CH7LIGHTCOLOURSIGHT
Diunggah oleh
Rachel LimDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CH7LIGHTCOLOURSIGHT
Diunggah oleh
Rachel LimHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CHAPTER 7 LIGHT, COLOUR AND SIGHT
1. THE FORMATION OF IMAGES BY PLANE MIRRORS AND LENSES
The characteristics of an image formed on a plane mirror are
1. virtual
2. inverted laterally
3. upright
4. the same size as the object
5. image distance and object distance from the plane mirror are the same
The characteristics of an image formed by a convex lens are
1. virtual or real
2. upright or inverted
3. diminished or enlarge
The characteristics of an image formed by a concave lens are
1. virtual
2. upright
3. diminished
Object distance is the distance between the object and the optical central.
Image distance is the distance between the image and the optical central.
Optical central is the point at the centre of a lens.
Principal axis is the straight line which passes through the optical central at a right
angle to the axis of the lens.
Focal point is the point on the principal axis where light rays that are parallel to the
principal axis will converge after passing through a lens.
2. THE FORMATION OF IMAGES BY OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
1. A periscope consists of two plane mirrors arranged facing one another at an angle
of 45°.
The image formed by a periscope is virtual, upright and same size as the object
2. A magnifying glass is made of biconvex lens.
The image formed by a magnifying glass is virtual, upright and larger than the actual
size of the object.
3. A microscope consists of two convex lenses, i.e. objective lens and eyepiece.
The focal length of the objective lens of the microscope is shorter than of the
eyepiece.
4. A telescope consist of the convex lenses, i.e. objective lens and eyepiece.
The objective lens of the telescope has a longer focal length while the eyepiece
has a shorter focal length.
5. A camera consists of three main parts, which are the lens, the shutter and the film.
The image formed on a photography film is real, invented and smaller than the
actual size of the object.
6. In eye - The characteristics of the images formed on the retina and the pin-hole camera are
real, invented and smaller than the actual size of the object.
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 105
3. LIGHT DISPERSION
Light dispersion is a process in which white light is split into its colour constituents
called a spectrum when it passes through a prism.
A spectrum consists of seven colours in this order: red, orange, yellow, green, blue,
indigo and violet.
Light dispersion occurs because each colour constituents travels at a different speed
through the prism.
Rainbow is formed when sunlight passes through raindrops. The sunlight is
refracted and dispersed into its colour constituents.
4. LIGHT SCATTERING
Light scattering occurs when white light is directed incident to particles like gas
molecules, water vapour and dust, and the light rays are obstructed and reflected.
The light rays will scatter in all directions.
Lights with shorter wavelengths are refracted more. Blue light is refracted more than red light.
Examples of light scattering which occurs in natural phenomena are blue sky at noon
and red sun during sunset.
5. THE ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION OF COLOURED LIGHT
Primary colours are colours which cannot be obtained from mixing others colours.
The primary colours of light are red, blue and green.
Secondary colours are colours produced from adding two primary colours. The
secondary colours produced from lights are yellow, mangenta ang cyan.
The absorption of coloured light by a coloured filter is called subtraction of
coloured lights.
A primary-coloured object only reflects light of the same colour.
A secondary-coloured object reflects light of the same colours as well as the
primary colours that form the colour.
Magenta
White
Blue Red
Cyan Yellow
Green
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 106
6. THE APPEARANCE OF COLOURED OBJECTS
A white object appears white in white light because it reflects all colours while a
black object appears black because all colours are absorbed by it.
The absorption of light by a coloured object is based on the principle of subtraction
of coloured lights.
The rod cell in the retina is sensitive to light of low intensity. This cell is not sensitive
to colours.
The cone cell can detect colour as it is sensitive to high intensity light.
7. THE EFFECTS OF MIXING PIGMENTS
Pigments are materials that absorb certain coloured lights and reflect coloured lights
that are not absorbed by the pigments.
The primary colours of pigments are red, blue and yellow.
Mixing pigments is based on the principle of subtraction of coloured lights.
