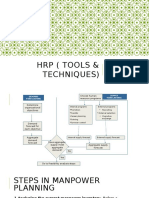
Human Resource Planning
Diunggah oleh
Rohit ChaudharyJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Human Resource Planning
Diunggah oleh
Rohit ChaudharyHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Human Resource Planning
ROHIT KUMAR
Human Resource Planning
Human Resource Planning
Human resource planning may be defined as a
strategy for the acquisition, utilization, improvement
& preservation of the human resource of the enterprise.
Specifically HRP is the process by which an organisation
ensures that it has the right no. & kind of people, at the
right places at the right time, capable of effectively
completing those tasks that will help the organisation
achieve its overall objective.
The major activities of HRP include:
– Forecasting
– Inventoring
– Anticipating
– Planning
Human Resource Planning
Human Resource Planning
• Human Resources Planning (HRP)
– Process of anticipating and making provision for the
movement (flow) of people into, within, and out of an
organization.
– HRP’s purpose is the effective deployment of human
resources through:
• Anticipating organizational labor supply and demand.
• Providing expanded employment opportunities for women,
minorities, and the disabled.
• Guiding the development and training the workforce.
Human Resource Planning
Objectives of HRP
• To ensure optimum use of human resources
currently employed
• To link HRP with Organizational planning
• To meet the need of expansion programmes
• To identify areas of surplus personnel or area
in which there is a shortage of personnel
• To determine recruitment levels
• To replace those who have grown old, retired, died
or become incapacitated because of
physical/mental ailment.
Human Resource Planning
Interaction Between Business Planning
& Human Resource Planning
Business Planning Human Resource Planning
Strategic planning Environmental scanning
Long range
Cor. Philosophy Labour supply analysis
Planning Labour force changes
Mission
Strengths & weakness Legal/regulatory agency changes
Forecasting
Operational planning
Middle range Projected personnel need by
Organisational goals & job category
Planning objective
Attrition
Budgeting Projected staffing requirement
Short range Budgets Surplus/deficit
Planning
Performance goals Succession Planning
Annual plans
Human Resource Planning
Human Resource Planning
Forecast
demand
for labor
Conduct analysis
Forecast
internal supply
of labor
Forecast
external
Develop plan to supply of
match demand labor
with supply
Human Resource Planning
Forecasting Employee Needs
• This requires estimation of the demand for labor that
answers these three questions:
– What employees will be needed in future
– What kinds of skills & talents will the employees need
– When will the new employees be needed
• Forecasting Employee Needs involves two quite
different time periods: short term forecasting & long
term forecasting.
Short Term Forecasting Long Term Forecasting
Budgeting Unit demand
Work-load Analysis Expert Opinion
Trend Projection
Human Resource Planning
Forecasting Demand for Employees
Quantitative
QuantitativeMethods
Methods
Forecasting
Forecasting Demand
Demand
Qualitative
QualitativeMethods
Methods
Human Resource Planning
Quantitative Approach: Trend Analysis
• Forecasting labor demand based on an organizational index
such as sales:
– Select a business factor that best predicts human resources
needs.
– Plot the business factor in relation to the number of
employees to determine the labor productivity ratio.
– Compute the productivity ratio for the past five years.
– Calculate human resources demand by multiplying the
business factor by the productivity ratio.
– Project human resources demand out to the target year(s).
Human Resource Planning
Example of Trend Analysis of HR
Demand
BUSINESS LABOR = HUMAN RESOURCES
FACTOR PRODUCTIVITY DEMAND
YEAR (SALES IN THOUSANDS) (SALES/EMPLOYEE) (NUMBER OF EMPLOYEES)
1997 $2,351 14.33 164
1998 $2,613 11.12 235
1999 $2,935 8.34 352
2000 $3,306 10.02 330
2001 $3,613 11.12 325
2002 $3,748 11.12 337
2003 $3,880 12.52 310
2004* $4,095 12.52 327
2005* $4,283 12.52 342
2006* $4,446 12.52 355
*Projected figures
Human Resource Planning
Qualitative Approaches to Demand
Forecasting
• Management Forecasts
– The opinions (judgments) of supervisors, department
managers, experts, or others knowledgeable about the
organization’s future employment needs.
• Delphi Technique
– An attempt to decrease the subjectivity of forecasts by
soliciting and summarizing the judgments of a preselected
group of individuals.
– The final forecast represents a composite group judgment.
