Aux Power Saving
Diunggah oleh
rs_the0129Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Aux Power Saving
Diunggah oleh
rs_the0129Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ENERGY AUDIT OF AUXILIARY POWER CONSUMPTION
ATAR SINGH Dy. DIRECTOR NPTI FARIDABAD
Energy Conservation in Power Utility
Power plant produces electrical energy
and also consumes a substantial amount of energy in the form of auxiliary consumption required for various plant equipments and services
Energy Conservation in Power Utility
Achieved mainly by:
Operating the equipments at maximum efficiency and Reduction of auxiliary Power consumption
The auxiliary power consumption (APC) varies from 6-14% ,
depending on Size of plant ,use of TDBFP &age of plant The 500 MW units register the least APC, largely due to the incorporation of TDBFP. In some of the old 110 MW plants, APC consumption of 14% is also observed. Energy audit in a vast thermal power station (TPS) is better tackled when the thermal power plant operations are segregated into different sub-areas like: main plant auxiliaries, draft system (consisting of ID/FD/PA fans), feed water system [consisting of Boiler Fed Pumps (BFPs) / Condensate Extraction Pumps (CEPs), Circulating Water (CW) system-including Cooling Tower (CTs)], and off sites (consisting of coal handling plants, ash handling plants, air compressors, AC plants, station lightings etc.).
APC Scenario In India
Auxiliary Power Consumption in Thermal
Power Plant is major source of energy consumption. During the financial year 2007-08 total generation by coal plant was 488157.46 MUs with PLF 78.75. Auxiliary Power Consumption was 8.17%. If this APC gets reduced only by 0.17% then it is equivalent to fresh capacity addition of 120 MW without any investment.
Trombay Station of Tata Power Co. Ltd achieved lowest
auxiliary power consumption (4.30%) in the country. Among Central Sector Stations, Talcher STPS of NTPC achieved the lowest auxiliary power consumption (5.34%).
Among State Sector Stations, Chandrapur STPS of MAHAGENCO achieved the lowest auxiliary power consumption (7.40%). Among different capacity groups, the lowest auxiliary power consumption was 6.13% in 500 MW group.
Requirement of works power with load
Factors Affecting Auxiliary Power Consumption
- Unit Generation and load Pattern - Operation of Plant Auxiliaries - Service auxiliary such as Illumination , air conditioning - Unit Startup / shutdown
STEPS INVOLVED IN CONDUCTING ENERGY AUDIT
Data collection Measurements & Observations Exploration for energy conservation measures Report preparation
STEPS INVOLVED IN CONDUCTING ENERGY AUDIT
DATA COLLECTION
Motor details requiredID code, Application, Make, Brief details of driven equipment, Type of the Motor, Motor kW, Motor frame, Duty, Rated RPM, Rated p.f., Rated motor efficiency ,Motor make, Motor voltage, Rated current of motor, Year, Operating hours, Energy meter installed or Not times the motor is rewound
, No. of
Collect the above information for all motors to be covered in the energy audit. Collect the motor efficiency curves
STEPS INVOLVED IN CONDUCTING ENERGY AUDIT
Instruments Required Power Analyzer: Used for measuring electrical parameters
such as kW, kVA, pf, V, A and Hz Infrared pyrometer (In case any heating of cable or motor is suspected) Stroboscope: To measure the speed of the driven equipment and motor The above instruments can be used in addition to the calibrated online / plant instruments
STEPS INVOLVED IN CONDUCTING ENERGY AUDIT
