Nota Peta Minda Tahun 4,5,6 Sains 2010
Diunggah oleh
mbarathi20 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
8 tayangan57 halamansains
Judul Asli
Nota Peta Minda Tahun 4,5,6 Sains~2010
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inisains
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
8 tayangan57 halamanNota Peta Minda Tahun 4,5,6 Sains 2010
Diunggah oleh
mbarathi2sains
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 57
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 1 -
SK Permatang Tok Mahat
14300 Nibong Tebal, SPS,
Pulau Pinang
Name :
Class :
Teacher : En. Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria
Mind Maps Mind Maps Mind Maps Mind Maps
Science Science Science Science- -- -018 018 018 018
UPSR 2010 UPSR 2010 UPSR 2010 UPSR 2010
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 2 -
MENYIASAT ALAM KEHIDUPAN MENYIASAT ALAM KEHIDUPAN MENYIASAT ALAM KEHIDUPAN MENYIASAT ALAM KEHIDUPAN
Year 4
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 3 -
Basic Needs of Human
Keperluan Asas Manusia
Food /
Makanan
Air / Udara
Give energy / Beri tenaga
Grow / Membesar
Stay healthy / Sihat
1.1 Understanding that humans have basic needs
Memahami bahawa manusia mempunyai keperluan
asas
Water / Air
Drinks / Minuman
Grow / Membesar
Stay healthy / Sihat
Shelter / Tempat
perlindungan
To protect from
Untuk melindungi daripada
- danger / bahaya
- extreme weather / cuaca
melampau
-sun & rain / matahari dan
hujan
To breathe / Bernafas
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 4 -
Basic Needs of Animals
Keperluan Asas Haiwan
Food /
Makanan
Shelter / Tempat
Perlindungan
Air / Udara
Water / Air
To breathe / Bernafas
To protect from
Untuk melindungi daripada
- danger / bahaya
- extreme weather / cuaca
melampau
- sun & rain / matahari dan hujan
Give energy / Beri tenaga
Grow / Bertumbuh @ Membesar
Stay healthy / Sihat
Drinks / Minuman
Grow / Bertumbuh @ Membesar
Stay healthy / Sihat
1.2 Understanding that animals have basic needs
Memahami bahawa manusia mempunyai keperluan
asas
Types / Jenis :
- holes / lubang
- cave / gua
- nest / sarang
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 5 -
Plants Have Basic Needs
Tumbuhan Mempunyai Keperluan Asas
Air /
Udara
Sunlight /
Cahaya matahari
Water /
Air
With water / Ada air :
- grow healthy / tumbuh dengan sihat
- grow well / tumbuh dengan baik
- not wilted / tidak layu
Without water / Tanpa air:
- wilted / layu
- turn yellow / menjadi kuning
- die / mati
1.3 Understanding that plants have basic needs
Memahami bahawa tumbuhan mempunyai keperluan
asas
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 6 -
2.1 Analysing life processes in humans
Analisa proses hidup manusia
Life Processes of
Humans
Proses Hidup Dilalui
Manusia
Respond To
Stimuli
Bergerak balas
Terhadap
Ransangan
Breathing
Pernafasan
Reproduce
Membiak
Organs
Organ
Inhale take in air
Tarik nafas ambil udara
Exhale give out air
Hembus nafas- keluarkan udara
Nose/Mouth Wind-pipe Lungs
Hidung/Mulut Trakea Paru-paru
A process to produce
their young or offspring
Proses untuk
menghasilkan anak
Rate of breath
Kadar pernafasan
Number of chest movement in a
period of time
Bilangan pergerakan dada dalam
sesuatu masa
Organs
Organ
Eyes Sight
Mata - Melihat
Nose Smell
Hidung - Menghidu
Tongue Taste
Lidah - Merasa
Ears Sound
Telinga - Mendengar
bunyi
Skin Touch
Kulit - Sentuhan
Excrete
Berkumuh
Defecate
Bernyahtinja
Kidney ( urine + mineral salt )
Ginjal ( air kencing + garam mineral )
Faeces
Najis
Purpose / Tujuan :
- avoid danger
elak bahaya
- avoid getting hurt
elak dapat luka
- avoid getting injured
elak dapat cedera
- to survive
untuk terus hidup
Lungs ( Carbon dioxide + water vapour )
Paru-paru ( Karbon dioksida + wap air )
Skin ( Sweat + mineral salt )
Kulit ( peluh + garam mineral )
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 7 -
2.2 Being aware that certain behaviour can disturb life processes
Menyedari bahawa sesetengah perlakuan mengganggu
proses hidup
Smoking /
Merokok
Drinking Alcohol / Minum
Alkohol
Effects / Kesan
- Lung cancer
Kanser paru-paru
- Coughing
Batuk
Effects / Kesan
- Delay respond to stimuli
Lambatkan ransangan terhadap
ransangan
- Lose ability to walk in straight
line
Hilang keupayaan berjalan dengan
lurus
- Can cause accidents
Menyebabkan kemalangan
How to avoid / Bagaimana untuk
hindari
Participate in a campaign
Ambil bahagian dalam kempen
Advise from their peers
Nasihat daripada rakan sebaya
Occupied time with beneficial
activities
Memenuhi masa dengan
aktiviti berfaedah
Behaviour That Can Disturb Life Processes
Perlakuan yang boleh mengganggu proses hidup
Taking Drug / Mengambil
Dadah
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 8 -
2.3 Analysing the life processes in animals
Analisa proses hidup haiwan
Animals Life Processes/Proses Hidup Haiwan
Breathing /
Bernafas
Excrete /
Perkumuhan
Reproduce /
Membiak
Lay Eggs /
Bertelur
Give Birth /
Lahirkan anak
Organs /
Organ
Lungs/
Paru-paru
- monkey
monyet
- bird
burung
- whale
paus
Gills/Insang
- fish
ikan
- prawn
udang
Lungs-
book
- crab
ketam
Moist skin/Kulit
lembap
- frog
katak
- earthworm
cacing tanah
Trachea Structre/Sistem
Trakea
- insects
serangga
Defecate /
Bernyahtinja
To get rid of waste product from their
bodies
Untuk menyingkirkan bahan buangan
dari badan
cat
kucing
tiger
harimau
bat
kelawar
whale
paus
butterfly
rama-rama
bird
burung
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 9 -
Life
processes
plants
undergo
Proses hidup
tumbuhan
plants respond to stimuli.
water, sunlight, touch, gravity.
tumbuhan bergerak balas
terhadap ransangan
air,cahaya
matahari,sentuhan,graviti
2.4 Understanding the life processes in plants
Memahami proses hidup tumbuhan
the part of plant that responds to
gravity.
bahagian pokok yang bertindak
balas terhadap graviti
roots
akar
the part of plant that responds
to water
bahagian pokok yang
bertindak balas terhadap
ransangan
the part of plant that responds to
sunlight.
bahagian pokok yang bertindak balas
terhadap cahaya matahari
Permul Akhir
plants reproduce.
tumbuhan membiak
Seeds balsam, corn,
durian
Biji benih-keembung,
jagung,durian
various ways plants reproduce
throughseeds, spores, suckers,
stem cutting, leaves,
underground stem.
berbagai cara tumbuhan membiak
melalui.bji benih, spora, anak
pokok,keratan batang, daun,
batang bawah tanah
the part of plant that responds
to touch.
bahagian pokok yang bertindak
balas terhadap sentuhan
why plants need to reproduce
to ensure the survival of the species.
mengapa tumbuhan perlu membiak
untuk memastikan kemandirian
spesisnya
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 10 -
Specific characteristics and behaviour
Sifat-sifat dan tingkah laku khas
Sharp claws ( tiger, cat )
Kuku tajam ( harimau, kucing )
Thick and hard skin
( rhinoceros )
Kulit tebal dan keras ( badak
sumbu )
Spines ( porcupine )
Berduri ( landak )
Hard scales ( pangolin,
crocodiles )
Sisik keras ( tenggiling,buaya )
Hard shell ( tortoise, snails )
Cengkerang keras ( kura-kura,
Horns ( buffalo, seladang )
Tanduk ( kerbau, seladang )
Pretend to be dead ( beetle, )
Berpura-pura mati ( kumbang )
Camouflage ( cameleon )
Menyamar ( sumpah-sumpah )
Poisonous sting or fang
( centipede, snake )
Sengat atau taring berbisa
( kala jengking, ular )
Spray black ink ( squid )
Mengeluarkan dakwat hitam
( sotong )
Special
characteristics
Ciri-ciri khas
Special behaviour
Tingkah-laku khas
3.1 Understanding that animals have specific characteristics and behaviour to protect
themselves from danger
Memahami bahawa haiwan mempunyai ciri dan perlakuan khas untuk melindungi
diri
mereka daripada bahaya
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 11 -
Specific characteristics and behavior
Sifat-sifat dan tingkah laku khas
Hot weather
Cuaca panas
Cold weather
Cuaca sejuk
Wrinkled Skin
(Elephant ,hippopotamuses
and buffaloes)
Kulit berkedut
(Gajah. badak sumbu, kerbau)
Wallowing
(Elephant, hippopotamuses
and buffaloes)
Berkubang
(Gajah, badak sumbu, kerbau)
Humps
(Camel)
Bonggol
(Unta)
Thick Fur
(Polar bears)
Berbulu tebal
(Beruang kutub)
Fat Layers Under The Skins
(Penguins, seals, and whales)
Lapisan lemak di bawah kulit
(Penguin, anjng laut, ikan
paus)
Small Ears
(Seals and Walruses)
Telinga kecil
(Anjing laut, singa laut)
Hibernate
(Polar bears)
Berhibenasi
(Beruang kutub)
3.2/3.3 Understanding that animals have specific characteristics and behaviour to
protect themselves from extreme weather
Memahami bahawa haiwan mempunyai sifat-sifat dan tingkah laku khas untuk
melindungi diri daripada cuaca melampau
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 12 -
The specific
characteristics
Sifat-sifat khas
Have thorns
Berduri
Poisonous
Beracun
Have fine hairs
Berbulu halus
Produces latex
Keluarkan getah
Close leaflets when touch
Daun tertutup bila disentuh
3.4 Understanding that plants have specific characteristics to protect themselves
from enemies
Memahami bahawa tumbuhan mempunyai ciri-ciri khas untuk melindungi diri
mereka daripada musuh
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 13 -
strong wind
angin kuat
dry region
kawasan kering
Eg : cactus
kaktus
Long roots to absorb water
Akar panjang untuk serap air
Succulent stem can store
water
Batang menyimpan air
Thorn can can prevent the
excessive loss of water
Duri yang mencegah
kehilangan banyak air
.
Eg: Coconut tree, bamboo tree,
pokok kelapa, pokok buluh
a. Have stems that bend easily
Batang yang mudah bengkok
b. Have buttress roots
Akar banir
c. Have separated leaves
Daun berbilah-bilah
d. Needle- shaped leaves
Daun berbentuk jarum
Specific characteristics of plants to
protect themselves
Sifat-sifat khas tumbuhan untuk
melindungi diri
3.5 Understanding that plants have specific characteristics to protect themselves f
rom dry region and strong wind
Memahami bahawa tumbuhan mempunyai ciri-ciri khas untuk melindungi diri
mereka daripada kawasan kering dan angin kuat
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 14 -
The Basic Needs of Human and Animals
Keperluan Asas Manusia dan Haiwan
One evening, when Cik Ti crawled out from its shelter to search
for food, the day started to rain heavily. Cik Ti immediately crawled back to the shelter,
a hole near a woody house. Cik Ti was tired. She also felt hungry. She tried to find
some food but there was no food left in the hole. Oh no I will die without food.