Human Resource Planning
Forecasting Internal Labor Supply
The next step in developing a human resource
planning system is to analyze the organization's
present workforce which constitutes of :
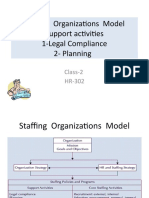
– Staffing Tables
– Markov Analysis
– Skill Inventories
– Replacement Charts
– Succession Planning
Human Resource Planning
Forecasting Internal Labor Supply
• Staffing Tables
– Graphic representations of all organizational jobs,
along with the numbers of employees currently
occupying those jobs and future (monthly or
yearly) employment requirements.
• Markov Analysis
– A method for tracking the pattern of employee
movements through various jobs.
Human Resource Planning
Forecasting Internal Labor Supply
• Skill Inventories
– Files of personnel education, experience, interests,
skills, etc., that allow managers to quickly match job
openings with employee backgrounds.
• Replacement Charts
– Listings of current jobholders and persons who are
potential replacements if an opening occurs.
• Succession Planning
– The process of identifying, developing, and tracking
key individuals for executive positions.
Human Resource Planning
An Executive Replacement Chart
Human Resource Planning
Projected Staffing
Requirements
• This analysis involves a comparison of the supply &
demand for labor as well as an assessment of how
many employees will leave.
– Net Projections
– Turnover Analysis
– Surplus Personnel
• Layoffs
• Attrition
• Reduced hours
• Early Retirements
– Management Succession & Development
Human Resource Planning
Human Resource Planning
Model
Forecasting Demand
Considerations
Considerations Techniques
Techniques
• •Product/service • •Trend
(Shortage)
Product/servicedemand
demand Trendanalysis
analysis
• •Technology • •Managerial Recruitment
Technology Managerialestimates
estimates
• •Financial
Financialresources
resources • •Delphi technique
Delphi technique
Full-time
• •Absenteeism/turnover
Absenteeism/turnover Part-time
• •Organizational
Organizationalgrowth
growth Recalls
• •Management philosophy
Management philosophy
Techniques
Techniques External
ExternalConsiderations
Considerations (Surplus)
• •Staffing
Staffingtables • •Demographic
Demographicchanges
tables changes Reductions
• •Markov
Markovanalysis • •Education
Educationofofthe
theworkforce
analysis
• •Skills inventories • •Labor Mobility
workforce Layoffs
Skills inventories Labor Mobility
• •Management • •Government Terminations
Managementinventories
inventories Governmentpolicies
policies
• •Replacement
Replacementcharts
charts • •Unemployment
Unemploymentrate rate
Demotions
• •Succession
SuccessionPlanning
Planning Retirements
Forecasting Supply
Human Resource Planning
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- HR Planning GuideDokumen49 halamanHR Planning GuideSadman Shihab ChoudhuryBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource Planning OR Manpower PlanningDokumen13 halamanHuman Resource Planning OR Manpower PlanningimadBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource Planning: Robert L. Mathis John H. JacksonDokumen15 halamanHuman Resource Planning: Robert L. Mathis John H. JacksonPriyanka NayakBelum ada peringkat
- Mod 2 Human Resource PlanningDokumen26 halamanMod 2 Human Resource PlanningAnubhab GhoshBelum ada peringkat
- HR Planning EssentialsDokumen31 halamanHR Planning EssentialsHANY SALEMBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource Planning: DR Premalatha.P Adhoc SH&M Nit ApDokumen36 halamanHuman Resource Planning: DR Premalatha.P Adhoc SH&M Nit ApSushma NelapatiBelum ada peringkat
- 4 - HRPDokumen17 halaman4 - HRPParthBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 - Human Resource PlanningDokumen44 halamanChapter 2 - Human Resource PlanningFaiz ZakariaBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource PlanningDokumen34 halamanHuman Resource PlanningKunal BeheraBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resources PlanningDokumen30 halamanHuman Resources Planningsuraj_iamsingleBelum ada peringkat
- HRP Demand and Supply ForecastsDokumen52 halamanHRP Demand and Supply Forecastsnoel gonsalvesBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource PlanDokumen30 halamanHuman Resource PlanEmmnualBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource PlanningDokumen27 halamanHuman Resource PlanningAbhishek Acharya100% (1)
- Human Resource Planning: Objectives Need & Importance ProcessDokumen50 halamanHuman Resource Planning: Objectives Need & Importance ProcesssdsBelum ada peringkat