Violet
Black
Blue Red
Green Orange
Yellow
8. THE IMPORTANCE OF COLOUR IN DAILY LIFE
The uses of colour in daily life are printing, electrical writing, traffic lights, symbols
and signals.
The importance of colour to animals is to protect themselves from danger, to attract
attention of the females species and to warn other animal to keep away.
The importance of colour to plants include to attract animals for pollination purposes
and to warn animals and humans of its toxicity.
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 107
PAPER 1
1. Which of the following causes the formation of image in a plane mirror ?
A. Addition of light
B. Refraction of light
C. Reflection of light
D. Scattering of light
2. What are the characteristics of image formed by the plane mirror?
A. Real, inverted and same size
B. Virtual, inverted and smaller size
C. Real, laterally inverted and bigger size
D. Virtual, laterally inverted and same size
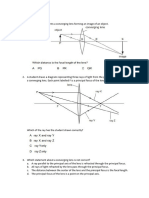
3. The diagram shows an object which is placed in front of a plane mirror.
Object Plane mirror
Which image appears in the plane mirror ?
A.
B.
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 108
4. A student stands 3.0 m in front of a plane mirror . If the mirror is moved 1.0m away from
the student , how far is the image from the student?
A. 3.0m
B. 4.0 m
C. 6.0 m
D. 8.0 m
5 . The characteristics of an image formed by a concave lens for an object placed at a
distance of two focal length are
A. Real, upright and larger size
B. Real, inverted and same size
C. Virtual, inverted and larger size
D. Virtual, upright and smaller size
6. Which of the following correctly represents the part of a light ray passing through the lens?
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 109
7. Which of the following ray diagram is correct?
A C
B D
8. A driver wants to overtake the car in front of him, takes a quick look at the side mirror.
Which of the following image he has seen?
A. Real and upright
B. Real and inverted
C. Virtual and upright
D. Virtual and inverted
9. Which of the following can formed a real image?
A. A plane mirror
B. A convex lens
C. A concave lens
D. A glass prism
10. Which of the following image cannot be seen on a screen?
A. Real image
B. Virtual images
C. Inverted images
D. Diminished image
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 110
11. The diagram shows the position of an object W in front of a convex len. At which of the
following positions A,B,C and D is the image of object W formed.
Object W
A B C D
O
3F 2F F F 2F 3F
12 . Which of the following optical instrument uses plane mirrors?
A. Camera C. Telescope
B. Periscope D. Microscope
13. The diagram shows the word SCIENCE under a magnifying glass.
SCIENCE
Magnifying glass
What is the distance between the word and the lens?
A. Twice the focal length of the lens
B. Equal the focal length of the lens
C. Less than the focal length of the lens
D. More than the focal length of the lens
14. A student uses a convex len to check the internal components of a radio.
What is the distance between the lens and the radio in order to see a larger image?
A. Twice the focal length
B. The same as the focal length
C. Less than the focal length
D. More than twice the focal length
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 111
15 The diagram shows an image formed by a convex len.
Which of the following optical instrument uses this arrangement?
A. A glass
B A projector
C. A magnifying camera
D. A photographic enlarger
16 . Periscope can be formed by using two plane mirrors.
Which of the following is the correct arrangement of the mirrors in the periscope?
A B C D
17. The diagram shows an experiment using light.
Red
Light source
Violet
Glass Prism
Which of the following process occur in the glass prism?
A. Addition of light
B. Light scattering
C. Dispersion of light
D. Subtraction of light
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 112
18 . Which of the following causes rainbow?
A. Lights is refracted by droplets of water in the atmosphere
B. Lights is scattered by dust particles in the atmosphere after rain
C. Lights is reflected and scattered by dust particles in the atmosphere after rain
D. Lights is reflected and dispersed by droplets of water in the atmosphere after rain
19 . The diagram shows a beam of white light passing through a prism and forms a
spectrum of light on the white screen.
Which of the following represent he colour of the spectrum at Q?
A. Violet C. Yellow
B. Red D. Blue
20 . The diagram shows a beam of white light passes through prism R and S.
Which of the following is formed on the screen?
