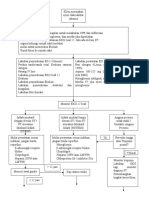
Gejala PPOK
Diunggah oleh
Eka Wahyu Santoso0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
23 tayangan8 halamanHak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
23 tayangan8 halamanGejala PPOK
Diunggah oleh
Eka Wahyu SantosoHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 8
Gejala PPOK
Medical Author: George Schiffman, MD, FCCP Pengarang Kedokteran:
Schiffman George, MD, FCCP
Medical Editor: William C. Shiel Jr., MD, FACP, FACR Kedokteran Editor:
William C. Shiel Jr, MD, FACP, FACR
Symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in smokers include
chronic cough, shortness of breath, and frequent respiratory infections. Gejala penyakit paru
obstruktif kronik (PPOK) pada perokok termasuk batuk kronis, sesak napas, dan infeksi
pernapasan sering. In patients with emphysema shortness of breath is the primary symptom.
Pada pasien dengan emfisema sesak napas adalah gejala utama. In patients with bronchitis and
bronchiectasis , symptoms include chronic cough and sputum production. Pada pasien dengan
bronkitis dan bronkiektasis, termasuk gejala batuk kronis dan produksi sputum.
Advanced COPD symptoms include cyanosis, headaches, weight loss, pulmonary hypertension,
and coughing up blood. Advanced PPOK termasuk gejala sianosis, sakit kepala, penurunan
berat badan, hipertensi paru, dan batuk darah.
What is COPD? Apa itu PPOK?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is comprised primarily of three related
conditions - chronic bronchitis , chronic asthma , and emphysema . Penyakit paru obstruktif
kronis (PPOK) adalah terutama terdiri dari tiga kondisi istimewa - bronkitis kronis , asma kronis
, dan emfisema . In each condition there is chronic obstruction of the flow of air through the
airways and out of the lungs, and the obstruction generally is permanent and may be progressive
over time. Dalam kondisi setiap ada obstruksi kronis aliran udara melalui saluran udara dan
keluar dari paru-paru, dan penyumbatan pada umumnya bersifat permanen dan dapat progresif
dari waktu ke waktu.
While asthma features obstruction to the flow of air out of the lungs, usually, the obstruction is
reversible. Sedangkan asma obstruksi fitur untuk aliran udara keluar dari paru-paru, biasanya,
obstruksi adalah reversible. Between "attacks" of asthma the flow of air through the airways
typically is normal. Antara "serangan" asma aliran udara melalui saluran udara biasanya adalah
normal. These patients do not have COPD. Pasien ini tidak memiliki PPOK. However, if asthma
is left untreated, the chronic inflammation associated with this disease can cause the airway
obstruction to become fixed. Namun, jika asma tidak diobati, peradangan kronis yang
berhubungan dengan penyakit ini dapat menyebabkan obstruksi jalan napas menjadi tetap. That
is, between attacks, the asthmatic patient may then have abnormal air flow. Artinya, antara
serangan, pasien asma maka mungkin memiliki aliran udara yang abnormal. This process is
referred to as lung remodeling. Proses ini disebut sebagai remodeling paru-paru. These asthma
patients with a fixed component of airway obstruction are also considered to have COPD. pasien
asma ini dengan komponen tetap penyumbatan saluran napas juga dianggap memiliki PPOK.
Often patients with COPD are labeled by the symptoms they are having at the time of an
exacerbation of their disease. Seringkali pasien dengan PPOK diberi label oleh gejala mereka
mengalami pada saat suatu eksaserbasi dari penyakit mereka. For instance, if they present with
mostly shortness of breath , they may be referred to as emphysema patients. Misalnya, jika
mereka hadir dengan sebagian besar sesak napas , mereka mungkin disebut sebagai pasien
emfisema. While if they have mostly cough and mucus production, they are referred to as having
chronic bronchitis. Sementara jika mereka memiliki sebagian besar produksi batuk dan lendir,
mereka disebut sebagai memiliki bronkitis kronis. In reality, it is better to refer to these patients
as having COPD since they can present with a variety of lung symptoms. Pada kenyataannya,
lebih baik untuk merujuk pasien tersebut memiliki PPOK karena mereka bisa hadir dengan
berbagai gejala paru-paru.
