Buku Rujukan Nilam BIOLOGI F4 KSSM-72-84
Diunggah oleh
wongiz227Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Buku Rujukan Nilam BIOLOGI F4 KSSM-72-84
Diunggah oleh
wongiz227Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
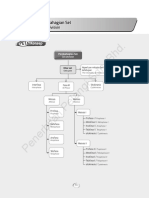
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
UNIT
Pembahagian Sel
6 Cell Division
6.1 Pembahagian Sel / Cell Division SK 6.1 Ekstra / Extra
SP 6.1.1 Memerihalkan kariokinesis (pembahagian nukleus) dan sitokinesis (pembahagian sitoplasma)
Takrifan kariokinesis dan sitokinesis. / Definition karyokinesis and cytokinesis.
• Kariokinesis melibatkan pembahagian nukleus.
Karyokinesis involves the division of nucleus.
• Sitokinesis melibatkan pembahagian sitoplasma.
Cytokinesis involves the division of cytoplasm.
SP 6.1.2 Memerihalkan haploid, diploid, kromatin, kromosom homolog, kromosom paternal, kromosom maternal
Haploid
• Satu set kromosom (n)
One set of chromosome (n)
• Dalam manusia bilangan haploid (n) = 23
In human, the number of haploid (n) = 23
• Sel pembiakan manusia mengandungi kromosom haploid.
Human reproduction cells contain the haploid chromosomes.
Diploid
• Dua set kromosom (2n)
Two sets of chromosome (2n)
• Dalam manusia bilangan haploid (2n) = 46
In human, the number of haploid (2n) = 46
• Sel soma manusia mengandungi kromosom diploid.
Human somatic cells contain the diploid chromosomes.
Kromosom homolog / Homologous chromosomes
• Kromosom berpasangan yang terdiri daripada kromosom paternal (ayah) dan kromosom maternal (ibu).
A pair of chromosomes consists of a paternal chromosome (father) and a maternal chromosome (mother).
• Kromosom homolog mempunyai saiz, struktur yang sama dan mengandungi
maklumat genetik yang sama.
The homologous chromosomes have similar size, structure and contain similar genetic information .
• Kromosom homolog hanya terdapat dalam sel soma .
Hamologous chromosomes are only found in somatic cells.
Unit 6
Kromosom paternal Kromosom maternal
Paternal chromosome Maternal chromosome
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 70
06-Biologi F4 Unit6(p70-82)csy4p.indd 70 11/01/2020 11:46 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
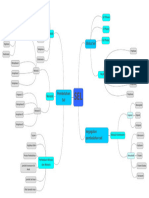
6.2 Kitar Sel dan Mitosis / Cell Cycle and Mitosis SK 6.2
SP 6.2.1 Memerihalkan fasa dalam kitar sel
1 Kitar sel. / Cell cycle.
Fasa G1
G1 phase
Sit
Cy okin
tok es
in is
Telo esis
Telo fasa
pha
se
Anafasa
Fasa M Anaphase
Pembahagian
terphase
M phase Metafasa
sis / Mitosis
sel / Cell
Metaphase Fasa S
division
S phase
/ In
asa
Prof hase a
sa
Prop rf
Mito
Inte
Fasa G2
G2 phase
Interfasa / Interphase Fasa M / M phase
• Fasa G1: Sintesis organel baharu dan • Terdiri daripada mitosis dan
protein . sitokinesis .
new mitosis cytokinesis
Phase G1: The synthesis of organelles Consists of and .
and protein . • Terdapat empat peringkat mitosis:
• Kromosom tidak jelas kelihatan dan membentuk profasa , metafasa ,
struktur bebenang halus dan panjang yang anafasa dan telofasa .
dinamakan kromatin . There are four stages of mitosis:
Chromosomes are not visible and form thread prophase , metaphase ,
like structures which are thin and long known as
anaphase and telophase .
chromatin .
• Sitokinesis adalah pembahagian sitoplasma
• Fasa S: Replikasi DNA berlaku. Dua sel induk untuk membentuk dua sel anak yang
kromosom seiras hasil daripada replikasi DNA seiras.
dinamakan kromatid kembar . Cytokinesis is the separation of parent cell’s
Phase S: Replication of DNA occurs. The two cytoplasm to form two identical daughter cells.
identical chromosomes that result from DNA replication
are called sister chromatids .
Unit 6
• Fasa G2: Sintesis enzim ,
protein dan ATP untuk pembahagian
sel.
Phase G2: The synthesis of enzymes ,
proteins and ATP for cell division.
71 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
06-Biologi F4 Unit6(p70-82)csy4p.indd 71 11/01/2020 11:46 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
6.2.2 Menyusun mengikut urutan peringkat dalam proses mitosis
SP
6.2.3 Berkomunikasi tentang struktur sel dalam setiap peringkat mitosis dan sitokinesis melalui lukisan berlabel
2 Peringkat-peringkat mitosis.
Stages of mitosis.