A. Red spot
B. Black spot
C. White spot
D Yellow spot
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 113
21. The diagram shows the structure of a camera
Which of the following is the function of X?
A. Allow the light through
B. Control the amount of light
C. Adjust the position of the image
D. Control the duration of light exposure
22 . Diagram shows a human eye
X
Which part of the camera has a similar function to part X in the human eye?
A. Lens C. Diaphragm
B. Aperture D. Focusing ring
23 . The figure shows a pinhole camera with three holes.
Which of the following image is formed on the screen?
Screen
Hole
Object
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 114
A C
B D
24. What happens to the lens of our eyes when we look at a distant object?
A. Thinner
B. Thicker
C. Shorter
D. No change.
25 . Which of the following pair functions to control the amount of light?
Eye Camera
A. Iris Diaphragm
B. Pupil Shutter
C. Cilliary body Focus adjuster
D. Retina Lens
26 . Which of the following shows the correct adjustment of the eye when we move from a
bright room into a dark room?
A. The lens become thinner
B. The lens becomes thicker
C. The pupil becomes bigger
D. The pupil becomes smaller
27. Why is a colour blind person not able to identify red and green objects ?
A. Damage of iris
B. Damage of lens
C. Damage of retina
D. Damage of cone cell
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 115
28 . The diagram shows the natural phenomenon of the sky at noon.
Which colour of the sunlight is dispersed most?
A. Blue C. Green
B. White D. Yellow
29. Which of the following statement is correct about light scattering?
A. Light splits into its component colours
B Light is subtracted from its component colours
C. Light is reflected and dispersed into different coloured light
D. Light is reflected and scattered in all directions by suspended particles
30 . At noon the sky is blue. Which of the following cause this phenomenon?
A. Reflection of the blue light from the sea water
B. Reflection of the blue light from the surface of the earth
C. Absorption of blue light by the particles in the atmosphere
D. Scattering of the blue light by the particles in the atmosphere
31. The diagram shows a blue light passing through a coloured filter.
Blue light Black
Filter
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 116
Which of the following is the colour of the flter ?
A. Cyan B. Magenta C. Blue D. Yellow
32. The diagram shows a red light and a cyan light which are projected onto a white screen.
What colour can be seen at X,Y and Z?
X Y Z
A. Red Magenta Blue
B. Blue Cyan Yellow
C. Blue White Yellow
D. White Black Red
33 . The diagram shows an overlapping of coloured lights.
What is the colour of light in the shaded area?
A. White C. Cyan
B. Green D. Blue
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 117
34 . The diagram shows a beam of white light passing through a glass prism. A yellow and
magenta filter is placed between the prism and the screen.
Yellow Magenta
filter filter
White screen
Beam of
white light
Glass Prism
Which of the following colour do you expect to observe on the screen?
A. Red C. Magenta
B. Green D. Yellow
35 . Which of the following pairs of coloured light addition could form white colour?
A. Cyan and red
B. green and yellow
C. Yellow and cyan
D. Magenta and blue
36 . Which of the following statement is correct about black objects?
A. The objects transfer any light
B. The objects reflects any light
C. The objects absorbed any light
D. The objects scattered any light
37. The diagram shows a beam of white light that is allowed to pass through a yellow filter,
green filter and red filter.
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 118
What is the colour of P,Q and R?
P Q R
A Yellow Green Red
B Red Red No light
C Green Red No light
D Yellow Green No light
38 . The figure below shows the overlapping of three primary colours.
Blue
Q
Red
Green
Which of the following colour is formed at Q?
A. White C. Indigo
B. Orange D. Magenta
39. Why does a white object appear white?
A. Absorb any light
B. Reflects any light
C. Transmits any light
D. Absorb green light
40. The diagram shows a coloured object under the coloured light.
Eye
Blue light
Red Object
Which of the following is the colour of the object appeared?
A. Blue C. White
B. Red D. Black
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 119
41. The diagram shows an experiment on the subtraction of coloured light.
Red light
Green leaf
The colour of the leaf will appear
A. Green C. Red
B. Black D. Yellow
42. The diagram shows a flower.
Which of the following coloured lights can make the petal appears red?