There is frequent overlap among COPD patients. Ada sering tumpang tindih antara pasien
PPOK. Thus, patients with emphysema may have some of the characteristics of chronic
bronchitis and chronic asthma and vice a versa. Dengan demikian, pasien dengan emfisema
mungkin memiliki beberapa karakteristik dari bronkitis kronis dan asma kronis dan wakil
sebaliknya.
How does the normal lung work? Bagaimana cara kerja paru-paru normal?
The lung is the organ for gas exchange; it transfers oxygen from the air into the blood and carbon
dioxide (a waste product of the body) from the blood into the air. paru-paru adalah organ untuk
pertukaran gas, tetapi transfer oksigen dari udara ke dalam darah dan karbon dioksida (produk
limbah tubuh) dari darah ke udara. To accomplish gas exchange the lung has two components;
airways and alveoli. Untuk mencapai pertukaran gas paru-paru memiliki dua komponen; saluran
udara dan alveoli. The airways are branching, tubular passages like the branches of a tree that
allow air to move in and out of the lungs. Saluran udara yang bercabang, bagian tubular seperti
cabang-cabang pohon yang memungkinkan udara bergerak masuk dan keluar dari paru-paru. The
wider segments of the airways are the trachea and the two bronchi (going to either the right or
left lung). Segmen yang lebih luas saluran udara trakea dan dua bronkus (akan baik paru-paru
kanan atau kiri). The smaller segments are called bronchioles. Segmen yang lebih kecil disebut
bronkiolus. At the ends of the bronchioles are the alveoli, thin-walled sacs. Pada ujung
bronkiolus adalah alveoli, kantung berdinding tipis. (The airways and alveoli can be
conceptualized as bunches of grapes with the airways analogous to the stems and the alveoli
analogous to the grapes.) Small blood vessels (capillaries) run in the walls of the alveoli, and it is
across the thin walls of the alveoli where gas exchange between air and blood takes place. (The
saluran napas dan alveoli dapat dikonseptualisasikan sebagai tandan buah anggur dengan saluran
udara analog dengan batang dan alveoli analog dengan anggur.) Pembuluh darah kecil (kapiler)
berjalan di dinding alveoli, dan itu adalah di dinding tipis alveoli dimana pertukaran gas antara
udara dan darah berlangsung.
Breathing involves inspiration followed by exhalation. Pernapasan melibatkan inspirasi diikuti
dengan pernafasan. During inspiration, muscles of the diaphragm and the rib cage contract and
expand the size of the chest (as well as the airways and alveoli) causing negative pressure within
the airways and alveoli. Selama inspirasi, otot diafragma dan kontrak tulang rusuk dan
memperluas ukuran dada (juga saluran udara dan alveoli) menyebabkan tekanan negatif dalam
saluran udara dan alveoli. As a result, air is sucked through the airways and into the alveoli and
the chest wall is enlarged. Akibatnya, udara dihisap melalui saluran udara dan ke dalam alveoli
dan dinding dada diperbesar. During exhalation, the same muscles relax and the chest wall
springs back to its resting positions, shrinking the chest and creating positive pressure within the
airways and alveoli. Selama napas, otot-otot yang sama rileks dan dinding dada akan kembali ke
posisi yang istirahat, menyusut dada dan menciptakan tekanan positif di dalam saluran udara dan
alveoli. As a result, air is expelled from the lungs. Akibatnya, udara dikeluarkan dari paru-paru.
The walls of the bronchioles are weak and have a tendency to collapse, especially while
exhaling. Dinding-dinding bronkiolus yang lemah dan memiliki kecenderungan untuk runtuh,
terutama saat menghembuskan napas. Normally, the bronchioles are kept open by the elasticity
of the lung. Biasanya, bronchioles disimpan terbuka dengan elastisitas paru-paru. Elasticity of
the lung is supplied by elastic fibers which surround the airways and line the walls of the alveoli.
