Waste Heat Recovery
Diunggah oleh
AMIT PRAJAPATIDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Waste Heat Recovery
Diunggah oleh
AMIT PRAJAPATIHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
5/24/12
WASTE HEAT RECOVRY SYSTEM IN POWER PLANTS
Click to edit Master subtitle style
Mr. AMIT PRAJAPATI
5/24/12
CONTENTS:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Introduction Need of Recovering Waste Heat List of Sources of Waste Heat & its quality Types of Waste Heat Recovery Benefits of Waste Heat Recovery Commercial Devices used for Waste Heat Recovery in Power Plants
5/24/12
INTRODUCTION
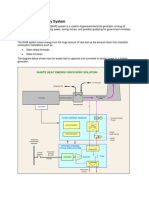
Waste heat is heat, which is generated in a process by way of fuel combustion or chemical reaction, and then dumped into the environment even though it could still be reused for some useful and economic purpose. The essential quality of heat is not the amount but rather its value. The strategy of how to recover this heat depends in part on the temperature of the waste heat gases and the economics involved. Large quantity of hot flue gases is generated from Boilers, Kilns, Ovens and Furnaces. If some of this waste heat could be recovered, a considerable amount of primary fuel could be saved. The energy lost in waste gases cannot be fully recovered.
However, much of the heat could be recovered and loss minimized with the help of different equipments.
Depending upon the type of process, waste heat can be rejected at virtually any temperature from that of chilled cooling water to high temperature waste gases from an industrial furnace or kiln. Usually higher the temperature, higher the quality and more cost effective is the heat recovery. In any study of waste heat recovery, it is absolutely necessary that there should be some use for the recovered heat.
5/24/12
e.g. preheating of combustion air, space heating, or preheating boiler feed water or process water.
Sources of Waste Heat with the quality of Heat loss
1.
5/24/12
SOURCES
Heat in flue gases.
HEAT
1.
LOSS QUALITY
The higher the temperature, the greater the potential value for heat recovery. As above but when condensed, latent heat also recoverable.
2. 2.
Heat in vapour streams.
1.
2.
Convective and radiant heat lost from exterior of equipment. Heat losses in cooling water.
Low grade if collected may be used for space heating or air preheats. Low grade useful gains if heat is exchanged with incoming fresh water. a) High grade if used to reduce demand for refrigeration. b) Low grade if used as heat pump.
3.
2.
3. 2.
Heat losses in providing chilled water or in the disposal of chilled water.
6.
6.
Heat stored in products leaving
Quality depends temperature.
upon
There are mainly three types of heat recovery which depends on the temperatures of the waste heat gases:
High Temperature H.R.- Temp. Range is 650 oC-1650 c & results from direct fuel fired processes like Ni/Al/Cu/Zn refining furnace, Cu reverberatory furnace, Open Hearth furnace etc
5/24/12
Medium Temperature H.R.- Temp. Range is 230 c-650 c & results from exhaust of direct fuel fired processes like Steam Turbine/Boiler exhaust, Reciprocating engine exhaust etc
Low Temperature H.R.- Temp. Range is 55 c-230 c & used for need of low pressure steam from the processes like Process steam condensate, Cooling water from Furnace doors,
Benefits of Waste Heat Recovery:
5/24/12
Benefits
of waste heat recovery can be broadly classified in two categories:
Direct Benefits:-
Recovery of waste heat has a direct effect on the efficiency of the process. This is reflected by reduction in the utility
5/24/12
Commercial Waste Heat Recovery Devices:
After identifying source of waste heat and the possible use of it, the next step is to select suitable heat recovery system and equipments to recover and utilize the same which are as follows: Recuperators Pipe Exchanger Wheel or Rotary Heat Exchanger
Regenerators Heat
Thermal
Economizer Heat
Pumps
5/24/12
RECUPERATORS:
In a recuperator, heat exchange takes place between the flue gases and the air through metallic or ceramic walls. Duct or tubes carry the air for combustion to be pre-heated, the other side contains the waste heat stream.