A. Blue light C. Magenta
B. Green light D. Cyan light
43. When certain coloured light is shined on to magenta object, the object appears red.
Which of the following is the coloured light?
A. White C. Yellow
B. Green D. Magenta
44 . The diagram shows the colours of a shirt and skirt seen under different coloured light.
Red Black
Green Green
Seen under Seen under
white light light X
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 120
What is the colour of light X ?
A. Blue C. Red
B. Green D. Yellow
45 . The diagram shows a circular cardboard painted with three different pigments.
White
Blue
Red
When the cardboard is seen under a blue light, which of the following is the correct
appearance of the cardboard?
A C
Blue Blue
Red
Blue Black
B
D
Blue Blue
Black
Blue
46. A yellow flower appears red when seen under a red light. Which of the following
statements is correct about the observation?
A. The yellow flower reflect red light.
B. The yellow flower has absorbed the blue colour.
C. The mixing of yellow colour and the light gives red colours.
D. We only can see the colour of the light and can not see the colour of the flower.
47 . If a white shirt is to be turned to an orange colour, which colour dyes must be used?
A. Blue and green C. Yellow and red
B. Red and blue D. Green and red
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 121
48. The diagram shows a batik-printing process
Printing Block
Blue Cloth
Q turns green
What is the original colour of Q?
A. Red C. Green
B. Cyan D. Yellow
49. Which of the following coloured inks are used in colour printing?
A. Red, blue, green and black
B. Blue, green, yellow, and black
C. Cyan, magenta, red and black
D. Magenta, yellow, cyan and black
50. Which of the following is the importance of colours to human being?
A. Helps in pollination
B. Used in electrical wiring
C. As a warning to other animals
D. Enable us to hide from danger
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 122
PAPER 2
SECTION A
1. Diagram 1 shows an experiment to measure the focal length of convex lens.
White screen Convex lens
Light from
distance object
Convex lens
White screen
Light from
distance object
DIAGRAM 1
Type of convex lens Focal length
Thin lens
Thick lens
(a) State the hypothesis of the experiment.
…………….……………………………………………………………………………
[ 1 Mark]
(b) Fill the table above. [2 Marks]
(c) Name the following variable for the above experiment
(i) Manipulated
…………………………………………………………………….
(ii) Responding
…………………………………………………………………….
(iii) Constant
……………………………………………………………………. [2 Marks]
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 123
(d) What is operational definition for focal length in this experiment?
……………………………………………………………………………………
……..……………………………………………………………………..………
[ 1 Mark]
2. Diagram 2 shows an experiment using pin-hole camera .
Pin-hole camera
S
DIAGRAM 2
The results of the experiment is shown in the table below
Size of pin-hole Characteristics of image
Small Sharp image
Big Blurred
a) State the hypothesis of the experiment.
…………….……………………………………………………………………………
…………….……………………………………………………………………………
[ 1 Mark]
b) What is the observation of the experiment?
…………….……………………………………………………………………………
…………….……………………………………………………………………………
[ 1 Mark]
c) What inference could be made from the experiment?
…………….……………………………………………………………………………
…………….……………………………………………………………………………
[ 1 Mark]
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 124
d) Name the following variable for the above experiment
(i) Manipulated
…………………………………………………………………….
(iv) Responding
…………………………………………………………………….
(v) Constant
…………………………………………………………………….
[3 Marks]
e) Predict the image formed when a convex lens is placed at S in Diagram 3.
…………………………………………………………………………….
[1 Mark]
SECTION B
1. Diagram 3 shows the addition of coloured lights.
S
R
DIAGRAM 3
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 125
(a) Complete the table below.
Area Colour of light
P
Q
R
S
(b) What is the name for colour Q and R?
………………………………………………………………………………
[ 1 Mark]
(c) (i) What is the colour of green object located at S?
………………………………………………………………………………
[ 1 Mark]
(ii) Give reason for your answer.
………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………… [2
Marks]
2. Diagram 4 shows a periscope. An observer is looking at an object.
Plane mirror
Object
Obstacle
Observer
Plane mirror
DIAGRAM 4
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 126
(a) Draw the light rays reaching the eye of the observer.
