Tingkatan 4: Bab 1 Pengukuran
Diunggah oleh
IceStrong 123Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Tingkatan 4: Bab 1 Pengukuran
Diunggah oleh
IceStrong 123Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Modul Platinum Fizik
Tingkatan 4
Bab 1 Pengukuran
Measurement
KERTAS 2
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
1 (a) T berkadar terus dengan l/T is directly proportional to l. 1 1
(b) Mengurangkan panjang bandul/Decreases the length of the pendulum 1 1
(c) (i) 100 cm 1 1
(ii) 1.414 s 1 1
(iii) 0.04 s2 cm-1 1 1
JUMLAH 5
2 (a)
FIZIK
Kuantiti asas Kuantiti terbitan
Base quantity Derived quantity
Jisim Halaju
Mass Velocity
Masa Pecutan
Time Acceleration
Jarak
Distance 2 2
(b) (i) Daya tujahan = Jisim 3Pecutan
Thrust = Mass 3 Acceleration
= kg 3 m s-2 1
= kg m s-2 1 2
(ii) Daya tujahan = Jisim 3 Pecutan
Thrust = Mass 3 Acceleration
= 1500 kg 3 20 m s-2 1
= 30 000 kg m s-2 1 2
JUMLAH 6
3 (a) Kereta Masa, t (s) Kelajuan (m s-1)
Car Time, t (s) Velocity (m s-1)
5000
A 166.68 166.68 = 30.00 2
5000
B 133.37 133.37 = 37.49 2
5000
C 198.37 198.37 = 25.21 2
5000
D 150.15 150.15 = 33.30 2
5000
E 206.60 206.60 = 24.20 2 10
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 1
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 1 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
(b) Kedua-dua mereka menggunakan walkie-talkie atau telefon pintar. Masa yang diambil 5 5
untuk melalui jarak 5 km direkodkan dan selang masa, t ditentukan atau kaedah lain
yang munasabah.
Both of them use walkie-talkie or smart phone. The time taken to pass through distance of 5 km is
recorded and the time interval, t is determined or other reasonable method.
(c) Had laju lebuh raya di Malaysia = 110 km j-1 1
Malaysian highway speed = 110 km h-1
= 30.56 m s-1 1
Maka, kereta B telah melebihi had laju lebuh raya di Malaysia. 1 3
Thus, car B exceed the speed limit in Malaysian highway.
(d) Gunakan pengesan ultrabunyi, aplikasi penjejak masa atau kaedah lain yang munasabah. 2 2
Rekod beberapa bacaan pada kelajuan 5 km dan mengira nilai purata.
Use ultrasound detector, time tracker application or other reasonable method. Record several
readings on speed within 5 km and calculate the average values.
JUMLAH 20
Bab 2 Daya dan Gerakan I
Force and Motion I
KERTAS 2
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
1 (a) Kadar perubahan sesaran/Rate of change of displacement 1 1
(b) (i) Kereta mainan bergerak dengan pecutan sifar pada PQ 1 1
The toy car moves with zero acceleration at PQ
(ii) s = Luas di bawah graf
Area under the graph
1
s = (10 + 4)(2.0) 1
2
= 14.0 m 1 2
JUMLAH 4
2 (a) Jumlah momentum awal suatu sistem adalah sama dengan jumlah momentum akhir 1 1
sistem itu jika tiada sebarang daya luar bertindak pada sistem itu
The total initial momentum of a system is equal to the final momentum of the system if no external
force acts on the system
(b) Jumlah momentum troli dalam Rajah 2.1 adalah sifar 1 1
Total momentum of the trolleys in Diagram 2.1 is zero
(c) • Magnitud s1 adalah sama dengan magnitud s2 1
Magnitude of s1 is equal to the magnitude of s2
• Magnitud v1 adalah sama dengan magnitud v2 tetapi pada arah yang bertentangan 1 2
Magnitude of v1 is equal to the magnitude of v2 but in opposite direction
(d) Jumlah momentum sebelum pin itu diketuk adalah sama dengan jumlah momentum 2 2
selepas pin itu diketuk
The total momentum before the pin is hit is equal to the total momentum after the pin is hit
(e) • Pembakaran cecair oksigen dan cecair hidrogen dalam satu kebuk pembakaran 1
menghasilkan gas ekzos yang panas
Combustion of hydrogen liquid and oxygen liquid in a combustion chamber produces hot
exhaust gas
• Gas ekzos yang panas dilancarkan ke bawah dengan laju yang tinggi 1
The hot exhaust gas ejected downward with high speed
• Dan menghasilkan satu momentum ke bawah 1
And produces a downward momentum
• Berdasarkan Prinsip Keabadian Momentum, satu momentum ke atas dihasilkan 1 4
According to the Principle of Conservation of Momentum, an upward momentum is produced