Rajah / Diagram Struktur / Structure
Kromatid
Profasa / Prophase
kembar pendek tebal
Sister
Kromosom memadat serta menjadi dan .
chromatid Kromatid kembar berpaut di sentromer . Membran nukleus dan
nukleolus menghilang.
Sentromer Chromosomes condense and become shorter and thicker .
Centromere centromere
The sister chromatid are joined at . The nucleus membrane
and nucleolus are disappear.
Metafasa / Metaphase
Gentian Kromatid kembar tersusun di satah khatulistiwa .
gelendong Gentian gelendong
Spindle fibre memegang sentromer.
The sister chromatids align at the metaphase plate . The spindle fibres
hold the centromeres.
Anafasa / Anaphase
Kutub
bertentangan Sentromer membahagi . Kromatid kembar berpisah dan
Opposite pole
membentuk kromosom anak . Kromosom anak ini tertarik ke
Kromosom kutub bertentangan dengan didahului oleh sentromer disebabkan
anak
Daughter oleh pengecutan gentian gelendong.
chromosome
The centromeres divides . The sister chromatids separate and form
daughter chromosomes . The daughter chromosomes are pulled to the
opposite poles led by the centromere due to the contraction of
the spindle fibre.
Telofasa / Telophase
Nukleolus
Nucleolus Kromosom anak tiba di kutub bertentangan. Kromosom mula membuka
lingkaran dan menjadi panjang dan halus semula.
Membran Membran nukleus dan nukleolus muncul semula.
nukleus Dua
Nuclear
sel anak terhasil di akhir mitosis. Sel anak
membrane yang terhasil adalah seiras dengan sel induk dari segi bilangan
kromosom dan maklumat genetik .
The daughter chromosomes reach the opposite poles. The chromosomes start
to uncoil and become long and thin again. The
nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear. Two
Unit 6
daughter cells are produced at the end of mitosis. The daughter cells produced
are identical to the parent cell in terms of the number of chromosomes
and their genetic information.
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 72
06-Biologi F4 Unit6(p70-82)csy4p.indd 72 11/01/2020 11:46 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
SP 6.2.4 Membanding dan membezakan mitosis dan sitokinesis antara sel haiwan dengan sel tumbuhan
3 Sitokinesis dalam sel haiwan dan tumbuhan.
Cytokinesis in animal and plant cells.
Sitokinesis dalam sel haiwan / Cytokinesis in animal cells
Gelang pencerutan Sitokinesis berlaku apabila mikrofilamen di bahagian tengah
Cleavage furrow
sel mengecut . Membran plasma mencerut ke dalam membentuk
gelang pencerutan . Ini menyebabkan membran plasma mencerut ke
dalam sehingga sel induk terpisah kepada dua sel anak.
Cytokinesis occurs when the microfilament at the equator of the cell
contract . The plasma membrane is indented and forms cleavage furrow .
This causes the plasma membrane to be pinched inwards until the parent cell
Mikrofilamen
Microfilament is separated into two daughter cells.
Sitokinesis dalam sel tumbuhan / Cytokinesis in plant cells
Vesikel bermembran berkumpul di khatulistiwa
Vesikel sel induk. Vesikel-vesikel ini bergabung untuk membentuk
Vesicle
plat sel yang akan berkembang keluar sehingga sisinya
bercantum dengan membran plasma . Dinding sel
dan membran plasma baharu akan terbentuk dan seterusnya
membahagikan sel induk kepada dua sel anak.
Plat sel
Cell plate Membrane-enclosed vesicles gather at the equator of the
parent cell. The vesicles fuse together to form a cell plate which
grows outwards until its edges fuse with the plasma membrane .
New cell wall and plasma membrane are formed which later divide
the parent cell into two daughter cells.
Membincangkan keperluan mitosis dalam:
• Pertumbuhan (perkembangan embrio dan pertumbuhan organisma)
SP 6.2.5 • Penyembuhan tisu (luka pada kulit)
• Penjanaan semula
• Pembiakan aseks
4 Antara keperluan mitosis dalam kehidupan:
Among the necessities of mitosis in life:
(a) Perkembangan embrio / Development of embryo
Unit 6
Zigot Dua sel Empat sel Lapan sel Morula Blastosista
Zygote Two cells Four cells Eight cells Morula Blastocyst
73 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
06-Biologi F4 Unit6(p70-82)csy4p.indd 73 11/01/2020 11:46 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
(b) Penjanaan semula / Regeneration
Palanaria induk Kepala baharu
dipotong kepada dua New head
Planari induk
Parent planaria is cut
Parent planaria Ekor baharu
into two
New tail
(c) Penyembuhan luka / Healing of the wound
Mitosis
Sel epitelium kulit di bahagian tercedera membahagi secara mitosis Sel-sel epitelial terus membahagi secara mitosis sehingga
menghasilkan sel-sel baharu dan bergerak ke bahagian tengah luka. ketebalan lapisan kulit yang baharu menjadi normal.
