lecture 5Dokumen10 halamanLecture 5Smasher AustineBelum ada peringkat
- VirusesDokumen46 halamanVirusesJohn TharakanBelum ada peringkat
- Viral Structure and Components Properties of VirusesDokumen4 halamanViral Structure and Components Properties of Virusescanela1527100% (1)
- Rhabdoviruses by KennedyDokumen36 halamanRhabdoviruses by KennedyIGA ABRAHAMBelum ada peringkat
- Veterinary Virology PDFDokumen96 halamanVeterinary Virology PDFShem Peter Mutua Mutuiri100% (1)
- Asean DoxcDokumen24 halamanAsean DoxcGian AndrewBelum ada peringkat
- Particulate Nature of MatterDokumen43 halamanParticulate Nature of MatterGian AndrewBelum ada peringkat
- Bacteriophage Definition Parts and FunctionDokumen4 halamanBacteriophage Definition Parts and FunctionGian AndrewBelum ada peringkat
- Bacteriophages: Dr.T.V.Rao MDDokumen35 halamanBacteriophages: Dr.T.V.Rao MDGian AndrewBelum ada peringkat
- Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) A Promising Enzyme in The Area of Biopharmaceuticals in Its Native and Immobilized Form A ReviewDokumen9 halamanSuperoxide Dismutase (SOD) A Promising Enzyme in The Area of Biopharmaceuticals in Its Native and Immobilized Form A ReviewIJRASETPublicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Forensic ReportDokumen4 halamanForensic ReportSam SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Fig.1: Vegetative Morphology of EctocarpusDokumen21 halamanFig.1: Vegetative Morphology of EctocarpusAmrit Mund EducationalBelum ada peringkat
- Does DNA Emit LightDokumen7 halamanDoes DNA Emit LighttherobroyBelum ada peringkat
- Protein Denaturation: (A Home Experiment)Dokumen6 halamanProtein Denaturation: (A Home Experiment)jestoni langgidoBelum ada peringkat
- Multiple Choice Questions: Patterns of Chromosome InheritanceDokumen10 halamanMultiple Choice Questions: Patterns of Chromosome InheritanceArwaBelum ada peringkat
- Liquichek Elevated CRP Control Levels 1, 2 and 3: Revision Date 2022-05-26 Indicates Revised InformationDokumen1 halamanLiquichek Elevated CRP Control Levels 1, 2 and 3: Revision Date 2022-05-26 Indicates Revised InformationowoladeidowuBelum ada peringkat
- Rainsure Company, Instrument and Assays Introduction CLVDokumen61 halamanRainsure Company, Instrument and Assays Introduction CLVMohammed H. KeshtaBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution The History of An Idea Bowler PDFDokumen2 halamanEvolution The History of An Idea Bowler PDFJessica0% (4)
- Blotting TechniquesDokumen31 halamanBlotting TechniquesRahul Amin Sheikh 19MSM0114Belum ada peringkat
- Antioxidant Properties of Spices, Herbs and Other SourcesDokumen589 halamanAntioxidant Properties of Spices, Herbs and Other SourcesAna MariaBelum ada peringkat
- 4 - Levels of Organization of Living ThingsDokumen20 halaman4 - Levels of Organization of Living ThingsFrancisco jezziel dominguez fernandezBelum ada peringkat
- The Detritus Food-Web and The Diversity of Soil Fauna As Indicators of Disturbance Regimes in Agro-EcosystemsDokumen9 halamanThe Detritus Food-Web and The Diversity of Soil Fauna As Indicators of Disturbance Regimes in Agro-EcosystemsFábio Luís MostassoBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Calories - Nutrition, Energy & MetabolismDokumen7 halamanUnderstanding Calories - Nutrition, Energy & MetabolismHas KazBelum ada peringkat
- Full Download Book Basic Clinical Pharmacology 15Th Edition PDFDokumen41 halamanFull Download Book Basic Clinical Pharmacology 15Th Edition PDFalvin.vincent421100% (15)
- Western BlottingDokumen8 halamanWestern BlottingAnupam KaulBelum ada peringkat
- Brazil Anvisa in 03 2015 Ivd Families enDokumen2 halamanBrazil Anvisa in 03 2015 Ivd Families enElaine NascimentoBelum ada peringkat
- Rabies: Dr. Fitzroy A. Orrett, MB - BS, MSC, D (Abmm), Fccm. Clinical MicrobiologistDokumen42 halamanRabies: Dr. Fitzroy A. Orrett, MB - BS, MSC, D (Abmm), Fccm. Clinical MicrobiologistPatriceBelum ada peringkat
- Topical Test Biology Form 4Dokumen14 halamanTopical Test Biology Form 4Siti Wahida SuleimanBelum ada peringkat
- Franklin, Watson, Crick and WilkinsDokumen3 halamanFranklin, Watson, Crick and WilkinsRussell MorrisonBelum ada peringkat
- שיטות מעבדה ביולוגיה מולקולריתDokumen53 halamanשיטות מעבדה ביולוגיה מולקולריתKamal KabhaBelum ada peringkat
- Kitar KrebsDokumen5 halamanKitar KrebsAlfonso RobertBelum ada peringkat
- Haemogram: Blood CountsDokumen3 halamanHaemogram: Blood CountsAbhi PrajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- AP Bio Essay #29Dokumen2 halamanAP Bio Essay #29Elioth Gomez100% (1)
- 11th Biology-Botany English Medium TextDokumen320 halaman11th Biology-Botany English Medium Textmadhusudhanan.scholarBelum ada peringkat
- The Five Kingdom Classification System ArticleDokumen3 halamanThe Five Kingdom Classification System ArticleNermine AbedBelum ada peringkat
- Informative EssayDokumen5 halamanInformative EssayLaDarius Doaks100% (1)
- HumaCount 5D ENDokumen8 halamanHumaCount 5D ENAhmed MoeenBelum ada peringkat