5/24/12
The simplest configurati on for a recuperato r is the metallic
5/24/12
Second common configuration for recuperators is called the tube type or convective recuperator:
The hot gases are carried through a number of parallel small diameter tubes, while the incoming air to be heated enters a shell surrounding the tubes and passes over the hot tubes one or more times
5/24/12
RADIATION/CONVECTIVE HYBRID RECUPERATOR
For maximum effectiveness of heat transfer, combinations of radiation and convective designs are used, with the hightemperature radiation recuperator being first followed by convection type. These are more expensive than simple metallic radiation recuperators, but are less bulky.
5/24/12
REGENERATORS
The Regeneration which is preferable for large capacities has been very widely used in glass and steel melting furnaces. Important relations exist between the size of the regenerator, time between reversals, thickness of brick, conductivity of brick and heat storage ratio of the brick. In a regenerator, the time between the
HEAT WHEELS
5/24/12
A heat wheel is finding increasing applications in low to medium temperature waste heat recovery systems. Figure 8.6 is a sketch illustrating the application of a heat wheel. It is a porous sizable disk,
5/24/12
The overall efficiency of sensible heat transfer for this kind of regenerator can be as high as 85 percent. Heat wheels have been built as large as 21 meters in diameter with air capacities up to 1130 m3 / min. Its main area of application is where heat exchange between large masses of air having small temperature
5/24/12
HEAT PIPE
5/24/12
A Heat pipe can transfer up to 100 times more thermal energy than copper, the best known conductor. In other words, heat pipe is a thermal energy absorbing and transferring system and have no moving parts and hence require minimum maintenance. The capillary wick structure is integrally fabricated into the interior surface of the container
5/24/12
Performance & Advantage
The heat pipe exchanger (HPHE) is a lightweight compact heat recovery system. It virtually does not need mechanical maintenance, as there are no moving parts to wear out. It does not need input power for its operation and is free from cooling water and lubrication systems. It also lowers the fan horsepower requirement and increases the overall thermal efficiency of the system. The heat pipe heat recovery systems are capable of operating at 315oC. with 60% to 80% heat recovery capability.
ECONOMIZER
5/24/12
In case of boiler system, economizer can be provided to utilize the flue gas heat for preheating the boiler feed water. On the other hand, in an air pre-heater, the waste heat is used to heat combustion air. In both the cases, there is a corresponding reduction in the fuel requirements of the boiler. For every 220 C reduction in flue gas temperature by passing through an economizer or
5/24/12
THANK YOU.!!!
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Waste Heat RecoveryDokumen17 halamanWaste Heat Recoverynayan100% (2)
- WEAST HEAT RECOVERY Heating Purpose For Woldia University CaftiriaDokumen10 halamanWEAST HEAT RECOVERY Heating Purpose For Woldia University CaftiriaMisge ChekoleBelum ada peringkat
- Waste Heat Recovery: Reclaiming Lost EnergyDokumen19 halamanWaste Heat Recovery: Reclaiming Lost EnergyAnjanKumarMahanta100% (2)
- Waste heat recovery technologies and applications overviewDokumen17 halamanWaste heat recovery technologies and applications overviewSazid ZamanBelum ada peringkat
- Waste Heat RecoveryDokumen37 halamanWaste Heat Recoveryommech2020Belum ada peringkat
- Thermal power plant economiser guideDokumen7 halamanThermal power plant economiser guideSteve M D'souzaBelum ada peringkat
- Co Generation Unit 4Dokumen52 halamanCo Generation Unit 4Johnson Johnson100% (2)