[ 1 Mark]
(b) What principle is applied in a periscope.
……………………………………………………………………
[ 1 Mark]
(c) Name one other material which can be used to replace the plane mirror.
………………………………………………………………………………
[ 1 Mark]
(d) State one other use of the periscope.
………………………………………………………………………………
[ 1 Mark]
3. Diagram 5 shows an object P placed in front of a pinhole camera.
Hole Y
Screen
Object
Z
Pinhole camera
DIAGRAM 5
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show how an image is formed in diagram 5.
[ 1 Mark]
(b) Measure and write the size of image formed.
..............................cm [ 1 Mark]
(c) Predict the characteristics of image if the number of hole Y is increase to three?
.....................................................................................................................
[ 1 Mark]
(d) Name other optical device which has the same characteristics as the
image produced in Diagram 5.
.....................................................................................................................
[ 1 Mark]
(e) What is the size of image formed if the object is placed at Z?
.....................................................................................................................
[ 1 Mark]
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 127
4. Diagram 6 shows a convex lens and an object.
2F
O
2F F F
DIAGRAM 6
(a) Complete the ray diagram above to show the image formed. [ 2 Marks]
(b) Give two characteristics of the image formed.
(i) ..............................................................................
ii) ..............................................................................
[ 2 Marks]
(c ) If the object is moved far away from the convex lens, what will happen to the
image formed?
.....................................................................................................................
[ 1 Mark]
(d) What is the characteristics of the image if convex lens is replaced with concave
lens?
.....................................................................................................................
[ 1 Mark]
(e) Give one optical instrument that has similar arrangement as shown in
Diagram 6.
……………………………………………………………………………….
[ 1 Mark]
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 128
5. Diagram 7(a) shows two filters are placed in front of two torchlight X and Y
respectively . The lights falls on the white screen and overlaps as shown in
Diagram 7 (b).
DIAGRAM 7(a) DIAGRAM 7(b)
(a) What are the colours seen at A and B?
.....................................................................................................................
[ 1 Mark]
(b) What are the primary colours formed in (a)?
............................................................................................................
[ 1 Mark]
(c ) If a magenta filter is placed in front of the blue filter Y , what colour is seen at A?
.....................................................................................................................
[ 1 Mark]
(d) A bunches of red roses stands under the B light.
What is the colour of the
(i) roses
...........................................................................................................
(ii) leaves
............................................................................................................
[ 2 Marks]
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 129
SECTION C
1.
The spectacles of old people have shorter focal lengths than those of a student who in
long-sighted. This is because the lenses in their spectacles have a different thickness.
You are given the convex lens with different thickness.
(a) Suggest a hypothesis to investigate the above statement. [1 Mark]
(a) Describe an experiment to test your hypothesis in (a) based on the following
criteria.
i) Aim of the experiment. [1 Mark]
ii) Identification of variables [ 2 Marks]
iii) List of apparatus and materials [1 Mark]
iv) Procedure or method [3 Marks]
v ) Tabulation of data [1 Mark]
vi) Conclusion [1 Mark]
2. (a) What are the differences between images formed by a convex lens and
a plane mirror ? [4 Marks]
(b) Diagram shows three instruments which use convex lens.
Telescope Microscope
Instruments use
convex lens
Magnifying glass
Study the above diagram and develop a concept of optical instruments.
Your answer should be based on the following aspects.
Identify two common characteristics of optical instruments.
Develop an initial concept of a optical instruments.
Give one example of a optical instrument which uses convex lens and
one which does not use convex lens.
Give reason for each choice.
Develop the actual concept. [6 Marks]
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 130
3. (a) Make comparisons between focusing an image in human eye and
camera. [ 4 Marks]
(c) A student wants to look at something behind a wall. However, he unable to do
so. Based on your knowledge in science, suggest an apparatus and explain how
it works to the student to solve his problem.
Your answer should include the following:
Identify the problem.