- Effectiveness of Fenbendazole and Metronidazole Against Giardia Infection in Dogs Monitored For 50-Days in Home-ConditionsDokumen7 halamanEffectiveness of Fenbendazole and Metronidazole Against Giardia Infection in Dogs Monitored For 50-Days in Home-ConditionsBrieBelum ada peringkat
- Transgene: Transparent FrogDokumen3 halamanTransgene: Transparent Froggeobee emmanuelBelum ada peringkat
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (9)
- There Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceDari EverandThere Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PricePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (15)
- The Gut-Immune Connection: How Understanding the Connection Between Food and Immunity Can Help Us Regain Our HealthDari EverandThe Gut-Immune Connection: How Understanding the Connection Between Food and Immunity Can Help Us Regain Our HealthBelum ada peringkat
- Do You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineDari EverandDo You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineBelum ada peringkat
- Uncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicDari EverandUncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicBelum ada peringkat
- Vax-Unvax: Let the Science SpeakDari EverandVax-Unvax: Let the Science SpeakPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- The Inescapable Immune Escape PandemicDari EverandThe Inescapable Immune Escape PandemicPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Deaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismDari EverandDeaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (30)
- The Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsDari EverandThe Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (6)
- Sickening: How Big Pharma Broke American Health Care and How We Can Repair ItDari EverandSickening: How Big Pharma Broke American Health Care and How We Can Repair ItPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (9)
- Clean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyDari EverandClean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (18)
- Heat Wave: A Social Autopsy of Disaster in ChicagoDari EverandHeat Wave: A Social Autopsy of Disaster in ChicagoPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (40)
- The Truth about Wuhan: How I Uncovered the Biggest Lie in HistoryDari EverandThe Truth about Wuhan: How I Uncovered the Biggest Lie in HistoryPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- Fatal Conveniences: The Toxic Products and Harmful Habits That Are Making You Sick—and the Simple Changes That Will Save Your HealthDari EverandFatal Conveniences: The Toxic Products and Harmful Habits That Are Making You Sick—and the Simple Changes That Will Save Your HealthPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (7)
- Summary: The Real Anthony Fauci: Bill Gates, Big Pharma, and the Global War on Democracy and Public Health by Robert F. Kennedy Jr: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDari EverandSummary: The Real Anthony Fauci: Bill Gates, Big Pharma, and the Global War on Democracy and Public Health by Robert F. Kennedy Jr: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Health and Occupational Health & SafetyDari EverandEnvironmental Health and Occupational Health & SafetyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (9)
- Profiles of the Vaccine-Injured: "A Lifetime Price to Pay"Dari EverandProfiles of the Vaccine-Injured: "A Lifetime Price to Pay"Penilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (3)
- Breaking out of the Health Care Abyss: Transformational Tips for Agents of ChangeDari EverandBreaking out of the Health Care Abyss: Transformational Tips for Agents of ChangeBelum ada peringkat
- The Wuhan Cover-Up: And the Terrifying Bioweapons Arms RaceDari EverandThe Wuhan Cover-Up: And the Terrifying Bioweapons Arms RaceBelum ada peringkat
- There Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceDari EverandThere Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PricePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (11)
- Healthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityDari EverandHealthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- The Bodies of Others: The New Authoritarians, COVID-19 and The War Against the HumanDari EverandThe Bodies of Others: The New Authoritarians, COVID-19 and The War Against the HumanPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (12)
- Epic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.Dari EverandEpic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (13)
- Mama Might Be Better Off Dead: The Failure of Health Care in Urban AmericaDari EverandMama Might Be Better Off Dead: The Failure of Health Care in Urban AmericaBelum ada peringkat
- Vaccines Did Not Cause Rachel's Autism: My Journey as a Vaccine Scientist, Pediatrician, and Autism DadDari EverandVaccines Did Not Cause Rachel's Autism: My Journey as a Vaccine Scientist, Pediatrician, and Autism DadPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)