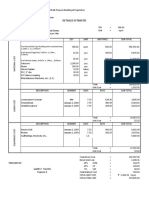
Growth in Banking Sector
Diunggah oleh
Harish Rawal Harish RawalDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Growth in Banking Sector
Diunggah oleh
Harish Rawal Harish RawalHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Submitted by Harish rawal
Indias banking sector is booming at a great pace. Indian banking sector has been found lucrative. Most of the banks paid their focus on the retail sector
and provide internet banking, phone banking and mobile banking services to their customers and have cornered one of the largest segments of the India's banking sector by targeting the India's growing middle income class. The Indian banking sector has been a proliferation of new services.
A banker or bank is a financial institution whose primary activity is to act as a payment agent for customers and to borrow and lend money
Lending money to public (loans) Transferring money from one place to another (Remittances) Acting as trustees Keeping valuables in safe custody Government business
Public sector Banks Private sector Banks Co-operative Bank Development Bank/Financial institutions
RBI is the banker to bankswhether commercial, cooperative, or rural. The relationship is established once the name of a bank is included in the Second Schedule to the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. Such bank, called a scheduled bank, is entitled to facilities of refinance from RBI.
subject to fulfillment of the following conditions laid down in Section 42 (6) of the Act, as follows: It must have paid-up capital and reserves. It must satisfy RBI that its affairs.
Demat Account Lockers Cash Management Insurance Product Mutual Fund Product Loans ECS (Electronic clearance system) Taxes
Growth in Indian banking assets
The first bank in India, though conservative, was established in 1786. From 1786 till today, the journey of Indian Banking System can be segregated into three distinct phases. They are as mentioned below: Early phase from 1786 to 1969 of Indian Banks Nationalization of Indian Banks and up to 1991 prior to Indian banking sector Reforms. New phase of Indian Banking System with the advent of Indian Financial & Banking Sector Reforms after 1991
The following are the steps taken by the Government of India to Regulate Banking Institutions in the Country: 1949: Enactment of Banking Regulation Act. 1955: Nationalization of State Bank of India. 1959: Nationalization of SBI subsidiaries. 1961: Insurance cover extended to deposits. 1969: Nationalization of 14 major banks. 1971: Creation of credit guarantee corporation. 1975: Creation of regional rural banks. 1980: Nationalization of seven banks with deposits over 200 crore.
After the nationalization of banks, the branches of the public sector bank India rose to approximately 800% in deposits and advances took a huge jump by 11,000%
Mergers of banks took place in India in the 1960s under the direction of the Reserve Bank of India. From 566 reporAting commercial banks (of which non-scheduled banks were 474) at the end of 1951, the number came down to 292 (of which 210 were non-scheduled) at end 1961, to 100 (27 non-scheduled) at the end of 1966; and to 85 (14 non-scheduled) by the end of 1969.
According to the RBI definition, commercial banks which conduct the business of banking in India and which (a) have paid up capital and reserves of an aggregate real and exchangeable value of not less than Rs 0.5 mn and (b) satisfy the RBI that their affairs are not being conducted in a manner detrimental to the interest of their depositors, are eligible for inclusion in the Second Schedule to the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, and when included are known as Scheduled Commercial Banks.
Banks in India are categorized in five different groups according to their ownership and/or nature of operation. These bank groups are (i) State Bank of India and its associates, (ii) Nationalised Banks, (iii) Regional Rural Banks, (iv) Foreign Banks and (v) Other Indian Scheduled Commercial Banks
There are 71,177 bank offices spread across the country, of which 43 % are located in rural areas, 22% in semiurban areas, 18% in urban areas and the rest (17 %) in the metropolitan areas. The major bank groups (as defined by RBI) functioning are State Bank of India and its seven associate banks, 19 nationalized banks and the IDBI Ltd, 19 Old Private Sector Banks, 8 New Private Sector Banks and 29 Foreign Banks
Among the Public Sector Banks in India, United Bank of India is one of the 14 major banks which were nationalized on July 19, 1969. Its predecessor, in the Public Sector Banks, the United Bank of India Ltd., was formed in 1950 with the amalgamation of four banks viz. Comilla Banking Corporation Ltd. (1914), Bengal Central Bank Ltd. (1918), Comilla Union Bank Ltd. (1922) and Hooghly Bank Ltd. (1932).