Clarification of the problem
Solving methods
Explain the method using. [ 6 Marks]
SES 1511 Kelantan 2007 www.sciencespmform4.blogspot.com 131
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Physics 2Dokumen11 halamanPhysics 2bort kortBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE Test Paper-01 Chapter 10 Light Reflection and RefractionDokumen11 halamanCBSE Test Paper-01 Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refractionshubham sehgalBelum ada peringkat
- Module 6Dokumen9 halamanModule 6chef curryBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Science TP 10 1Dokumen8 halaman10 Science TP 10 1Ajjuu ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Sci10 SLM Q2 M4Dokumen29 halamanSci10 SLM Q2 M4Jairos Marata BrasileñoBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Unit 7 Part 2 NotesDokumen38 halamanPhysics Unit 7 Part 2 NotesTaylor Waddell-SmithBelum ada peringkat
- Properties of LightDokumen10 halamanProperties of LightKesanam SpBelum ada peringkat
- LightDokumen5 halamanLightnarayanaBelum ada peringkat
- 08 Science Light 01Dokumen5 halaman08 Science Light 01Ranjan RoyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Light Class 7 Chapter Q and ADokumen9 halamanChapter Light Class 7 Chapter Q and ADaiwik GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Science 10 Module 2 Week 6-8 - MabiniDokumen27 halamanScience 10 Module 2 Week 6-8 - MabiniChristine Joy EngoBelum ada peringkat
- X April Physics LightDokumen2 halamanX April Physics Lightprasidh2021Belum ada peringkat
- Worksheet Answers - Vii - Light (Part 2)Dokumen6 halamanWorksheet Answers - Vii - Light (Part 2)Suvam Dasgupta100% (1)
- Thin LensesDokumen5 halamanThin Lenseszamrafathi58Belum ada peringkat
- Light - AnswersDokumen3 halamanLight - AnswersSanyam 1 BBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-10 - Light: Reflection and RefractionDokumen15 halamanChapter-10 - Light: Reflection and RefractionVineet SierraBelum ada peringkat
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 12: Reflection of Light in A Plane MirrorDokumen12 halamanScience: Quarter 2 - Module 12: Reflection of Light in A Plane MirrorMichaela Teodoro100% (1)
- Class Test 10 (RRH)Dokumen3 halamanClass Test 10 (RRH)Jeevanshu SoniBelum ada peringkat
- X Study MaterialDokumen10 halamanX Study MaterialbharatshrawagiBelum ada peringkat
- GR 7 - LIGHT - ANSWER KEYDokumen3 halamanGR 7 - LIGHT - ANSWER KEYJoseph JayakanthanBelum ada peringkat
- Science: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDokumen26 halamanScience: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsFhien Garcia100% (2)
- Summative-2 3Dokumen2 halamanSummative-2 3Al Bert JaymeBelum ada peringkat
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 7 Science Chapter 15Dokumen7 halamanNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 7 Science Chapter 15deepak.idea84Belum ada peringkat
- LP Test 2Dokumen6 halamanLP Test 2Jade Thong EchaviaBelum ada peringkat
- Title Card: Lesson 12: Mirror Images Are Laterally InvertedDokumen16 halamanTitle Card: Lesson 12: Mirror Images Are Laterally InvertedNathan Francis Enzo NicolasBelum ada peringkat
- Sci10 Q2 M4 EditedaftercontentlayoutlanguageevaluationDokumen37 halamanSci10 Q2 M4 EditedaftercontentlayoutlanguageevaluationAqua AvilaBelum ada peringkat
- Class VIII LightDokumen2 halamanClass VIII Lightbose baraniBelum ada peringkat
- Class 7 Chapter 12 LightDokumen12 halamanClass 7 Chapter 12 Lightsiddharthsg37Belum ada peringkat
- 7th ch-16 Light and Its Reflaction Solution Living ScienceDokumen3 halaman7th ch-16 Light and Its Reflaction Solution Living SciencesabletarsingBelum ada peringkat