- Heat Recovery Steam Generators Cut Energy CostsDokumen6 halamanHeat Recovery Steam Generators Cut Energy CostsJenniferValleBelum ada peringkat
- Waste Heat Recovery SystemDokumen16 halamanWaste Heat Recovery SystemAsrar Uddin100% (1)
- Waste HeatDokumen10 halamanWaste HeatRizwanKhanBelum ada peringkat
- Recover Waste Heat from Processes and EquipmentDokumen30 halamanRecover Waste Heat from Processes and Equipmentsaadiis100% (2)
- Improve Air Cooled Heat Exchanger PerformanceDokumen14 halamanImprove Air Cooled Heat Exchanger PerformanceVíctor LeónBelum ada peringkat
- Waste Heat Recovery FactsheetDokumen2 halamanWaste Heat Recovery FactsheetMajid JafariBelum ada peringkat
- Steam Turbines: Session Delivered By: Prof. Q.H. NagpurwalaDokumen50 halamanSteam Turbines: Session Delivered By: Prof. Q.H. NagpurwalaPappuRamaSubramaniam100% (1)
- C.O.P Derivation and Thermodynamic Calculation of Ammonia-Water Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System-2 PDFDokumen10 halamanC.O.P Derivation and Thermodynamic Calculation of Ammonia-Water Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System-2 PDFErGiteshAroraBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Management Tutorial SolutionsDokumen9 halamanEnergy Management Tutorial SolutionsLucas LentzBelum ada peringkat
- Waste Heat To Power ApplicationsDokumen10 halamanWaste Heat To Power ApplicationsArul PrakashBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Recovery Steam GeneratorsDokumen94 halamanHeat Recovery Steam GeneratorshoangpalestineBelum ada peringkat
- University's 500 kW Biomass Boiler Cuts Carbon by 500 Tonnes AnnuallyDokumen4 halamanUniversity's 500 kW Biomass Boiler Cuts Carbon by 500 Tonnes AnnuallySuppachai DanpreechakulBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Performance Assessment of BoilersDokumen43 halamanEnergy Performance Assessment of BoilersPradyumna Dhamangaonkar100% (1)
- Boiler 5Dokumen4 halamanBoiler 5Shams TabrezBelum ada peringkat
- Waste Heat Recovery System (WHRS)Dokumen32 halamanWaste Heat Recovery System (WHRS)Дмитрий ЗинченкоBelum ada peringkat
- Bono Thermal Heater RangeDokumen6 halamanBono Thermal Heater RangeMūhāmmād MōāžžāmBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Recovery Steam Generator 5Dokumen29 halamanHeat Recovery Steam Generator 5Hitesh SinglaBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Analysis of Air PreheaterDokumen14 halamanDesign and Analysis of Air PreheaterTJPRC Publications100% (1)
- Accord Boiler Safety Program Infopack PDFDokumen10 halamanAccord Boiler Safety Program Infopack PDFTimeBelum ada peringkat
- Lect 5 - Liquefaction - 2015 PDFDokumen6 halamanLect 5 - Liquefaction - 2015 PDFAnonymous oqlnO8e100% (1)
- Thermal Oil Heater1Dokumen31 halamanThermal Oil Heater1Evans MandinyanyaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction Thermal Oil Heaters Type VTODokumen7 halamanIntroduction Thermal Oil Heaters Type VTOMomar Talla DiawBelum ada peringkat
- Waste Heat Recovery 1311947494Dokumen2 halamanWaste Heat Recovery 1311947494Cem AlpaslanBelum ada peringkat
- Fuel Characteristic BiomassDokumen365 halamanFuel Characteristic BiomassCalvin JunBelum ada peringkat
- How To Calculate Overall Thermal Efficiency of Combined Cycle Power PlantsDokumen10 halamanHow To Calculate Overall Thermal Efficiency of Combined Cycle Power PlantsManoj SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Fuel Savings and Efficiency CalculatorDokumen6 halamanFuel Savings and Efficiency Calculatorrajayu20002724Belum ada peringkat
- Central Steam Boiler Plants PDFDokumen134 halamanCentral Steam Boiler Plants PDFGabriel GabrielBelum ada peringkat
- Extending the Range of Single-Shaft Combined Cycle Power PlantsDokumen12 halamanExtending the Range of Single-Shaft Combined Cycle Power PlantsSrinivasa Rao PallelaBelum ada peringkat