Parameters to be measured Energy consumption pattern of motors (daily / monthly
/yearly consumption if available) Motor electrical parameters (kW, kVA, Pf, A, V, Hz, etc.) for individual motors Equipment operational details
While conducting the measurement or performance
evaluation of any system simultaneously, the following need to be noted Unit load of the plant Date & time of measurement Instruments used for measurement Frequency of the measurement
STEPS INVOLVED IN CONDUCTING ENERGY AUDIT
MEASUREMENTSAND OBSERVATIONS
System details
Detailed interactions with the plant personnel
Energy consumption Pattern
If the plant is monitoring the energy consumption, it is suggested to record the data and monitor the daily and monthly consumption pattern
STEPS INVOLVED IN CONDUCTING ENERGY AUDIT
Equipment Annual Consumption MWH Average Load KW % of Total Generation % of total APC
Air Compressors Coal Handling Plant
Raw Water pumps DM water pumps A/C systems ESP Total
STEPS INVOLVED IN CONDUCTING ENERGY AUDIT
Equipment Annual Consumption MWH Average Load KW % of Total Generation % of total APC
Boiler Feed Pump Condensate extraction Pump CW Pumps ID Fans FD Fans PA Fans Mils CT Fans
STEPS INVOLVED IN CONDUCTING ENERGY AUDIT
Total Generation Auxiliary Power Consumption Contribution To APC By BFP's CEP's FD's ID's PA's Coal Mills CHP AHP Air Compressors Others (CWPs, RWPs, DM Plant, etc ) Unit 1 MW 4.52 0.43 0.35 2.26 2.31 1.21 0.57 0.47 0.42 3.89 % 2.78 0.26 0.22 1.38 1.41 0.74 0.35 0.29 0.26 2.37 Unit 2 MW 4.29 0.43 0.31 2.08 2.38 1.53 0.57 0.47 0.42 4.21 % 2.98 0.30 0.22 1.44 1.65 1.06 0.39 0.33 0.29 2.92 MW 1305.57 111.7 Unit 3 MW 4.52 0.41 0.30 2.34 2.36 1.69 0.57 0.47 0.42 4.11 % 3.39 0.31 0.23 1.51 1.52 1.08 0.36 0.30 0.27 2.64 Unit 4 MW 1.69 1.21 8.18 4.85 2.92 1.11 0.52 0.38 10.28 % 0.45 0.29 2.24 1.34 0.81 0.31 0.14 0.11 2.84 % 81.60 (of installed capacity) 8.56 (of actual generation) Unit 5 MW 1.78 1.26 7.25 4.82 2.92 1.11 0.52 0.38 10.22 % 0.42 0.29 1.51 1.00 0.61 0.23 0.11 0.08 2.13 Over All MW 13.34 4.73 3.43 22.12 16.72 10.25 3.92 2.45 2.04 32.70 % 1.02% 0.36% 0.26% 1.69% 1.28% 0.79% 0.30% 0.19% 0.16% 2.50%
Total 16.42
10.06
16.67
11.58
17.18
11.61
31.14
8.53
30.26
6.38
111.70
8.56%
Motor loading survey
Details Rated Kw Rated Efficiency Rated Speed Measurement of parameters Power factor kVA KW drawn Frequency Harmonics Motor speed Driven Voltage Current Power equipment speed Driven equipment parameters Operational observations Transmission % loading on the motor
STEPS INVOLVED IN CONDUCTING ENERGY AUDIT
Motor loading can be estimated by:
Loading =
Input kW to motor x 100 --------------------------------------------------------------------Name plate kW /Name plate full load motor efficiency
STEPS INVOLVED IN CONDUCTING ENERGY AUDIT
While conducting motor load survey,
observations on machine side:
parameters such as speed, load, pressure, temperature, etc., (as relevant) are also taken
availability of load-end capacitors for PF
correction & energy meters for monitoring is also looked into for each case.
STEPS INVOLVED IN CONDUCTING ENERGY AUDIT
Motor Rewinding History
comparison of no load current and stator resistance per phase of a rewound motor with the original no-load current and stator resistance at the same voltage can be one of the indicators to assess the efficacy of rewinding.
STEPS INVOLVED IN CONDUCTING ENERGY AUDIT
Power Factor Correction
Induction motors are characterized by power factors less than unity, leading to lesser efficiency (higher overall operating cost) associated with a plant's electrical system.