Said Cik Ti frustrated. Cil Ti moved into the kitchen in that woody house. Arghh I
am hungry!. Cik Ti screamed. Wow, cheese. Emmm. Delicious. After she had her
food, she was thirsty. She saw a cup of water on the table. Cik Ti drank the water. Tap!
Tap! Tap! Without her knowing, Mamat was ready to trap her into a plastic bag. He
tighten the bag tightly. Help! Help! I cant breath where is the air. Shouted Cik Ti
.. Her voice slow down time by time. Lastly Cik Ti dead without air..
Suatu petang ketika Cik Ti merangkak di luar rumahnya untuk mencari
makanan, tiba-tiba hujan turun dengan lebatnya. Cik Ti bergerak pantas kembali semula
ke kediamannya, sebuah lubang di tepi sebuah rumah kayu. Cik Ti penat. Dia mula rasa
lapar. Cik Ti cuba mencari makanan tetapi dia tidak menemuinya di lubang itu. Matilah
aku kalau tak ada makanan. rungut Cik Ti . Cik Ti terus ke dapur rumah itu. Arghh..
laparnya. Tiba-tiba Cik Ti menjerit, wow, keju.. emmm sedapnya. Selepas makan Cik
Ti terasa dahaga. Dia ternampak secawan air di atas meja tersebut. Cik Ti minum air
tersebut dengan gelojohnya. Tap! Tap! Tap! Tanpa disedarinya Mamat telah bersedia
untuk menangkap Cik Ti. Cik Ti terperangkap. Mamat memasukkan Cik Ti ke dalam sebuah
beg plastic dan mengikat beg itu dengan kuatnya. Tolong! Tolong! Aku tak boleh
bernafas.. mana udara ni. Jerit Cik Ti.. Suaranya semakin perlahan...... akhirnya Cik
Ti mati tanpa udara.....
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 15 -
What Plants eed to Stay Healthy?
Thank you for giving me enough water. I
can use it to make my food.
Terima kasih kerana memberikan saya air
yang cukup. Saya akan gunakannya untk
membuat makanan.
Oh, it is my pleasure. Hope you grow
healthy soon.
Oh , itu sudah tanggungjawab saya.
Harap awak akan hidup subur kelak.
Thank you for placing me to the
direct sunlight. Now I get enough
light. I can use it to make my food.
Terima kasih kerana meletakkan saya
di bawah cahaya matahari. Kini
saya telah mendapat cahaya yang
mencukupi. Saya boleh gunakkanya
untuk membuat makanan.
Oh, it is my pleasure. Hope you
can grow healthy soon .
Oh , itu sudah tanggungjawab
saya. Harap awak akan hidup
subur kelak.
Thank you for giving me enough
fertilizer. Now I can get enough
mineral. I can use it to make my
food.
Terima kasih kerana memberikan
saya cukup baja. Kini saya telah
mendapat baja yang mencukupi.
Saya boleh gunakkanya untuk
membuat makanan.
Oh, it is my pleasure. Hope you
can grow healthy soon .
Oh , itu sudah tanggungjawab
saya. Harap awak akan hidup
subur kelak.
Emmm I feel fresh. I can breath
smoothly. Thank you. Now I can get
enough air. I can use it to make my
food.
Emmm....saya rasa segar. Terima
kasih. Kini saya telah mendapat
udara yang mencukupi. Saya boleh
gunakkanya untuk membuat
makanan.
Oh, it is my pleasure. Hope you
can grow healthy soon .
Oh , itu sudah tanggungjawab
saya. Harap awak akan hidup
subur kelak.
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 16 -
EXCRETION PROCESS
PROSES PERKUMUHAN
No.
Bil
Organs Diagram
Gambarajah Organ
Waste Products
Bahan Buangan
1. Kidney / Buah Pinggang
Urine + water vapour
Air Kencing + wap air
2.
Lungs/ Paru-Paru
Carbon Dioxide + water
Vapour
Karbon dioksida + wap air
3.
Skin/Kulit
Sweat + Water Vapour +
Mineral salt
Peluh + wap air + garam
mineral
Ureter
Kidney
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 17 -
Plants Respond To Stimuli
Tumbuhan bergerakbalas terhadap ransangan
(Pussy Cat Song)
Oh Fresh Roots, Oh Fresh Roots what are you see?
I want to go down to meet my gravity.
Oh Fresh Roots, Oh Fresh Roots why are you here?
Im going down to the soil to absorb water.
Oh green shoot, Oh green Shoot what make you bright?
I can go up to search for sunlight.
The roots respond to water.
Akar bergerakbalas terhadap
air.
The shoot responds to sunlight
Pucuk bergerakbalas terhadap
cahaya matahari..
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 18 -
The Breathing Structure of Animals
Gill
Insang
Trachea Structure
Struktur Trakea
Windpipe
Salur Trakea
Nose
Hidung
Lung
Paru-paru
Moist Skin
Kulit Lembab
Lung
Paru-paru
Trachea Structure
Struktur Trakea
Nose Wind Pipe Lungs
Hidung Trakea
Paru-paru
Air Passage
Peredaran Udara
Lung
Paru-paru
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 19 -
Animal Defense From extreme weather
How I Survived
Long Ears Desert Fox
Small Ears Cold Region
Animals
Thick Fat In Tails
Kangaroo Rats
Rest Desert Animals
Wallowing In Mud -
Rhinoceroses
Thick Layers Of Fat
Penguins
Thick Furs - Polar
Hump - Camels
Penguin
Kangaroo Rat Camel
Unit 3/Lesoon 2
Living in Extreme Danger
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 20 -
MENYIASAT ALAM KEHIDUPAN MENYIASAT ALAM KEHIDUPAN MENYIASAT ALAM KEHIDUPAN MENYIASAT ALAM KEHIDUPAN
Year 5
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 21 -
1.1 Understanding that microorganism is a living things
Memahami mikroorganisma adalah benda hidup
Microorganism
Mikroorganisma
Bacteria
Bakteria
Fungi
Kulat
Protozua
Protozoa
Virus
Virus
Cannot see with
naked eyes
Tidak boleh dilihat
dengan mata kasar
Grow
Membesar
Move
Bergerak
Breathe
Bernafas
Characteristics
Ciri.Ciri
Cause the dough rise
Menyebabkan adunan
tepung menaik.
Rotten oranges/
limau busuk
Mouldy rice / Nasi
berkulat
Tiny
Halus
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 22 -
1.2 Understanding that some microorganism are harmful and some are useful
Memahami beberapa mikroorganisma yang berbahaya dan berguna
Some Organisms Are Harmful And
Some Are Useful
Beberapa mikoorganisma yang berbahaya
dan berguna
Useful / berguna Harmful / Berbahaya
Can cause
Boleh
Illness
Sakit
Food
Poisoning
Keracunan
makanan
Food
Stale
Makanan
basi
Tooth
Decay
Gigi mereput
Prevention
Cara mencegah
Disease
Penyakit
Stomach
upset
Sakit perut
Cough
batuk
Tooth decay
Gigi mereput
Conjunctivity
Sakit mata
Washing hand
Membasuh
tangan
Drink boiled
water
Minum air yang
dimasak
-Making food/ buat
makanan
(bread/tapai/tempe/yogurt)
( roti,tapai,tempe, yogurt )
-Making fertilizer/ baja
-Making medcine/ ubat
Covering mouth
& nose when
coughing &
sneezing
Menutup mulut
dan
hidung apabila
batuk dan bersin
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 23 -
Survival of
Animal
Species
Kemandirian
Spesies Haiwan
Examples animals that take
care of their eggs and young.
Contoh haiwan yang menjaga telur
dan anak.
HOW ANIMALS TAKE CARE OF
THEIR EGGS AND YOUNG.
Bagaimana haiwan menjaga telur
dan anak mereka .
Why animals take care of
their eggs and young.
Mengapa haiwan melindungi
telur dan anaknya
Bird - Eggs with shell covering
Burung Telur disaluti oleh cangkerang
Frog - Eggs are thick, slimy and having bad
smell
Katak Telur tebal,berlendir dan berbau
busuk
Spider - kept in a bag underneath its body
Labah-labah simpan dalam beg di bawah
badan
Fish - keep their young in their mouths
Ikan - Memasukkan anaknya ke dalam
mulut
Snake, Tiger - attack in order to protect
their eggs
Ular,harimau menyerang untuk
menyelamatkan telur
Turtle - hide their eggs
Penyu Menyembunyikan telurnya
Kangaroo - carry their young in their
pouches
Kanggaroo Membawa anaknya di dalam
kantung
Elephant - stay in herds
Gajah - Tinggal dalam kumpulan
Importance
Kepentingan
Shortage of food resource
Sumber makanan berkurangan
Animals and plants species
may face extinction.
Spesis haiwan dan tumbuhan
akan mengalami kepupusan.
bird, spider, fish,snake,
burung,labah-labah,ikan,ular
turtle, kangroo, elephant
penyu,kanggaro,gajah
To ensure the survival
of their species
Memastikan kemandirian
spesisnya.
2.1 Understanding that different animals have their own ways to ensure the survival
of their species
Memahami bahawa haiwan berlainan mempunyai cara sendiri untuk memastikan
kemandirian spesisnya
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 24 -
Survival of Plant
Species
Kemandirian
spesies
tumbuhan
Water
Air
Explosive
mechanism
Mekanisme
letupan
Wind
Angin
Animal
haiwan
Light / Ringan
Air Space in the
fruits
Ruang udara di
dalam buah
Not water
absorbent
Air tidak boleh
diserap
Light / Ringan
Small in size /
saiz kecil
Winged /
berkepak
Dry when ripe
Kering apabila
masak
Explodes when
mature
Meletup apabila
matang
Brightly
coloured
Warna yang
terang
Edible / Boleh
dimakan
Have smells /
berbau
Have hook
bercangkuk
Coconut /
kelapa
Water Lily /
Kiambang
Shorea
Angsana
Lalang
Rubber fruit /
buah getah
Balsam fruit /
keembong
Ladys finger/
kacang bendi
Rambutan
Mango/
mangga
Love grass /
kemuncup
Agents of
dispersal
Agen
Special
characteristic
Ciri-ciri
Examples
Contoh
2.2 Understanding that different plants have their own ways to ensure the survival
of their species
Memahami bahawa tumbuhan berlainan mempunyai cara sendiri untuk
memastikan kemandirian spesisnya
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 25 -
Food Chain
Rantai Makanan Animals and the
food they eat
Haiwan dan
makanannya
Classify animals
Pengkelasan
haiwan
Producer
Pengeluar
Consumer
Pengguna
Construct food chain
Membina rantai makanan
Green plant obtain
energy from
the sun to make
food. Green
Plant as a producer
Tumbuhan hijau
Memerlukan tenaga
daripada Matahari
untuk membuat
makanan.
Tumbuhan
adalah pengeluar
Herbivore :
Animals that eat plants
only.
e.g.: cow, goat, deer
Herbivor
Haiwan makan
tumbuhan sahaja
Cth:
lembu,kambing,rusa
Carnivore:
Animals that eat other
animals.
e.g.: tiger, lion
Karnivor
Haiwan yang makan
haiwan lain
Cth : harimau,singa
Omnivore:
Animals that eat plants
and other animals
Omnivor
Haiwan makan
tumbuhan dan
haiwan lain.
The food
relationship
among living
things
can be shown by
a food chain.
Hubungan antara
makanan
dan benda hidup
ditunjukkan
melalui
rantai makanan
To construct food
chain It must start
with plant as
a producer.
Untuk membina
rantai makanan ia
bermula daripada
tumbuhan sebagai
pengeluar.
In a food chain
the arrow means
eaten by
Dalam rantai
makanan anak
panah bermaksud
dimakan oleh
All living things
need food to
survive.Green plant
can make their own
food. However
animals cannot
make their own
make their own
food.
