Flash Memory
Diunggah oleh
Priyadarshini SahooDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Flash Memory
Diunggah oleh
Priyadarshini SahooHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Technical Seminar Presentation-2004
National Institute of Science & Technology
Flash Memory
By
Arjun Sabat Roll No: EE 200113365
Under the guidance of
Mr. Gayadhar Panda
Presented By: Arjun Sabat [EE200113365]
Technical Seminar Presentation-2004
INTRODUCTION
National Institute of Science & Technology
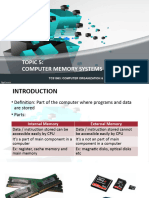
• Flash Memory is solid state non-volatile
memory.
• It stores electrical charges rather than
magnetic media.
• Flash memory is light,compact,energy
efficient and less expensive.
• it is a ideal storage medium for digital
camera,smart card etc.
Presented By: Arjun Sabat [EE200113365]
[2]
Technical Seminar Presentation-2004
WHAT IS FLASH MEMORY?
National Institute of Science & Technology
• Flash memory is electronically erasable,
electronically programmable, (generally)
read-only memory.
• From an embedded system designer’s
perspective, the key difference between
flash memory and EEPROM is that flash
devices are block structured; that is, while
flash memory locations are individually
programmable, they are not individually
erasable the way they are with EEPROM.
Presented By: Arjun Sabat [EE200113365]
[3]
Technical Seminar Presentation-2004
National Institute of Science & Technology
• Flash memory is erased in sections
whose sizes and locations in the chip are
defined by the part’s manufacturer.
• As a result, once a flash memory location
is programmed, the entire section
containing the location must be erased
before that location can be programmed
again.
Presented By: Arjun Sabat [EE200113365]
[4]
Technical Seminar Presentation-2004
HOW FLASH MEMORY WORKS
National Institute of Science & Technology
• Flash memory is a type of EEPROM chip.
• Flash memory cell consists of two transistors
and these transistors are separated by a thin
oxide layer.
• One transistor is called floating and other one
is control gate.
• A cell censor monitor the level of charge
passing through floating gate. if the flow
through the gate is greater than 50%of charge
its value is ‘1’. If charge passing drops below
50% threshold it’s value is ‘0’.
Presented By: Arjun Sabat [EE200113365]
[5]
Technical Seminar Presentation-2004
MLC TECHNOLOGY
National Institute of Science & Technology
• MLC stands for Multi Level Cell
• MLC Technology allows storage multiple bits
per memory cell by charging memory cell to
different voltage level.
• These significantly increase the number of
bits stored per area.
• It may store per cell or thee bits per cell.
• It significantly decrease the cost per
Megabyte.
Presented By: Arjun Sabat [EE200113365]
[6]
Technical Seminar Presentation-2004
HOW TO ERASE & WRITE TO FLASH?
National Institute of Science & Technology
• Flash memory is a type of EEPROM chip.
It has a grid of columns and rows with a
cell that has two transistors at each
intersection. The two transistors are
separated from each other by a thin oxide
layer.
• Programming algorithms specified to Flash
controller is used to control Flash memory.
Presented By: Arjun Sabat [EE200113365]
[7]
Technical Seminar Presentation-2004
ADVANTAGES
National Institute of Science & Technology
• Flash memory is noise less.
• It allows faster access.
• It is smaller size and lighter.
• It has no moving parts.
Presented By: Arjun Sabat [EE200113365]
[8]
Technical Seminar Presentation-2004
LIMITATIONS
National Institute of Science & Technology
• Flash memory costs five to ten times
more than standard DRAM.
• Another downside is the overabundance
of formats.
• Huge premium to pay power saving of
flash memory.
Presented By: Arjun Sabat [EE200113365]
[9]
Technical Seminar Presentation-2004
FLASH APPLICATIONS
National Institute of Science & Technology
Nonvolatile storage needed but battery
not desirable.
In an application where long-term data
storage is required but a battery is not
desirable, flash provides an ideal alternative
to battery-backed static RAM.
Presented By: Arjun Sabat [EE200113365]
[10]
Technical Seminar Presentation-2004
CONCLUSION
National Institute of Science & Technology
• Flash memory thus can provide an
alternative to conventional DRAM memory.
But it’s cost has to be decreased
drastically to ensure that it replays the
DRAM quickly.
• By use of MLC technology the memory
capacity of flash memory can be increased
and thus the cost can be decreased.
Presented By: Arjun Sabat [EE200113365]
[11]
Technical Seminar Presentation-2004
National Institute of Science & Technology
Thank
You!