- Notebook Work CH - 16 (Light)Dokumen9 halamanNotebook Work CH - 16 (Light)Adhya MisraBelum ada peringkat
- SCIENCE10 Q2 M4 LightsMirrorsandLenses v3-EDITEDDokumen22 halamanSCIENCE10 Q2 M4 LightsMirrorsandLenses v3-EDITEDRusty Gabriel Suyom100% (1)
- CHAPTER 7 Light, Sight and ColourDokumen43 halamanCHAPTER 7 Light, Sight and ColourAkmar MataliBelum ada peringkat
- Lenses Q and AnsDokumen13 halamanLenses Q and AnsAnkita SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Form 1 Light and OpticsDokumen25 halamanForm 1 Light and OpticsZern MegaBelum ada peringkat
- Questions On Mirrors and LensesDokumen29 halamanQuestions On Mirrors and LensesKamal Naser100% (2)
- 11 Chapter Section 3 & 4Dokumen38 halaman11 Chapter Section 3 & 4eherrerahghsBelum ada peringkat
- Quarter 1 - Module 4 Reflection of Light in Mirrors Week 6Dokumen20 halamanQuarter 1 - Module 4 Reflection of Light in Mirrors Week 6Anjelo Marick AvilesBelum ada peringkat
- Science10 Q2 Mod3 Qualitative-Characteristics-Of-Images Ver2Dokumen24 halamanScience10 Q2 Mod3 Qualitative-Characteristics-Of-Images Ver2layannakei.maghanoyBelum ada peringkat
- The Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDokumen2 halamanThe Human Eye and The Colourful WorldXxxxxxBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Plan in Science 10: Unit Topic: Content Standard: Learning CompetenciesDokumen13 halamanLearning Plan in Science 10: Unit Topic: Content Standard: Learning Competenciesakoaysijoy100% (1)
- Cbse Test Paper-05 11 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDokumen7 halamanCbse Test Paper-05 11 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldTanmay KatyalBelum ada peringkat
- Class 7 Answers CH 15Dokumen4 halamanClass 7 Answers CH 15Vibhuti Bhushan RaiBelum ada peringkat
- F1-C8 PHY LightDokumen78 halamanF1-C8 PHY LightNurul FadhilahBelum ada peringkat
- Class 7 L 15 Light QADokumen3 halamanClass 7 L 15 Light QAMinnilaBelum ada peringkat
- A GENERAL PHYSICS II Q4M4 Teacher Copy Final LayoutDokumen38 halamanA GENERAL PHYSICS II Q4M4 Teacher Copy Final LayoutJimros CabigBelum ada peringkat
- B GENERAL PHYSICS II Q4M4 Learner Copy Final LayoutDokumen37 halamanB GENERAL PHYSICS II Q4M4 Learner Copy Final LayoutJimros CabigBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Science TP 11 1Dokumen5 halaman10 Science TP 11 1Ananaya BansalBelum ada peringkat
- Coursebook: Track Your ProgressDokumen5 halamanCoursebook: Track Your ProgressKrishaBelum ada peringkat
- Science - Winter Vacation Homework N StarDokumen50 halamanScience - Winter Vacation Homework N Starishaansinha2728Belum ada peringkat
- Mirror (Assessment)Dokumen3 halamanMirror (Assessment)Jhun Dimate FerreroBelum ada peringkat
- LIGHT Physics Form 4Dokumen11 halamanLIGHT Physics Form 4Amrita KaurBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Activity Sheet 4 q4 and ST 2Dokumen14 halamanLearning Activity Sheet 4 q4 and ST 2Daniel Angelo Esquejo ArangoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 9Dokumen84 halamanChapter 9rohit murmuBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7: Light, Colour and Sight: 7.1 Formation of ImagesDokumen9 halamanChapter 7: Light, Colour and Sight: 7.1 Formation of ImagesTensa ZhangetsuBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd Quarter Summative 5Dokumen12 halaman2nd Quarter Summative 5Angelito MadesBelum ada peringkat
- Study Material Class 10 Chapter 11 2017Dokumen13 halamanStudy Material Class 10 Chapter 11 2017satishBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Lesson PLan - Image Formation by LensesDokumen9 halamanDetailed Lesson PLan - Image Formation by LensesCyril Cauilan100% (1)