Semua benda
hidup perlu
makanan untuk
hidup.
Tumbuhan hijau
boleh
membuat makanan
sendiri.
3.1 Understanding food chains
Memahami rantai makanan
Animals that
eat plant
or other
animals
are called
consumers.
Haiwan yang
makan
tumbuhan
dipanggil
pengguna.
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 26 -
Synthesizing food chains
to construct food web.
Sintesis siratan makanan untuk
membentuk rantai makanan
Food web
Siratan makanan
What will happen If there is
a change in population of a
certain species in a food
web
Apa akan berlaku jika
terdapat perubahan spesies
dalam rantai makanan
Food web of different
habitats
Siratan makanan
daripada berlainan
habitat.
What will happento a
certain species of animals
if they eat only one type of
food?
Apa akan berlaku
sebahagian spesis haiwan
makan hanya
satu jenis makanan
sahaja?
A change in the population
of a certain species will
effect the population of
other species
Perubahan populasi
beberapa haiwan memberi
kesan kepada populasi
haiwan lain.
They will face difficulty
to survive if the source
of food runs out
Mereka akan
mengalami
kesukaran jika sumber
makanan kehabisan.
3.2 Synthesizing food chains to construct food web.
Sintesis siratan makanan untuk membentuk rantai makanan
Paddy field
Sawah padi
paddy plant
tanaman padi
caterpillar
ulat beluncas
birds
burung eagles
helang
snakes
ular
mice
tikus
grasshoppers
belalang
frogs
katak
Garden
Taman
spinach
bayam
grasshopper
belalang
frog
katak
bird
burung
caterpillar
ulat beluncas
eagle
helang
snail
siput
snake
ular
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 27 -
MICROORGANISMS
MIKROORGANISMA
One day, while reading a book, Ali comes across one word. The word is
microorganisms. He doesnt understand what it is and he ask his mother
immediately. (Suatu hari, semasa Ali sedang membaca buku, dia terbaca satu perkataan.
Perkataan itu ialah mikroorganisma. Dia tidak faham dan terus bertanya kepada ibunya.)
Ali : Mother, what is a microorganism?
(Ibu, apa itu mikro organisma?)
Mother : Microorganism is tiny living things that can only be seen
through a microscope. There are four types of
microorganisms.
(Mikro organisma adalah benda hidup yang sangat halus dan hanya boleh
dilihat melalui mikroskop. Terdapat empat jenis mikro organisma.)
Ali : What are those?
(Apa itu?)
Mother : Bacteria, Protozoa, Fungi and Virus.
(Bakteria, Protozoa, Fungus dan Virus.)
Ali : What picture is that, mother?
(Gambar apa tu, ibu?)
Mother : It is Bacteria. It exists in different shapes, sizes and colours.
(Itu ialah Bakteria. Ia wujud dalam berlainan bentu, saiz dan warna.)
Ali : That picture is
(Gambar itu)
Mother : It is Protozoa. Most of it are found mainly in ponds, lakes and
rivers.
(Itu ialah Protozoa. Kebanyakkan daripadanya dijumpai di kolam, tasik dan
sungai.)
Ali : That must be Fungi. Right, mother?
(Itu pasti fungus. Betul tak, ibu?)
Mother : Yes, it is. I know you have seen it many time on mouldy bread,
rotten food, trees and forest floors.
(Ya. Ibu tahu kamu selalu lihatnya di atas roti yang berkulat, buah yang reput,
pokok-pokok dan lantai hutan.)
Ali : And this picture, mother?
(Dan gambar itu, ibu?)
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 28 -
Mother : It is a virus. Virus is the tiniest microorganism.
(Itu ialah Virus. Virus ialah mikro organisma yang paling
halus.)
Ali : Wow, thats interesting. Tell me more, mother.
(Wow, menariknya. Ceritalah lagi ibu.)
Mother : Okay. Yeast is an example of microorganisms. Since
Microorganism is a living things, it can breathe, grow and
move.
(Okay. Yis ialah satu contoh mikro organisma. Memandangkan mikro organisma
adalah benda hidup, ia boleh bernafas, membesar dan bergerak.)
Ali : Thank you, mother.
(Terima kasih, ibu.)
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 29 -
HARMFUL
Keburukan
Form fertilizer
Membuat baja
Produce antibiotic
Menghasilkan antibiotic
Chicken pox
Campak
Mumps
Beguk
Measles
Cacar
Conjunctivitis
Sakit mata
Tooth decay
Kerosakan gigi
Flu
Selsema
Food poisoning
Keracunan makanan
Making tempe
Membuat tempe
Making cheese
Membuat keju
USEFUL
KEBAIKAN
Making tapai
Membuat tapai
Making yogurt
Membuat yogurt
THE USEFUL AND THE HARMFUL OF MICROORGANISMS
KEBAIKAN DAN KEBURUKAN MIKROORGANISMA
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 30 -
We take care of our eggs
Kami menjaga telur kami
We take care of our youngs
Kami menjaga anak kami
Frog
Katak
Penguin
Penguin
Bird
Burung
Sea horse
Kuda laut
Snake
Ular
Cockroach
Lipas
Crocodile
Buaya
Bat
Kelawar
Dolphin
Ikan lumba
Cow
Lembu
Elephant
Gajah
Tiger
Harimau
Kangaroo
Kangaroo
ANIMAL SURVIVAL
KEMANDIRIAN HAIWAN
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 31 -
AGENT
AGEN
EXAMPLE
CONTOH
CHARACTERISTICS
CIRI-CIRI
Lotus
Teratai
Coconut
Kelapa
Pong-pong
Pong-pong
We dispersed by water
because we are light,
covered with waxy skin,
waterproof, has air spaces
and has spongy
receptacles.
Kami dipencarkan melalui air
kerana kami ringan, diselaputi
dengan kulit yang berlilin, kalis
air dan mempunyai rongga
yang berspan.
Shorea
Meranti
Lallang
Lallang
Angsana
Angsana
Cotton
Kapas
We dispersed by wind
because we are small, light,
dry, have wing-like
structure, have hairs and
fine hairs. Therefore it is
easily carried by wind.
Kami dipercarkan melalui
angina kerena kami kecil,
ringan, kering, mempunyai
struktur seperti sayap, ada
bulu yang halus. Sebeb itu
kami senang dibawa pergi
oleh angin.
PLANT SURVIVAL
KEMANDIRIAN TUMBUHAN
WATER
AIR
WIND
ANGIN
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 32 -
Mangga
Mango
Watermelon
Tembikai
Mimosa
Semalu
Lovegrass
Kemucup
We dispersed by animal
because we have brightly
colour, fleshy, edible and
have smells. Our seed is
also hard.
Kami dipencarkan oleh haiwan
kerana kami mempunyai
warna yang terang, berisi,
boleh dimakan dan
mempunyai bau. Biji benih
kami juga keras.
We are also dispersed by
animal because have hooks
that can be attached to
animals.
Kami juga dipencarkan oelah
haiwan kerana kami
mempunyai cangkuk yang
boleh melekat kepada haiwan
Flame of forest
Semarak api
Balsam
Keembung
Okra
Bendi
Rubber seed
Biji getah
We dispersed by explosive
mechanism because we dry
up when we ripe and burst
to push the seeds out from
the fruits.
Kami dipencarkan melalui
mekanisma letupan kerana
buah kami menjadi kering
apabila masak ranum dan
seterusnya meletup dan biji
benih kami terpelanting keluar.
ANIMAL
HAIWAN
Explosive Mechanism
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 33 -
deer
rusa
herbivores
herbivor
rabbits
arnab
carnivores
karnivor
Animals such as deer and rabbits get their energy by eating plants. They are called
herbivores, which means 'plant eaters.' There are many more herbivores on our planet than
carnivores, which are animals that eat meat.
Haiwan seperti rusa dan arnab mendapat tenaga dengan memakan tumbuh-tumbuhan. Mereka dikenali
sebagai herbivor, yang bermaksud makan tumbuhan. Terdapat banyak herbivor daripada karnivor iaitu
haiwan yang makan daging di planet kita
predators
pemangsa
hunt
memburu
prey
mangsa
top
atas
lions
singa
Predators such as wolves and lions are at the top of the food chain. Predators are animals
that hunt other animals. The animals that they hunt are called prey. Some animals are both
predator and prey.
Pemangsa seperti serigala dan singa adalah di bahagian atas rantai makanan. Pemangsa adalah
haiwan yang memburu haiwan lain. Haiwan yang diburu dikenali sebagai mangsa. Sesetengah haiwan
adalah kedua-duanya; pemangsa dan mangsa.
connected
berhubung
energy
tenaga
web
jaringan
more
lebih
Most animals belong to more than one food chain, which means many food chains are
connected together. Many food chains together form a food web. The food web shows how the
sun's energy moves from plants to animals to animals.
Kebanyakan haiwan mempunyai lebih daripada satu rantai makanan, iaitu banyak rantai makanan
dihubung bersama. Rantai makanan berhubung bersama membentuk jaringan makanan. Jaringan
makanan menunjukkan bagaimana matahari memindahkan tenaganya kepada tumbuhan dan
seterusnya daripada tumbuhan kepada haiwan.
bottom
bawah
trees
pokok
sun
matahari
grass
rumput
chain
rantai
Plants such as grass and trees are at the bottom of the food chain. Plants get their energy
from the sun.
Tumbuhan seperti rumput dan pokok adalah di bahagian bawah rantai makanan. Tumbuhan mendapat
tenaga daripada matahari.