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 2
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 2 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
(f) Ciri-ciri Huraian
Characteristics Explanation
Bahan yang digunakan mestilah kuat Roket tidak mudah pecah apabila 2
The material used must be strong dikenakan tekanan
The rocket does not break easily when
pressure is applied
Bentuk roket ialah aerodinamik Rintangan udara dikurangkan 2
The shape of the rocket is aerodynamic The air resistance is reduced
Sudut pelancaran pada 45oC Roket boleh bergerak pada jarak 2
The angle of launching at 45oC mengufuk yang maksimum
The rocket can travel to a maximum
horizontal distance
Isi padu air di dalam roket adalah 1/3 Roket menjadi ringan dan boleh 2
daripada isi padu keseluruhan dilancarkan dengan mudah
The volume of water in the rocket is 1/3 of the The rocket becomes light and can take-off
whole volume easily
Struktur tambahan seperti sayap dipasang Roket dapat bergerak dengan lancar dan 2 10
pada hujung roket stabil
Additional structure such as fins are fixed at The rocket can move smoothly and stable
the tail of the rocket
JUMLAH 20
FIZIK
Bab 3 Kegravitian
Gravitational
KERTAS 2
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
1 (a) Hukum Kegravitian Semesta Newton 1 1
Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation
(b) berkadar terus; berkadar songsang 1, 1 2
directly proportional; inversely proportional
(c) Berkurang/Decreases 1 1
JUMLAH 4
2 (a) Daya semesta // Daya yang bertindak di antara mana-mana dua jasad dalam alam semesta 1 1
Universal force // A force acting between any two bodies in the universe
(b) (i) N m2 atau m3 kg-1 s-2 1 1
N m2 or m3 kg-1 s-2
(6.67 3 10-11)(70)(53) 1
(ii) F= (1.0)2
= 2.45 3 10-7 N 1 2
(c) Daya graviti terlalu kecil
The gravitational force is too small 1 1
JUMLAH 5
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 3
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 3 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
3 (a) (i) Tenaga keupayaan graviti bermaksud tenaga yang diperolehi oleh suatu objek disebabkan 1 1
kedudukannya dari pusat Bumi
Gravitational potential energy means the energy gained by an object due to its position from the
center of the Earth
(ii) GMm
U=−
R+r
(6.67 3 10-11)(5.97 3 1024)(300)
=− 1
(6.37 3 106) + (3 3 105)
= −1.79 3 1010 N m 1 2
(iii) 4p2r3
M=
GT2
√MGT2
3
r= 1
4p2
√
3 (5.97 3 1024) 3 (6.67 3 10-11) 3 (86400)2
= 1
4p2
= 4.22 3 107 m 1 3
(b) • Arah putaran satelit sama dengan arah putaran Bumi 1
The direction of rotation of the satellite is same as the direction of rotation of the Earth
• Tempoh orbit adalah 24 jam 1
The orbital period is 24 hours
• Berada di atas tempat yang sama di permukaan Bumi 1
Being on the same place on the surface of the Earth
• Sesuai digunakan untuk komunikasi 1 4
Suitable to be used for communication
(c) Ciri-ciri Huraian
Characteristics Explanation
Bahan badan satelit diperbuat daripada Kadar peningkatan suhu badan satelit 2
bahan yang mempunyai muatan haba yang sedikit
tentu tinggi Slightly increase of the satellite body
The materials of the satellite body are made temperature
up from the materials that contains high
specific heat capacity
Warna badan satelit adalah warna putih Memantulkan cahaya dan haba 2
The colour of the satellite body is white colour Reflects light and heat
Sumber kuasa menggunakan sel-sel suria Sumber tenaga boleh diperbaharui,
The power source is using solar cells jimat kos dan tidak perlu ditukar selalu 2
Energy sources are renewable, cost-effective
and do not need to be changed often
Jisim yang kecil Tidak memerlukan tenaga yang tinggi
Smaller mass
2
semasa penghantaran ke angkasa lepas
Does not require high energy during
transmission into space
Satelit yang paling sesuai ialah satelit R kerana mempunyai bahan badan satelit diperbuat 2 10
daripada bahan yang mempunyai muatan haba tentu tinggi, warna badan satelit adalah
warna putih, sumber kuasa menggunakan sel-sel suria dan jisim yang kecil.