Elastisitas paru-paru dipasok oleh serat elastis yang mengelilingi saluran udara dan garis dinding
alveoli. When lung tissue is destroyed, as it is in patients with COPD who have emphysema,
there is loss of elasticity and the bronchioles can collapse and obstruct the flow of air. Ketika
jaringan paru-paru rusak, karena pada pasien dengan PPOK yang memiliki emfisema, ada
kehilangan elastisitas dan bronchioles dapat menutup dan menghambat aliran udara. Normal lung
tissues look a lot like a normal sponge. jaringan paru-paru normal terlihat sangat mirip spons
normal. Emphysema often looks like an old sponge with large irregular holes and loss of the
spring and elasticity. Emfisema sering terlihat seperti spons tua dengan lubang-lubang tidak
teratur besar dan hilangnya musim semi dan elastisitas.
Apakah bronkitis kronis?
Chronic bronchitis involves inflammation and swelling of the lining of the airways that leads to
narrowing and obstruction of the airways. Bronkitis kronis melibatkan inflamasi dan
pembengkakan pada lapisan saluran udara yang menyebabkan penyempitan dan penyumbatan
saluran udara. The inflammation also stimulates production of mucous (sputum), which can
cause further obstruction of the airways. peradangan ini juga merangsang produksi lendir
(dahak), yang dapat menyebabkan obstruksi saluran udara lebih lanjut. Obstruction of the
airways, especially with mucus, increases the likelihood of bacterial lung infections. Obstruksi
saluran udara, terutama dengan lendir, meningkatkan kemungkinan infeksi paru-paru bakteri.
Chronic bronchitis usually is defined clinically as a daily cough with production of sputum for
three months, two years in a row. Bronkitis kronis biasanya klinis didefinisikan sebagai batuk
sehari-hari dengan produksi dahak selama tiga bulan, dua tahun berturut-turut. This definition
was developed primarily for research so that like patients could be compared. Definisi ini
dikembangkan terutama untuk penelitian sehingga pasien seperti bisa dibandingkan.
What is emphysema? Apa itu emfisema?
There is permanent enlargement of the alveoli due to the destruction of the walls between alveoli
in emphysema . Ada pembesaran permanen alveoli karena kerusakan dinding antara alveoli di
emphysema . The destruction of the alveolar walls reduces the elasticity of the lung overall.
Kerusakan dinding alveolar mengurangi elastisitas paru-paru keseluruhan. Loss of elasticity
leads to the collapse of the bronchioles obstructing airflow out of the alveoli. Kehilangan
elastisitas menyebabkan runtuhnya bronchioles menghalangi aliran udara keluar dari alveoli. Air
becomes "trapped" in the alveoli and reduces the ability of the lung to shrink during exhalation.
Udara menjadi "terjebak" dalam alveoli dan mengurangi kemampuan paru-paru menyusut
selama pernafasan. This trapped air takes up space and results in a reduced amount of air that can
be taken in during the next breath. Udara yang terjebak ini memakan ruang dan menghasilkan
berkurangnya jumlah udara yang dapat diambil dalam selama napas berikutnya. As a result, less
air gets to the alveoli for the exchange of gasses. Akibatnya, udara kurang sampai ke alveoli
untuk pertukaran gas. This trapped air also can compress adjacent less damaged lung tissue,
preventing it from functioning to its fullest capacity. Udara yang terjebak ini juga dapat menekan
jaringan paru-paru yang berdekatan kurang rusak, mencegah dari yang berfungsi untuk kapasitas
maksimalnya.
The exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between air and the blood in the capillaries takes
place across the thin walls of the alveoli. Pertukaran karbon dioksida dan oksigen antara udara
dan darah dalam kapiler terjadi di dinding tipis alveoli. Destruction of the alveolar walls
decreases the number of capillaries available for gas exchange. Penghancuran dinding alveolar
mengurangi jumlah kapiler yang tersedia untuk pertukaran gas. This adds to the decrease in the
ability to exchange gases. Hal ini menambah penurunan kemampuan untuk pertukaran gas.
Usually, energy is only required for inhalation to inflate the lungs. Biasanya, energi hanya
diperlukan untuk inhalasi untuk memompa paru-paru. The stretch of the lungs and distension of
the chest cavity springs back to rest during exhalation, a passive process that does not require
energy. Bentangan distensi paru-paru dan rongga dada akan kembali untuk beristirahat selama
pernafasan, proses pasif yang tidak memerlukan energi. However, in emphysema, inefficient
breathing occurs because extra effort and energy has to be expended to empty the lungs of air
due to the collapse of the airways. Namun, dalam emfisema, bernafas tidak efisien terjadi karena
usaha ekstra dan energi harus dikeluarkan untuk mengosongkan paru-paru udara karena
runtuhnya saluran udara. This essentially doubles the work of breathing, since now energy is
required for both inhalation and exhalation. Hal ini pada dasarnya menggandakan karya
bernapas, karena sekarang energi yang dibutuhkan untuk kedua inhalasi dan pernafasan. In
addition, because of the reduced capacity to exchange gases with each breath (due to the collapse
of the bronchioles and loss of capillaries), it is necessary to breathe more frequently. Selain itu,
karena kapasitas berkurang untuk menukar gas dengan setiap napas (karena runtuhnya
bronchioles dan hilangnya kapiler), perlu untuk bernapas lebih sering.
Apakah asma kronis?
Asthma , like chronic bronchitis, is a disease of the airways. Asma , seperti bronkitis kronis,
merupakan penyakit saluran udara. Obstruction to the flow of air is due to inflammation of the
airways as well as spasm of muscles surrounding the airways in asthma. Obstruksi pada aliran
udara karena radang saluran napas serta kejang otot sekitar saluran udara di asma. The narrowing
that results from spasm of the muscles is called bronchospasm. Penyempitan bahwa hasil dari
spasme otot disebut bronkospasme. Generally, bronchospasm in asthma is reversible and
subsides spontaneously or with the use of bronchodilators (medications that relax the muscles
surrounding the airways). Umumnya, bronkospasme pada asma adalah reversibel dan reda secara
spontan atau dengan penggunaan bronkodilator (obat yang mengendurkan otot-otot sekitar
saluran udara). We now know that a major component of asthma is inflammation of the airways,
and this inflammation causes thickening of the walls of the airways. Kita sekarang tahu bahwa
komponen utama asma adalah radang saluran napas, dan peradangan ini menyebabkan penebalan
dinding saluran udara. This inflammation involves different inflammatory cells and mediators
than those seen in chronic bronchitis. inflamasi ini melibatkan sel-sel inflamasi dan mediator
yang berbeda dari yang terlihat pada bronkitis kronis. This may play a role in the choice of
antiinflammatory medications for these similar yet different entities. Hal ini dapat memainkan
peran dalam pilihan obat-obat antiperadangan untuk entitas-entitas serupa namun berbeda. In
many asthmatics, antiinflammatory medications such as inhaled steroids are required to reduce
this inflammation. Dalam banyak penderita asma, obat-obat antiperadangan seperti steroid
inhalasi yang diperlukan untuk mengurangi peradangan ini. In long standing asthma, this chronic
inflammation can lead to scarring and fixed airway obstruction. Dalam asma berdiri lama,
peradangan kronis ini dapat menyebabkan obstruksi jalan napas jaringan parut dan tetap.
What is bronchiectasis? Apa itu bronkiektasis?