(1932). Oriental Bank of Commerce (OBC), a Government of India Undertaking offers Domestic, NRI and Commercial banking services. OBC is implementing a GRAMEEN PROJECT in Dehradun District (UP) and Hanumangarh District (Rajasthan) disbursing small loans. This Public Sector Bank India has implemented 14 point action plan for strengthening of credit delivery to women and has designated 5 branches as specialized branches for women entrepreneurs
Allahabad Bank Andhra Bank Bank of Baroda Bank of India Bank of Maharashtra Canara Bank
Private banking in India was practiced since the beginning of banking system in India. The first private bank in India to be set up in Private Sector Banks in India was IndusInd Bank. It is one of the fastest growing Private Sector Bank in India. IDBI ranks the tenth largest development bank in the world as Private Banks in India and has promoted a world class institution in India.
The first Private Bank in India to receive an in principle approval from the Reserve Bank of India was Housing Development Finance Corporation Limited, to set up a bank in the private sector banks in India as part of the RBI's liberalization of the Indian Banking Industry. It was incorporated in August 1994 as HDFC Bank Limited with registered office in Mumbai and commenced operations as Scheduled Commercial Bank in January 1995.
ING Vysya, yet another Private Bank of India was incorporated in the year 1930. Bangalore has a pride of place for having the first branch inception in the year 1934. With successive years of patronage and constantly setting new standards in banking, ING Vysya Bank has many credits to its account.
Some of the major reform initiatives in the last decade that have changed the face of the Indian banking are:Interest Rate Deregulation-Interest
Government equity in banks
New private sector banks
New areas have been opened up for bank financing
The Indian banking sector has seen an acceleration with the introduction of technological transformation like ATMs, telephone banking, online banking, web based products, e-cheques, call centers credit cards, debit cards.
Even the old public sector banks are keeping themselves tune with the new technological changes. SBI: Like State Bank of India (SBI) has set aside more than Rs 500 crore during its 3 years of of time span for the up gradation. Presently, SBI has more than 3000 computerized branches and over 1000 new ATMs. Similarly, UTI: United Bank of India (UTI) has started its computerization process in 1986 and so far it has completed its computerization work of more than 774 branches. It has also set up 25 ATMs in throughout the India
Due to the advantages of inherent conveniences, : 24x7 internet banking has proved to be an attractive service Transactions done through the internet cost Some banks also offer unique features of internet banking
Transfer of money to your account at the same bank's branch in another city. Opening of a fixed deposit Issuing of a banker's cheque or a demand draft. Checking of bank balance. Stopping the clearance of cheque. Request for the cheque book. Retail Sector Growth
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Regional Rural Banks of India: Evolution, Performance and ManagementDari EverandRegional Rural Banks of India: Evolution, Performance and ManagementBelum ada peringkat
- Securitization in India: Managing Capital Constraints and Creating Liquidity to Fund Infrastructure AssetsDari EverandSecuritization in India: Managing Capital Constraints and Creating Liquidity to Fund Infrastructure AssetsBelum ada peringkat
- Indian Banking System ReportDokumen55 halamanIndian Banking System ReportPinky KusumaBelum ada peringkat