Epithelium skin cells at the wound divide mitotically and produce new cells Epithelial cells continue to divide mitotically until the thickness
which migrate to the centre of the wound. of the new skin layer approaches normal.
(d) Pembiakan aseks / Asexual reproduction
Hidra induk
Parent hydra Tunas
Bud
Bonggolan kecil terbentuk Hidra induk membentuk Tunas membesar. Tunas tertanggal dari
pada hidra induk. tunas. The bud grows. hidra induk.
Tiny bump formed on parent Parent hydra develops bud. The bud breaks off from
hydra. the parent hydra.
AKTIVITI PENGUKUHAN KBAT
REINFORCEMENT ACTIVITY HOTS
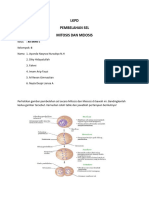
Rajah (a) menunjukkan kaedah penanaman sejenis tanaman di kebun A dan Rajah (b) menunjukkan kaedah
penanaman berbeza bagi tanaman yang sama di kebun B.
Diagram (a) shows a method of growing a type of plant in farm A and Diagram (b) shows a different method of growing the
same plant in farm B.
Rajah (a) / Diagram (a) Rajah (b) / Diagram (b)
(a) Pada pendapat anda, kebun yang manakah akan menghasilkan keuntungan yang lebih tinggi dalam tempoh
sepuluh tahun akan datang? Berikan alasan bagi pendapat anda.
Unit 6
In your opinion, which farm will generate more profit in the next ten years? Give reasons for your opinion
Kebun A. Anak-anak pokok dihasilkan secara pembiakan seks yang melibatkan persenyawaan gamet.
Terdapat variasi pada anak-anak pokok. Oleh itu, anak-anak pokok tersebut mempunyai daya rintangan
terhadap penyakit yang berbeza serta dapat menyesuaikan diri dengan perubahan yang berlaku di
persekitaran. Ini dapat memastikan anak-anak pokok tersebut dapat hidup dengan lebih lama.
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 74
06-Biologi F4 Unit6(p70-82)csy4p.indd 74 11/01/2020 11:46 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
Farm A. The plantlets are produced by sexual reproduction which involves fertilisation of gametes. There are
varieties of plantlets produced. Therefore, the plantlets have resistance towards different diseases as well as able to
adapt to the changes in the environment. This will ensure the plantlets can live longer.
(b) Pekebun yang menggunakan kaedah dalam Rajah (b) mendapati kesemua tumbuhannya mati selepas serangan
sejenis penyakit. Cadangkan langkah yang perlu diambil oleh pekebun tersebut sebelum dia memulakan
kaedah dalam Rajah (b) pada masa akan datang.
The farmer who used method in Diagram (b) found that all plants died after being attacked by a certain disease. Suggest
ways to be taken by the farmer before he starts the method in Diagram (b) in the future.
1. Pilih tumbuhan yang mempunyai daya rintangan terhadap pelbagai jenis penyakit.
Choose a plant that is resistant to various types of diseases.
2. Pilih tumbuhan yang telah diubah suai secara genetik.
Choose a plant which has been genetically modified.
3. Pilih tumbuhan yang mempunyai daya rintangan yang tinggi terhadap racun serangga dan racun rumpai.
Choose a plant that has high resistant to insecticides and pesticides.
6.3 Meiosis / Meiosis SK 6.3
6.3.1 Menyatakan pengertian meiosis
SP 6.3.2 Mengenal pasti jenis sel yang menjalankan meiosis
6.3.3 Menyatakan keperluan meiosis
Satu proses pembahagian sel yang menghasilkan gamet yang mempunyai
1 Meiosis bilangan kromosom separuh daripada sel induk.
Meiosis A process of cell division which forms gametes with the number of chromosomes
half of those in the parent cell.
2
Mengekalkan bilangan kromosom diploid dari satu generasi ke satu generasi.
Maintain the number of diploid chromosomes from one generation to another generation.
Kepentingan meiosis
The significance of meiosis
Unit 6
Menghasilkan gamet . Menghasilkan variasi genetik.
Produce gametes . Produce genetic variation .
75 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
06-Biologi F4 Unit6(p70-82)csy4p.indd 75 11/01/2020 11:46 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
6.3.4 Menerangkan peringkat dalam meiosis
SP
6.3.5 Melukis dan melabel struktur sel dalam setiap peringkat meiosis I, meiosis II dan sitokinesis
3 Peringkat-peringkat meiosis.
The stages of meiosis.
Meiosis I
Profasa I / Prophase I
Sinapsis berlaku di mana kromosom homolog mendekati satu
Kiasma sama lain dan membentuk bivalen. Pindah silang
Chiasmata
(pertukaran maklumat genetik antara kromosom kembar bukan
seiras) berlaku di kiasma . Membran nukleus dan
nukleolus menghilang.