Bronchiectasis is another abnormality that can be found in patients with COPD. Bronkiektasis
adalah kelainan lain yang dapat ditemukan pada pasien dengan PPOK. In bronchiectasis, serious
and repeated infections of the lung as well as abnormal development of the lung results in
permanent damage to the airways. Pada bronkiektasis, infeksi serius dan berulang-ulang paru-
paru serta pengembangan abnormal hasil paru-paru dalam kerusakan permanen pada saluran
udara. The damaged airways become enlarged tubes or, in more severe cases, large sacs. Rusak
saluran udara menjadi tabung diperbesar atau, dalam kasus yang lebih berat, kantung-kantung
besar. These segments of lung can impair clearance of secretions. Segmen ini dapat merusak
paru-paru clearance sekresi. The damaged, mucus-filled airways often become infected, resulting
in further inflammation and damage to the airways. The, rusak saluran udara yang dipenuhi
lendir sering menjadi terinfeksi, mengakibatkan peradangan lebih lanjut dan kerusakan pada
saluran udara. Patients with bronchiectasis often have a vigorous cough producing large amounts
of infected mucus. Pasien dengan bronkiektasis sering memiliki batuk yang kuat menghasilkan
sejumlah besar lendir yang terinfeksi.
What causes COPD? Apa yang menyebabkan PPOK?
Cigarette smoking and second-hand smoke Merokok dan asap rokok pasif
Smoking is responsible for 90% of COPD in the United States. Merokok bertanggung jawab atas
90% dari PPOK di Amerika Serikat. Although not all cigarette smokers will develop COPD, it is
estimated that 15% will. Meskipun tidak semua perokok akan mengembangkan COPD,
diperkirakan bahwa 15% akan. Smokers with COPD have higher death rates than nonsmokers
with COPD. Perokok dengan PPOK memiliki tingkat kematian yang lebih tinggi dibanding
bukan perokok dengan PPOK. They also have more frequent respiratory symptoms (coughing,
shortness of breath, etc.) and a more rapid deterioration in lung function than non-smokers.
Mereka juga memiliki gejala pernafasan lebih sering (batuk, sesak napas, dll) dan lebih cepat
penurunan fungsi paru dibandingkan non-perokok. It is important to note that when a COPD
patient stops smoking, their decline in lung function slows to the same rate as a nonsmoker.
Penting untuk dicatat bahwa ketika seorang pasien PPOK berhenti merokok, penurunan fungsi
paru-paru mereka dalam memperlambat dengan tingkat yang sama seperti bukan perokok.
Therefore, it is never "too late" to quit. Oleh karena itu, tidak pernah "terlambat" untuk berhenti.
Effects of passive smoking or "second-hand smoke" on the lungs are not well-known; however,
evidence suggests that respiratory infections, asthma, and symptoms are more common in
children who live in households where adults smoke. Pengaruh merokok pasif atau "perokok
pasif" pada paru-paru yang tidak terkenal, namun bukti menunjukkan bahwa infeksi pernapasan,
asma, dan gejala lebih sering terjadi pada anak-anak yang tinggal di rumah tangga di mana orang
dewasa asap.
Cigarette smoking damages the lungs in many ways. Merokok merusak paru-paru dalam banyak
cara. For example, the irritating effect of cigarette smoke attracts cells to the lungs that promote
inflammation. Sebagai contoh, efek iritasi dari asap rokok menarik sel ke paru-paru yang
mempromosikan peradangan. Cigarette smoke also stimulates these inflammatory cells to release
elastase, an enzyme that breaks down the elastic fibers in lung tissue. Asap rokok juga
merangsang sel-sel inflamasi untuk melepaskan elastase, sebuah enzim yang memecah serat-
serat elastis pada jaringan paru-paru.
Air pollution Polusi udara
Air pollution can cause problems for persons with lung disease, but it is unclear whether outdoor
air pollution contributes to the development of COPD. Polusi udara dapat menyebabkan masalah
untuk orang dengan penyakit paru-paru, tetapi tidak jelas apakah polusi udara luar ruangan
memberikan kontribusi terhadap perkembangan PPOK. However, in the non-industrialized
world, the most common cause of COPD is indoor air pollution. Namun, di dunia non-industri,
penyebab paling umum PPOK adalah polusi udara dalam ruangan. This is usually due to indoor
stoves used for cooking. Hal ini biasanya karena kompor indoor digunakan untuk memasak.