- Customer Satisfaction Towards HDFC BANKS AND SBI PDFDokumen90 halamanCustomer Satisfaction Towards HDFC BANKS AND SBI PDFKrishma RatheeBelum ada peringkat
- HDFC Black Book - Print PDFDokumen42 halamanHDFC Black Book - Print PDFShruti PalekarBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction and Functions of Nationalized BankDokumen10 halamanIntroduction and Functions of Nationalized BankPrashant MunnolliBelum ada peringkat
- Comparative Study Between Private Sectors Bank and Public Sector BanksDokumen36 halamanComparative Study Between Private Sectors Bank and Public Sector BanksjudeBelum ada peringkat
- Final Project SBI ProductDokumen56 halamanFinal Project SBI Productkunal hajareBelum ada peringkat
- Kotak Mahindra Bank 121121123739 Phpapp02Dokumen112 halamanKotak Mahindra Bank 121121123739 Phpapp02RahulSinghBelum ada peringkat
- Boi ProjectDokumen66 halamanBoi Projectnitin0010Belum ada peringkat
- Banking ProjectDokumen56 halamanBanking ProjectViki Sakpal100% (1)
- Bhavin kkkkkkkkk38Dokumen87 halamanBhavin kkkkkkkkk38Sandip ChovatiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Retail Banking of Allahabad BankDokumen50 halamanRetail Banking of Allahabad Bankaru161112Belum ada peringkat
- Comparative Analysis On NPA of Private & Public Sector BanksDokumen86 halamanComparative Analysis On NPA of Private & Public Sector BanksNagireddy Kalluri100% (1)
- Project On SbiDokumen50 halamanProject On SbiAshish Yadav100% (1)
- Co Operative BankDokumen39 halamanCo Operative BankAkshay Kumbhare50% (2)
- State Bank of IndiaDokumen7 halamanState Bank of Indiajay_kanjariaBelum ada peringkat
- Corporate BankingDokumen63 halamanCorporate BankingRicha SinhaBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution and Organizational Structure of SBIDokumen6 halamanEvolution and Organizational Structure of SBIpandisivaBelum ada peringkat
- SBI (State Bank of India)Dokumen2 halamanSBI (State Bank of India)dashgreevlankeshBelum ada peringkat
- Loans and Advances of The Sutex Co-Opertive Bank Ltd.Dokumen62 halamanLoans and Advances of The Sutex Co-Opertive Bank Ltd.sumesh8940% (1)
- State Bank of IndiaDokumen25 halamanState Bank of IndiabsragaBelum ada peringkat
- Ms Archana. Wali MBA II Semester Exam No. MBA0702009Dokumen78 halamanMs Archana. Wali MBA II Semester Exam No. MBA0702009vijayakooliBelum ada peringkat
- Study of The Procedure of Disbursemet of Home Loan of HDFC Bank in Bareilly CityDokumen37 halamanStudy of The Procedure of Disbursemet of Home Loan of HDFC Bank in Bareilly CityVivek GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Study On Retail Banking in IndiaDokumen12 halamanStudy On Retail Banking in IndiashwethaBelum ada peringkat
- Perception of CustomersDokumen14 halamanPerception of CustomersChandrika DasBelum ada peringkat
- Housing Finance A Comparative Study of SBI and HDFC BankDokumen3 halamanHousing Finance A Comparative Study of SBI and HDFC BankEditor IJTSRDBelum ada peringkat
- Rural Banking in MaharashtraDokumen4 halamanRural Banking in MaharashtraRohit UbaleBelum ada peringkat
- History of SBI in 38Dokumen57 halamanHistory of SBI in 38Mitali AmagdavBelum ada peringkat
- Indian Banking StructureDokumen5 halamanIndian Banking StructureKarthik NadarBelum ada peringkat
- HDFC BankDokumen79 halamanHDFC BankAnkit YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Project Study Report of Aditya KhandelwalDokumen87 halamanProject Study Report of Aditya KhandelwalAditya khandelwalBelum ada peringkat
- Rutuja Ambre FINAL BLACK BOOK-1 (PDF - Io)Dokumen43 halamanRutuja Ambre FINAL BLACK BOOK-1 (PDF - Io)rutuja ambreBelum ada peringkat
- Synopsis On Home LoanDokumen9 halamanSynopsis On Home Loanyash jejaniBelum ada peringkat
