Endangered Ecosystem
Diunggah oleh
ridwan100%(9)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (9 suara)
8K tayangan26 halamanproper management of development activities and the ecosystem
Judul Asli
ENDANGERED ECOSYSTEM
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Iniproper management of development activities and the ecosystem
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
100%(9)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (9 suara)
8K tayangan26 halamanEndangered Ecosystem
Diunggah oleh
ridwanproper management of development activities and the ecosystem
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 26
• The need for development and the
• The importance of proper managem
• Measures taken in the managemen
The need for development and the effects of
an increasing population on the ecosystem
• Population of the world always increase, so do
their needs.
• The needs for more food supplies, water, home
has led to development.
• These development involves deforestation, the
building more dams, and production of more
domestic and industrial waste.
• The unmanaged and unplanned development
leads to a pollution of environment.
• To reduces the negative effects of developments,
human must have efforts to manage the
environment properly.
The importance of proper management
of development activities
• Way to balance the needs for resources with the
needs to conserve the natural resources.
• To make a sustainable development without
jeopardising or depleting the natural resources.
• Ensure that short-term gains be balance with the
long-term effects on the environment.
• To exploit natural resources in a sustainable
way, so these resources can be replenished and
renewed for future generations to continue to
use them.
• To minimize the negative effects of development
towards the environment.
Measures taken in the management
of development activities
1. Implementations of laws
2. Use of technology
3. Education on the management of resourc
4. Preservation and conservation of soil, wa
5. The practice of biological control
6. The use of renewable energy
7. The efficient use of energy
Implementations of laws
• Many laws and regulations are designed to
control pollution which affects the quality of
lands, air and water. Examples of the act;
- The Environment Quality Acts, 1974, 1989
* Motor Vehicle Noise Regulations,1987
* Scheduled Wastes Treatment and
Disposal Facilities Regulations, 1989
* Clean Air Regulations, 2000 (Amendment)
- The National Forestry Act, 1984
- The Pesticides Act, 1974
- The Fisheries Act, 1985
- The Protection of Wildlife Act, 1972
Use of technology
• Install catalytic converters in vehicle to clean up
exhaust emissions and convert harmful gases
released to less harmful gases.
• Use unleaded petrol to reduce the emissions of
leads into environment.
• Treat sewage in sewage treatment plants before it
is discharged to reduce water pollution.
• Treat toxic waste from factories before it is
discharged into the environment.
• Use microorganisms to clean up the environment.
• Develop hydrogen-based fuel-cell vehicle to
reduce the burning of fossil fuels.
Education on the management of resources
• The public must be educated on the concept of
the 4R.
• Recycle means collecting segregating waste
according to the types of materials and turning
this waste into new products.
• Reuse means use things such as old plastics
containers and bottles again instead of throwing
them away.
• Reduce means cutting down on the use of
materials which are non-biodegradable.
• Renew means to use materials such as bottles
and plastic containers after they are cleaned.
Recycling is important because;
• Fewer landfills will be needed to
dispose of rubbish.
• It cuts down the use of resources, for
example, fewer trees will be cut down
to make furniture and paper.
• It saves energy. For example, less
energy is needed to melt down scrap
metal and use it again than to extract
it from the ore.
Preservation and conservation
• Preservations involves efforts to protect
an ecosystem.
• Conservations involves efforts to return an
affected ecosystem to its natural
equilibrium and keep them good.
• Preservations is better than conservations.
• The efforts of conservations includes;
- Preservations of soil
- Preservations of water
- Preservations of flora and fauna of forest
- Preservations of mangrove swamps
Preservations of soils
• Make a sustainable agricultural
development effectively.
• Good farming technique will prevent
erosion and soil depletion.
• Good agricultural practices include;
Crop rotation
Contour farming
Controlled grazing
Planting cover crops
The appropriate use of fertilisers
Effective drainage and irrigations
Preservations of water
• Clean water is a precious resource and
commodity.
• As such, water sources and water
catchment areas must be preserved.
Rivers must not be regarded as dumping
sites for domestic and toxic wastes which
can pollutes the water.
The use of nitrates and phosphates in
agriculture must be controlled to prevent
run-offs into rivers and ponds.
Preservations of flora and fauna of rainforest
• Biologist have estimated that Malaysian rainforest
contain more than 50% of the world’s plant. 15000
of them has not studied yet.
• If deforestation proceed faster than afforestation,
many of these species could become extinct
before they can be documented.
• Important of forest;
- As a diverse storehouse of plant and animal
species which can provide useful and medicine for
mankind.
-play an important role in the regulation of
microclimate and the concentration of
atmospheric carbon dioxide.
-sites for research and education.
Example of sustainable and planned project
• Selective harvesting
- Means only mature trees are removed.