Capacitors connected in parallel (shunted) with the motor are typically used to improve the power factor
The impacts of PF correction include reduced kVA drawn , KVAR & current, reduction of transformer load, Reduction of cable losses, reduction of switch gear rating, Enhanced life of equipment
STEPS INVOLVED IN CONDUCTING ENERGY AUDIT
EXPLORATION OF ENERGY CONSERVATION
MEASURES Replacement / sizing of motors Opting for energy efficient motors, Use of high efficiency motors, Use of energy efficient transmission Replacement of pulleys Direct coupling
STEPS INVOLVED IN CONDUCTING ENERGY AUDIT
Analysis of observations o o
Loading pattern % loading Comments of power supply quality
The BIS standards specify that a motor should be capable of delivering its rated output with a voltage variation of 6 % and frequency variation of 3 %. Motor o Identified motors with less than 50 % loading, 50 75 % loading, 75- 100 % loading, over 100 % loading o Identified motors with machine side losses / inefficiencies like idle operations, throttling/damper operations o Motor load survey is aimed not only as a measure to identify motor efficiency areas but equally importantly, as a means to check combined efficiency of the motor, driven machine and controller
AUXILIARY POWER CONSUMPTION
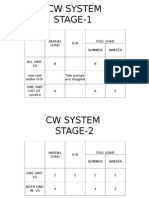
Operating only 4 mills instead of 5 mills in 210 MW units Shutting of CTs cells in conjunction with favorable weather
conditions and replacing existing aluminum cast and GRP blades with FRP
avoiding idle running of conveyors & crushers
incorporating soft starter - energy savers etc.
AUXILIARY POWER CONSUMPTION
STRATEGY
Variable frequency drive for PA Fans & ID Fans & CEPs
Air in-leaks in draft system (O2 measurement) blanketing Replacement of inefficient BFPs as a part of R& M of the old plants. Clipping of one stage from the multi stage BFPs to balance the pressure drop requirements between HP heaters, economizer and boiler drum etc. Use of higher pressure in the deareator to commensurately reduce BFP power consumption (reduced head developed) Running of two CEPs instead of 3 CEPs (3 CEPs are run to avoid tripping due to lower frequency in some of the power plants) Application of variable speed drives Installation of hydraulic turbine instead of feed regulating section to avoid pressure drops and to generate additional power
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Apc PPT PDFDokumen15 halamanApc PPT PDFrasiganeshBelum ada peringkat
- Presented By: Souvanik Chakravorty S Anil Kumar Tatithuri G SrikantDokumen30 halamanPresented By: Souvanik Chakravorty S Anil Kumar Tatithuri G Srikants anil kumar tatithuriBelum ada peringkat
- CEP - SavingDokumen6 halamanCEP - SavingManoj UpadhyayBelum ada peringkat
- Auxiliary Power Consumption Reduction in Thermal Power StationsDokumen3 halamanAuxiliary Power Consumption Reduction in Thermal Power StationsbarunBelum ada peringkat
- Operation Best PracticesDokumen30 halamanOperation Best Practicesjp mishraBelum ada peringkat
- To Reduce Auxiliary PowerDokumen15 halamanTo Reduce Auxiliary PowerMohit GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- 01 Boiler Design General (Compatibility Mode) PDFDokumen82 halaman01 Boiler Design General (Compatibility Mode) PDFTaraknath MukherjeeBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Rate Recovery PlanDokumen31 halamanHeat Rate Recovery PlanGopal Chandra SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Air Pre-Heater: - An Essential Component in Fossil Fuel Fired PlantDokumen66 halamanAir Pre-Heater: - An Essential Component in Fossil Fuel Fired PlantRaushan Kumar100% (1)
- Difficulties FacedDokumen6 halamanDifficulties FacedJackSparrow86Belum ada peringkat
- Aux Power OptimisationDokumen18 halamanAux Power Optimisationjp mishraBelum ada peringkat
- BHEL FANS - Best Operation PracticesDokumen19 halamanBHEL FANS - Best Operation Practiceshonchoabhi100% (1)