The most suitable satellite is satellite R because it contains the materials of the satellite body are
made up from the materials that contains high specific heat capacity, the colour of the satellite
body is white colour, the power source is using solar cells and smaller mass.
JUMLAH 20
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 4
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 4 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Bab 4 Haba
Heat
KERTAS 2
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
1 (a) (i) Bertambah/Increases 1 1
(ii) Tekanan udara/Air pressure 1 1
(b) Hukum Gay-Lussac/Gay-Lussac Law 1 1
(c) P2 T1
T2 =
P1
230 3 300 1
=
200 1 2
= 345 K //72 °C
(d) (i) Luas permukaan tayar lebih lebar/Wider surface area of the tyre 1 1
Sebab: Mengurangkan tekanan yang berindak ke atas jalan 1 1
Reason: The pressure exerted on road is reduced
(ii) Alur tayar tebal/Thick thread of the tyre 1 1
Sebab: Lebih cengkaman tayar ke atas jalan 1 1
Reason: To give better grip to the road
JUMLAH 9
2 (a) (i) Haba ialah tenaga yang berpindah daripada objek panas kepada objek sejuk//Pemindahan 1 1
tenaga berlaku kerana perbezaan suhu
FIZIK
The energy transferred from a hot object to a cold object//The transmission energy occurs because
of the difference in temperature
(ii) Suhu dahi lebih tinggi daripada suhu pelapik 1 1
The temperature of the forehead is higher than the temperature of the pad
Haba dipindahkan daripada dahi ke pelapik 1 1
Heat is transferred from the forehead to the pad
(b) Dq = 36 – 15
Q = 30 g 3 4.3 J g–1 oC–1 3 (36 – 15) oC 1
= 2709 J 1 2
(c) Jisim gel ditambah/Increase the mass of the gel 1 1
Sebab: Tenaga haba dipindahkan bertambah apabila jisim gel bertambah//Haba 1 1
dipindahkan berkadar terus dengan jisim
Reason: The heat removed increases with the mass of the gel//The heat removed is directly
proportional to the mass
Gunakan gel yang bermuatan haba tentu lebih tinggi 1 1
Use a gel with higher specific heat capacity
Sebab: Tenaga haba dipindahkan bertambah apabila muatan haba tentu gel bertambah// 1 1
Haba dipindahkan berkadar terus dengan muatan haba tentu gel
Reason: The heat removed increases with the specific heat capacity of the gel//The heat removed is
directly proportional to the specific heat capacity of the gel
JUMLAH 9
3 (a) (i) Kuantiti haba yang diperlukan untuk mengubah suhu 1 kg bahan sebanyak 1°C 1 1
Quantity of heat needed to change the temperature of 1 kg substance by 1°C
(ii) • Mi sup mengandungi banyak air 1
Noodle soup contains more//a lot of water
• Air mempunyai muatan haba tentu yang tinggi 1
Water has a high specific heat capacity
• Dapat menyerap lebih banyak haba semasa dimasak 1
Can absorb more heat during cooking
• Mengambil masa lebih lama untuk membebaskan haba selepas dimasak 1 4
Takes a longer time to release heat after cooking
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 5
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 5 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
(b) Ciri-ciri Huraian
Characteristics Explanation
Muatan haba tentu jubin bumbung adalah Penebat/dapat menyerap lebih banyak 2
tinggi haba tanpa panas
High specific heat capacity of the roof tile Insulator/able to absorb high quantities of
heat without getting hot
Warna jubin bumbung adalah cerah Memantulkan haba 2
Bright colour of the roof tile Reflects heat
Panjang ambang bumbung adalah panjang Peneduhan lebih baik
Longer length of the roof eaves Provides better shade 2
Memiliki ventilator turbin Udara disalurkan menerusi bumbung
Owns a turbine ventilator Air is circulated through the roof
2
Sistem bumbung yang paling sesuai ialah sistem bumbung Q kerana mempunyai muatan 2 10
haba tentu jubin bumbung yang tinggi, warna jubin bumbung yang cerah, panjang
ambang bumbung yang panjang dan memiliki ventilator turbin.