- HR Planning and Job Analysis: Vanitha Chadha Deptt. of CommerceDokumen33 halamanHR Planning and Job Analysis: Vanitha Chadha Deptt. of CommerceAzhar KhanBelum ada peringkat
- HRM CH 2Dokumen44 halamanHRM CH 2ayda aliBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource PlanningDokumen23 halamanHuman Resource PlanningPriyanka SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource Planning Human Resource Planning Human Resource Planning Human Resource PlanningDokumen15 halamanHuman Resource Planning Human Resource Planning Human Resource Planning Human Resource Planningsam_sumit67% (3)
- Human Resource PlanningDokumen22 halamanHuman Resource Planninggourab mohapatraBelum ada peringkat
- Manpower Planning & Job AnalysisDokumen25 halamanManpower Planning & Job Analysismanoj54065Belum ada peringkat
- 2.2.1 Human Resource PlaningDokumen25 halaman2.2.1 Human Resource PlaningTewodros TadesseBelum ada peringkat
- HRM Chapter 2Dokumen11 halamanHRM Chapter 2Fatikchhari USOBelum ada peringkat
- Forecasting Human Resource NeedsDokumen30 halamanForecasting Human Resource NeedsNidhinraj Menon75% (4)
- Chapter 2Dokumen28 halamanChapter 2Hoài NhưBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2: Human Resource: Strategic PlanningDokumen20 halamanUnit 2: Human Resource: Strategic PlanningRA T NA BCBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 - HRA&RDokumen60 halamanUnit 2 - HRA&RanuradhakampliBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 - The Acquisition of Human ResourceDokumen57 halamanChapter 4 - The Acquisition of Human ResourceafityzolaBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource PlanningDokumen13 halamanHuman Resource PlanningAilyn Laurente MosquitoBelum ada peringkat
- 6th Nov - HR Coursework Day 2Dokumen71 halaman6th Nov - HR Coursework Day 2saharsh narangBelum ada peringkat
- Zora Nayaka Widyadhana - HUMAN RESOURCES PLANNINGDokumen4 halamanZora Nayaka Widyadhana - HUMAN RESOURCES PLANNINGZora Nayaka WidyadhanaBelum ada peringkat
- HR PlanningDokumen27 halamanHR PlanningarchitBelum ada peringkat
- Screenshot 2022-11-04 at 7.01.17 PMDokumen16 halamanScreenshot 2022-11-04 at 7.01.17 PMrockBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource Planning: Prof. RajasshrieDokumen36 halamanHuman Resource Planning: Prof. RajasshriepgundechaBelum ada peringkat
- HRM Lesson 1Dokumen15 halamanHRM Lesson 1Christian Bryan CuencoBelum ada peringkat
- HRMP - Session 4 - Human Resource PlanningDokumen13 halamanHRMP - Session 4 - Human Resource PlanningviewpawanBelum ada peringkat
- HRM lecture 3Dokumen25 halamanHRM lecture 3hossamBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT - 2 Human Resource PlanningDokumen19 halamanUNIT - 2 Human Resource PlanningEshaan ChadhaBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resourse PlaningDokumen49 halamanHuman Resourse PlaningarrpitBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource Planning Process: Slide Editing By: Mursyida MahsharDokumen25 halamanHuman Resource Planning Process: Slide Editing By: Mursyida MahsharMa Hdi ChoudhuryBelum ada peringkat
- #3 HRMDokumen4 halaman#3 HRMApril AcedoBelum ada peringkat
- HRP PDFDokumen36 halamanHRP PDFArnav ShresthaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 19-24Dokumen86 halamanLecture 19-24Mayuri Chauray-shindeBelum ada peringkat
- HRM Module 4Dokumen30 halamanHRM Module 4shaziafirdoosBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 7 HRM HRPDokumen24 halamanLec 7 HRM HRPShrenik SethiaBelum ada peringkat
- HRP (Tools & Techniques) Chapt 3 Part 2Dokumen12 halamanHRP (Tools & Techniques) Chapt 3 Part 2vidsrinivasBelum ada peringkat
- HR Planning & Recruitment InsightsDokumen42 halamanHR Planning & Recruitment InsightsanshariBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 - HRPDokumen23 halamanChapter 2 - HRPElla MoonstoneBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource ManagementDokumen33 halamanHuman Resource Managementhewia1921Belum ada peringkat
- RVU Part 2Dokumen33 halamanRVU Part 2Hiwot NimanieBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource Planning: Definition of HRP Importance of HRP Process of HRP Factors Affecting HRP Barriers To HRPDokumen24 halamanHuman Resource Planning: Definition of HRP Importance of HRP Process of HRP Factors Affecting HRP Barriers To HRPvipin goyal83% (6)
