New Product Development: Entrepreneurship & Innovation
Diunggah oleh
vivekhanna4u0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
42 tayangan15 halamanThis document discusses new product development and entrepreneurship. It covers the new product development process, defining entrepreneurs as risk-taking innovators who create new opportunities and economic growth. It also examines the traits of successful entrepreneurs, sources of innovation both internal and external to companies, and models for diffusion of innovations from initial adoption to widespread use. Barriers to entrepreneurship like different types of risk and uncertainty are explored, as are goals and catalysts for entrepreneurial activity.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
IIPM_NPD_Lecture_1
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThis document discusses new product development and entrepreneurship. It covers the new product development process, defining entrepreneurs as risk-taking innovators who create new opportunities and economic growth. It also examines the traits of successful entrepreneurs, sources of innovation both internal and external to companies, and models for diffusion of innovations from initial adoption to widespread use. Barriers to entrepreneurship like different types of risk and uncertainty are explored, as are goals and catalysts for entrepreneurial activity.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
42 tayangan15 halamanNew Product Development: Entrepreneurship & Innovation
Diunggah oleh
vivekhanna4uThis document discusses new product development and entrepreneurship. It covers the new product development process, defining entrepreneurs as risk-taking innovators who create new opportunities and economic growth. It also examines the traits of successful entrepreneurs, sources of innovation both internal and external to companies, and models for diffusion of innovations from initial adoption to widespread use. Barriers to entrepreneurship like different types of risk and uncertainty are explored, as are goals and catalysts for entrepreneurial activity.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 15
New Product Development
Entrepreneurship & Innovation
Course Content
• Entrepreneurship & Innovation
• Opportunity Analysis
• New Product Development Process
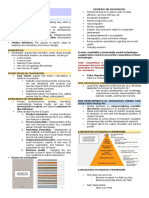
Who is Entrepreneur?
• Person
• keen & willing
• new idea/invention
• start a venture
• take risk
• force creative destruction/disruption
• CREATE NEW PATHS
eg of Entrepreneur
Types of Risk/Uncertainity
• Measurable : all required information is available and the
probability and impact of risk can be determined.
• Ambiguity : some information is available; but not complete
and hence, probability can not be determined, impact can be.
• True Uncertainity : no information is available, neither
probability nor the complete impact can be determined. Dark
Tunnel
Benefits of Entrepreneurship
• Financial Gains
• Increased jobs
• New Sectors, Industries
• Encourage more research
• Economic growth
Traits of Entrepreneur
• Self-confidence
• Need to Control and Direct.
• Sense of Urgency.
• Comprehensive Awareness
• Realistic Outlook
• Conceptual Ability
• Low Need for Status
• Objective Approach
• Emotional Stability
• Attraction to Challenges
• Describing with Numbers.
• Good health
Catalysts for Entrepreneurship
• What factors are required for entrepreneurship/entrepreneur
to flourish?
– Availability of Innovative Ideas
– Access to capital (at affordable cost)
– Conducive environment (PEST) to support innovation and
risk
– Competence of entrepreneur
Entrepreneurial Style of Management
• How can large organisations work like entrepreneurs?
– Innovation drive to be high
– Create independent units, companies for innovations
– Encourage risk taking ; avoid penalizing risk
– Hire entrepreneurial people
Innovation
New way of doing something (product/process/thinking)
– Incremental
– Radical or revolutionary
Invention: an idea made manifest and
Innovation: ideas applied successfully.
Goals of Innovation
• Creation of new markets
• Extension of the product range Increase Revenue
• Replacement of products/services
• Improved quality
• Reduced labour costs
• Improved production processes Decrease Cost
• Reduced materials
• Reduced energy consumption
• Reduced environmental damage Meet Social /legal
permission
• Conformance to regulations
Sources of Innovation
• R&D : breakthrough research, inventions.
• On the job : mostly incremental
• User needs
Sources of Innovation
Internal(to co./industry) External
• Unexpected event • Demographic change
• Incongruity • Changing perceptions
• Process need /values / beliefs
• Change in industry • New Knowledge /
technology
Linear model of Innovation
The Linear Model of Innovation is an early model of innovation that
suggests technical change happens in a linear fashion from
Invention to Innovation to Diffusion.
R&D (scientific research) has a priority as the basis of innovation,
and plays down the role of later players in the innovation process.
Diffusion of Innovation
Innovations may spread from the
innovator to other individuals and groups
Has a Life Cycle – ‘S’ shaped diffusion
curve
Growth is slow at the start
Increases rapidly with wider adoption
Plateaus or declines after most users
have adopted.