FOOD CHAIN AND FOOD WEB
RANTAI MAKANAN DAN JARINGAN MAKANAN
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 34 -
MENYIASAT ALAM KEHIDUPAN MENYIASAT ALAM KEHIDUPAN MENYIASAT ALAM KEHIDUPAN MENYIASAT ALAM KEHIDUPAN
Year 6
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 35 -
Group
Berkumpulan
Solitary
Bersendirian
Ants, lions
Semut, singa
Tigers, bears
Harimau, beruang
To avoid competition for food and space
Untuk hindari persaingan mendapatkan
makanan dan ruang
For safety and food
Untuk keselamatan dan makanan
Group animals and solitary animals
Haiwan berkumpulan dan haiwan
1.1 Understanding that some animals live in group and others live in solitary
Memahami bahawa sesetengah haiwan hidup berkumpulan dan selebihnya
bersendirian
Interaction among living things
Interaksi antara benda hidup
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 36 -
Compete for
Bersaing untuk
Among animals
Antara haiwan
Among plants
Antara tumbuhan
INTERACTION AMONG LIVING THINGS
Interaksi antara benda hidup
Competition
Persaingan
Food
Makanan
Water
Air
Mate
Pasangan
Shelter
Tempat
Space /
territory
Ruang /
kawasan
Compete for
Bersaing untuk
Sunlight
Cahaya
Water
Air
Space
Ruang
Mineral
Mineral
Intraspecies
Intraspesis
Interspecies
Interpesis
Competition between the
same species
Persaingan di antara
spesis yang sama
Competition between the
different species
Persaingan di antara spesis
yang berbeza
Type
Jenis
1.2 Understanding that competition is a form of interaction among living things
Memahami bahawa persaingan membentuk interaksi antara benda hidup
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 37 -
Protecting endangered species
Melindungi spesis yang
terancam
Interaction among living things
Interaksi antara benda hidup
1.3 Understanding the responbility of human beings in protecting endangered
species
Memahami tanggungjawab manusia untuk melindungi spesis yang terancam
Extinct animals
Haiwan pupus
Dinosours,
dodos
Dinosur,
dodo
Endangered animals
and plants
Haiwan dan tumbuhan
yang terancam
Orang utan, tiger, Raflesia,
pitcher plant
Orang utan, harimau, bunga
pakma,pokok periuk kera
Factors
Faktor
Illegal or excessive logging
Pembalakan haram atau
berleluasa
Hunting
Pemburuan
Development
Pembangunan
Ways to prevent
Cara untuk mencegah
Campaign
Kempen
Educating the public
Mendidik orang
awam
Enforcing law
Kuat kuasa undang-
undang
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 38 -
Interaction among living things
Interaksi antara benda hidup
Impact of human activities
Kesan daripada aktiviti manusia
Destructions of the environment
Kemusnahan alam sekitar
Erosion
Hakisan
Landslides
Runtuhan
Flash floods
Banjir kilat
Water pollution
Pencemaran air
Activities
Aktiviti
Illegal and excessive
logging
Pembalakan haram dan
berleluasa
Illegal and excessive
hunting
Pemburuan haram dan
berleluasa
Improper management of
development
Kelemahan pengurusan
pembangunan
1.4 Knowing the impact of human activities on environment
Memaham kesan daripada aktiviti manusia ke atas alam sekitar
Air pollution
Pencemaran udara
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 39 -
MENYIASAT DAYA DAN TENAGA MENYIASAT DAYA DAN TENAGA MENYIASAT DAYA DAN TENAGA MENYIASAT DAYA DAN TENAGA
Year 4
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 40 -
1.7 Standard units
Unit seragam
1.5 Mass
Berat
1.6 Time
Masa
1.2 Area
Luas
1.3 Volume
Isipadu
1.3 Solid
Pepejal
1.4 Liquid
Cecair
1.1 Understanding the measurement of length
Memahami ukuran panjang
Measurement
Ukuran
1.1 Length
Panjang
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 41 -
Length
Panjang
Terminology
Istilah
-The distance between
two points/ place /
position
Jarak di antara dua
titik/tempat/kedudukan
Ways to measure
Cara menyukat
Measuring
tape
Pita
pengukur
Cubit
Hasta
Arm
span
Depa
String
Tali
Ruler
Pembaris
Standard Tools
Alat seragam
Measuring
tape
Pita
pengukur
Ruler
Pembaris
Unit
Unit
mm
mm
cm
sm
m
m
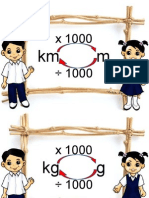
km
km
Correct technique
Teknik yang betul
-The eye must be
directly above
the end of object
Mata mesti tepat pada
bahagian bawah
hujung benda
1.1 Understanding the measurement of length
Memahami ukuran panjang
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 42 -
1.2 Area
Luas
-Area is the amount of
space taken up by the
surface of an object.
Luas ialah jumlah ruang
yang
dipenuhi pada permukaan
sesuatu objek
Terminology
Istilah
-Using square card with a
sides of 1 centimetre
Menggunakan kad segi empat dengan
tepinya 1 sentimeter
Standard unit
Unit piawai
-Square millimetre (mm
2
)
Milimeter persegi (mm)
-Square centimetre (cm
2
)
Sentimeter persegi (sm)
-Square metre (m
2
)
Meter persegi (m)
-Square kilometre (km
2
)
Kilometer persegi (km)
1cm
1cm
Different ways to measure area
Berbeza cara untuk menyukat luas
-Using formula
Guna rumus
Area = length X width
Luas = panjang X lebar
2c
m
4c
m
= 4cm X 2 cm
= 8cm
2
3cm
3cm
- by placing uniform objects
such as tiles, books and
stamps on the surface of
the objects
dengan meletakkan objek
seperti jubin, buku dan setem
pada permukaan objek
1.2 Understanding how to calculate area
Memahami cara mengira luas
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 43 -
Volume
Isipadu
Terminology
Istilah
The amount of space that something takes up
Jumlah ruang yang dipenuhi oleh sesuatu
1.3 Solid
Pepejal
1.4 Liquid
Cecair
Formula
Rumus
Length x width x height
Panjang x lebar x tinggi
Standard Units
Unit seragam
Tools
Alat
Measuring cylinder
Silinder penyukat
ml, l
ml, l
Correct technique
Teknik yang betul
a) taking the reading at the lowest part of the meniscus.
mengambil bacaan pada bahagian paling rendah pada
meniskus
b) eyes must be at the same level as the lowest part of the
meniscus
mata mesti sama pada aras paling rendah pada
meniskus
Standard Units
Unit piawai
mm, cm, m
mm, sm, m
1.2/1.3 Understanding how measure the volume of solid and liquid
Memahami cara mengira isipadu pepejal dan cecair
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 44 -
Mass
Berat
Terminology
Istilah
-Amount of matter in an object
Jumlah benda dalam objek
Tools
Alat
Electronic balance
Neraca elektronik
Beam balance
Neraca palang
Kitchen scale
Penimbang dapur
Bathroom scale
Penimbang berat
badan
Lever balance
Neraca tuas
Standard unit
Unit piawai
Mg
mg
g
g
kg
kg
Correct technique
Teknik yang betul
1.5 Understanding how measure mass
Memahami cara menyukat berat
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 45 -
Time
Masa
Terminology
Istilah
-Duration between two event
Tempoh antara dua ketika
Way to measure
Cara untuk mengukur
-Sundial , sand clock , candle clock
-Jam bayang, jam pasir, jam lilin
Process that repeats uniformly can be
used to measure time
Proses yang berulang secara sekata
boleh digunakan untuk menyukat masa
-swinging pendulum
ayunan bandul
-pulse rate candle
denyutan nadi
-water dripping
titisan air
-changing day and night
perubahan siang dan
malam
Tool
Alatan
Standard unit
Unit piawai
- Second , minute , hour
Saat, minit, jam
-Digital clock, watch, wrist watch
Jam digital, jam, jam tangan
Old clock
Jam lama
Events can be used measuring time
Kejadian boleh digunakan untuk
menyukat masa
1.6 Understanding how to measure time
Memahami cara mengukur masa
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 46 -
The Importance of Standard Units
Kepentingan unit yang piawai
-for accuracy and consistency
untuk tepat dan konsisten
-easy to communicate and understanding
mudah untuk memahami dan
berkomunikasi
1.7 Realising importance of using standard units
Menyedari kepentingan menggunakan unit yang piawai
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 47 -
THE STORY OF TIME
CERITA TETAG MASA
Galileo Galilei was the first person to use events that repeat uniformly
to measure time such as the pendulum clock. From then onwards, the wall clock
and modern clock were invented.
Galileo Galilei merupakan orang pertama menggunakan peristiwa yang
berulang secara seragam untuk mengukur masa seperti jam bandul. Daripada
situ, jam dinding dan jam moden telah dicipta.
Sand Clock Sundial Clock Candle Clock
Ancient Clocks
Wall clock Stop Watch Watch
Modern Clock
Unit 4/Lesson 1
Measuring Length/Mass
Defense Of Plants
Unit 4/Lesson 6
Measuring Time
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 48 -
MENYIASAT DAYA DAN TENAGA MENYIASAT DAYA DAN TENAGA MENYIASAT DAYA DAN TENAGA MENYIASAT DAYA DAN TENAGA
Year 5
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 49 -
ENERGY
TENAGA
INVESTIGATING FORCE AND ENERGY
Menyiasat Daya dan Tenaga
The Uses of Energy
Kegunaan Tenaga
Why energy
is needed?
Mengapa tenaga
diperlukan
- by living things to carry
out life processes.
Ex : moving, breathing,
growing
- bergerak,bernafas
- membesar
The Sources of Energy
Sumber-sumber Tenaga
-main source of energy
sumber utama tenaga
- produces light and heat
menghasilkan cahaya dan
haba
-food contains
stored energy
-mengadungi tenaga
tersimpan
Sun
Matahari
- Moving air
Udara bergerak
-Used to pump
water
Mengepam air,
- to move, boil, melt,
or bounce non-living things
- menggerakkan ,didih,cair atau
melantun benda bukan hidup
-wood, coal,
petroleum,
natural gas
-Kayu,
petrol,gas
asli
- moving or
falling water
produce
energy
-Air yang
bergerak
Menghasilkan
tenaga
Food
makanan
Wind
Angin
Fuell
Bahan
api
Batteries
Bateri
Water
air
- Device that generated
electrical energyfrom
chemical energy
-Alat yang menghasilkan
tenaga elektrik
daripada tenaga kimia
1.1 Understanding the uses of energy
Menyedari kegunaan tenaga
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 50 -
Energy can be transformed from one form to another
Tenaga boleh berubah dari satu bentuk kepada bentuk lain.
Form of energy
Bentuk Tenaga
Sound energy
Tenaga bunyi
Heat energy
Tenaga Haba
Light energy
Tenaga Cahaya
Electrical energy
Tenaga Elektrik
Kinetic energy
Tenaga Kinetik
Chemical energy
Tenaga Kimia
Potential energy
Tenaga Keupayaan
Energy can be transformed
Tenaga boleh diubahkan
a) lighting a candle/Nyalaan lilin
Chemical energy heat energy + light energy
Tenaga kimia Tenaga haba + Tenaga Cahaya
b) Kicking a ball / Menendang bola
Chemical energy kinetic energy heat energy
Tenaga kimia Tenaga Kinetik Tenaga haba
Example of appliance that make use of
energy transformation.
Contoh alatan yang menggunakan
perubahan tenaga
a) Electric iron / Seterika elektrik
Electrical energy heat energy
Tenaga elektrik Tenaga haba
b) Radio
Electrical energy sound energy
Tenaga elektrik Tenaga bunyi
c) Television
Electrical energy sound energy + light energy
Tenaga elektrik Tenaga bunyi + tenaga cahaya
1.2 Understanding that energy can be transformed from one form to another
Memahami bahawa tenaga boleh berubah dari satu bentuk ke bentuk yang
lain
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 51 -
Renewable and Non-renewable Energy
Tenaga yang boleh diperbaharui dan
Tidak boleh diperbaharui
Renewable energy
Tenaga yang boleh
diperbaharui
Energy that
cannot
be replaced
Tenaga yang
tidak
boleh diganti
Resources
solar, wind ,biomass
fuel,water
Sumber- Matahari,
angin,minyak,air,
biomass
Non-renewable energy
Tenaga yang tidak
boleh diperbaharui
Energy that be
replenished when it is
used up
Tenaga yang boleh
diganti
Resources -natural
gas,petroleum,coal
Sumber gas asli,
petroleum, arang.
Use energy wisely
Gunakan tenaga
dengan bijak
How to save energy
Bagaimana
menjimatkan tenaga
Some energy
resources cannot be
replenished
when used up.
Sesetengah sumber
tenaga tidak boleh
diganti bila habis
To save cost
Menjimatkan kos
Avoid wastage
Mengelakkan
pembaziran
Reduce pollution
Mengurangkan
pencemaran.
Turn off the
television when no
one watching it.
Tutup TV jika tidak
menonton.
Switch off the
lights if
not in use.
Tutup lampu jika
tidak
mengunakannya.
1.3 Understanding renewable anad renewable energy
Memahami tenaga yang boleh diperbaharui dan tidak boleh diperbaharui
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 52 -
Sources
Sumber
Dry cell
Sel Kering
Accumulator
Sel Basah
Dynamo
Dinamo
Solar cell
Tenaga Solar
2.1 Knowing the sources of electricity
Mengetahui sumber elektrik
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 53 -
Type of circuit
Jenis litar
Name
Nama
Symbol
Simbol
Dry cell
Sel Kering
Connecting
wire
Wayar
penyambung
Switch / Suis
Bulb / Mentol
Symbol and component
Simbol dan komponen
Parallel circuit
litar selari
Series circuit
litar bersiri
Differences
Perbezaan
The bulb in the parallel circuit is brighter then
the bulb in the series circuit
Mentol dalam litar selari lebih terang daripada
mentol dalam litar bersiri
2.2 Understanding a series circuit and a parallel circuit
Memahami litar bersiri dan litar selari
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 54 -
Precautions
Langkah keselamatan
Danger of mishandling electrical appliances
Bahaya kecuaian mengendali peralatan elektrik
Fire
Api
Burn
Bakar
Electric shock
Kejutan elektrik
Electrocution
Renjatan elektrik
Safety precautions to
be taken when using
appliances
Langkah-langkah
keselamatan ketika
mengunakan peralatan
Do not touch electrical
appliances with wet hand
Jangan sentuh alatan
elektrik dengan tangan
basah
Do not repair electrical
appliances on your own
Jangan baiki alatan
elektrik jika tidak tahu.