- Module 15 Voltaic CellDokumen7 halamanModule 15 Voltaic CellNor Azrul IkwanBelum ada peringkat
- MODULE 11: Chemical Bonding 2 Answer All QuestionDokumen2 halamanMODULE 11: Chemical Bonding 2 Answer All QuestionTan AylinBelum ada peringkat
- Science Form 1 Chapter 1Dokumen19 halamanScience Form 1 Chapter 1Mzari Mzain100% (5)
- Math f5 Melaka Midyear 2010 Paper 1 & 2 (QA)Dokumen53 halamanMath f5 Melaka Midyear 2010 Paper 1 & 2 (QA)SuLtano_Ehsano_6369Belum ada peringkat
- Module 14 ElectrolysisDokumen32 halamanModule 14 ElectrolysisTan AylinBelum ada peringkat
- Module 16 Acids N BasesDokumen6 halamanModule 16 Acids N BasesTan AylinBelum ada peringkat
- Module 13 Periodic Table & Chemical BondDokumen2 halamanModule 13 Periodic Table & Chemical BondTan AylinBelum ada peringkat
- MODULE 10: Chemical Bonding 1 Answer All QuestionDokumen2 halamanMODULE 10: Chemical Bonding 1 Answer All QuestionTan AylinBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1 Chemical FormulaeDokumen5 halamanModule 1 Chemical FormulaechongpeisiBelum ada peringkat
- MODULE 11: Chemical Bonding 2 Answer All QuestionDokumen2 halamanMODULE 11: Chemical Bonding 2 Answer All QuestionTan AylinBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1 Chemical FormulaeDokumen5 halamanModule 1 Chemical FormulaechongpeisiBelum ada peringkat
- Skema JawapanDokumen11 halamanSkema JawapanHalen WolfBelum ada peringkat
- Module 2 Chemical EquationDokumen4 halamanModule 2 Chemical EquationTan AylinBelum ada peringkat
- Chem f4 Chapter 5 PretestDokumen3 halamanChem f4 Chapter 5 PretestTan AylinBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolysis TestDokumen4 halamanElectrolysis TestTan AylinBelum ada peringkat
- MODULE 10: Chemical Bonding 1 Answer All QuestionDokumen2 halamanMODULE 10: Chemical Bonding 1 Answer All QuestionTan AylinBelum ada peringkat
- Skema Pemarkahan Percubaan Penilaian Menengah Rendah (PMR) 2010 Sains - K 1 Nombor Soalan JawapanDokumen5 halamanSkema Pemarkahan Percubaan Penilaian Menengah Rendah (PMR) 2010 Sains - K 1 Nombor Soalan JawapanTan AylinBelum ada peringkat
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 2 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMDokumen11 halamanCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 2 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMJay Bee83% (29)
- Marking Scheme Paper 3Dokumen13 halamanMarking Scheme Paper 3Tan AylinBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 2 MSDokumen9 halamanPaper 2 MSTeoh Han JieBelum ada peringkat
- Mid Year Exam Science Form 2 2011 LatestDokumen22 halamanMid Year Exam Science Form 2 2011 LatestTan AylinBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Modul of Pahang For RedoxDokumen37 halaman12 Modul of Pahang For RedoxkhayranizamBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 1 Mid Year Exam Form 4Dokumen14 halamanPaper 1 Mid Year Exam Form 4Dalila56% (16)
- 2 Atomic Structure and Isotopes (Lectures)Dokumen17 halaman2 Atomic Structure and Isotopes (Lectures)Ishraqi IlyasBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Coordinate GeometryDokumen8 halaman6 Coordinate GeometryLeong Mei LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Marking Scheme Paper 2Dokumen13 halamanMarking Scheme Paper 2Tan AylinBelum ada peringkat
- ABC Is Acute.: Solution of TrianglesDokumen5 halamanABC Is Acute.: Solution of TrianglesSyafiqah RedzwanBelum ada peringkat
- Bab3 PDFDokumen5 halamanBab3 PDFRodiyah SulaimanBelum ada peringkat
- Skema JawapanDokumen11 halamanSkema JawapanHalen WolfBelum ada peringkat