Bivalen
Bivalent Synapsis occur in which homologous chromosomes approaching each
other and form bivalent. Crossing over (exchange of genetic
information between non-sister chromatid) occurs at chiasmata .
The nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear.
Metafasa I / Metaphase I
Gentian
gelendong Bivalen tersusun di satah khatulistiwa . Gentian gelendong
Spindle fibre
memegang sentromer .
The bivalents align at the metaphase plate . The spindle fibre
hold the centromere .
Anafasa I / Anaphase I
Kromatid
kembar Bivalen berpisah. Setiap kromosom homolog berpisah dan
Sister
chromatids ditarik ke kutub bertentangan disebabkan oleh pengecutan
gentian gelendong .
The bivalents separate. Each homologous chromosomes separated
are pulled to the opposite poles due to the contraction of
the spindle fibres .
Telofasa I / Telophase I
Kromosom tiba di kutub bertentangan
. Membran
nukleus dan nukleolus muncul semula. Fasa ini diikuti
dengan sitokinesis yang membahagikan sitoplasma. Kedua-dua sel
anak yang terhasil berada dalam keadaan haploid .
The chromosomes reach the opposite poles . The nuclear
Unit 6
membrane and nucleolus reappear. This phase is followed by
Membran nukleus Nukleolus cytokinesis which divides the cytoplasm. Both daughter cells produced
Nuclear membrane Nucleolus haploid
are in state.
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 76
06-Biologi F4 Unit6(p70-82)csy4p.indd 76 11/01/2020 11:46 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
Meiosis II
Kromatid kembar Profasa II / Prophase II
Sister chromatids
Membran nukleus dan nukleolus menghilang . Setiap
kromosom terdiri daripada kromatid kembar yang bercantum di
sentromer. Gentian gelendong mula terbentuk di dalam kedua-dua
sel anak.
The nuclear membrane and nucleolus are disappear . Each
chromosomes consist of sister chromatids attached to the centromere.
The spindle fibre begin to form in both daughter cells.
Gentian gelendong Metafasa II / Metaphase II
Spindle fibres
Kromosom tersusun di satah khatulistiwa . Gentian
gelendong memegang sentromer.
The chromosomes align at the metaphase plate . The spindle
fibres hold the centromere.
Anafasa II / Anaphase II
Kromosom anak
Sentromer membahagi. Kromatid kembar berpisah dan
Daughter chromosome membentuk kromosom anak . Kromosom anak ini
tertarik ke kutub bertentangan
dengan didahului oleh
sentromer disebabkan oleh pengecutan gentian gelendong .
The centromeres divide. The sister chromatids separate and form
daughter chromosomes . The daughter chromosomes are pulled
to the opposite poles led by the centromere due to the
contraction of the spindle fibre .
Telofasa II / Telophase II
Kromosom kembar tiba di kutub bertentangan .
Kromosom membuka lingkaran dan menjadi panjang
dan halus semula. Membran nukleus dan nukleolus
muncul semula . Fasa ini diikuti dengan sitokinesis yang
membahagikan sitoplasma.
The daughter chromosomes reach the opposite poles . The
chromosomes uncoiled and become long and thin
again. The nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear . This is
followed by cytokinesis which divides the cytoplasm.
Empat sel anak terhasil di akhir meiosis II. Kesemua
Unit 6
sel anak mengandungi bahan genetik yang berlainan .
Membran nukleus
Nuclear membrane Four daughter cells are produced at the end of meiosis II. All
the daughter cells contains different genetic materials.
77 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
06-Biologi F4 Unit6(p70-82)csy4p.indd 77 11/01/2020 11:46 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
SP 6.3.6 Membanding dan membezakan antara meiosis dengan mitosis
4 Perbandingan antara mitosis dan meiosis. / Comparisons between mitosis and meiosis.
Sel induk bagi kedua-dua Kedua-duanya melibatkan Kedua-duanya melibatkan
pembahagian sel adalah pembahagian nukleus replikasi DNA
Persamaan sel diploid . dan sitoplasma . yang berlaku hanya sekali.
Similarities The parent cells of Both involve division of Both involve DNA
both cell division are nucleus and replication which
diploid cell. cytoplasm . occurs only once.
Mitosis / Mitosis Perbezaan / Difference Meiosis / Meiosis
Sel-sel soma . Jenis sel Sel di organ pembiakan .
Somatic cells. Type of cell Cells in reproductive organs.
Menghasilkan sel-sel baharu untuk
pertumbuhan , membaiki tisu
yang cedera dan mengganti sel-sel
Tujuan Menghasilkan gamet .
yang mati .
Purpose Produces gametes .
Produces new cells for growth ,
repairing injured tissues and replacing
dead cells.
Kromosom homolog tidak menjalani Kromosom homolog menjalani sinapsis
sinapsis. Sinapsis semasa profasa I .
Homologous chromosomes do not Synapsis Homologous chromosomes undergo synapsis
undergo synapsis. during prophase I .