Next innovation in same arena may lead
to decline
Constant innovations needed –
successive ‘S’ curves
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Leadership On Change and Innovation (Part-Two)Dokumen29 halamanLeadership On Change and Innovation (Part-Two)HaileBelum ada peringkat
- Creativity & Innovation: Kalpana SinhaDokumen27 halamanCreativity & Innovation: Kalpana SinhatanishqdivBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To INNOVATIONDokumen25 halamanIntroduction To INNOVATIONSachin GalaBelum ada peringkat
- Creativity, Innovation and Methods To Initiate VenturesDokumen30 halamanCreativity, Innovation and Methods To Initiate VenturesVinay KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Innovation: - Definitions - Dimensions - Drivers - DevelopmentsDokumen10 halamanIntroduction To Innovation: - Definitions - Dimensions - Drivers - DevelopmentsSunil Kumar VemuriBelum ada peringkat
- Innovation and InventionsDokumen12 halamanInnovation and InventionsSarthak NamdevBelum ada peringkat
- Innovation ManagementDokumen5 halamanInnovation Managementاحلام سعيدBelum ada peringkat
- Creativity & Developing The Business Ideas: Developing New Products & Services Topic 7Dokumen28 halamanCreativity & Developing The Business Ideas: Developing New Products & Services Topic 7Siti AishahBelum ada peringkat
- Intro To InnovationDokumen10 halamanIntro To Innovationfnab@hotmail.comBelum ada peringkat
- ITIS407: Sources of InnovationDokumen24 halamanITIS407: Sources of InnovationTala Tala1999Belum ada peringkat
- Inovasi, Kreativitas Dan IntrapreneurshipDokumen14 halamanInovasi, Kreativitas Dan IntrapreneurshipMuhammad Rayhan RaspatiBelum ada peringkat
- Design Thinking NotesDokumen36 halamanDesign Thinking NotesSandyBelum ada peringkat
- Linking Creativity Entrepreneurship and InnovationDokumen40 halamanLinking Creativity Entrepreneurship and InnovationBENEDICTA SEYRAM GBEKUBelum ada peringkat
- It's in Our NatureDokumen12 halamanIt's in Our Naturerider_3821Belum ada peringkat
- Topic 1Dokumen17 halamanTopic 1Farah HaniBelum ada peringkat
- Gns203 Innovation and Product DevelopmentDokumen78 halamanGns203 Innovation and Product DevelopmentAdufe ogunbodeBelum ada peringkat
- Executing Innovation: Expert Solutions to Everyday ChallengesDari EverandExecuting Innovation: Expert Solutions to Everyday ChallengesBelum ada peringkat
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation: PG Diploma in Entrepreneur DevelopmentDokumen86 halamanEntrepreneurship & Innovation: PG Diploma in Entrepreneur DevelopmentPooja SreeBelum ada peringkat
- Innovation Ppt1Dokumen41 halamanInnovation Ppt1anuj singhBelum ada peringkat
- Innovative ManagementDokumen14 halamanInnovative ManagementFaisal IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- 1 InnovationTypesDokumen46 halaman1 InnovationTypesAli RazaBelum ada peringkat
- Applied Entrepreneurship Cueb 203 Presented by DR N. Msipah 0772396325Dokumen52 halamanApplied Entrepreneurship Cueb 203 Presented by DR N. Msipah 0772396325Blessed MatsvaiBelum ada peringkat
- ITM - ADokumen60 halamanITM - AFrancisco NormanBelum ada peringkat
- Creativity & Innovation ManagementDokumen41 halamanCreativity & Innovation ManagementShweta RanadiveBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Meeting - Intro To InnovationDokumen86 halaman1 Meeting - Intro To Innovationrameshncm50% (2)
- Report in Innovation Management 2Dokumen22 halamanReport in Innovation Management 2Orlando AlijarBelum ada peringkat
- Ch-2-Clock Speed Strategic and VCD PDFDokumen44 halamanCh-2-Clock Speed Strategic and VCD PDFazyad8246Belum ada peringkat
- Fromideastoinnovation 121220155726 Phpapp02Dokumen30 halamanFromideastoinnovation 121220155726 Phpapp02moneyheistberlin09Belum ada peringkat
- File 1665394784 0004339 Unit 2ofMBAintegratedDokumen11 halamanFile 1665394784 0004339 Unit 2ofMBAintegratedAditya KumarBelum ada peringkat