• Reforestation
- Large-scale replanting of trees where
logging activities have been carried out.
• Restoration programmes
- Restore damage habitat to preserve
natural life and wildlife.
• Forest reserves
- To prevent destruction of existing
forest.
- As a habitat for flora and fauna.
Preservations of mangrove swamps
• Rich source of biodiversity.
• Play an important role in flood control,
nutrient retention, sediment control and
the prevention of coastal erosion. Also
act as a barrier against rising sea levels.
• When area of mangrove swamps is
cleared for aquaculture and development,
many plant and animal will extinct.
• Hence, mangrove swamps must be
preserved and protected as it gives much
benefit to mankind.
The practice of biological control
• Biological control is the use of natural predators
to control the population of pest species.
• Examples;
- the use of khaki chambel (a species of ducks)
to control the population of gold snails (siput
gondang emas) which feeds on paddy stalks.
- the use of owls to control the populations of
rats in oil palm plantations.
- th use of the hoverfly larvae to control aphids
which feed on crop plants.
•Biological control is better than using chemical
controls because;
The use of pesticides is indiscriminates and
sometimes harmless organisms as well as the
pest species are killed.
The effects of pesticides is persistent and
remain in the environment for long periods.
The concentration of pesticides are amplified
as they pass through food chains
(biomagnifications).this is dangerous to the
last consumers and may effects them.
The cost of using pesticides is high.
The extensive use of the pesticides pollutes
the environment.
The use of renewable energy
• Renewable energy is energy flow that occurs
naturally in the environment and can be
harnessed for the benefit of the humans.
• Renewable energy is inexhaustible and does
not pollute the air.
• Examples of renewable energy;
- Solar energy (generates electricity)
- Wind energy (to operate windmills)
- Flowing water (generate hydroelectric power)
- Wave energy (generates electricity)
- Geothermal energy (generates electricity)
- Biomass energy (produces biogas as fuel)
- Gasohol ( converted to ethanol as fuel)
- Palm oil (converted to methyl ester as fuel)
The efficient use of energy
• Reduce the burning of coal, petroleum
and other fossil fuels.
• Substitute natural gas for coal at power
plants.
• Improve fuel efficiency in vehicles-use
cars that run on energy-efficient engines.
• Use a cleaner fuel by reducing the
content of sulphur in diesel and switching
to gas.
• Improve energy efficiency in factories.
• Use more hybrid car which combine
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Functions: CSEB134: BS/2008 1Dokumen38 halamanFunctions: CSEB134: BS/2008 1ridwan100% (1)
- Input / Output in CDokumen19 halamanInput / Output in CridwanBelum ada peringkat
- 2.1 Reasons of Converting Double Room To Single RoomDokumen1 halaman2.1 Reasons of Converting Double Room To Single RoomridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Hydroxy Compound)Dokumen71 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Hydroxy Compound)ridwan100% (3)
- Matriculation Chemistry (Amino Acids) Part 1Dokumen24 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Amino Acids) Part 1ridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Amino Acids) Part 2Dokumen10 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Amino Acids) Part 2ridwanBelum ada peringkat
- ExercisesDokumen2 halamanExercisesridwanBelum ada peringkat
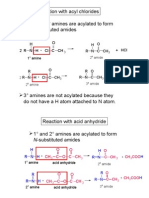
- Matriculation Chemistry (Amines) Part 2Dokumen13 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Amines) Part 2ridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Aromatic Compound)Dokumen87 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Aromatic Compound)ridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Carbonyl Compound)Dokumen50 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Carbonyl Compound)ridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Polymers)Dokumen19 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Polymers)ridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Carboxylic Acid)Dokumen68 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Carboxylic Acid)ridwan50% (2)
- Matriculation Chemistry (Haloalkane)Dokumen46 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Haloalkane)ridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Amines) Part 1Dokumen39 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Amines) Part 1ridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) AlkeneDokumen98 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Alkeneridwan100% (4)
- Matriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Part 2 AlkaneDokumen30 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Part 2 AlkaneridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 2Dokumen33 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 2ridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Electrochemistry)Dokumen77 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Electrochemistry)ridwan100% (3)
- Matriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 3Dokumen25 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 3ridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 2Dokumen13 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 2ridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Physics (Nucleus)Dokumen39 halamanMatriculation Physics (Nucleus)ridwan67% (3)
- Matriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 4Dokumen40 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 4ridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 2Dokumen18 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 2ridwan100% (2)
- Matriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Part 1 AlkaneDokumen44 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Part 1 AlkaneridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 1Dokumen24 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 1ridwan71% (7)
- Matriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 5Dokumen18 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 5ridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Thermochemistry)Dokumen54 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Thermochemistry)ridwan100% (2)
- Matriculation Physics (Nuclear Reaction)Dokumen39 halamanMatriculation Physics (Nuclear Reaction)ridwan67% (3)
- Matriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 4Dokumen13 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 4ridwan100% (1)
- Matriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 1Dokumen13 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 1ridwan100% (2)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- MSDS Capilene G 86 EDokumen4 halamanMSDS Capilene G 86 Ezubair1951Belum ada peringkat
- M32-W o IncineratorDokumen137 halamanM32-W o IncineratorAlex100% (1)
- Hazardous Substances ReportDokumen273 halamanHazardous Substances ReportDiny Mariza RhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Safety Sheet For Caco3Dokumen5 halamanSafety Sheet For Caco3Vaibhav D RavalBelum ada peringkat
- Einhell BC-BG 43 AsDokumen16 halamanEinhell BC-BG 43 AsCristiana LaviniaBelum ada peringkat
- English Form 2Dokumen13 halamanEnglish Form 2Subramaniam PeriannanBelum ada peringkat
- Jhalana GramDokumen59 halamanJhalana GramShraddha ChandanBelum ada peringkat
- FIRST Consultation, Environment and Calibration: 6/C Taksem El-Laselky, New Maadi, Cairo, EgyptDokumen27 halamanFIRST Consultation, Environment and Calibration: 6/C Taksem El-Laselky, New Maadi, Cairo, EgyptAhmed ElsayedBelum ada peringkat
- PCRA-8-LPG Saving & Safety Tips (Presentation)Dokumen15 halamanPCRA-8-LPG Saving & Safety Tips (Presentation)MinatiBindhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Genvi Notes Module 3 Unit 3 - 2023Dokumen9 halamanGenvi Notes Module 3 Unit 3 - 2023Jaeyun RuiBelum ada peringkat
- Global Phosphorus Scarcity and Full-Scale P-Recovery Techniques - A ReviewDokumen51 halamanGlobal Phosphorus Scarcity and Full-Scale P-Recovery Techniques - A ReviewphaneufdlBelum ada peringkat
- Cost Effective Construction Techniques GuideDokumen31 halamanCost Effective Construction Techniques GuidebuharimBelum ada peringkat
- Solar Power Plant Feasibility StudyDokumen48 halamanSolar Power Plant Feasibility StudyNasiru Bello100% (2)
- ACO Industrial DrainageDokumen230 halamanACO Industrial DrainageJohnBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 - Design of Goods and Services - 2Dokumen63 halamanChapter 5 - Design of Goods and Services - 2Donna Mae HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Overview of Industrial Pollution Management Policies in India and Context of ZLDDokumen23 halamanOverview of Industrial Pollution Management Policies in India and Context of ZLDVineeth SivarajBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1b - Environmental Rules & Regulations MalaysiaDokumen33 halamanChapter 1b - Environmental Rules & Regulations Malaysiascribd1991100% (6)
- μC2SE - electronic control - User manualDokumen72 halamanμC2SE - electronic control - User manualMuhidin Kozica100% (2)
- HSE Unit 005Dokumen8 halamanHSE Unit 005Tufail KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study of Coca Cola in Vietnam (Presentation)Dokumen15 halamanCase Study of Coca Cola in Vietnam (Presentation)Ahmed Jan Dahri100% (1)
- Ipal - Modul 7 - Perawatan IpalDokumen3 halamanIpal - Modul 7 - Perawatan IpalAndhika HerdiawanBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental AccountingDokumen27 halamanEnvironmental AccountingFaresh Haroon100% (1)
- Principles of Speech Writing: Oral Communication in ContextDokumen14 halamanPrinciples of Speech Writing: Oral Communication in ContextCherryl IbarrientosBelum ada peringkat
- NATRESDokumen33 halamanNATRESAleezah Gertrude RaymundoBelum ada peringkat
- Site Engineer Job - Huationg Contractor Pte LTD - 5337669 - JobStreetDokumen5 halamanSite Engineer Job - Huationg Contractor Pte LTD - 5337669 - JobStreetBan YTBelum ada peringkat
- Appendix 1 BICSc Cleaning Standards SpecificationsDokumen5 halamanAppendix 1 BICSc Cleaning Standards SpecificationsKifah Zaidan100% (3)
- Clarifier Sizing SpreadsheetDokumen1 halamanClarifier Sizing SpreadsheetsumitanuragBelum ada peringkat
- Alfa Laval SB Carlsberg Flask Instruction Manual Ese02966enDokumen18 halamanAlfa Laval SB Carlsberg Flask Instruction Manual Ese02966enpacocurroBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Allu Stabilization 2015Dokumen84 halaman6 Allu Stabilization 2015Marcin SteckiBelum ada peringkat
- Economic-Environment Interactions MatrixDokumen7 halamanEconomic-Environment Interactions MatrixArya Malik100% (1)