Occupational pollutants Pekerjaan polutan
Some occupational pollutants such as cadmium and silica do increase the risk of COPD.
Beberapa polutan kerja seperti cadmium dan silika melakukan meningkatkan risiko COPD.
Persons at risk for this type of occupational pollution include coal miners, construction workers,
metal workers, cotton workers, etc. (Most of this risk is associated with cigarette smoking and
these occupations, an issue not well controlled for. These occupations are more often associated
with interstitial lung diseases , especially the pneumoconioses) Nevertheless, the adverse effects
of smoking cigarettes on lung function are far greater than occupational exposure. Orang yang
beresiko untuk jenis pencemaran kerja termasuk penambang batu bara, pekerja bangunan,
pekerja logam, pekerja kapas, dll (Kebanyakan dari risiko ini berhubungan dengan merokok dan
pekerjaan ini, masalah tidak terkontrol dengan baik untuk. Ini pekerjaan lebih sering
berhubungan dengan penyakit paru-paru interstisial , khususnya pneumoconiosis) Namun
demikian, dampak negatif merokok pada fungsi paru-paru jauh lebih besar dari paparan kerja.
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Alpha-1 kekurangan antitrypsin
Another well-established cause of COPD is a deficiency of alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT). Lain-
didirikan menyebabkan sumur PPOK adalah defisiensi alfa-1 antitrypsin (AAT). AAT deficiency
is a rare genetic (inherited) disorder that accounts for less than 1% of the COPD in the United
States. defisiensi AAT adalah genetik langka (diwariskan) gangguan yang menyumbang kurang
dari 1% dari PPOK di Amerika Serikat.
As discussed previously, normal function of the lung is dependent on elastic fibers surrounding
the airways and in the alveolar walls. Seperti telah dibahas sebelumnya, fungsi normal paru-paru
tergantung pada serat elastis yang mengelilingi saluran udara dan di dinding alveolar. Elastic
fibers are composed of a protein called elastin. serat elastis terdiri dari protein yang disebut
elastin. An enzyme called elastase that is found even in normal lungs (and is increased in
cigarette smokers) can break down the elastin and damage the airways and alveoli. Sebuah
elastase disebut enzim yang ditemukan bahkan dalam paru-paru normal (dan meningkat pada
perokok rokok) dapat memecah elastin dan merusak saluran napas dan alveoli. Another protein
called alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) (produced by the liver and released into the blood) is present in
normal lungs and can block the damaging effects of elastase on elastin. protein lain yang disebut
alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) (diproduksi oleh hati dan dilepaskan ke dalam darah) hadir dalam
paru-paru normal dan dapat memblokir efek merusak dari elastase terhadap elastin.
The manufacture of AAT by the liver is controlled by genes which are contained in DNA-
containing chromosomes that are inherited. Pembuatan AAT oleh hati dikendalikan oleh gen
yang terkandung di dalam DNA yang mengandung kromosom yang diwarisi. Each person has
two AAT genes, one inherited from each parent. Setiap orang memiliki dua gen AAT, salah satu
warisan dari orang tua masing-masing. Individuals who inherit two defective AAT genes (one
from each parent) have either low amounts of AAT in the blood or AAT that does not function
properly. Individu yang mewarisi dua gen AAT yang cacat (satu dari setiap orangtua) memiliki
jumlah baik rendah AAT dalam darah atau AAT yang tidak berfungsi dengan baik. The reduced
action of AAT in these individuals allows the destruction of tissue in the lungs by elastase to
continue unopposed. Tindakan mengurangi AAT pada individu-individu memungkinkan
kerusakan jaringan dalam paru-paru oleh elastase untuk melanjutkan terlindung. This causes
emphysema by age 30 or 40. Hal ini menyebabkan emfisema pada umur 30 atau 40. Cigarette
smoking accelerates the destruction and results in an even earlier onset of COPD. Merokok
mempercepat kerusakan dan hasil dalam onset lebih awal dari PPOK.