- M&O - 7 Entrepreneurship (Student)Dokumen56 halamanM&O - 7 Entrepreneurship (Student)annaBelum ada peringkat
- Ic Lo1Dokumen24 halamanIc Lo1Zilen SalamBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - Innovation ManagementDokumen29 halamanChapter 1 - Innovation ManagementSankary CarollBelum ada peringkat
- Sources of InnovationDokumen14 halamanSources of InnovationSouravBelum ada peringkat
- Creativity Innovation and Entrepreneurial Manager 1Dokumen20 halamanCreativity Innovation and Entrepreneurial Manager 1Darcy CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Ideation, Creativity & InnovationDokumen15 halamanIntroduction To Ideation, Creativity & InnovationWeiting LinBelum ada peringkat
- Entreprenuership: Meaning in French - Entreprendre Means "To Undertake"Dokumen36 halamanEntreprenuership: Meaning in French - Entreprendre Means "To Undertake"Abhishek SinghBelum ada peringkat
- BCOM1001 Seting Business EnterpriseDokumen17 halamanBCOM1001 Seting Business EnterpriseMuskan KaurBelum ada peringkat
- Innovation Matters Now - TaggedDokumen19 halamanInnovation Matters Now - TaggedSuriya PrasanthBelum ada peringkat
- Business Excellence: Arun Kumar DavayDokumen15 halamanBusiness Excellence: Arun Kumar Davaypuneet guptaBelum ada peringkat
- Creativity and Innovation ManagementDokumen27 halamanCreativity and Innovation Managementsavjot_khandpur139245Belum ada peringkat
- Workpsychologyppt 200831035253Dokumen64 halamanWorkpsychologyppt 200831035253Salma KanaanBelum ada peringkat
- Creativity and InnovationDokumen32 halamanCreativity and Innovationason fredBelum ada peringkat
- Diffusion of Innovation: BY Pooja Patnaik Debi Prasad Sahu Ajay Kumar KarDokumen27 halamanDiffusion of Innovation: BY Pooja Patnaik Debi Prasad Sahu Ajay Kumar Karpooja_patnaik237Belum ada peringkat
- Corporate Entrepreneurship: Small Business ManagementDokumen32 halamanCorporate Entrepreneurship: Small Business Managementsarge1986Belum ada peringkat
- KAM1061 Entrepreneurship 1: Nor Hafez Bin Mokhtaruddin 017-6010261Dokumen44 halamanKAM1061 Entrepreneurship 1: Nor Hafez Bin Mokhtaruddin 017-6010261Hoy Seng KokBelum ada peringkat
- Entrepreneurial Heuristics:: A Presentation byDokumen31 halamanEntrepreneurial Heuristics:: A Presentation byM.V.S.Kameshwar RaoBelum ada peringkat
- Entrep Chapter 4Dokumen22 halamanEntrep Chapter 4Arnel De Los SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Group 9Dokumen21 halamanGroup 9Rhea llyn BacquialBelum ada peringkat
- Dti Unit-IiiDokumen8 halamanDti Unit-IiiJayamangalaSristiBelum ada peringkat
- Session 1 Creative Thinking and Problem Solving Session 1 26th July 2017Dokumen33 halamanSession 1 Creative Thinking and Problem Solving Session 1 26th July 2017sujata dawadiBelum ada peringkat
- Entrep-Module 2-Part 1Dokumen2 halamanEntrep-Module 2-Part 1Nika MatammuBelum ada peringkat
- Unpuzzling Innovation: Mastering Innovation Management in a Structural WayDari EverandUnpuzzling Innovation: Mastering Innovation Management in a Structural WayPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Innovation Management: Munir HasanDokumen25 halamanInnovation Management: Munir HasanJunaid MiajeBelum ada peringkat
- Technology and Innovation 1Dokumen57 halamanTechnology and Innovation 1ლიზა ქისტაურიBelum ada peringkat
- Iintroduction EntreprenerushipDokumen49 halamanIintroduction Entreprenerushipsuvarna hiremathBelum ada peringkat
- Entrepreneurial Implications For StrategyDokumen23 halamanEntrepreneurial Implications For StrategyMuhammad AliBelum ada peringkat
- Entrepreneurship Full NotesDokumen173 halamanEntrepreneurship Full Notesalokshri2587% (377)
- Lorenz Curves and The Gini CoefficientDokumen13 halamanLorenz Curves and The Gini Coefficientvivekhanna4u100% (2)
- 7P - Service Industry (E-Tutorials)Dokumen28 halaman7P - Service Industry (E-Tutorials)vivekhanna4u100% (2)
- TATA Motors and TATA SteelDokumen13 halamanTATA Motors and TATA Steelvivekhanna4u67% (3)
- TATA Motors and TATA SteelDokumen28 halamanTATA Motors and TATA Steelvivekhanna4u100% (3)