- HDFC ProfileDokumen10 halamanHDFC ProfilePunitha AradhyaBelum ada peringkat
- A Study On Various Deposit Schemes, Retail Banking and Internet Banking With Reference To Syndicate BankDokumen67 halamanA Study On Various Deposit Schemes, Retail Banking and Internet Banking With Reference To Syndicate BanklalsinghBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study of SbiDokumen6 halamanCase Study of Sbiसंजय साहBelum ada peringkat
- Final Presentation BANK OF BARODA 1Dokumen8 halamanFinal Presentation BANK OF BARODA 1Pooja GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- Internet Banking in SBI - Preeti Pawar 357358Dokumen90 halamanInternet Banking in SBI - Preeti Pawar 357358pawarprateek100% (3)
- Credit Appraisal in SBIDokumen123 halamanCredit Appraisal in SBIvivekdudejaBelum ada peringkat
- Project Report On Banking SystemDokumen16 halamanProject Report On Banking SystemArun Kumar0% (1)
- A Study On HDFC Bank LTDDokumen17 halamanA Study On HDFC Bank LTDbahaaraujlaBelum ada peringkat
- Management of NPA in BankingDokumen29 halamanManagement of NPA in BankingNagireddy KalluriBelum ada peringkat
- A Comparative Study On SBI and HDFC in Ambala City Ijariie5997Dokumen11 halamanA Comparative Study On SBI and HDFC in Ambala City Ijariie5997vinayBelum ada peringkat
- Union Bank of IndiaDokumen33 halamanUnion Bank of Indiaraghavan swaminathanBelum ada peringkat
- CANARA BANK INTRODUCTION TO BANKINGDokumen63 halamanCANARA BANK INTRODUCTION TO BANKINGRahul Rao MK100% (1)
- Loan Products of SBIDokumen46 halamanLoan Products of SBIvinodksrini007Belum ada peringkat
- Bank Credit AppraisalDokumen49 halamanBank Credit AppraisalJasmeet Singh100% (1)
- A Study on Retail Banking with Reference to HDFC BankDokumen69 halamanA Study on Retail Banking with Reference to HDFC BankbharatBelum ada peringkat
- COMPARATIVE STUDY OF PRIVATE AND PUBLIC SECTOR BANKS' SERVICESDokumen42 halamanCOMPARATIVE STUDY OF PRIVATE AND PUBLIC SECTOR BANKS' SERVICESSidharth GeraBelum ada peringkat
- Kittur Rani Channamma Urban Credit Souharda Sahakari LTDDokumen11 halamanKittur Rani Channamma Urban Credit Souharda Sahakari LTDshivaraj goudarBelum ada peringkat
- Retail Banking in India - An IntroductionDokumen73 halamanRetail Banking in India - An Introductionnatakhatnirmal33% (3)
- Comprehensive Study On Financial Analysis of HDFC Bank: Prepared byDokumen38 halamanComprehensive Study On Financial Analysis of HDFC Bank: Prepared byshrutilatherBelum ada peringkat
- Growth in Indian Banking SectorDokumen59 halamanGrowth in Indian Banking SectorKishan KudiaBelum ada peringkat
- Scenario of Foreign Banks in IndiaDokumen62 halamanScenario of Foreign Banks in IndiaYesha Khona100% (1)
- E-banking Satisfaction StudyDokumen88 halamanE-banking Satisfaction StudyAvtaar SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Aaqib Final ProjectDokumen58 halamanAaqib Final ProjectJkgi InstitutionsBelum ada peringkat
- Final Project Report - Docx Axis BankDokumen73 halamanFinal Project Report - Docx Axis BankSuraj GhongeBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Risk Management in Banks1933Dokumen24 halamanIntroduction To Risk Management in Banks1933Harish Rawal Harish RawalBelum ada peringkat
- Asset LiabilityDokumen10 halamanAsset LiabilityChetan BrahmankarBelum ada peringkat
- Aha Guidelines StemiDokumen94 halamanAha Guidelines StemiHarish Rawal Harish RawalBelum ada peringkat
- MR AmbaniDokumen15 halamanMR Ambanihemant100% (23)
- Harish RawalDokumen8 halamanHarish RawalHarish Rawal Harish RawalBelum ada peringkat
- Changing Landscape of Bancassurance in IndiaDokumen70 halamanChanging Landscape of Bancassurance in IndiaJaspal AroraBelum ada peringkat