- Measuring Boiler Efficiency - ASMEDokumen8 halamanMeasuring Boiler Efficiency - ASMEyvesdepermentier4622Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture 3 - Improving Performance - RegenerationDokumen5 halamanLecture 3 - Improving Performance - RegenerationMuhammad Alam Zaib KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Turbine Heat Rate CalculationDokumen2 halamanTurbine Heat Rate Calculationkaruna34650% (2)
- Steam TurbineDokumen77 halamanSteam TurbineAmit KhadkaBelum ada peringkat
- Boiler Excess Air Tune-UpDokumen15 halamanBoiler Excess Air Tune-UpAlif Nur FirdausBelum ada peringkat
- Combined Cycle Power Plant Design Information PDFDokumen2 halamanCombined Cycle Power Plant Design Information PDFOliviaBelum ada peringkat
- BDA30403 Gas TurbinesDokumen56 halamanBDA30403 Gas TurbinesShishajimooBelum ada peringkat
- Oversized Pumps & Fans Energy WasteDokumen25 halamanOversized Pumps & Fans Energy Wastebaldonado1Belum ada peringkat
- Boiler Water & Steam CycleDokumen50 halamanBoiler Water & Steam CycleRaviKushwahaBelum ada peringkat
- Design, Fabrication and Performance Analysis of Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System Powered by Solar Using NanofluidDokumen5 halamanDesign, Fabrication and Performance Analysis of Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System Powered by Solar Using NanofluidchilakaprakashBelum ada peringkat
- Calculate control valve CvDokumen3 halamanCalculate control valve CvRio SamudraBelum ada peringkat
- Furnaces classification and efficiency measuresDokumen31 halamanFurnaces classification and efficiency measuresVignesh NayakBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamic Analysis of Triple Pressure Heat Recovery Steam GeneratorDokumen7 halamanThermodynamic Analysis of Triple Pressure Heat Recovery Steam GeneratorIJIRSTBelum ada peringkat
- Boiler EfficiencyDokumen12 halamanBoiler Efficiencyswaroop351Belum ada peringkat
- Combustion Control Strategies for Boiler EfficiencyDokumen72 halamanCombustion Control Strategies for Boiler EfficiencyRantau SilalahiBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Turbine Cycles - LectureDokumen18 halamanGas Turbine Cycles - LectureSrinu Reddy100% (1)
- Shellmax Boiler Design CalculationDokumen2 halamanShellmax Boiler Design Calculationrahult19Belum ada peringkat
- Waste Heat RecoveryDokumen4 halamanWaste Heat RecoveryMudasar JavedBelum ada peringkat
- WASTE HEAT RECOVERY (HRSG) PerformanceDokumen17 halamanWASTE HEAT RECOVERY (HRSG) PerformanceEjaz AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Waste Heat Recovery Methods and Technologies ReviewDokumen11 halamanWaste Heat Recovery Methods and Technologies ReviewChem.Engg100% (2)
- Waste Heat Boiler Plate Heat ExchangersDokumen8 halamanWaste Heat Boiler Plate Heat ExchangerskondusamyBelum ada peringkat
- Waste Heat Recovery Devices and ApplicationsDokumen18 halamanWaste Heat Recovery Devices and Applicationsdivyank3dBelum ada peringkat
- Waste Heat Recovery: V. Shanthan MT21HPE001Dokumen9 halamanWaste Heat Recovery: V. Shanthan MT21HPE001Shanthan VardelliBelum ada peringkat
- Economizer: Economizers (US andDokumen8 halamanEconomizer: Economizers (US andprathapBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Recovery MechanismsDokumen13 halamanHeat Recovery MechanismsSuhailSharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Adv. Turbo - SyllDokumen1 halamanAdv. Turbo - SyllAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT 3 Gas TurbineDokumen2 halamanUNIT 3 Gas TurbineAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDokumen1 halamanMechanical Engineering DepartmentAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ASSIGNMENT ON CARNOT CYCLE, REGENERATION, RANKINE CYCLEDokumen1 halamanMECHANICAL ENGINEERING ASSIGNMENT ON CARNOT CYCLE, REGENERATION, RANKINE CYCLEAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- EC-II - Assign. 1Dokumen1 halamanEC-II - Assign. 1AMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- Scheme BTech AEDokumen1 halamanScheme BTech AEAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- MTech ADV TURBODokumen2 halamanMTech ADV TURBOAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus-Refrigeration & Air Conditioning (T) - ME3CO16 (T)Dokumen2 halamanSyllabus-Refrigeration & Air Conditioning (T) - ME3CO16 (T)AMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- EC-II - Assign. 2Dokumen1 halamanEC-II - Assign. 2AMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Engineering Department: DATE: 19.2.19 Assignment No.1Dokumen1 halamanMechanical Engineering Department: DATE: 19.2.19 Assignment No.1AMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- Medi-Caps University, Indore Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokumen1 halamanMedi-Caps University, Indore Department of Mechanical EngineeringAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- Medi-Caps University, Indore Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokumen1 halamanMedi-Caps University, Indore Department of Mechanical EngineeringAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- AU III Sem AE SyllabusDokumen2 halamanAU III Sem AE SyllabusAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Engineering Department: and After Last Date No Assignment Will Be TakenDokumen1 halamanMechanical Engineering Department: and After Last Date No Assignment Will Be TakenAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- Handmade Shoe Project ProfileDokumen2 halamanHandmade Shoe Project ProfileAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- Bio DieselDokumen1 halamanBio DieselSandeep PnsBelum ada peringkat
- R e G PDFDokumen1 halamanR e G PDFAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- Pithampur Industries ListDokumen1 halamanPithampur Industries ListAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- R e G PDFDokumen1 halamanR e G PDFAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- Noodle AgraDokumen11 halamanNoodle Agrarecio_seth09Belum ada peringkat
- Plastic cluster CFC proposalDokumen21 halamanPlastic cluster CFC proposalmeenakshi_ludBelum ada peringkat
- Cannedjackfruitgoa PDFDokumen9 halamanCannedjackfruitgoa PDFAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- Rice Mill & Poha Mill Industry Report (1) Industrial Visit ReportDokumen7 halamanRice Mill & Poha Mill Industry Report (1) Industrial Visit ReportAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- CH 21Dokumen5 halamanCH 21ProfNDAcharyaBelum ada peringkat
- Plastic cluster CFC proposalDokumen21 halamanPlastic cluster CFC proposalmeenakshi_ludBelum ada peringkat
- ReprocessingDokumen10 halamanReprocessingAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- ch8 Elastic Tape PDFDokumen4 halamanch8 Elastic Tape PDFAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- Project Profile On G. P. Bucket: Dcdi-Mzfpur - Dcmsme@gov - in WWW - Msmedimzfpur.bih - Nic.inDokumen8 halamanProject Profile On G. P. Bucket: Dcdi-Mzfpur - Dcmsme@gov - in WWW - Msmedimzfpur.bih - Nic.inAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- 11 PohaDokumen8 halaman11 PohapritamrbhadadeBelum ada peringkat
- A-619 136699 PDFDokumen25 halamanA-619 136699 PDFAMIT PRAJAPATIBelum ada peringkat
- Paper - 2 - SetA - 090410 - Key PDFDokumen12 halamanPaper - 2 - SetA - 090410 - Key PDFNataraj Singh SardarBelum ada peringkat
- VOLVO MicroturbinesDokumen64 halamanVOLVO MicroturbinesavryoneBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Treating Processes and Equipment GuideDokumen73 halamanHeat Treating Processes and Equipment GuideYuvaraj Chinth100% (1)
- WWW - Beeindia.in Energy Managers Auditors Documents Guide Books 2Ch4Dokumen31 halamanWWW - Beeindia.in Energy Managers Auditors Documents Guide Books 2Ch4samcat2009Belum ada peringkat