The most suitable roofing system is roofing system Q because it contains high specific heat capacity of
the roof tile, bright colour of the roof tile, long length of the roof eaves and owns a turbine ventilator.
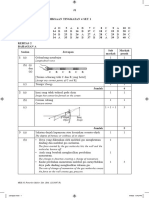
(c) (i) q/°C
30
t
0
−4 1+1 2
(ii) Q = Q1 + Q2 + Q3 1
= mcais Dq + mlf + mcair Dq
= (0.2 3 2100 3 4) + [0.2 3 (3.34 3 105)] + (0.2 3 4200 3 30) 1
= 93680 J 1 3
JUMLAH 20
Bab 5 Gelombang
Waves
KERTAS 2
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
1 (a) Sesaran maksimum suatu zarah dalam medium dari kedudukan keseimbangan. 1 1
The maximum displacement of a particle in the medium from its equilibrium position.
(b) (i) 8 cm 1 1
(ii) T = 0.2 s
1
f =
0.2
= 5.0 Hz 1 1
(iii) 5.0 cm 1 1
(iv) v = fλ
= 535 1
= 25 cm s-1 1 2
JUMLAH 6
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 6
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 6 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
2 (b) (i) Dua puncak atau dua lembangan bertemu dan menghasilkan amplitud yang maksimum 1 1
Two crests or two troughs superpose and produce maximum amplitude
(ii) Puncak bertemu dengan lembangan dan menghasilkan amplitud yang minimum 1 1
The crest superposes with the trough and produce minimum amplitude
(b) (i) Garis nodal/Nodal line 1 1
(ii) Garis antinodal/Antinodal line 1 1
(c) Untuk menghasilkan dua gelombang koheren 1 1
To produce two coherent waves.
(d) Bertambah/Increases 1 1
JUMLAH 6
3 (a) Penyebaran gelombang apabila gelombang itu melalui suatu bukaan kecil atau suatu 1 1
penghalang kcil
The spreading of waves when they pass through a small opening or a small obstacle
(b) (i) 1 1
(ii) • Untuk memantulkan gelombang laut bagi mencegah pemindahan terus tenaga
FIZIK
gelombang air ke pantai 1
To reflect the sea waves to prevent direct transfer of wave energy to the shore
• Untuk membentuk suatu bukaan kecil di laut supaya gelombang air dapat dibelaukan 1 2
To form a small opening in the sea for the waves to produce diffraction
(iii) Lebih banyak tenaga gelombang air akan sampai ke pelabuhan/Menyebabkan lebih 1 1
kerosakan kepada kapal di pelabuhan/Hakisan pantai
More waves energy will reach the harbor/Causes more damage to the ships at the harbor/Coastal
erosion
(c)
Ciri-ciri Huraian
Characteristics Explanation
Tembok penahan yang tinggi Melindungi pelabuhan daripada
High retaining wall gelombang yang tinggi 2
To protect the harbor from high waves
Bentuk tembok penahan yang melengkung Untuk memantulkan gelombang dari laut
Curve retaining wall shape To reflect the wave from the sea
2
Struktur tembok penahan yang cerun Laju//Tenaga//Amplitud gelombang air
The structure of the retaining wall is sloping berkurang apabila kedalaman berkurang
Speed//Energy//Amplitude of waves decreases
when the depth of water decreases 2
Lokasi terletak di teluk Tenaga gelombang berkurang di teluk//
Location at the bay Air tenang//Amplitud gelombang kecil
Wave energy decrease at the bay//Calmer 2
water//Small amplitude wave
Jenis tembok penahanan yang paling sesuai dibina ialah jenis tembok P kerana
mempunyai tembok penahan yang tinggi, tembok penahan yang melengkung, struktur
2 10
tembok penahan yang cerun dan lokasi terletak di teluk.