2.3 Understanding the safety precautions to be taken when handling electricl
appliances
Memahami langkah pencegahan yang perlu diambil semasa menggunakan
peralatan elektrik
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 55 -
3.1 Understanding that light travels in a straight line
Memahami bahawa cahaya bergerak dalam satu garis lurus
Light
Cahaya
Travels in straight line
Cahaya bergerak dalam satu garis lurus
search light from helicopter
cahaya dari helikopter pencari
prove
bukti
the beam of light from motorcycle
alur cahaya dari motosikal
the beam of light from lighthouse
alur cahaya dari rumah api
the ray of Sun,passing through a
hole in the roof
alur cahaya Matahari melalui
lubang atap rumah
How shadow is formed
Bagaimana bayang-bayang
terbentuk
When light is completely or
partially blocked by an
opaque object
Bila cahaya disekat
sepenuhnya atau separuh
oleh objek legap
Shadow form
Objek terbentuk
Opaque object
Objek legap
Light
Cahaya
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 56 -
Light
Cahaya
Can be reflected
Boleh dipantulkan
How ?
Bagaimana?
Uses of reflection
Kegunaan pantulan
Side mirror of a car
Cermin sisi kereta
Periscope Kaleidoscope
The light that falls on
objects bounces off the
objects and comes to your
eyes
Cahaya yang jatuh ke atas
objek melantunkannya ke
dalam mata
mirror/ cermin
3.2 Understanding that light can be reflected
Memahami cahaya boleh dipantulkan
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 57 -
Heat
haba
Gain
Ditambah
Loss
Hilang
Cooler
Sejuk
Warmer
panas
How to measure temperature
using the correct technique
Bagaimana untuk mengukur
suhu menggunakan cara yang
betul
The effects of heat on matter
Kesan haba ke atas bahan
Matter expands
when heated
Bahan
mengembang bila
dipanaskan
Matter contract
when cooled
Bahan mengecut
bila sejuk
4.1 Understanding that temperature in an indicator of degree of hotness
Memahami bahawa suhu adalah penunjuk darjah kepanasan
Thermometer
termometer
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 58 -
SUN WIND DRY CELL FUELS FOOD
Matahari Angin Sel kering Bahan bakar Makanan
Chemical energy light energy + heat energy
Tenaga kimia tenaga cahaya tenaga haba
Electrical energy light energy
Tenaga elektrik tenaga cahaya
Electrical energy heat energy
Tenaga elektrik tenaga haba
Electrical energy sound energy
Tenaga elektrik tenaga bunyi
Electrical energy kinetic energy
Tenaga elektrik tenaga kinetic
SOURCES OF ENERGY
PUNCA-PUNCA TENAGA
FORMS OF ENERGY
BENTUK-BENTUK TENAGA
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 59 -
DRY
CELL ACCUMULATOR DYNAMO SOLAR CELL HYDROELECTRIC
Sel kering Dynamo Sel solar Hidroelekrik
SERIES CIRCUIT
LITAR SESIRI
SOURCES OF ELECTRICITY
PUNCA-PUNCA ELEKTRIK
PARALLEL CIRCUIT
LITAR SELARI
ELECTRICITY
ELEKTRIK
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 60 -
( Song : This old man)
Light oh light Cahaya oh cahaya
Light travels Cahaya boleh gerak
Light travels in a straight line Cahaya bergerak lurus
Light travels in a straight line Cahaya bergerak lurus
Therefore it can form shadow Ia membentuk bayang
Light oh light Cahaya oh cahaya
Light reflects Cahaya boleh pantul
Light can be reflected Cahaya boleh dipantulkan
Light can be reflected Cahaya boleh dipantulkan
Can see image in mirror Boleh lihat dicermin
LIGHT
CAHAYA
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 61 -
MENYIASAT DAYA DAN TENAGA MENYIASAT DAYA DAN TENAGA MENYIASAT DAYA DAN TENAGA MENYIASAT DAYA DAN TENAGA
Year 6
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 62 -
INVESTIGATING FORCE AND ENERGY
MENYIASAT DAYA DAN TENAGA
FORCE
DAYA
Effects
Kesan
Concept
Konsep
A push or a pull
Tolak atau tarik
Can move a stationary object
Boleh gerakkan objek yang
pegun
Cannot be seen but the
effects can be felt
Tidak boleh dilihat tetapi
boleh dirasa
Changes the shapes of an object
Mengubah bentuk objek
An object become squeezed,
stretched, bent, twisted or
squashed
Objek menjadi kemek, regang,
bengkok,berpintal atau penyek
Changes the motion of an object
Mengubah pergerakan objek
Stops a moving object
Memberhentikan objek yang bergerak
Changes the direction of a moving object
Mengubah arah pergerakan objek yang bergerak
Makes an object move faster or slower
Menggerakkan objek lebih cepat atau perlahan
1.2 Understanding the effect of a force
Memahami kesan daya
1.1 Understanding that push and pull are forces
Memahami bahawa tolak dan tarik adalah daya
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 63 -
FRICTION
GESERAN
Effects of friction
Kesan geseran
Produces heat
Hasilkan haba
Opposes motion
Berlawanan gerakan
Causes wear and tear
Menyebabkan haus
dan koyak
Slows down and stops a
moving object
Memperlahankan dan
memberhentikan objek yang
bergerak
Disadvantages
Kekurangan
Advantages
Kelebihan
Factors that affect friction
Faktor yang menyebabkan
geseran
Condition of the
surface
Keadaan
permukaan
Weight of the
object
Berat objek
Ways to reduce friction
Cara kurangkan geseran
Use rollers or marbles
Guna penggelek atau
guli
Smoothen surfaces
Permukaan licin
Use oil, wax, grease,
talcum
powder, air cushion
Guna minyak, pelicin,
gris,
1.3 Analysing friction
Analisa geseran
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 64 -
Movement
Pergerakkan
Speed
Laju
Calculation of speed
Pengiraan laju
How fast an object moves
Berapa laju objek bergerak
Formula :
Rumus
Speed = Distance
Time
Laju = Jarak
Masa
A faster object travels
a longer distance in a
given time
Objek yang lebih laju
melalui jarak yang
lebih panjang mengikut
masa yang diberi
A faster object takes a shorter time
to travel a given distance
Objek yang laju mengambil masa
yang singkat
untuk melalui jarak yang diberi
Units :
km/h
km/j
m/s
m/s
cm/s
sm/s
2.1 Understanding speed
Memahami laju
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 65 -
MENYIASAT ALAM BAHAN MENYIASAT ALAM BAHAN MENYIASAT ALAM BAHAN MENYIASAT ALAM BAHAN
Year 4
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 66 -
Properties of materials
Sifat bahan
Insulator
Penebat
Float on water
Terapung atas air
Conduct electricity
Mengalirkan elektrik
metal
logam
Conduct heat
Mengalirkan
haba
Sink in water
Tenggelam
dalam air
Light to pass through
Cahaya boleh melaluinya
Can be stretch
Boleh diregangkan
wood
kayu
stone
batu
rubber ring
gelang getah
glass
kaca
carbon
karbon
plastics
plastik
metal
logam
wood
kayu
1.1 The properties of materials
Sifat bahan
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 67 -
Applying knowledge properties of materials in everyday life
Aplikasi pengetahuan sifat bahan dalam kehidupan seharian
Suggest ways to keep things hot
Cadangan untuk menyimpan
benda panas
Covered with insulators
Balut dengan bahan penebat
Suggest ways to keep things cold
Cadangan untuk menyimpan benda
sejuk
hot thing
benda panas
cold thing
benda sejuk
to prevent heat loss
untuk menghalang kehilangan haba
prevent from absorbing heat
halang daripada serap haba
1.2 Applying knowledge properties of materials in everyday life
Aplikasi pengetahuan sifat bahan dalam kehidupan seharian
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 68 -
Uses of materials based on their properties
Penggunaan bahan berdasarkan kandungan
transparent
lutsinar
glass
kaca
glasses
gelas
soft
lembut
wood
kayu
tissue
tisu
hard
keras
metal
logam
spoon
sudu
properties
sifat
materials
bahan
object
objek
cheap
murah
easy to get
senang
didapati
strength
kuat
good quality
kualiti baik
1.3 Synthesising the knowledge about uses of materials based on their properties
Sintesis pengetahuan mengenai penggunaan bahan berdasarkan kandungan
List of object and
materials that they are
made of
Senarai objek dan
bahan yang dibuat
daripada
Reason why particular
materials are used
to make an object
Keterangan mengapa bahan
tertentu digunakan untuk
membuat objek
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 69 -
Natural materials
Bahan semulajadi
Man-made materials
Bahan buatan
wood
kayu
metal
logam
rubber
getah
cotton
kapas
plastics
plastik
synthetic cloth
kain sintetik
glass
kaca
State that man-made materials comes from natural materials
Nyatakan bahan buatan berasal dari bahan semulajadi
reducing
mengurangkan
reusing
guna semula
recycling
kitar semula
public transport
pengangkutan awam
plastic bag
beg plastik
bottle
botol
plastics
plastik
glass
kaca
The importance of reuse, reduce and recycle of materials
Kepentingan guna semula, pengurangan dan kitar semula bahan
1.4 Knowing the importance of reuse, reduce and recycle
Memahami kepentingan guna semula, pengurangan dan kitar semula bahan
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 70 -
Rusting can be prevented
Pengaratan boleh dicegah
Different ways to prevent objects from rusting
Cara berbeza untuk menghalang objek
daripada berkarat
Coating with non rusting
materials
Menyadurkan dengan bahan
tidak berkarat
*paint
cat
*oil
The necessary to prevent rusting
Keperluan mencegah pengaratan
*Everlasting Live
Tahan lebih lama
*Save natural material
Selamatkan bahan asal
*Save cost
Jimat kos
*Looking good
Mencantikkan
*Conclusion; Rusting can be avoided by preventing iron contact with air and water.
* Kesimpulan;Pengaratan boleh dihindarkan dengan menghalang ia bertindak balas
dengan air dan udara
1.5 Understanding that some materials can rust
Memahami sesetengah bahan boleh perkarat
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 71 -
Rusting can be prevented
Pengaratan boleh dicegah
Rusty
objects
Non rusty objects
Objek tidak berkarat
Object made of iron and
steel
Objek yang diperbuat
daripada besi
Object made of glass, plastic,
wood, clay and silk
Objek yang diperbuat daripada
kaca,plastik, kayu, tanah liat
dan sutera
*Nail
Paku
*Spoon
Sudu
*Knife
Pisau
*Glass
Kaca
*Bottle
Botol
*Cup
Cawan
1.6 Understanding the rusting can be prevented
Memahami pengaratan boleh dicegah
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 72 -
MATERIALS AROUD YOU
-The Properties Of Materials-
MATERIALS
WOOD RUBBER PLASTIC GLASS
METAL COTTON
-Floats
on water
-Insulator
-Can
absorbs
water
-Insulator
-Conducts
electricity
-Conducts
heat
-Conductor
-Allow
light to
pass
through
them
-Insulator
-Can be
stretched
-Insulator
-Insulator
-Terapung
di atas air
-Penebat
-Boleh
menyerap
air
-Penebat
-Mengalirkan
elektrik
-Mengalirkan
haba
-Konduktor
Membenar
kan cahaya
menembusi
nya
-Penebat
-Boleh
diregang
-Penebat
-Penebat
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 73 -
Opaque, Translucent and Tranparent
Legap, Lutsinar dan Lutcahaya
Wood Door
(opaque)
Glass Door
(Translucent)
Clear glass Door
(Transparent)
I cant see you.