- SSTPS LMI On Optimaization of Ash Water Utilaization Revision-2 - Agupta SirDokumen18 halamanSSTPS LMI On Optimaization of Ash Water Utilaization Revision-2 - Agupta SirGautamupadhyayBelum ada peringkat
- TARIFF DESIGN For GENERATING STATIONSDokumen16 halamanTARIFF DESIGN For GENERATING STATIONSNaveen Chodagiri100% (1)
- Final Ea R-Infra Dahanu TpsDokumen84 halamanFinal Ea R-Infra Dahanu TpsLakshmi NarayanBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Rate ImprovementDokumen25 halamanHeat Rate ImprovementRanjeet KumarBelum ada peringkat
- LMI-Flexible Operation of Dadri Coal Fired UnitsDokumen8 halamanLMI-Flexible Operation of Dadri Coal Fired Unitssumit kontBelum ada peringkat
- 115 Flexibility Report WEBDokumen116 halaman115 Flexibility Report WEBThanasate PrasongsookBelum ada peringkat
- APC EEC WorkshopDokumen35 halamanAPC EEC WorkshopLalatendu PattanayakBelum ada peringkat
- 0 - Best Practices in Thermal Power Stations in IndiaDokumen186 halaman0 - Best Practices in Thermal Power Stations in IndiaRajesh RanjanBelum ada peringkat
- Coal Management SystemDokumen12 halamanCoal Management SystemBiswajit DuttaBelum ada peringkat
- Air Leak in Test of Esp ProcedureDokumen5 halamanAir Leak in Test of Esp Procedurenetygen1Belum ada peringkat
- PDFDokumen33 halamanPDFsourav mahapatraBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Audit Methodology For For Turbine Cycle: S.V.Malpe Dy - Director NPTI, NagpurDokumen34 halamanEnergy Audit Methodology For For Turbine Cycle: S.V.Malpe Dy - Director NPTI, Nagpurs anil kumar tatithuri100% (2)
- Spturbine Rolling CriteriasDokumen26 halamanSpturbine Rolling CriteriasSANDEEP PATEL100% (1)
- Cep 1Dokumen17 halamanCep 1Nilamani Umashankar Jena100% (1)
- Why Efficiency in Thermal Power Plant Is LowDokumen1 halamanWhy Efficiency in Thermal Power Plant Is LowNallathambiBelum ada peringkat
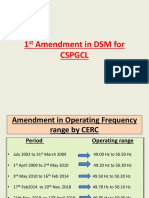
- 1 Amendment in DSM For CSPGCLDokumen19 halaman1 Amendment in DSM For CSPGCLashish jainBelum ada peringkat
- TG Referal DatapediaDokumen20 halamanTG Referal Datapediajp mishraBelum ada peringkat
- Major Overhauling of Boiler and Auxiliaries of U 4Dokumen32 halamanMajor Overhauling of Boiler and Auxiliaries of U 4appireddy_scribdBelum ada peringkat
- SESI-TSPL-OPN-SOP-BTG-012 (APH Fire)Dokumen9 halamanSESI-TSPL-OPN-SOP-BTG-012 (APH Fire)sourav mahapatraBelum ada peringkat
- CEP SamalkotDokumen96 halamanCEP SamalkotkukugargBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Feed WaterDokumen9 halamanAnalysis of Feed Watersanju0156Belum ada peringkat
- Unit Shut Down ProcedureDokumen41 halamanUnit Shut Down ProcedurePuspaanjaliBelum ada peringkat
- LMI For Internal AuditsDokumen16 halamanLMI For Internal Auditspreetivishwakarma100% (1)
- Power Plant - 180 - 09 - JSW - Energy - Ratnagiri - 0Dokumen37 halamanPower Plant - 180 - 09 - JSW - Energy - Ratnagiri - 0singhishpal24374Belum ada peringkat
- 02 Boiler Design in General - Part 2Dokumen70 halaman02 Boiler Design in General - Part 2sriramojBelum ada peringkat
- Gen-Seal&cool-New - 500 MWDokumen98 halamanGen-Seal&cool-New - 500 MWharisankar100% (2)
- 2.final Energy EfficiencyDokumen29 halaman2.final Energy EfficiencyVandana VanuBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of Coal QualityDokumen17 halamanEffect of Coal QualityAmit AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- 1-Introduction To Advanced in Power Plant ChemistryDokumen22 halaman1-Introduction To Advanced in Power Plant Chemistrybharath attaluriBelum ada peringkat
- COal Fired Plants FlexibilityDokumen32 halamanCOal Fired Plants FlexibilityVeerabhadra Rao KorimilliBelum ada peringkat
- 03 Combustion & Combustion Tuning Part 3Dokumen231 halaman03 Combustion & Combustion Tuning Part 3sriramojBelum ada peringkat
- Session 2 - 01 (Energy Efficiency Potential Assessment of Chandrapura TPS, DVC)Dokumen52 halamanSession 2 - 01 (Energy Efficiency Potential Assessment of Chandrapura TPS, DVC)pkumarBelum ada peringkat
- Research in Varying Burner Tilt Angle To Reduce Rear Pass Temperature in Coal Fired BoilerDokumen9 halamanResearch in Varying Burner Tilt Angle To Reduce Rear Pass Temperature in Coal Fired BoilerraitoBelum ada peringkat