- 2.2.1 Human Resource Planing (2) IDokumen25 halaman2.2.1 Human Resource Planing (2) IhayelomBelum ada peringkat
- CH 02Dokumen10 halamanCH 02Rashique Ul LatifBelum ada peringkat
- DR - Kiran - Implementation Strategy of HRP-finalDokumen76 halamanDR - Kiran - Implementation Strategy of HRP-finalSheilla Mae CalambaBelum ada peringkat
- Staffing Class 2Dokumen18 halamanStaffing Class 2Mehdi MohmoodBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Human Resource Planning (SHRP) : Dr. Vaneeta AggarwalDokumen44 halamanStrategic Human Resource Planning (SHRP) : Dr. Vaneeta AggarwalbosskeyBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource Management StudyMaterial 21-03-2023 1679383987Dokumen16 halamanHuman Resource Management StudyMaterial 21-03-2023 1679383987vanshika S.22.24Belum ada peringkat
- Manpower Planning PDFDokumen11 halamanManpower Planning PDFTushar PachlangiaBelum ada peringkat
- Manpower PlanningDokumen11 halamanManpower PlanningPooja VishnoiBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource PlanningDokumen22 halamanHuman Resource PlanningAldrich Theo MartinBelum ada peringkat
- Solutions for Forecasting Manpower Needs in an Organization!Dari EverandSolutions for Forecasting Manpower Needs in an Organization!Belum ada peringkat
- Training & DevelopmentDokumen42 halamanTraining & DevelopmentRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Rohit Dissertation ReportDokumen64 halamanRohit Dissertation ReportRohit Chaudhary75% (4)
- Behavioral Event Interview TechniquesDokumen14 halamanBehavioral Event Interview TechniquesRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Fake PHDDokumen9 halamanFake PHDRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Notes On Computer Networks Unit5Dokumen9 halamanNotes On Computer Networks Unit5Rohit Chaudhary100% (2)
- PF Calculation SheetDokumen3 halamanPF Calculation SheetRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource Management: Recruitment & Selection Rohit KumarDokumen35 halamanHuman Resource Management: Recruitment & Selection Rohit KumarRohit Chaudhary100% (1)
- Strategic Human Resource Management: Rohit KumarDokumen30 halamanStrategic Human Resource Management: Rohit KumarRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Personnel Planning and Recruiting: Gary DesslerDokumen34 halamanPersonnel Planning and Recruiting: Gary DesslerRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Payroll - Celestial Labs LimitedDokumen2 halamanPayroll - Celestial Labs LimitedlegendleosivaBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource ManagementDokumen22 halamanHuman Resource ManagementRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Notes On Computer Networks Unit4Dokumen12 halamanNotes On Computer Networks Unit4Rohit Chaudhary67% (3)
- Performance Management System: Rohit KumarDokumen34 halamanPerformance Management System: Rohit KumarRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- EID PF No. Name: Interest CalculationDokumen1 halamanEID PF No. Name: Interest CalculationRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- CTC StructureDokumen1 halamanCTC StructureRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Calculation PFDokumen4 halamanCalculation PFRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Labour Laws New NOTESDokumen17 halamanLabour Laws New NOTESRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Notes On Computer Networks Unit 3Dokumen13 halamanNotes On Computer Networks Unit 3Rohit Chaudhary83% (6)
- Notes On Computer Networks Unit1Dokumen14 halamanNotes On Computer Networks Unit1Rohit Chaudhary100% (4)
- T 13 MergesortDokumen36 halamanT 13 MergesortRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- An HR Manager Can Become A CeoDokumen9 halamanAn HR Manager Can Become A CeoRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Notes On Computer Networks Unit 2Dokumen14 halamanNotes On Computer Networks Unit 2Rohit Chaudhary100% (2)
- SortingDokumen31 halamanSortingRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- QuicksortDokumen67 halamanQuicksortwiflerBelum ada peringkat
- COSC 3101A - Design and Analysis of Algorithms 3: Recurrences Master's Method Heapsort and Priority QueueDokumen68 halamanCOSC 3101A - Design and Analysis of Algorithms 3: Recurrences Master's Method Heapsort and Priority QueueRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- NBFC'S: Made byDokumen23 halamanNBFC'S: Made byRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Quick-Sort 1 © 2004 Goodrich, TamassiaDokumen17 halamanQuick-Sort 1 © 2004 Goodrich, TamassiaRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- In This Session, You Will Learn To:: ObjectivesDokumen39 halamanIn This Session, You Will Learn To:: ObjectivesRohit ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Quick SortDokumen3 halamanQuick SortJaswinderBelum ada peringkat