- Catalogo COMINTER EngDokumen23 halamanCatalogo COMINTER EngosamaBelum ada peringkat
- SORG Glas - Melting TechnologyDokumen27 halamanSORG Glas - Melting Technologymetalman_m100% (2)
- Brochure Corporate enDokumen9 halamanBrochure Corporate enbizolutionBelum ada peringkat
- 21UTSR HeldDokumen52 halaman21UTSR HelddavidBelum ada peringkat
- IAC Student Webinar May SachinDokumen59 halamanIAC Student Webinar May SachinMirnes FejzicBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Project Report ON Waste Heat Recovery in Roller Kiln (Morbi Ceramic Cluster)Dokumen47 halamanDetailed Project Report ON Waste Heat Recovery in Roller Kiln (Morbi Ceramic Cluster)Assure TurbinesBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamic Analysis of Supercritical Organic Rankine Cycle With Propane (R-290) As A Working FluidDokumen16 halamanThermodynamic Analysis of Supercritical Organic Rankine Cycle With Propane (R-290) As A Working FluidHarmenBelum ada peringkat
- Optimizing Recuperator Design for a 90kW Turboprop/Turboshaft Gas Turbine EngineDokumen31 halamanOptimizing Recuperator Design for a 90kW Turboprop/Turboshaft Gas Turbine EnginebbbnilaBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Transfer and CombustionDokumen9 halamanHeat Transfer and CombustionmihailmiBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Balances ExplainedDokumen34 halamanEnergy Balances ExplainedAllen HuangBelum ada peringkat
- 1.5 NPS RecuperatorDokumen7 halaman1.5 NPS RecuperatorAnonymous pVoSWn8yh0Belum ada peringkat
- CO2 Reduction From Glass Melting Furnaces by Oxy-Guel Firing Combined With BatchCullet PreheatingDokumen5 halamanCO2 Reduction From Glass Melting Furnaces by Oxy-Guel Firing Combined With BatchCullet PreheatingtedmozbiBelum ada peringkat
- PHD Thesis, Md. HasanuzzamanDokumen159 halamanPHD Thesis, Md. Hasanuzzamandedi sanatraBelum ada peringkat
- Noc18 Me43 Assignment1Dokumen5 halamanNoc18 Me43 Assignment1Vivek SonagaraBelum ada peringkat
- Textron Lycoming AGT1500 Engine - Transitioning For Future ApplicationsDokumen11 halamanTextron Lycoming AGT1500 Engine - Transitioning For Future ApplicationsThallezBelum ada peringkat
- Clasificacion de IntercambiadoresDokumen73 halamanClasificacion de IntercambiadoresAviBelum ada peringkat
- ADokumen22 halamanAAntonio LoretoCortesBelum ada peringkat
- A DEH PR-2014-0016-GB CAIRpool BR R3-05-2016 150Dokumen16 halamanA DEH PR-2014-0016-GB CAIRpool BR R3-05-2016 150Eldin JelecBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Exchanger Design and SelectionDokumen44 halamanHeat Exchanger Design and Selectiondenizkund100% (1)
- Design and Optimisation of Organic Ranking Cycle and Absorption Chiller For Heat Recovery of Petroleum RefiningDokumen75 halamanDesign and Optimisation of Organic Ranking Cycle and Absorption Chiller For Heat Recovery of Petroleum RefiningAndRew SteFanusBelum ada peringkat
- Ecm Question BankDokumen1 halamanEcm Question BankSamar PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Iti Ecomax GB PDFDokumen78 halamanIti Ecomax GB PDFV MANOHAR SAIBelum ada peringkat
- Improved Design For Supercritical Co2 Brayton Cycle Powered Coal-Fired Power PlantDokumen51 halamanImproved Design For Supercritical Co2 Brayton Cycle Powered Coal-Fired Power PlantIrshad AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Microturbine Generators: Fig 1.block Diagram of A Microturbine Generator SystemDokumen21 halamanMicroturbine Generators: Fig 1.block Diagram of A Microturbine Generator SystemanoopijtBelum ada peringkat
- Publication: Billet Homogenizing - Batch or Continuous?Dokumen11 halamanPublication: Billet Homogenizing - Batch or Continuous?조기현Belum ada peringkat
- Nozzles and Diffusers, Turbines, Compressors and Pumps, Heat Exchangers, and Throttling DevicesDokumen19 halamanNozzles and Diffusers, Turbines, Compressors and Pumps, Heat Exchangers, and Throttling Devicesvicencio390% (1)