Saya tak nampak awak.
I can see you but not clear.
Saya nampak awak tapi kurang
jelas.
I can see you clearly.
Saya nampak awak dengan jelas.
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 74 -
SYNTHETC
CLOTH
KAIN
SINTETIK
ATURAL AD MA MADE
BAHA SEMULAJADI DA BUATA MAUSIA
NATURAL
MADE
MATERIALS
BAHA
SEMULAJADI
MAN-MADE
MATERIALS
BAHA
BUATA
MAUSIA
RUBBER
GETAH
SILK
SUTERA
LEATHER
KULIT
WOOD
KAYU
METAL
LOGAM
GLASS
KACA
COTTON
KAPAS
CLAY
TANAH
LIAT
FUR
BULU
PLASTIC
PLASTIK
NYLON
NILON
RAYON
RAYON
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 75 -
MENYIASAT ALAM BAHAN MENYIASAT ALAM BAHAN MENYIASAT ALAM BAHAN MENYIASAT ALAM BAHAN
Year 5
Unit 5/Lesson7
Natural and Man made
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 76 -
Solid
Pepejal
Liquid
Cecair
gas
has mass
mempunyai
berat
Properties of solid
Sifat-sifat pepejal
Properties of liquid
Sifat sifat cecair
Properties of gas
Sifat-sifat gas
fixed volume
isipadu tetap
fixed shape
bentuk tetap
has mass
mempunyai
berat
Examples
Contoh
Water
Air
Milk
Susu
Air
Udara
no permanent shape
bentuk tidak tetap
fixed
volume
isipadu
tetap
Steam
wap
Wood
Kayu
Stone
batu
can't fixed
shape
Tidak
mempunyai
bentuk tetap
has mass
Mempunyai
berat
Can't fixed
volume
Isipadu
tidak
tetap
can compressed
boleh
dimampatkan
1.1 Matter exist in the form of solid, liquid or gas
Bahan wujud dalam bentuk pepejal,cecair atau gas
Matter
Bahan
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 77 -
CHANGING
STATES OF
WATER
Perubahan
Bentuk
Air
gas liquid
gas - cecair
liquid gas
cecair - gas
liquid gas
Cecair - gas
solid liquid
Pepejal - cecair
Melting
Peleburan
Boiling
Pendidihan
Evaporation
Penyejatan
Condensation
Kondensasi
Freezing
Pembekuan
1.2 Understanding that matter can change from one state to another
Memahami bahawa benda boleh berubah bentuk dari satu ke bentuk yang lain
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 78 -
T Th he e w wa at te er r c cy yc cl le e. .
K Ki it ta ar ra an n a ai ir r
C Ci ir rc cu ul la at ti io on n o of f w wa at te er r i in n
t th he e e en nv vi ir ro on nm me en nt t. .
K Ki it ta ar ra an n a ai ir r d da al la am m p pe er rs se ek ki it ta ar ra an n
F Fo or rm ma at ti io on n o of f c cl lo ou ud ds s
a an nd d r ra ai in n. .
P Pe em mb be en nt tu uk ka an n a aw wa an n d da an n
h hu uj ja an n
I Im mp po or rt ta an nc ce e o of f w wa at te er r
K Ke ep pe en nt ti in ng ga an n a ai ir r. .
C Ch ha an ng ge es s i in n t th he e s st ta at te es s o of f
m ma at tt te er r i in n t th he e w wa at te er r c cy yc cl le e
P Pe er ru ub ba ah ha an n b be en nt tu uk k b ba ah ha an n
d da al la am m k ki it ta ar ra an n a ai ir r
L Li iq qu ui id d t to o g ga as s ( (e ev va ap po or ra at ti io on n) )
C Ce ec ca ai ir r k ke ep pa ad da a g ga as s ( ( P Pe en ny ye ej ja at ta an n ) )
D Dr ro op pl le et ts s o of f w wa at te er r w wi il ll l b be ec co om me e
b bi ig gg ge er r a an nd d h he ea av vi ie er r rain
Titisan air menjadi besar dan
berat hujan
Evaporation
Penyejatan
Condensation
Kondensasi
G Ga as s l li iq qu ui id d ( (C Co on nd de en ns sa at ti io on n) )
G Ga as s C Ce ec ca ai ir r ( ( K Ko on nd de en ns sa as si i ) )
1.3 Understanding the water cycle
Memahami kitaran air
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 79 -
Importance of water resources.
Kepentingan sumber air
To prevent living aquatic from being
destroyed and undergoing
extinction
Untuk mengelakkan hidupan air
musnah dan mengalami kepupusan
Reasons to keep our
water resources clean.
Sebab untuk
mengekalkan
sumber air yang bersih
To ensure the cleanliness
of water supply
Memastikan air yang bersih
dibekalkan
To regulate
the formation of
clouds and rain
Untuk
mengekalkan
pembentukan
awan dan hujan
To avoid infected
diseases
Mengelakkan
penyakit berjangkit
Ways to keep our water
resources clean
Cara mengekalkan sumber
air bersih
Keep the rivers clean
Jadikan sungai besih
Cleanliness campaign
Kempen kebersihan
1.4 Appreciating the importance of water resources
Menghargai kepentingan sumber air
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 80 -
The properties of acid,
alkaline and neutral substances.
Ciri-ciri asid , alkali dan bahan nutral
Identify the taste of acidic and
alkaline food.
Mengenal pasti rasa makanan
yang berasid dan berakali
Identify acidic, alkaline and neutral
substances using litmus paper.
Mengenal pasti keasidan,alkali dan
nutral bahan menggunakan kertas
litmus
Conclude the properties of
acidic, alkaline and neutral
substances.
Kesimpulan ciri-ciri bahan asid,
alkali dan neutral .
Changes in colour of
litmus papers
Menukarkan warna kertas
litmus
blue to red
biru ke
merah
red to blue
merah ke
biru
no change
tidak
berubah
Bitter
Pahit
Sour
masam
Properties of alkali
Ciri-ciri alkali
Properties
of acid
Ciri-ciri asid
Properties of
neutral substances
Ciri-ciri bahan
neutral
Taste bitter &
change red litmus
paper to blue
Rasa pahit dan
menukarkan
Kertas litmus
merah kepada biru
Taste sour &
change blue
litmus paper red
Rasa masam dan
menukarkan
kertas litmus
merah
Other tastes no
changes in litmus paper
Tidak menukarkan
warna kertas litmus
Acid
asid
Alkaline
alkali
neutral
neutral
2.1 Understanding the properties of acidic, alkaline and neutral substances
Memahami sifat asid, alkali dan bahan neutral
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 81 -
STATE OF MATTER
KEADAAN BAHAN
Ali is eating an ice cream. After a while, the ice cream
melt. Melting process changes solid to liquid.
Ali sedang makan ais krim. Selepas beberapa ketika,
ais krim itu menjadi cair. Proses pencairan
menukarkan pepejal kepada cecair.
Liquid
Solid
Abu feels like to drink cold water. He need some ice
cubes. He put water in the freezer. Freezing turn solid
to solid.
Abu ingin minum air sejuk. Dia perlukan ais batu. Dia
masukkan air ke dalam peti sejuk. Proses pembekuan
menukarkan cecair kepada pepejal.
Upins mother wants to boil some water. She knows
that the water is boiling because it produces steam or
water vapour. Boiling changes liquid to gas.
Ibu Upin ingin menjerang air. Dia tahu bahawa air itu
sudah mendidih kerana terhasilnya wap air atau stim.
Pendidihan menukarkan cecair kepada gas.
Ipins mother hangs clothe on the cloth line. After a
while, the cloth dries. This is because evaporation
process occurs. Evaporation turn liquid to gas.
Ibu Upin menjemur kain di ampaian.
Ah Seng forget to drink his ice lemon tea because his
mother as him to go to the shop. When he went back,
he saw many water droplets on the glass.
Condensation turn gas to liquid.
Ah Seng terlupa untuk minum airnya kerana ibunya
menyuruhnya ke kedai. Setelah pulan, dia dapati
banyak titisan air di luar gelas. Kondensasi
menukarkan gas kepada cecair.
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 82 -
I am a droplet of water.
Saya setitis air
Ouch! Where I am. Wow! It is big. Opss! Mmm cold and fresh. Where am I? Oh, I see, this
is a seamy new place. I came from river.
Ouch! Di mana saya. Wow! Besarnya. Opss! Mmmsejuk dan segar. Di mana saya? Oh,
saya tahu, saya di lauttempat baru untuk saya. Saya datang dari sungai.
Arghh! Hot, very hotOh no! Im moving up. What happen??? It is very hot. The sun makes
me very hot. It evaporate me to the sky. Evaporation change me as a water vapour.
Arghh! Panasnya, sangat panas Tidak! Saya sedang bergerak ke atas. Apa dah jadi nih???
Sangat panas. Matahari membuatkan saya panas. Ia menyejat saya ke langit. Penyejatan
menukarkan saya menjadi wap air.
Oh no! Im shivering. It cold now. The condensation process turn me into water droplet.
Wow! There are many droplets like me. Hey! Lets join together. Lets form cloud. Ahhit is
better now.
Oh no! Saya sedang menggigil. Ia sejuk sekarang. Proses kondensasi menukar saya menjadi
titisan air. Wow! Banyaknya tiisan air macam saya. Hey! Jom bergabung. Jom bentuk awan.
Ahhleganya dah jadi awan.
Opss! Im heavy now. Let me out. Ahh! Im out now as rain. Ouch! I fall down into the river
again. My home sweet home. Yea!
Opss! Saya semakin berat sekarang. Saya nak keluar. Ahh! Saya dah keluar sebagai hujan
sekarang. Ouch! Saya jatuh kembali kedalam sungai. Rumah saya yang dirindui. Yea!
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 83 -
Fill in the missing letters.
Lengkapkan perkataan dengan huruf yang betul.