- M. Abdul Awal TQM in The Construction IndustryDokumen10 halamanM. Abdul Awal TQM in The Construction Industryammar_raza1905Belum ada peringkat
- Model of Heavy Work InvestmentDokumen12 halamanModel of Heavy Work InvestmentaBelum ada peringkat
- BRMDokumen34 halamanBRManil_049Belum ada peringkat
- Autosys JobDokumen26 halamanAutosys JobkondalraodBelum ada peringkat
- UCSP EssayDokumen1 halamanUCSP EssayLovely SalvatierraBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study On Employees Retention in Summit BankDokumen5 halamanCase Study On Employees Retention in Summit BankHaniya KhanBelum ada peringkat
- 2017-01 Brent Cross Cricklewood CPO No.3 Statement of CaseDokumen37 halaman2017-01 Brent Cross Cricklewood CPO No.3 Statement of CasescribdstorageBelum ada peringkat
- CH 01Dokumen2 halamanCH 01Sandeep Kumar PalBelum ada peringkat
- Role of Public & Private Sector in IndiaDokumen13 halamanRole of Public & Private Sector in IndiaAppan Kandala Vasudevachary50% (2)
- Train Infographic Income Tax 01102018Dokumen3 halamanTrain Infographic Income Tax 01102018John Elnor Pable JimenezBelum ada peringkat
- Educational Consultant India Limited (EdCIL) Recruitment 2014 - Executive Assistant VacanciesDokumen4 halamanEducational Consultant India Limited (EdCIL) Recruitment 2014 - Executive Assistant Vacanciessureshreddy1234Belum ada peringkat
- Module in Fabm 1: Department of Education Schools Division of Pasay CityDokumen6 halamanModule in Fabm 1: Department of Education Schools Division of Pasay CityAngelica Mae SuñasBelum ada peringkat
- Data AnalyticsDokumen11 halamanData AnalyticsSatyam TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- Labor Law Review-Assignment No. 6Dokumen104 halamanLabor Law Review-Assignment No. 6ptdwnhroBelum ada peringkat
- Nilsson 2012Dokumen22 halamanNilsson 2012Aiftinca AdinaBelum ada peringkat
- Aligning Industry Certs with DAWIA QualsDokumen55 halamanAligning Industry Certs with DAWIA Qualsbaynte nwebeBelum ada peringkat
- Contractor Employee Biographical Data Sheet: Code)Dokumen2 halamanContractor Employee Biographical Data Sheet: Code)Grey BarralBelum ada peringkat
- Form13 Application To Transfer-Out PF To New CompanyDokumen2 halamanForm13 Application To Transfer-Out PF To New Companyshail daveBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8Dokumen20 halamanChapter 8keshav TyagiBelum ada peringkat
- LABREL Digests Week 4 COMPLETEDokumen62 halamanLABREL Digests Week 4 COMPLETEMetha DawnBelum ada peringkat
- Discrimination Against Disabled Job Candidates ExposedDokumen3 halamanDiscrimination Against Disabled Job Candidates Exposeddigimon123Belum ada peringkat
- AgencyDokumen33 halamanAgencyJustine Louise Bravo FerrerBelum ada peringkat
- BSBDIV501 in Class Activity Class ActivityDokumen3 halamanBSBDIV501 in Class Activity Class ActivityÇrox Rmg PunkBelum ada peringkat
- Connext BPO and The Philippines 1Dokumen10 halamanConnext BPO and The Philippines 1Ricky HagosBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource Management Practices in The Multinational Company: A Test of System, Societal, and Dominance EffectsDokumen32 halamanHuman Resource Management Practices in The Multinational Company: A Test of System, Societal, and Dominance EffectsMd. Mahin MiaBelum ada peringkat
- Salary Statement 10 01 2018Dokumen7 halamanSalary Statement 10 01 2018lewin neritBelum ada peringkat
- Cap 47-03 Workmens Compensation BotswanaDokumen24 halamanCap 47-03 Workmens Compensation BotswanaGarnette ChipongweBelum ada peringkat
- Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500: St. Paul University PhilippinesDokumen58 halamanTuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500: St. Paul University Philippinesmarchelly simon0% (1)
- Security Officer Job Description: Duties, Skills & ResponsibilitiesDokumen10 halamanSecurity Officer Job Description: Duties, Skills & ResponsibilitiesBC LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Job Interview Matching: CCSF EL Civics 2009 2010Dokumen13 halamanJob Interview Matching: CCSF EL Civics 2009 2010David DaemmejBelum ada peringkat