Individuals with one normal and one defective AAT gene have AAT levels that are lower than
normal but higher than individuals with two defective genes. Individu dengan satu normal dan
satu gen AAT AAT cacat memiliki tingkat yang lebih rendah dari normal tetapi lebih tinggi
daripada individu dengan dua gen yang cacat. These individuals MAY have an increased risk of
developing COPD if they do not smoke cigarettes; however, their risk of COPD probably is
higher than normal if they smoke. Orang-orang ini MUNGKIN memiliki peningkatan risiko
PPOK jika mereka tidak merokok, namun risiko PPOK mungkin lebih tinggi dari normal jika
mereka merokok. Though their Alpha-1 antitrypsin blood levels may be in the normal range, the
function of this enzyme is impaired relative to normal patient. Meskipun Alpha-1 tingkat
antitrypsin darah mereka mungkin berada dalam kisaran normal, fungsi enzim ini terganggu
relatif terhadap pasien normal. Some may even develop bronchiectasis instead of emphysema.
Beberapa bahkan dapat mengembangkan bronkiektasis bukan emphysema.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Referat SinusitisDokumen12 halamanReferat SinusitisRina AnggrainiBelum ada peringkat
- Set Soal 1 Medina 20jr15Dokumen52 halamanSet Soal 1 Medina 20jr15Wildana Aqila DzakiyBelum ada peringkat
- UKMPPD November 15Dokumen2 halamanUKMPPD November 15Eka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Ukdi Ilmu Kedokteran Jiwa 0214Dokumen8 halamanSoal Ukdi Ilmu Kedokteran Jiwa 0214Isti Iryan PriantiBelum ada peringkat
- Set Soal 1 Medina 20jr15Dokumen52 halamanSet Soal 1 Medina 20jr15Wildana Aqila DzakiyBelum ada peringkat
- Referat SinusitisDokumen12 halamanReferat SinusitisRina AnggrainiBelum ada peringkat
- Algoritma STEMIDokumen4 halamanAlgoritma STEMIEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- MakalahDokumen21 halamanMakalahEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- BioorganikDokumen8 halamanBioorganikEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- BIOANORGANIKDokumen12 halamanBIOANORGANIKEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- MakalahDokumen11 halamanMakalahEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Kimia PanganDokumen34 halamanKimia PanganEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah BiotekDokumen18 halamanMakalah BiotekEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Box 25 1 Lehninger TranslateDokumen2 halamanBox 25 1 Lehninger TranslateEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Referat Rhinitis AkutDokumen7 halamanReferat Rhinitis AkutEka Wahyu Santoso0% (1)
- FOTOSINTESISDokumen23 halamanFOTOSINTESISEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah StreptokinaseDokumen27 halamanMakalah StreptokinaseEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- InulinaseDokumen13 halamanInulinaseEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal KulitDokumen8 halamanJurnal KulitEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah UnyilDokumen4 halamanMakalah UnyilEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Rhinitis Atrofi EditDokumen13 halamanRhinitis Atrofi EditEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Penyuluhan DHFDokumen11 halamanPenyuluhan DHFEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Status Pasien KulitDokumen3 halamanStatus Pasien KulitEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal THTDokumen1 halamanJurnal THTEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- TB ParuDokumen25 halamanTB ParuEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Retinopati PrematuritasDokumen15 halamanRetinopati PrematuritasEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- P ('t':'3', 'I':'669151515') D '' Var B Location Settimeout (Function ( If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') ( B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Dokumen39 halamanP ('t':'3', 'I':'669151515') D '' Var B Location Settimeout (Function ( If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') ( B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Eka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Gagal JantungDokumen5 halamanGagal JantungDewi AnggrainiBelum ada peringkat
- Status Pasien GonerrheaDokumen12 halamanStatus Pasien GonerrheaEka Wahyu SantosoBelum ada peringkat