E _ a _ _ _ a _ _ _ n
C _ _ d _ _s _ _ i o _
S __ _
R _ v _ _
C _ _ _ _
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 84 -
MENYIASAT ALAM BAHAN MENYIASAT ALAM BAHAN MENYIASAT ALAM BAHAN MENYIASAT ALAM BAHAN
Year 6
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 85 -
FOOD PRESERVATION
Pengawetan makanan
Food spoilage
Kerosakan makanan
Characteristics of spoilt food
Ciri-ciri makanan yang rosak
The conditions for microorganisms to grow
Keadaan untuk mikroorganisma membesar
Unpleasant smell
Bau tidak menyenangkan
Unpleasant taste
Rasa tidak menyenangkan
Changed colour
Berubah warna
Changed texture
Berubah jalinan
Mouldy
Berkulat
Air
Udara
Water
Air
Nutrients
Zat makanan
Suitable temperature
Suhu yang sesuai
Suitable acidity
Keadaan asid yang sesuai
1.1 Understanding food spoilage
Memahami kerosakan makanan
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 86 -
Food Preservation
Pengawetan makanan
Drying
Pengeringan
Fish, prawns, cuttlefish, fruits
Ikan, udang, sotong, buah
Boiling
Pemanasan
Cooling
Pendinginan
Vacuum packing
Pembukusan
vakum
Pickling
Penjerukan
Freezing
Penyejukbekuan
Bottling/Canning
Pembotolan/pengeti
nan
Pasteurising
Pempausteran
Salting
Pengasinan
Smoking
Pengasapan
Waxing
Pelilinan
Vegetables, fruits
Sayur, buah
Nuts, crackers, powder milk
Kacang, biskut, susu tepung
Fruits, vegetables
Buah, sayur
Chicken, meat, prawns, cuttlefish
Ayam, daging, udang, sotong
Meat, fish, fruits, vegetables
Daging, ikan, buah, sayur
Milk, juices, ice cream
Susu, jus, ais krim
Fish, meat, eggs, vegetables,
fruits
Ikan, daging, telur, sayur, buah
Vegetables, fruits
Sayur, buah
Meat, fish
Daging, ikan
1.2 Synthesising the concept of food preservation
Sintesis konsep pengawetan makanan
Meat ,fish, vegetables
daging, ikan, sayur
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 87 -
The importance of preserving food
Kepentingan pengawetan makanan
1.3 Realising the importance of preserving food
Menyedari kepentingan pengawetan makanan
Food Preservation
Pengawetan makanan
To make last longer
Tahan lebih lama
To make food easily to store
Makanan lebih mudah disimpan
To reduce wastage food
Mengurangkan makanan terbuang
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 88 -
Waste Management
Pegurusan bahan buangan
Plastics, glass, chemical waste, organic waste, metal
Plastik, kaca, sisa kimia, sisa organik, logam
Homes, factories, agriculture, motor vehicles
Rumah, kilang, pertanian, kenderaan bermotor
Proper
Betul
Improper
Tidak betul
2.1 Understanding the effects of improper disposal of waste on the environment
Memahami kesan kesalahan mengurus pembuangan bahan buangan kepada
persekitaran
Types of waste
Jenis bahan
Sources of waste
Sumber bahan
Ways of
disposing waste
Cara buang
bahan buangan
Dispose of waste in the right place
Buang bahan buangan di tempat
yang betul
Treat waste before disposing it into
the drain
Rawat bahan buangan sebelum ia
mengalir keluar
Bury waste that can decay in soil
Bakar bahan buangan yang boleh
reput dalam tanah
Reuse of recycle waste
Guna semula bahan kitar semula
Littering
Tidak teratur
Open burning
Pembakaran terbuka
Release of waste into the rivers
Melepaskan bahan buangan ke
dalam sungai
Release of smoke into the air
Melepaskan asap ke udara
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 89 -
Air pollution
Pencemaran udara
Water pollution
Pencemaran air
Sickness &
diseases
Kesakitan &
penyakit
Damages our lungs, initiates our eyes
Merosakkan paru-paru.tidak elok
dipandang
Thypoid, dengue fever
demam denggi
Acid rain
Hujan asid
Flash floods
Banjir kilat
Can kill plants and erode building
Boleh membunuh tumbuhan dan
menghakis bangunan
Damage property
Merosakkan harta
Can kill fish and water plants
Boleh membunuh ikan dan tumbuhan
2.1 Understanding the effects of improper disposal of waste on the environment
Memahami kesan kesalahan mengurus pembuangan bahan buangan kepada
persekitaran
Harmful effects of improper
disposal of waste
Kesan buruk daripada pembuangan
bahan buangan yang tidak betul
Waste that can
decay
Bahan buangan
yang boleh reput
Waste that does
not decay
Bahan buangan
yang
tidak boleh reput
Food, paper, wood
Makanan, surat
khabar, kayu
Plastics, glass,
metal
Plastik, gelas,
logam
2.1 Understanding the effects of improper disposal of waste on the environment
Memahami kesan kesalahan mengurus pembuangan bahan buangan kepada
persekitaran
Advantage :
To make the soil fertiile
Kelebihan :
Untuk menyburkan tanah
Disadvantage :
Gives out poisonous
gases
Kelemahan :
Mengeluarkan gas
beracun
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 90 -
MENYIASAT BUMI & ALAM SEMESTA MENYIASAT BUMI & ALAM SEMESTA MENYIASAT BUMI & ALAM SEMESTA MENYIASAT BUMI & ALAM SEMESTA
Year 4
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 91 -
The solar system
Sistem Solar
List of
constituents
Senarai
pembentukan
List of planets
Senarai planet
Planets move around the Sun
Planet beredar mengelilingi
matahari
-Nine Planets
Sembilan planet
-Natural satellites
Satelit semulajadi
-Meteors
Meteor
-Comets
Komet
-Asteroids
Asteroid
1.1 Understanding the Solar System
Memahami Sistem Solar
Mercury My
Utarid
Venus Very
Zuhrah
Earth Excellent
Bumi
Mars Mother
Marikh
Jupiter Just
Musytari
Saturn Served
Zuhal
Uranus Us
Uranus
Neptune Nine
Neptun
Pluto Pudding
Pluto
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 92 -
The relative size
and distance
between
the Earth, the
Moon and the
Sun
Saiz dan jarak
relatif di antara
Bumi, Bulan dan
Size of the Sun relative to
the size
of the Earth.
Saiz Matahari relatif saiz
Bumi
Size of the Earth relative to
the size
of the Moon.
Saiz Bumi relatif saiz Bulan
The relative distance from the Earth to
the Sun compared
to the relative distance from the Earth
to the Moon.
Jarak relatif dari Bumi ke Matahari
berbanding jarak relative dari Bumi ke
Bulan
the Sun
Matahari
1
the Earth
Bumi
100
the Earth
Bumi
1
the Moon
Bulan
4
the Sun
Matahari
the Earth
Bumi
the Moon
Bulan
150 000 000 km
382 500 km
1 : 400
1.2 Understanding the relative size and distance between the Earth, the Moon and
the Sun
Memahami perbandingan saiz dan jarak antara Bumi, Bulan dan Matahari
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 93 -
Earth in the Solar
System
Bumi dalam
Sistem Solar
Why certain planets are not
conducive for living things.
Mengapa sesetengah
planet tidak sesuai
untuk benda hidup
Effect
Kesan
The Earth is the only planet
in the Solar System that has
living things.
Hanya planet Bumi dalam
Sistem Solar yang
mempunyai benda hidup
The nearer a planet to the Sun is,
the hotter is the surface of the planet.
Planet yang dekat dengan matahari
mempunyai permukaan yang paling
panas
The farther a planet from the Sun is,
the colder is the surface of the planet.
Planet yang paling jauh dari matahari
mempunyai perrmukaan yang paling
sejuk.
Do not have enough air and water.
Tidak mempunyai air dan udara yang
mencukupi
Much nearer :
Lebih dekat
The temperature on the Earth
would rise.
Suhu di bumi akan meningkat
Water on Earth would evaporate.
Air di bumi akan tersejat
No water and the temperature
would be very hot.
Tiada air, suhu akan jadi lebih
panas.
Much farther :
Lebih jauh
The temperature on the Earth
would drop.
Suhu di bumi akan menurun
Water would freeze into ice.
Air akan membeku menjadi ais.
All living things would die.
Semua benda hidup aka mati.
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, it receives enough
light and heat from the Sun.
Bumi adalah planet ketuga dari matahari, ia menerima
cahaya dan haba secukupnya
It is not too hot or too cold.
Ia tidak terlalu sejuk atau panas.
The atmosphere of the Earth contains air and there is
water on Earth.
Atmosfera bumi mengandungi udara dan air di bumi
1.3 Appreciating the perfect placement of the planet Earth in the Solar System
Menghargai kedudukan yang sempurna planet Bumi dalam Sistem Solar
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 94 -
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM
SISTEM SOLAR KITA
MERCURY MAKAN
VENUS VITAMIN
EARTH E
MARS MULUT
JUPITER JADI
SATURN SENGET
URANUS URAT
NEPTUNE AK
PLUTO PUTUS
The nine planets from the sun.
9 Planet daripada Matahari.
MY
VERY
EASY
METHOD
JUST
STOP
USING
NINE
PLANET
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 95 -
MENYIASAT BUMI & ALAM SEMESTA MENYIASAT BUMI & ALAM SEMESTA MENYIASAT BUMI & ALAM SEMESTA MENYIASAT BUMI & ALAM SEMESTA
Year 5
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 96 -
Indicates Seasons
Menunjukkan musim
A group of stars that form
a certain pattern in the sky
Gugusan bintang-bintang
di langit yang membentuk
corak tertentu
Importance of
Constellation
Kepentingan buruj
Identify
Constellation
Kenal pasti buruj
What constellation is
Apa itu buruj
Constellation
Buruj
Big dipper
Biduk
Scorpion
Skorpio
Orion
Belantik
Southern Cross
Pari
North
Utara
North
Utara
South
Selatan
April June
Kite or Cross
Layang-layang atau
Palang
Scorpion
Kala jengking
Hunter
Pemburu
Water dipper
Gayung
South
Selatan
December - January
June - August
Planting
Musim menanam
Harvesting
Musim menuai
Desert
Padang pasir
Sea
Laut
1.1 Understanding the constellation
Memahami buruj
Show
Directions
Menunjukkan arah
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 97 -
The movements
of the Earth, the Moon
and the Sun
Pergerakan Bumi,Bulan
dan Matahari
Earth rotates
on it axis
Bumi berputar
pada paksinya
Earth rotates and at
the same time moves
around the sun
Bumi berputar dan
pada masa yang
sama bergerak
mengelilingi matahari
Moon rotates
on it axis
Bulan berputar
pada paksinya
Moon rotates and at
the same time
moves around
the Earth
Bulan berputar dan
pada masa
yang sama
beredar mengeliligi
Mathari
The Moon and the Earth
move round the Sun at the
same time
Bulan dan Bumi bergerak
mengeliligi
Matahari pada masa yang
sama
The earth rotates on its
axis from west to east
Bumi berputar pada
paksinya
The changes in length and
position of the shadow
throughout the day
Perubahan panjang dan
kedudukan bayang-bayang
sepanjang hari
2.1 Understanding the movement of the Earth, the Moon and the Sun
Memahami pergerakan Bumi, Bulan dan Matahari
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 98 -
The occurrence of day and night
Kejadian siang dan malam
It is day time for the part
of the Earth facing the Sun.
Pada waktu siang sebahagian Bumi
menghadap Matahari
At night part of
Earth do not face Sun.
Pada waktu malam sebahagian
Bumi tidak menghadap matahari
Day and night occur due to the
rotation of the Earth on its axis.
Kejadian siang dan malam berlaku
kerana putaran Bumi pada paksinya.
the Sun
Matahari
N Ni ig gh ht t- -t ti im me e
W Wa ak kt tu u m ma al la am m
D Da ay yt ti im me e
W Wa ak kt tu u s si ia an ng g
A Ax xi is s
P Pa ak ks si i
W We es st t
B Ba ar ra at t
E Ea as st t
T Ti im mu ur r
2.1 Understanding the occurrence o day and night
Memahami kejadian siang dan malam
the Earth
Bumi
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 99 -
Phases Of The Moon
Fasa-fasa Bulan
The Moon Does
Not Emit Light
Bulan tidak
mengeluarkan
cahaya
The Moon appear
bright when it reflect
sunlight
Bulan jadi terang
akibat pantulan
cahaya matahari.
Describe the phases of
the moon
Menerangkan fasa-fasa
bulan
1-New moon, 3- New half moon, 5- Full moon
1- Anak Bulan 3, Bulan separa baru 5. Bulan penuh
7- Old half moon
Bulan separa lama
2.3 Understanding the phases of tne Moon
Memahami fasa bulan
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 100 -
MENYIASAT BUMI & ALAM SEMESTA MENYIASAT BUMI & ALAM SEMESTA MENYIASAT BUMI & ALAM SEMESTA MENYIASAT BUMI & ALAM SEMESTA
Year 6
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 101 -
Eclipse of The Moon
Gerhana bulan
Eclipse of The Sun
Gerhana matahari
Eclipse
Gerhana
The Earth is between the Sun and
the Moon and the three of them lie in
a straight line.
