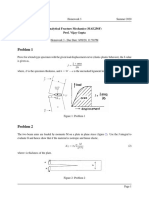
Basic Economics
Diunggah oleh
verdza23Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Basic Economics
Diunggah oleh
verdza23Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Lecture 1 By Dimuth Nambuge Office Hours : Room no :701
What Is Economics??
Definition of Economics
o Economics is a science which studies human behaviour as a relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses. (L.Robbins 1935) o Economics is the social science that examines how people choose to use limited or scarce resources in attempting to satisfy their unlimited wants.
Wants (dopyt) Needs (potreby) Scarcity (nedostatok) Factors of Production/Resources
Wants
This is simply the desire of the citizens of a country. Each individuals wants are different and varies time to time.
Needs
These are basic requirements human must have in according to survive. A need is something that you have to have. Want is something you would like to have
Scarcity
Is the fundamental economic problem of having seemingly unlimited human needs and wants, in a world of limited resources. Meaning that society has limited productive resources to fulfil unlimited human needs and wants.
Opportunity Cost
Is the cost we pay when we give up something to get something else. There can be many alternatives that we give up to get something else, but the opportunity cost of a decision is the most desirable alternative we give up to get what we want. Example: Guns or Butter
Factors of Production
These are the resources employed to produce goods and services. They facilitate production but do not become part of the final product. The efficiency of using factors of production determines the measure of success a nation has. Land Capital Natural Resources Man made physical goods used to produce other goods and services Labour - Labour is the human input into the production. Enterprise - The entrepreneurship provides the initial ideas, They risk their own resources in business ventures
What to produce? How to produce? For whom to produce?
These are the questions all nations must ask when dealing with scarcity and efficiently allocating their resources.
Gross Domestic Production Average wage level Work Force Employment Rate Unemployment Rate Balance of Payments Inflation Rate Interest Rates Exchange Rates
Free Products
Air, sunshine are and other items so plentiful no one could own them
Goods
Tangible commodities. These are produced, bought, sold, and traded. Consumer Goods Goods that are intended for final use by the consumer. Capital Goods Goods used in the process of production of other goods.
Services
An Act by one person or group that benefits another. Services are intangible.
Durable Goods
Goods intended to use for a long period of time.
Non Durable Goods
Goods intended to use for a short period of time.
Consumers
People who use these Goods and Services
Value
An assignment of worth. The assignment is usually based upon the utility (usefulness) or scarcity of the item (supply and demand)
Paradox of Value
Assignment of the highest value to those things we need the least.
Wealth
The sum of collection of those economic products that are tangible, scarce and useful.
Productivity
The amount of output per unit of input. There are different ways of measuring productivity.
Demand
Demand for a product or service is defined as the quantity of that particular product or service consumers are willing to purchase. Factors that affect the demand for a product
Price of the Product Income of the consumers Availability of product Alternative products Promotion of the product Demographics
Supply
The supply of a product is defined as the quantity of the product which producers or manufacturers are willing to produce and sell. Factors that affects the Supply of a product
Price of inputs (Raw materials, Labor) Availability of Inputs Technology changes Government policies Natural influences
www.ft.com www.economist.com http://dictionary.cambridge.org/ www.sciencedirect.com
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Appendix I - Plant TissuesDokumen24 halamanAppendix I - Plant TissuesAmeera ChaitramBelum ada peringkat
- Inventory Management Final ProjectDokumen65 halamanInventory Management Final ProjectMAHESH MUTHYALABelum ada peringkat
- Types of Vegetation in Western EuropeDokumen12 halamanTypes of Vegetation in Western EuropeChemutai EzekielBelum ada peringkat
- 7 кмжDokumen6 halaman7 кмжGulzhaina KhabibovnaBelum ada peringkat
- BROADCAST Visual CultureDokumen3 halamanBROADCAST Visual CultureDilgrace KaurBelum ada peringkat
- Bimetallic ZN and HF On Silica Catalysts For The Conversion of Ethanol To 1,3-ButadieneDokumen10 halamanBimetallic ZN and HF On Silica Catalysts For The Conversion of Ethanol To 1,3-ButadieneTalitha AdhyaksantiBelum ada peringkat
- Social Networking ProjectDokumen11 halamanSocial Networking Projectapi-463256826Belum ada peringkat
- Horgolás Minta - PulcsiDokumen5 halamanHorgolás Minta - PulcsiCagey Ice-RoyBelum ada peringkat
- Mutants & Masterminds 3e - Power Profile - Death PowersDokumen6 halamanMutants & Masterminds 3e - Power Profile - Death PowersMichael MorganBelum ada peringkat
- Coerver Sample Session Age 10 Age 12Dokumen5 halamanCoerver Sample Session Age 10 Age 12Moreno LuponiBelum ada peringkat
- Construction Agreement SimpleDokumen3 halamanConstruction Agreement Simpleben_23100% (4)
- Fireware EssentialsDokumen499 halamanFireware EssentialsEmmanuel RodríguezBelum ada peringkat
- Project CharterDokumen10 halamanProject CharterAdnan AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- EEN 203 Slide Notes Year 2018: PART I - Numbers and CodesDokumen78 halamanEEN 203 Slide Notes Year 2018: PART I - Numbers and CodesSHIVAM CHOPRABelum ada peringkat
- Problem Based LearningDokumen23 halamanProblem Based Learningapi-645777752Belum ada peringkat
- Mae (256F) - HW3 PDFDokumen2 halamanMae (256F) - HW3 PDFClaireBelum ada peringkat
- RPS Manajemen Keuangan IIDokumen2 halamanRPS Manajemen Keuangan IIaulia endiniBelum ada peringkat
- GMAT Sentence Correction Practice Test 03Dokumen5 halamanGMAT Sentence Correction Practice Test 03krishnachivukulaBelum ada peringkat
- Soul Winners' SecretsDokumen98 halamanSoul Winners' Secretsmichael olajideBelum ada peringkat
- Waldorf Curriculum ChartDokumen1 halamanWaldorf Curriculum Chartplanetalingua2020100% (1)
- Value Chain AnalaysisDokumen100 halamanValue Chain AnalaysisDaguale Melaku AyeleBelum ada peringkat
- Economis Project-MCOM SEM 1Dokumen19 halamanEconomis Project-MCOM SEM 1Salma KhorakiwalaBelum ada peringkat
- Agrarian ReformDokumen40 halamanAgrarian ReformYannel Villaber100% (2)
- Curriculum Vitae For Modern MutumwaDokumen4 halamanCurriculum Vitae For Modern MutumwaKudakwashe QuQu MaxineBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Award Sheet Government College University, FaisalabadDokumen1 halamanDetailed Award Sheet Government College University, FaisalabadAnayat KhetranBelum ada peringkat
- IAB Digital Ad Operations Certification Study Guide August 2017Dokumen48 halamanIAB Digital Ad Operations Certification Study Guide August 2017vinayakrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Sugar Industries of PakistanDokumen19 halamanSugar Industries of Pakistanhelperforeu50% (2)
- Filipino Chicken Cordon BleuDokumen7 halamanFilipino Chicken Cordon BleuHazel Castro Valentin-VillamorBelum ada peringkat
- Event Planning Sample Cover Letter and ItineraryDokumen6 halamanEvent Planning Sample Cover Letter and ItineraryWhitney Mae HaddardBelum ada peringkat
- Bakery Management SynopsisDokumen13 halamanBakery Management SynopsisSHiVaM KRBelum ada peringkat