Tiada pindah silang berlaku antara Pindah silang berlaku antara kromosom
kromosom homolog. Pindah silang homolog semasa profasa I .
No crossing over occurs between Crossing over Crossing over occurs between homologous
homologous chromosomes. chromosomes during prophase I .
Dua Bilangan sel anak terhasil Empat
Two Number of daughter cells
Four
produced
Bilangan kromosom adalah Bilangan kromosom Bilangan kromosom adalah separuh
sama dengan sel induk. dalam sel anak dari sel induk.
The number of chromosomes is Number of chromosomes The number of chromosomes is half
similar to the parent cell. in daughter cells from the parent cell.
Unit 6
Kandungan bahan genetik
Sama dalam sel anak Berbeza
Similar The content of genetic Different
materials in daughter cells
Tidak berlaku / Not occur Variasi / Variation Berlaku / Occur
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 78
06-Biologi F4 Unit6(p70-82)csy4p.indd 78 11/01/2020 11:46 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
6.4 Isu Pembahagian Sel terhadap Kesihatan Manusia / Issue of Cell Division on Human Health SK 6.4
6.4.1 Menghuraikan kesan ketidaknormalan mitosis terhadap kesihatan manusia
SP
6.4.2 Menilai kesan ketidaknormalan meiosis terhadap kesihatan manusia
1 Kesan mitosis yang tidak terkawal. / The effects of uncontrolled mitosis. Sel normal Sel abnormal
Normal cell Abnormal cell
(a) • Sel-sel normal akan membahagi secara mitosis tidak terkawal jika
gen yang mengawal kitar sel tidak berfungsi akibat mutasi .
Pembahagian sel tanpa kawalan ini menghasilkan sel-sel abnormal .
Sekumpulan sel-sel abnormal ini dikenali sebagai tumor .
Normal cells will divide through uncontrolled mitosis when the
genes that control the cell cycle are not function due to mutation .
This uncontrolled cell division forms abnormal cells. A group of this
abnormal cells is known as tumor .
• Jika tumor ini mula merebak dan menyerang tisu-tisu di sekelilingnya, ianya dinamakan sebagai tumor
malignan atau sel kanser . Sel-sel kanser ini bersaing dengan sel-sel di sekelilingnya
untuk mendapatkan nutrien dan tenaga. Sel-sel ini sering membawa maut .
If the tumor starts to spread and intrude the tissues around them, it is called malignant tumor or
cancerous cells. The cancerous cells compete with the cells around them to obtain nutrients
and energy. The cells often lead to death .
• Terdapat tumor yang akan kekal di tapak asal dan tidak mengancam nyawa kerana ianya tidak
memusnahkan tisu-tisu normal. Tumor ini dikenali sebagai tumor benigna .
There is a tumor which remains at the original site and not life threatening as it does not destroy normal tissues.
The tumor is known as benign tumor.
(b) Penyakit Sindrom Down / Down Syndrome disease
Jika kromosom homolog atau kromatid kembar ke-21 gagal berpisah
Di dalam pembahagian meiosis yang sewaktu anafasa I atau II, satu sel anak mempunyai dua kromosom
normal, setiap sel anak akan mempunyai ke-21 dan satu sel anak tidak mempunyai sebarang kromosom ke-21.
bilangan kromosom yang sama. If the 21st homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate
In a normal meiotic division, daughter cells during anaphase I or II, one daughter cell will have two 21st chromosome
have equal number of chromosomes. and the other cell has no 21st chromosome.
Kromosom ke-21
21st chromosome
Normal / Normal Normal / Normal
Tak disjunksi Normal Tak disjunksi Normal
Nondisjunction Normal Nondisjunction Normal
Unit 6
Jika persenyawaan antara kedua gamet berlaku, zigot terhasil akan mempunyai tiga
kromosom ke-21. Oleh itu, anak akan menghidap Sindrom Down.
If fertilisation occurs between the two gamets, the zygote produced has three 21st chromosomes.
Therefore, the offspring suffers from Down Syndrome.
79 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
06-Biologi F4 Unit6(p70-82)csy4p.indd 79 11/01/2020 11:46 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
PRAKTIS SPM / SPM PRACTICE
SOALAN OBJEKTIF / OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
1 Rajah 1 menunjukkan satu proses dalam 4 Antara berikut, yang manakah kepentingan
pembahagian sel. meiosis?
Diagram 1 shows a process in cell division. Which of the following is the importance of meiosis?
A Menggantikan sel yang mati.
Replacing dead cells.
B Menghasilkan gamet.
Producing gametes.
C Membaiki tisu-tisu rosak.
Repairing injured tissues.
D Menambahkan bilangan sel.
Increase the number of cells.
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1
Apakah peringkat yang dilalui oleh sel tersebut? 5 Antara sel-sel berikut, yang manakah hasil
What is the stage undergone by the cell? meiosis?