Presented By: Arjun Sabat [EE200113365]
[12]
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- სიკვდილთან დიალოგი - ელ.ვერსია PDFDokumen228 halamanსიკვდილთან დიალოგი - ელ.ვერსია PDFMarita Beltadze83% (76)
- Cópia de Softwares Atualizados Com NEs09!05!22Dokumen25 halamanCópia de Softwares Atualizados Com NEs09!05!22Robismar Caze100% (1)
- 變速箱 A245E,A246E ZZE121Dokumen136 halaman變速箱 A245E,A246E ZZE121esquisof67% (9)
- Flash Memory: Technical Seminar ReportDokumen15 halamanFlash Memory: Technical Seminar Reportuname0708Belum ada peringkat
- FT01Dokumen4 halamanFT01api-3721578100% (1)
- 001-99111 AN99111 Parallel NOR Flash Memory An OverviewDokumen8 halaman001-99111 AN99111 Parallel NOR Flash Memory An Overviewprashant wagreBelum ada peringkat
- Theoretical FrameworkDokumen11 halamanTheoretical FrameworkMark AbadiesBelum ada peringkat
- Ovonic Unified Memory PPT1Dokumen20 halamanOvonic Unified Memory PPT1pankaja143Belum ada peringkat
- Design and Scaling of A SONOS Multidielectric Device For Nonvolatile Memory Applications-OmsDokumen8 halamanDesign and Scaling of A SONOS Multidielectric Device For Nonvolatile Memory Applications-Omsjulio perezBelum ada peringkat
- Flash MemoryDokumen13 halamanFlash MemoryRam021Belum ada peringkat
- EC304Dokumen17 halamanEC304api-3853441Belum ada peringkat
- An Analysis of Program and Erase Mechanisms For Floating Channel Type Surrounding Gate Transistor Flash Memory CellsDokumen9 halamanAn Analysis of Program and Erase Mechanisms For Floating Channel Type Surrounding Gate Transistor Flash Memory CellsKKiranKumarBelum ada peringkat
- Application: Chip Non-Volatile Floating-Gate Transistors Ultraviolet Fused Quartz Silicon UltravioletDokumen4 halamanApplication: Chip Non-Volatile Floating-Gate Transistors Ultraviolet Fused Quartz Silicon UltravioletfeysalnurBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Organization Architecture - Topic 5Dokumen36 halamanComputer Organization Architecture - Topic 5asj233510377Belum ada peringkat
- Ovonic Unified Memory PPT1Dokumen20 halamanOvonic Unified Memory PPT1Vinod YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Non-Volatile Memory:: A Review of Past and Present Concepts and ApplicationsDokumen10 halamanNon-Volatile Memory:: A Review of Past and Present Concepts and ApplicationsMisa 99Belum ada peringkat
- Flash Memory Lifespan and Reliability White PaperDokumen10 halamanFlash Memory Lifespan and Reliability White PaperpepeparraBelum ada peringkat
- Embedded System Application: History of Microprocessors For Embedded SystemsDokumen37 halamanEmbedded System Application: History of Microprocessors For Embedded SystemsMULLAIVANESH A VBelum ada peringkat
- Eeprom: Stmicro M24C02 (HTTP://WWW - St.Co M/Resource/En/Datasheet/M24C02-F. PDF) I C Serial Type EepromDokumen9 halamanEeprom: Stmicro M24C02 (HTTP://WWW - St.Co M/Resource/En/Datasheet/M24C02-F. PDF) I C Serial Type EepromAndrés Alejandro PereiraBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 5 - Introduction To Memory ArchitectureDokumen65 halamanLecture 5 - Introduction To Memory ArchitectureSalman ArifBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter3 Memory System1Dokumen47 halamanChapter3 Memory System1Elias HedamoBelum ada peringkat
- Flash Mem BasicsDokumen9 halamanFlash Mem BasicsananthBelum ada peringkat
- Embedded System of Shibu K VDokumen10 halamanEmbedded System of Shibu K Vshahebgoudahalladamani0% (1)
- The Cpu and Memory - OrganizationDokumen54 halamanThe Cpu and Memory - Organization2022680924Belum ada peringkat
- ch01 2 PDFDokumen32 halamanch01 2 PDFpratik kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Ovonic Unified MemoryDokumen39 halamanOvonic Unified MemoryNishantPatelBelum ada peringkat