- Michael Porter's Five Forces Analysis - TATA MotorsDokumen9 halamanMichael Porter's Five Forces Analysis - TATA Motorsvivekhanna4u75% (12)
- What Is Philosophy in Your Own Words EssayDokumen1 halamanWhat Is Philosophy in Your Own Words EssayВікторія НікітюкBelum ada peringkat
- HANDOUTS IN Trends Networks and Critical Thinking in The 21st Century PDFDokumen81 halamanHANDOUTS IN Trends Networks and Critical Thinking in The 21st Century PDFJEREMY ALAGAOBelum ada peringkat
- A Balanced Scorecard For Small BusinessDokumen8 halamanA Balanced Scorecard For Small BusinessmoussumiiBelum ada peringkat
- SPM English NotesDokumen22 halamanSPM English NotesAzimi Azmin100% (1)
- Group Work 1 1Dokumen21 halamanGroup Work 1 1hopeboyd36Belum ada peringkat
- 2023 RPT English Year 2Dokumen19 halaman2023 RPT English Year 2Gitanjli GunasegaranBelum ada peringkat
- English of Oral Communication (September 2020)Dokumen10 halamanEnglish of Oral Communication (September 2020)ESTRADABelum ada peringkat
- Math Lesson PlanDokumen36 halamanMath Lesson PlanCM SilarioBelum ada peringkat
- Emotional IntelligenceDokumen5 halamanEmotional Intelligenceapi-436999044Belum ada peringkat
- Loans Subject To VerificationDokumen49 halamanLoans Subject To Verificationapi-67201372Belum ada peringkat
- Customer-Centric Companies Are 60% More Profitable!Dokumen1 halamanCustomer-Centric Companies Are 60% More Profitable!Pham Van ThanhBelum ada peringkat
- Providing Educational Feedback: Higher Education ServicesDokumen8 halamanProviding Educational Feedback: Higher Education Servicesدكتور محمد عسكرBelum ada peringkat
- Intelligence: Psychological AssessmentDokumen31 halamanIntelligence: Psychological AssessmentKian LaBelum ada peringkat
- THE IMITATION GAME Teaching Guide Jim OttavianiDokumen2 halamanTHE IMITATION GAME Teaching Guide Jim OttavianiAbrams Books100% (2)
- DepEd ICT PoliciesDokumen2 halamanDepEd ICT PoliciesJessemar Solante Jaron Wao100% (14)
- Commerce Scheme Form 4Dokumen15 halamanCommerce Scheme Form 4methembe dubeBelum ada peringkat
- Professional Aspects of Teacher PreparationDokumen6 halamanProfessional Aspects of Teacher PreparationswethashakiBelum ada peringkat
- Child and AdolescenceDokumen11 halamanChild and AdolescenceXyZa EdlarecilBelum ada peringkat
- Meaning and Definitions of Group Dynamics - ImportanceDokumen3 halamanMeaning and Definitions of Group Dynamics - ImportanceanjicieflBelum ada peringkat
- References: BooksDokumen2 halamanReferences: BooksJohnpatrick DejesusBelum ada peringkat
- Socialization and Personality DevelopmentDokumen17 halamanSocialization and Personality Developmentmeck josephBelum ada peringkat
- Siegel-2009-American Journal of Political ScienceDokumen17 halamanSiegel-2009-American Journal of Political SciencearturassisBelum ada peringkat
- Czarniawska, Barbara Good Novels, Better Managment.Dokumen343 halamanCzarniawska, Barbara Good Novels, Better Managment.Carlos Roberto Zamora Bugueño0% (1)
- Maslow's Hierarchy of NeedsDokumen7 halamanMaslow's Hierarchy of NeedsMaan MaanBelum ada peringkat
- Ing GrisDokumen13 halamanIng GrisF & I creationBelum ada peringkat
- Empower Second Edition Starter ESOL MapDokumen10 halamanEmpower Second Edition Starter ESOL MaphgfbvdcsxBelum ada peringkat
- Reinventing Marketing Strategy by Recasting Supplier/customer RolesDokumen13 halamanReinventing Marketing Strategy by Recasting Supplier/customer RolesnitsBelum ada peringkat
- Training Writing Skills PDFDokumen26 halamanTraining Writing Skills PDFfirja praditiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Multiple Intelligences Test - Based On Howard Gardner's MI ModelDokumen3 halamanMultiple Intelligences Test - Based On Howard Gardner's MI Modeljoshua zabalaBelum ada peringkat
- Dissertation Overview - Therapeutic Landscaping - Ifrah TanweerDokumen22 halamanDissertation Overview - Therapeutic Landscaping - Ifrah TanweerifrahBelum ada peringkat