A Profasa / Prophase C Anafasa / Anaphase Which of the following cell is the product of meiosis?
B Metafasa / Metaphase D Telofasa / Telophase A
2 Mengapakah bilangan dan kandungan genetik
kromosom sel anak yang terhasil dari mitosis
kekal sama dengan sel induk? B
Why are the number and genetic composition of
daughter cell’s chromosomes produced by mitosis
remain the same as in the parent cell?
A Kromatid kembar berpisah sewaktu anafasa. C
Sister chromatids separates during anaphase.
B Setiap kromosom membentuk dua kromatid.
D
Each chromosome forms two chromatids.
C Kromosom berpisah sewaktu metafasa.
Chromosomes separate during metaphase.
D Sitoplasma membahagi kepada dua sewaktu
6 Rajah 3 menunjukkan sel diploid yang menjalani
anafasa.
meiosis.
Cytoplasm divides into two during anaphase.
Diagram 3 shows a diploid cell undergoing meiosis.
3 Rajah 2 menunjukkan satu peringkat sewaktu
meiosis. / Diagram 2 shows an event during meiosis.
Rajah 2 / Diagram 2
Antara berikut, yang manakah menjelaskan Rajah 3 / Diagram 3
peringkat tersebut?
Which of the following describes the event? Sekiranya salah satu pasangan kromosom homolog
tidak berpisah sewaktu Meiosis I, berapakah
Unit 6
A Gentian gelendong terurai.
Spindle fibre breaks down. bilangan kromosom yang boleh didapati di dalam
B Pertukaran bahan genetik. gamet?
Exchange of genetic materials. If one of the homologous chromosome pairs does not
C Pembentukan semula membran nukleus. separate during Meiosis I, how many chromosomes
Reformation of nuclear membrane. can be found in the gametes?
D Kromosom bereplikasi. A 4 C 7
Chromosome replicates. B 5 D 8
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 80
06-Biologi F4 Unit6(p70-82)csy4p.indd 80 11/01/2020 11:46 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
SOALAN STRUKTUR / STRUCTURE QUESTIONS
1 Rajah 1 menunjukkan sel kulit satu organisma. / Diagram 1 show a skin cell of an organism.
Q: Sentromer
S: Membran nukleus
Centromere
Nuclear membrane
R: Kromosom
T: Membran plasma
Chromosome
Plasma membrane
Rajah 1 / Diagram 1
(a) (i) Namakan struktur Q, R, S dan T dalam Rajah 1. / Name the structures Q, R, S and T in Diagram 1.
[4 markah/marks]
(ii) Nyatakan fungsi R. / State the function of R.
Menyimpan maklumat // bahan genetik / Store genetic information // material
[1 markah/mark]
(b) Sel dalam Rajah 1 mengalami pembahagian sel. / The cell in Diagram 1 undergoes cell division.
(i) Nyatakan jenis pembahagian sel tersebut. / State the type of cell division.
Mitosis / Mitosis
[1 markah/mark]
(ii) Cadangkan kepentingan jenis pembahagian sel di (b)(i) ke atas organisma hidup.
Suggest the importance of the type of cell division in (b)(i) to the living organisms.
I. Menambahkan bilangan sel untuk membolehkan pertumbuhan berlaku.
Increase the number of cells to allow growth to occur.
II. Menggantikan sel-sel yang telah mati. / Replace dead cells.
III. Membaiki tisu-tisu rosak. / Repair injured tissues.
[3 markah/marks]
(c) Nyatakan bilangan sel anak dan bilangan kromosom yang akan terhasil di akhir pembahagian sel dalam
Rajah 1.
State the number of daughter cells and number of chromosomes produced at the end of cell division in Diagram 1.
(i) Bilangan sel anak / Number of daughter cells: 2
(ii) Bilangan kromosom dalam sel anak / Number of chromosomes in the daughter cells: 4
[2 markah/marks]
2 Rajah 2 menunjukkan sel P dan Q sedang menjalani peringkat M dalam pembahagian sel.
Diagram 2 shows cell P and cell Q undergoing stage M of a cell division.
Unit 6
Sel P Sel Q
Cell P Cell Q
Rajah 2 / Diagram 2
81 Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
06-Biologi F4 Unit6(p70-82)csy4p.indd 81 11/01/2020 11:46 AM
MODUL • Biologi Tingkatan 4
(a) Nyatakan jenis pembahagian sel yang dijalani oleh sel P dan Q.
State the type of cell division undergone by cell P and cell Q.
Sel P / Cell P: Mitosis
Sel Q / Cell Q: Meiosis
[2 markah/marks]
(b) Nyatakan perbezaan antara pembahagian sel yang dijalani oleh sel P dan Q.
State the difference between the function of cell division undergone by cell P and cell Q.
Sel P / Cell P Sel Q / Cell Q
I. Menambahkan bilangan sel untuk I. Menghasilkan gamet.
membolehkan pertumbuhan berlaku. Produce gametes.