- De La Salle University - Dasmarinas College of Engineering, Architecture and Technology Technology DepartmentDokumen7 halamanDe La Salle University - Dasmarinas College of Engineering, Architecture and Technology Technology DepartmentHennesey LouriceBelum ada peringkat
- Flash Memory Is An Electronic: Citation NeededDokumen1 halamanFlash Memory Is An Electronic: Citation NeededrijoiBelum ada peringkat
- Computer MemoryDokumen14 halamanComputer MemoryShiela Marie BanggotBelum ada peringkat
- Lec10 Sram1Dokumen19 halamanLec10 Sram1VenkatGollaBelum ada peringkat
- ELEC3300 10-Memory InterfaceDokumen35 halamanELEC3300 10-Memory InterfaceKwun Hok ChongBelum ada peringkat
- WINSEM2021-22 ECE5023 TH VL2021220505491 Reference Material I 17-03-2022 NVMDokumen75 halamanWINSEM2021-22 ECE5023 TH VL2021220505491 Reference Material I 17-03-2022 NVMBhargavi PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Cte 421 Material Batch3Dokumen10 halamanCte 421 Material Batch3DivineBelum ada peringkat
- CM305Dokumen14 halamanCM305api-3853441Belum ada peringkat
- Design For Shock Isolation: VibrationdataDokumen68 halamanDesign For Shock Isolation: VibrationdataRonaldo Cachi DelgadoBelum ada peringkat
- The Cpu and Memory - OrganizationDokumen57 halamanThe Cpu and Memory - OrganizationNooraFukuzawa NorBelum ada peringkat
- Flash Memory: Presented By: Amit Raj 09EE6406 Instrumentation EnggDokumen21 halamanFlash Memory: Presented By: Amit Raj 09EE6406 Instrumentation Enggrajelec100% (1)
- SYIT ES CH 5 & 6 PDFDokumen26 halamanSYIT ES CH 5 & 6 PDFtruptiBelum ada peringkat
- Information Technology CPUDokumen7 halamanInformation Technology CPUSafikul HossainBelum ada peringkat
- Polymer MemoryDokumen23 halamanPolymer MemorySumit DiwakerBelum ada peringkat
- Service Manual: Data ProjectorDokumen113 halamanService Manual: Data Projectorafranio batistaBelum ada peringkat
- Flash MemoryDokumen9 halamanFlash MemoryAshraf RodziBelum ada peringkat
- Flash WhitePaper FinalDokumen6 halamanFlash WhitePaper FinalseanBelum ada peringkat
- Syit ES Unit 4Dokumen23 halamanSyit ES Unit 4truptiBelum ada peringkat
- Internal Memory: William Stallings, Computer Organization and Architecture, 9 EditionDokumen38 halamanInternal Memory: William Stallings, Computer Organization and Architecture, 9 EditionDang Hai Binh (K16HCM)Belum ada peringkat
- Comparative Study of Technology in Semiconductor Memories-A ReviewDokumen5 halamanComparative Study of Technology in Semiconductor Memories-A ReviewAlexis RodríguezBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial Human Interfaces:: LCD (Segment and Graphical) Basics and Roadmap OverviewDokumen57 halamanIndustrial Human Interfaces:: LCD (Segment and Graphical) Basics and Roadmap OverviewRavi KumarBelum ada peringkat
- History of Nand Flash TechnologyDokumen6 halamanHistory of Nand Flash TechnologyHarshJainBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluation of Radiation Effects in Flash Memories: Tetsuo Miyahira and Gary SwiftDokumen7 halamanEvaluation of Radiation Effects in Flash Memories: Tetsuo Miyahira and Gary SwiftVijay KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Microprocessor Part2Dokumen84 halamanMicroprocessor Part2مهند عدنان الجعفريBelum ada peringkat
- Infineon SONOS - Technology Whitepaper v06 - 00 ENDokumen17 halamanInfineon SONOS - Technology Whitepaper v06 - 00 ENwolfzertBelum ada peringkat
- M3-01 Implementation ApproachesDokumen18 halamanM3-01 Implementation ApproachesAhmed ShafeekBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Organization and Architecture: Internal MemoryDokumen49 halamanComputer Organization and Architecture: Internal MemoryCông PhạmBelum ada peringkat