- 500mw Checking and Setting of Hydraulic and ElectroDokumen15 halaman500mw Checking and Setting of Hydraulic and Electrothangarajm1984Belum ada peringkat
- Flue Gas System-2Dokumen56 halamanFlue Gas System-2SamBelum ada peringkat
- Powerplant PerformanceDokumen161 halamanPowerplant PerformancePhanindra Kumar J100% (1)
- Partial Load O/H Full Load Summer WinterDokumen19 halamanPartial Load O/H Full Load Summer WinterNitin SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Required in Kcal For Unit Generation of ElectricityDokumen18 halamanHeat Required in Kcal For Unit Generation of ElectricityAyan ChattarajBelum ada peringkat
- Black Out Is Land OperationDokumen41 halamanBlack Out Is Land Operationstubborn002Belum ada peringkat
- Front & Rear Wall BoilerDokumen93 halamanFront & Rear Wall BoilerAravazhi Ramasami Thangaraj100% (1)
- Tdbfp-A Turbine LogicDokumen4 halamanTdbfp-A Turbine LogicE.C.MADHUDUDHANA REDDYBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Audit of Auxiliary Power Consumption: Atar Singh Dy. Director Npti FaridabadDokumen27 halamanEnergy Audit of Auxiliary Power Consumption: Atar Singh Dy. Director Npti FaridabadHiltonBelum ada peringkat
- Auxiliary Power Reduction in Thermal Power PlantDokumen27 halamanAuxiliary Power Reduction in Thermal Power PlantManoj Upadhyay100% (1)
- Efficiency For Motors and PumpsDokumen6 halamanEfficiency For Motors and Pumpsyamaha100% (1)
- Energy Audit PresentationDokumen30 halamanEnergy Audit PresentationSikander Girgoukar100% (1)
- Variable Frequency Drives IntroductionDokumen11 halamanVariable Frequency Drives Introductionvigneshwaranj87Belum ada peringkat
- Manajemen Energi Motor ListrikDokumen23 halamanManajemen Energi Motor ListrikJHOSA EITFA ALTISBelum ada peringkat
- 5.energy Audit of Pumps & FansDokumen49 halaman5.energy Audit of Pumps & Fanssuppan67% (3)
- CVP AnalysisDokumen41 halamanCVP AnalysisAbdulyunus Amir100% (1)
- LeaderDokumen34 halamanLeaderAbdulyunus AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamics On Industrial RelationsDokumen24 halamanDynamics On Industrial RelationsAbdulyunus AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Activity Based CostingDokumen51 halamanActivity Based CostingAbdulyunus AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Combustor InsulationDokumen4 halamanCombustor InsulationAbdulyunus AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Annex I UAT Name Plate 081210Dokumen1 halamanAnnex I UAT Name Plate 081210Abdulyunus AmirBelum ada peringkat
- What Does Regenerative Air Pre-Heater Means, Why They Named SoDokumen10 halamanWhat Does Regenerative Air Pre-Heater Means, Why They Named SoAbdulyunus AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Voltage Management A Hidden Energy Efficiency ResourceDokumen3 halamanVoltage Management A Hidden Energy Efficiency ResourceAbdulyunus AmirBelum ada peringkat
- What Are The Criteria For Selection of Non Metallic Expansion Joint (NMEJ) and Metallic Expansion Joint (MEJ)Dokumen3 halamanWhat Are The Criteria For Selection of Non Metallic Expansion Joint (NMEJ) and Metallic Expansion Joint (MEJ)Abdulyunus AmirBelum ada peringkat
- What Are The Reason A 33kV Bus PT Fuse Is Blowing Out FrequentlyDokumen10 halamanWhat Are The Reason A 33kV Bus PT Fuse Is Blowing Out FrequentlyAbdulyunus Amir100% (1)
- Three Phenomenons in The Iron of AC MachinesDokumen4 halamanThree Phenomenons in The Iron of AC MachinesAbdulyunus AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Voltage and Current UnbalanceDokumen2 halamanVoltage and Current UnbalanceAbdulyunus AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Utility ICS Current Practices Survey 2013Dokumen13 halamanUtility ICS Current Practices Survey 2013Abdulyunus AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Top 100 Engineering Interview QuestionsDokumen11 halamanTop 100 Engineering Interview QuestionsAbdulyunus AmirBelum ada peringkat