Increase the number of cells to allow the growth II. Menghasilkan variasi.
to occur. Produce variation.
II. Mengganti sel-sel yang telah mati. III. Mengekalkan bilangan kromosom dalam
Replace dead cells. zigot.
III. Membaiki tisu-tisu rosak. Maintain the number of chromosomes in a zygote.
Repair injured tissues.
[6 markah/marks]
(c) Nyatakan fasa yang dijalani oleh sel P dan sel Q.
State the phase undergone by cell P and cell Q.
Sel P / Cell P: Metafasa / Metaphase
Sel Q / Cell Q: Metafasa I / Metaphase I
[2 markah/marks]
(d) Cadangkan bagaimana perlakuan kromosom sel P dan Q berbeza.
Suggest how the chromosomal behaviour of cell P and cell Q is different.
Di dalam sel P, setiap kromosom tersusun di satah khatulistiwa, manakala di dalam sel Q, pasangan
kromosom homolog tersusun di satah khatulistiwa.
In cell P, each chromosome align at the metaphase plate, while in cell Q, the homologous chromosomes pairs align
at the metaphase plate.
[1 markah/mark]
(e) Lukis dan labelkan sel P dan sel Q untuk menunjukkan perlakuan kromosom selepas peringkat M.
Draw and label cell P and cell Q to show the chromosomal behaviour after stage M.
Kutub bertentangan
Opposite pole
Kromatid kembar
Sister chromatids
Kromosom anak
Daughter chromosome
Unit 6
Sel P / Cell P Sel Q / Cell Q
[4 markah/marks]
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd. 82
06-Biologi F4 Unit6(p70-82)csy4p.indd 82 11/01/2020 11:46 AM
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- JawapanBab6 1Dokumen15 halamanJawapanBab6 1Muhdikmal .arfizal0308Belum ada peringkat
- Kelompok 2 PPT Siklus SelDokumen24 halamanKelompok 2 PPT Siklus SelReynanda ApriliaBelum ada peringkat
- Mindmap Skenario 1Dokumen1 halamanMindmap Skenario 1A Z HasanBelum ada peringkat
- 25 - Nensyah P - Bio - Xii Mipa 3Dokumen7 halaman25 - Nensyah P - Bio - Xii Mipa 3Salsa ZalsyahBelum ada peringkat
- KD 3.4. Meiosis Dan OrganogenesisDokumen12 halamanKD 3.4. Meiosis Dan OrganogenesisBrisnoBelum ada peringkat
- Pembelahan SelDokumen10 halamanPembelahan Selkhoirotul wijayantiBelum ada peringkat
- Pembelahan SelDokumen20 halamanPembelahan SelWan Mhd FikriBelum ada peringkat
- Pembelahan SelDokumen42 halamanPembelahan SelRensi TodingBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan Ke 2 Pembelahan Sel HidayatiDokumen18 halamanPertemuan Ke 2 Pembelahan Sel Hidayatimuhammad.ichwan863Belum ada peringkat
- Materi Pembelahan Sel Kelas XiiDokumen7 halamanMateri Pembelahan Sel Kelas XiiRuth BiologiBelum ada peringkat
- LKPD Meiosis, GametogenesisDokumen5 halamanLKPD Meiosis, GametogenesisTEUKUBelum ada peringkat
- Reprduksi Jantan - Risma Irfiyani - 4401419042Dokumen15 halamanReprduksi Jantan - Risma Irfiyani - 4401419042Risma IrfiyaniBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 4 Pembelahan SelDokumen27 halamanBab 4 Pembelahan SelFauzan2104Belum ada peringkat
- SEPT 2020 Bab 4 SIKLUS SELDokumen19 halamanSEPT 2020 Bab 4 SIKLUS SELAndhila IntanBelum ada peringkat
- Pembelahan SelDokumen21 halamanPembelahan SelBilqis Safira KhairaniBelum ada peringkat
- Mitosis MeiosisDokumen1 halamanMitosis MeiosisAngeline TancherlaBelum ada peringkat
- Biologi - 12 SMA - Pembelahan SelDokumen63 halamanBiologi - 12 SMA - Pembelahan SelMuhammad jufri NursyamBelum ada peringkat
- Topik 1 Pembelahan SelDokumen5 halamanTopik 1 Pembelahan SelSirait SeniorBelum ada peringkat
- Modul FSI Modul 2 BMS Tahun 2017Dokumen24 halamanModul FSI Modul 2 BMS Tahun 2017nadaBelum ada peringkat
- Materi Pembelahan SelDokumen40 halamanMateri Pembelahan SelShirtflowerssBelum ada peringkat
- Bio-5 Pembelahan SelDokumen5 halamanBio-5 Pembelahan SelRoslelyBelum ada peringkat