- Operating System: Memory Management StrategiesDokumen25 halamanOperating System: Memory Management Strategiesamaday shwanBelum ada peringkat
- Polymer Memory: Bachelor of Technology IN Electronics and Communication EngineeringDokumen25 halamanPolymer Memory: Bachelor of Technology IN Electronics and Communication EngineeringSateesh Kuna100% (1)
- Eeprom MicrochipDokumen27 halamanEeprom MicrochipAhmed AlsheikhBelum ada peringkat
- Non Volatile Memory1Dokumen14 halamanNon Volatile Memory1Jane D'SouzaBelum ada peringkat
- F940got SWD e PDFDokumen6 halamanF940got SWD e PDFdinhcpsBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4Dokumen10 halamanUnit 4kisu kingBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Four: Memory OrganizationDokumen16 halamanChapter Four: Memory OrganizationbelihuBelum ada peringkat
- Polymer MemoryDokumen27 halamanPolymer MemorysansureBelum ada peringkat
- Gain-Cell Embedded DRAMs for Low-Power VLSI Systems-on-ChipDari EverandGain-Cell Embedded DRAMs for Low-Power VLSI Systems-on-ChipBelum ada peringkat
- En PSR S950Dokumen2 halamanEn PSR S950Carlos FrancoBelum ada peringkat
- Sandisk 09132017 SanDisk COM-AUTO-INDUST DISTI LIN-1145140 PDFDokumen5 halamanSandisk 09132017 SanDisk COM-AUTO-INDUST DISTI LIN-1145140 PDFKelvin LimBelum ada peringkat
- Computer SportDokumen2 halamanComputer SportKhaerul QuBelum ada peringkat
- PPTDokumen12 halamanPPTajaydev2224Belum ada peringkat
- Flash Memory Design Pohang 2010-05-071Dokumen48 halamanFlash Memory Design Pohang 2010-05-071teomondo100% (1)
- Export Log 6.6.0.0034 2022-12-16Dokumen4 halamanExport Log 6.6.0.0034 2022-12-16ivoBelum ada peringkat
- H-1Dokumen18 halamanH-1altair_xmsBelum ada peringkat
- Flash MemoryDokumen15 halamanFlash MemoryCRT07Belum ada peringkat
- The Inventor of USB Flash DriveDokumen4 halamanThe Inventor of USB Flash Drivezue1411Belum ada peringkat
- Solid State Drive FAQ UsDokumen12 halamanSolid State Drive FAQ UsPatrick EwaltBelum ada peringkat
- Camera InvoiceDokumen1 halamanCamera InvoiceAlon BonehBelum ada peringkat
- C MAP Chart CompatibilityDokumen18 halamanC MAP Chart CompatibilityMartín Andrés GarcíaBelum ada peringkat
- Price ListDokumen98 halamanPrice ListVeaceslav Gheorghe VrabieBelum ada peringkat
- Burst 120GB Product SheetDokumen1 halamanBurst 120GB Product SheeterikbdBelum ada peringkat
- Datasheet XPG SX6000 Lite en 20190619Dokumen2 halamanDatasheet XPG SX6000 Lite en 20190619tiponatisBelum ada peringkat
- PS2134 64 Schematic Kingston DTDokumen3 halamanPS2134 64 Schematic Kingston DTluis_may22Belum ada peringkat
- 61 - Solid State DiskDokumen17 halaman61 - Solid State DiskManthan PandyaBelum ada peringkat
- Digital KaosDokumen1 halamanDigital KaosPoon Electronic Training CentreBelum ada peringkat
- Mascaras Componentes MotorolaDokumen12 halamanMascaras Componentes MotorolaWillian da FonsecaBelum ada peringkat
- I11 Immo Emu Renault CAN ENx SolDokumen21 halamanI11 Immo Emu Renault CAN ENx Solacb . bBelum ada peringkat
- Psa Modules Wiring Diagrams: Obd2 DB9Dokumen9 halamanPsa Modules Wiring Diagrams: Obd2 DB9Missoum TerrasBelum ada peringkat
- SSD A100 DatasheetDokumen2 halamanSSD A100 Datasheetrute silvaBelum ada peringkat
- Eprom Service BoschDokumen5 halamanEprom Service BoschRick Castillo0% (1)
- Improving Ceph Performance While Reducing Costs: Applications and Ecosystem Solutions Development Rick StehnoDokumen13 halamanImproving Ceph Performance While Reducing Costs: Applications and Ecosystem Solutions Development Rick StehnoDot-InsightBelum ada peringkat
- 實驗報告1Dokumen6 halaman實驗報告1SuzanneBelum ada peringkat
- Programcion Nortel-Avaya (Axsa) Aura Con Una PriDokumen520 halamanProgramcion Nortel-Avaya (Axsa) Aura Con Una Prirromeros3691Belum ada peringkat
- Guía ChiaDokumen25 halamanGuía ChiaxczcBelum ada peringkat