Bumi berada di antara Matahari dan
Bulan dan ketiga-tiganya berada
dalam satu garis yang lurus
The Moon is between the Sun and
the Earth and the three of them lie
in a straight line.
Bulan berada di antara Matahari
dan Bumi dan ketiga-tiganya berada
dalam satu garis yang lurus
The Earth blocks
sunlight from
reaching the Moon
Bumi menghalang
cahaya Matahari
daripada sampai
ke Bulan
The Moon
looks reddish,
dark gray or
brown
Bulan kelihatan
kemerahan,
kelabu atau
perang
Sunlight is
blocked by
the Moon
Cahaya
Matahari
dihalang
oleh bulan
The Moon
shadow falls
on the Earth
surface
Bayang-
bayang Bulan
jatuh ke atas
permukaan
Bumi
Daylight
becomes
dark during
the total
eclipse
Hari siang
menjadi
gelap
menjelang
gerhana
penuh
1.1 Understanding the eclipse of the moon
Memahami gerhana bulan
1.2 Understanding the eclipse of the sun
Memahami gerhana matahari
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 102 -
MENYIASAT MENYIASAT MENYIASAT MENYIASAT DUNIA TEKNOLOGI DUNIA TEKNOLOGI DUNIA TEKNOLOGI DUNIA TEKNOLOGI
Year 4
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 103 -
Importance of technology in everyday life
Kepentingan teknologi dalam kehidupan seharian
Examples of human limitations are
Contoh had keupayaan manusia
Unable to see fine objects
Tidak boleh melihat objek yang kecil
Unable to speak loud
Tidak boleh bercakap dengan kuat
Unable to walk for long distance
Tidak boleh berjalan jauh
Unable to see far away objects
Tidak boleh melihat objek yang jauh
Microscope
Mikroskop
- The usage of lens to see fine
features of objects and microbes
Penggunaan kanta untuk melihat benda
dan mikrob yang halus
Microphone
Mikrofon
-To increase the voice volume
Untuk meninggikan suara
Telephone
Telefon
-To communicate from long distance
Untuk berkomunikasi dari jarak yang jauh
Bicycle, motorcycle, airplanes
Basikal,motosikal , kapal terbang
-Can travel long distance in a shorter time
Boleh pergi ke tempat jauh dalam masa
yang singkat
Telescope, binocular
Teleskop, binokular
-To see far away objects
Untuk melihat objek yang jauh
Limitation of human ability
Had keupayaan manusia
Devices to overcome human
limitation
Alat mengatsai had
keupayaan manusia
1.1 Understanding the importance of technology in everyday life
Memahami kepentingan teknologi dalam kehidupan seharian
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 104 -
Development
Of Technology
Pembangunan
teknologi
Examples
Contoh
Technology
Teknologi
1.2 Understanding the development of technology
Memahami pembangunan teknologi
Agriculture
Pertanian
e.g.:
hoe plough tractor combine harvester
Lubang bajak traktor mesin penuai
Transportation
Pengangkutan
Land:/ Darat
Animal bicycle car train
Haiwan basikal kereta kereta api
Air:/Udara
Hot air balloon airship glider aeroplane
Belon panas kapal udara glider kapal terbang
Water:/Air
Canoe raft sampan ferry ship
Kenu rakit sampan feri kapal
Construction
Pembinaan
Cave hut wooden house apartment
Gua pondok rumah kayu rumah pangsa
Communication
Komunikasi
Drawing carrier pigeon telephone
Lukisan pembawa utusan telefon
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 105 -
Problems they encounter in their
daily life
Masalah yang dihadapi dalam
kehidupan sehari
Ideas to solve the problems identified
Idea untuk menyelesaikan masalah
dikenal pasti
Technology solve problems
Teknologi menyelesaikan masalah
Cannot move and lift heavy thing
Tidak boleh beregerak dan angkat
benda berat
Cannot move farther
Tidak boleh bergerak jauh
Sketch the model
Lakar model
Brain storming
Mencari idea
Wheel barrow
Kereta sorong
1.3 Synthesising how technology can be used to solve problem
Sintesis bagaimana teknologi boleh digunakan untuk menyelesaikan masalah
Device to solve the problem
identified.
Alat untuk menyelesaikan masalah
dikenalpasti
Lever
Tuas
Demonstrate that device invented
can be used to solve the problem
identified
Demontrasi bahawa alat yang dicipta
boleh digunakan untuk
menyelesaikan masalah yang
dikenal pasti
Wheel barrow can move heavy thing
easily
Kereta sorong-boleh mengangkat benda
berat dengan senang
Pulley can lift everything
Takal boleh mengangkat apa sahaja
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 106 -
Advantages of
Technology
Kelebihan teknologi
Disadvantages of
Technology
Kelemahan teknologi
Communication
Komunikasi
Enable human to learn more about
things happening around the world
Membolehkan manusia mengetahui
benda yang berlaku di seluruh dunia
Transportation
Pengangkutan
Enable human to travel far away places
in shorter time
Membolehkan manusia pergi ke tempat
jauh dalam masa yang singkat
Agriculture
Pertanian
Machines make it easier to plants and
harvest their crops
Mesin memudahkan untuk menanam
dan menuai
Construction
Pembinaan
Roads, highways, bridges and
building is easier and faster to build
Memudahkan pembinaan jalan, lebuh
raya,jambatan dan bangunan
Environmental pollution from increase in
waste materials
Pencemaran alam daripada
penambahan sisa buangan
Environmental destruction result from
excessive usage of natural resources
Kemusnahan alam kesan daripada
penggunaan sumber semulajadi
yang berleluasa
Social problem
Masalah sosial
Bad effects on health result from
environmental pollution and excessive
use of chemicals
Kesan buruk kepada kesihatan kesa
daripada pencemaran sekitar dan
penggunaan bahan kimia secara
berleluasa
1.4 Analysing that technology can benefit mankind if used misely
Analisa bahawa teknologi memberi manfaat jika digunakan secara bijaksana
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 107 -
HUMAN LIMITATIONS AND WAYS TO OVERCOME
KETIDAKUPAYAAN MANUSIA DAN CARA MENTASAINYA
Use the phone Use the car Use the aeroplane Use the computer
We cant fly.
Kami tak boleh
terbang.
Can we save the
data?
Boleh tak kita
simpan data ini?
I cant walk,
anymore.
Saya tak boleh
berjalan lagi.
I cant hear you.
Saya tak dengar
awak
HOW TO OVERCOME THE PROBLEM?
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 108 -
MENYIASAT MENYIASAT MENYIASAT MENYIASAT DUNIA TEKNOLOGI DUNIA TEKNOLOGI DUNIA TEKNOLOGI DUNIA TEKNOLOGI
Year 5
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 109 -
The shape of objects
Bentuk-bentuk benda
Identify shape in structure
Mengenal pasti bentuk di
dalam struktur
Cuboid
Kuboid
Cube
Kiub
Cylinder
Silinder
Sphere
Sfera
Cone
Kon
Pyramid
Piramid
Sphere
sfera
Cylinder
Silinder
1.1 Knowing the shapes of objects in structures.
Mengetahui bentuk objek di dalam struktur
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 110 -
Strength and Stability
Kekuatan dan Kestabilan
Shapes of objects that are stable
Bentuk benda yang stabil
The factors that affect stability of
objects
Faktor-faktor yang memberi kesan
kestabilan objek
The factors that affect the
strength of a structure
Faktor-faktor yang memberi
kesan sesuatu struktur
Cube, cone, cylinder
Kiub.kon,silinder
Height , base area
Ketinggian , luas tapak
Bigger base area more stable
Semakin luas tapak bertambah
kestabilan
Smaller base area less stable
Semakin kecil luas tapak kurang
kestabilan
Lower object more stable
Semakin rendah objek bertambah
kestabilan
Higher object less stable
Tinggi objek kurang kestabilan
1.2 Understanding the strength and stability of a structure.
Memahami kekuatan dan kestabilan struktur.
Types of materials used
Steel, iron, wood
Jenis bahan yang digunakan
Keluli, besi, kayu
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 111 -
MENYIASAT MENYIASAT MENYIASAT MENYIASAT DUNIA TEKNOLOGI DUNIA TEKNOLOGI DUNIA TEKNOLOGI DUNIA TEKNOLOGI
Year 6
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 112 -
MACHINES
Mesin
To carry or move heavy objects easily
Untuk membawa atau menggerak benda
berat dengan mudah
To cut or separate objects
Untuk memotong atau mengasing objek
To lift heavy objects easier
Untuk mengangkat objek dengan mudah
To fix two objects together
Untuk mengetatkan dua benda bersama
To move objects easily
Untuk menggerakkan objek dengan mudah
To carry or move heavy objects easily
Untuk membawa atau menggerak benda
berat dengan mudah
To carry or to lift objects to higher place
Untuk membawa atau mengangkat objek ke
tempat tinggi
Simple
machines
Mesin
ringkas
Lever
Tuas
Wheel and axle
Roda dan gandar
Pulley
Takal
Wedge
Baji
Inclined plane
Satah condong
Screw
Skru
Gear
Gear
1.1 Understanding simple machines
Memahami mesin ringkas
_____________________
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 113 -
Machine
make
life easier
Mesin
membuat
kehidupan
lebih mudah
Made up of more than
one simple machine
Terdiri lebih dari satu
mesin ringkas
Crane, lift
Kren, lif
Aeroplane, bus
Kapal terbang, bas
Computer, satelite
Komputer, satelit
Tractor
Trektar
e.g Wheelbarrow, bicycle, a pair of
scissors, fishing rod
Kereta sorong. basikal, gunting,
rod pancing
To carry, move or lift heavy
things more easily
Untuk membawa atau
mengangkat benda dengan mudah
To travel from one place to another
Untuk pergi dari satu tempat ke
tempat yang lain
To make work faster
Untuk membuat kerja lebih cepat
To make communication with
people faster and easier
Untuk berkomunikasi dengan
manusia lebih cepat dan mudah
To treat diseases
Untuk mengesan penyakit
Dialysis machine
Mesin dialisis
Complex
Machine
Mesin
kompleks
1.2 Analysing a complex machines
Analisa mesin yang kompleks
1.3 Appreciating the invention of machines that make life easier
Menghargai mesin yang dicipta membuatkan hidup menjadi senang
Zazolnizam Bin Zakaria Mind Maps Science
SK Permatang Tok Mahat-Edited from Modul Sinar
- 114 -
Catatan :
_____________________
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Seni 2Dokumen1 halamanSeni 2mbarathi2Belum ada peringkat
- Bab 5 Komponen KomputerDokumen33 halamanBab 5 Komponen Komputerfads93% (14)
- PPPMDST Tmktahun3 PDFDokumen9 halamanPPPMDST Tmktahun3 PDFNagaretnam NagaBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Perkakasan KomputerDokumen2 halamanContoh Perkakasan Komputermbarathi2Belum ada peringkat
- Kemalangan Jalan RayaDokumen4 halamanKemalangan Jalan RayaSingAnnBelum ada peringkat
- Penukaran Unit MatematikDokumen16 halamanPenukaran Unit Matematikmbarathi2Belum ada peringkat
- Seni - Tahun 1-6 - 7Dokumen9 halamanSeni - Tahun 1-6 - 7Sekolah Portal100% (8)
- Sistem Rangkaian Dan Dunia InternetDokumen14 halamanSistem Rangkaian Dan Dunia InternetAminBelum ada peringkat
- Kemalangan Jalan RayaDokumen4 halamanKemalangan Jalan RayaSingAnnBelum ada peringkat