- Siklus SelDokumen50 halamanSiklus SelM ARIEL FAZLIBelum ada peringkat
- LKPD MitosisDokumen9 halamanLKPD Mitosisshzraaa025Belum ada peringkat
- 000 Pts Ipa Ganjil 9Dokumen4 halaman000 Pts Ipa Ganjil 9Milly YulihartikaBelum ada peringkat
- MEIOSISiDokumen34 halamanMEIOSISiOtha MinartiBelum ada peringkat
- Reproduksi Sel PDFDokumen22 halamanReproduksi Sel PDFVivi AfifahBelum ada peringkat
- Pembelahan SelDokumen20 halamanPembelahan SelM'muZack D'ertoseBelum ada peringkat
- LKS 3 Pembelahan Sel - Gracia Natalia Herawati - XII IPA 4 - 12Dokumen10 halamanLKS 3 Pembelahan Sel - Gracia Natalia Herawati - XII IPA 4 - 12Hermawan HermawanBelum ada peringkat
- Konsep Dasar Genetik, Respirasi Sel, Reproduksi Sel, Metabolisme Sel - PPT Kel.2 - S1kep.bDokumen12 halamanKonsep Dasar Genetik, Respirasi Sel, Reproduksi Sel, Metabolisme Sel - PPT Kel.2 - S1kep.bAladinBelum ada peringkat
- Angga Sanjaya (Meiosis Mitosis)Dokumen9 halamanAngga Sanjaya (Meiosis Mitosis)Fariz HelgusmanBelum ada peringkat
- 4401419005-Herusetiawan-Reproduksi SelDokumen5 halaman4401419005-Herusetiawan-Reproduksi SelHeru SetiawanBelum ada peringkat
- Perbedaan Mitosis Dan MeiosisDokumen15 halamanPerbedaan Mitosis Dan MeiosisNi Putu Dewik AgustinaBelum ada peringkat
- 4a. KONSEP HEREDITAS (SIKLUS SEL) 2024Dokumen59 halaman4a. KONSEP HEREDITAS (SIKLUS SEL) 2024Yulia TrifitriaBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 1 Sistem ReproduksiDokumen50 halamanBab 1 Sistem ReproduksiYenny Christina NapitupuluBelum ada peringkat
- Materi Pembelahan SelDokumen27 halamanMateri Pembelahan SelGood BoyBelum ada peringkat
- PDFDokumen22 halamanPDFKevin AjaBelum ada peringkat
- Media Pembelajaran-Ppt Kd. Pembelahan Sel-Klp 3-HafDokumen42 halamanMedia Pembelajaran-Ppt Kd. Pembelahan Sel-Klp 3-Hafeko suajiBelum ada peringkat
- Indikator Pencapaian Kompetensi: Anafase Dan TelofaseDokumen5 halamanIndikator Pencapaian Kompetensi: Anafase Dan TelofaserachelBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 4 Pembelahan SelDokumen21 halamanBab 4 Pembelahan SelWildan ErdiansyahBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 4 Pembelahan SelDokumen21 halamanBab 4 Pembelahan SelrosaliaBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Pembelahan SelDokumen21 halaman4 Pembelahan Selmy1212408Belum ada peringkat
- Pembelahan Sel Bab 4Dokumen21 halamanPembelahan Sel Bab 4JuniBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 4 PEMBELAHAN SELDokumen21 halamanBab 4 PEMBELAHAN SELHeri HaerudinBelum ada peringkat
- KEL 6 - XII MIPA 5 - LKPD Meiosis Dan MitosisDokumen5 halamanKEL 6 - XII MIPA 5 - LKPD Meiosis Dan MitosisAN-NASYWA WANARAJABelum ada peringkat
- Praktikum Biologi - Reproduksi SelDokumen6 halamanPraktikum Biologi - Reproduksi SelCassandraMills100% (2)
- Tugas Dasgen 1Dokumen13 halamanTugas Dasgen 1Prayogya0% (1)
- Pert 3. Pembelahan SelDokumen21 halamanPert 3. Pembelahan SelkusriantynellyBelum ada peringkat
- K3 Siklus SelDokumen19 halamanK3 Siklus SelaiBelum ada peringkat
- Kelompok 3Dokumen5 halamanKelompok 3santi santiBelum ada peringkat
- Perkembangan Sel Biomedik 2Dokumen24 halamanPerkembangan Sel Biomedik 2Eky SusilowatiBelum ada peringkat
- Allisya Oktaviasary - Artikel Pembelahan Mitosis - Prak 2Dokumen5 halamanAllisya Oktaviasary - Artikel Pembelahan Mitosis - Prak 2ALLISYA OKTAVIASARYBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan Ke 2 Pembelahan Sel HidayatiDokumen18 halamanPertemuan Ke 2 Pembelahan Sel HidayatiChris BenntBelum ada peringkat
- Sel Dan JaringanDokumen31 halamanSel Dan JaringanDanielHutabaratBelum ada peringkat
- Artikel Emboh YaDokumen8 halamanArtikel Emboh Yaadelia rcBelum ada peringkat