- Success StoryDokumen27 halamanSuccess StoryEr Raghav GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- HeadHunt Issue 137Dokumen20 halamanHeadHunt Issue 137Bovino EddsterBelum ada peringkat
- Agreements - HTML: Dassault Systemes Biovia Corp.Dokumen5 halamanAgreements - HTML: Dassault Systemes Biovia Corp.Joakin BahamondesBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Worksheets 05Dokumen2 halamanEssential Worksheets 05Daniela MedinaBelum ada peringkat
- Beginner's Guide to Manual TestingDokumen17 halamanBeginner's Guide to Manual TestingMilan MilanBelum ada peringkat
- UOIT Academic Calendar 2010Dokumen306 halamanUOIT Academic Calendar 2010uoitBelum ada peringkat
- Alacan (48 Bakal)Dokumen107 halamanAlacan (48 Bakal)Marc Dared CagaoanBelum ada peringkat
- Performance ManagementDokumen38 halamanPerformance ManagementNatania SitorusBelum ada peringkat
- B e F U L L y P A I: Basis of The Intellectual Property Law (R.A. 8293, As Amended)Dokumen4 halamanB e F U L L y P A I: Basis of The Intellectual Property Law (R.A. 8293, As Amended)Dred OpleBelum ada peringkat
- Sepp AKDokumen112 halamanSepp AKnieschopwitBelum ada peringkat
- Fit Four v. Raww - ComplaintDokumen19 halamanFit Four v. Raww - ComplaintSarah BursteinBelum ada peringkat
- Week 12 Compulsory Quiz - Attempt Review 2ndDokumen5 halamanWeek 12 Compulsory Quiz - Attempt Review 2nd정은주Belum ada peringkat
- HR Practices of Marks and Spencer Selfri PDFDokumen46 halamanHR Practices of Marks and Spencer Selfri PDFbalach100% (1)
- ANNEX O of GAMDokumen15 halamanANNEX O of GAMKelvin CaldinoBelum ada peringkat
- BIM Execution Plan ExampleDokumen20 halamanBIM Execution Plan ExampleDarell IvanderBelum ada peringkat
- Maru Batting Center Case Study Excel Group YellowDokumen26 halamanMaru Batting Center Case Study Excel Group YellowAshish PatwardhanBelum ada peringkat
- TMForum - EtomDokumen61 halamanTMForum - EtomJosé EvangelistaBelum ada peringkat
- PT041000 Relatedresources Trade Secret Case Law Report 2013cDokumen78 halamanPT041000 Relatedresources Trade Secret Case Law Report 2013cGulshatRaissovaBelum ada peringkat
- Hargreaves Ch. 11 Bankruptcy FilingDokumen24 halamanHargreaves Ch. 11 Bankruptcy FilingNick HalterBelum ada peringkat
- EmaarDokumen15 halamanEmaarAdeel BajwaBelum ada peringkat
- Adjusting Entries Quiz - Accounting CoachDokumen4 halamanAdjusting Entries Quiz - Accounting CoachSudip BhattacharyaBelum ada peringkat
- Management Final Proj.Dokumen17 halamanManagement Final Proj.aaaaaaaaaaaaBelum ada peringkat
- Media Gateway SoftswitchDokumen10 halamanMedia Gateway SoftswitchMahmoud Karimi0% (1)
- Build Better Gantt Charts With Teamgantt For Free!: First Sample ProjectDokumen10 halamanBuild Better Gantt Charts With Teamgantt For Free!: First Sample ProjectMuhammad Khairul HafiziBelum ada peringkat
- The Procurement Alignment FrameworkDokumen8 halamanThe Procurement Alignment FrameworkZhe TianBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Data Sheet: Page 1 of 2 HCD-15208 (Rev. 9/4/2014 3:42:32 AM)Dokumen2 halamanTechnical Data Sheet: Page 1 of 2 HCD-15208 (Rev. 9/4/2014 3:42:32 AM)Akhtar AliBelum ada peringkat
- The Companies' (Incorporation) Procedure in Japan: Akash Saxena - 17A014 Semester - VIDokumen13 halamanThe Companies' (Incorporation) Procedure in Japan: Akash Saxena - 17A014 Semester - VIMeghna SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Mini Project Financial Reporting Statements and Analysis MB20104Dokumen11 halamanMini Project Financial Reporting Statements and Analysis MB20104KISHORE KRISHBelum ada peringkat
- IBM Oil - Cognos Performance Blueprint Offers Solutions For UpstreamDokumen7 halamanIBM Oil - Cognos Performance Blueprint Offers Solutions For UpstreamIBM Chemical and PetroleumBelum ada peringkat