The most suitable type of the retaining wall to be built is P because it contains high retaining wall,
curve retaining wall, the structure of the retaining wall is sloping and location at the bay.
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 7
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 7 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
(d) (i) t = 120 ms = 0.12 s
vt
d=
2 1
1400 3 0.12
= 1
2
= 84 m 1 3
(ii) v = fλ
1400 = (70 3 103) λ 1
λ = 0.02 m 1 2
JUMLAH 20
Bab 6 Cahaya dan Optik
Light and Optics
KERTAS 2
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
1 (a) Indeks biasan ialah nisbah sin sudut tuju terhadap sin sudut pembiasan
Refractive index is the ratio of sine of angle of incidence to sine angle of refraction
atau/or
sin i 1
n= 1
sin r
i = Sudut tuju/Angle of incidence
r = Sudut biasan/Angle of refraction
(b) 120o – 90o = 30º 1 1
sin 60°
(c) n = sin 30°
1
= 1.73 1 2
(d)
Udara
X Air
•
Cecair P
Liquid P
120°
60° 1 1
JUMLAH 5
2 (a) Cermin cembung/Convex mirror 1 1
(b) ƒ =10 cm 1 1
(c) X
C
•
Objek F
Object
20 cm 2 2
(d) Maya//Diperkecil//Tegak 1 1
Virtual//Diminished//Upright
JUMLAH 5
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 8
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 8 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
3 (a) Jarak di antara titik fokus dan pusat optik kanta 1 1
Distance between focal point and the optical centre of a lens
(b) • Kanta cembung difokuskan kepada satu objek jauh (infiniti) 1
The convex lens is aimed//focused to a distant object(infinity)
• Kedudukan skrin dilaraskan sehingga imej yang tajam terbentuk pada skrin 1
The screen is adjusted until a sharp image is formed on the screen
• Jarak di antara skrin dan kanta diukur 1
The distance between the screen and the lens is measured
• Panjang fokus = jarak di antara skrin dan kanta 1 4
Focal length = distance between the screen and the lens
(c) Ciri-ciri Penjelasan
Characteristics Explanation
Panjang fokus lebih besar Menghasilkan imej nyata, songsang dan kecil
Longer focal length Produce real, inverted and smaller image 2
Pembesaran yang tinggi Menghasilkan imej yang besar
High magnification Produce bigger image
2
Jarak di antara kanta objek dan kanta Menghasilkan imej pada pelarasan normal//
mata = fo + fe imej di infiniti
Distance between objective lens and eyepiece Produce image at normal adjustment//image at
= fo + fe infinity 2
Diameter lebih besar Lebih banyak cahaya masuk ke dalam kanta
FIZIK
Bigger diameter objek//Lebih cerah
More light can enter objective lens//Brighter 2
L dipilih Panjang fokus lebih besar, tinggi pembesaran,
L is chosen jarak di antara dua kanta = fo + fe dan 2 10
diameter besar.
Longer focal length, higher magnification, distance
between two lenses = fo + fe and bigger diameter
(d) (i) 1 1 1
= +
f u v
1 1 1
= − 1
v 5 400
v = 5.063 cm 1 2
h2 v
(ii) = 2
h1 v1
h2 5.063
= 1
100 400
h2 = 1.27 cm 1 2
(iii) Nyata, songsang dan diperkecil. 1 1
Real, inverted and diminished.
JUMLAH 20
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 9
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 9 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Tingkatan 5
Bab 1 Daya dan Gerakan II
Force and Motion II
KERTAS 2
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
1 (a) (i) Sifar atau F = 0 1 1
Zero or F = 0
(ii) Hukum Gerakan Newton Ketiga//Keseimbangan daya 1 1
Newton's Third Law of Motion//Forces in equilibrium
(b) (i) Kapal terbang itu mengalami pecutan atau pertambahan halaju. 1 1
The aircraft will experience acceleration or increase in velocity.
(ii) Daya bersih wujud (F ≠ 0) 1 1
A net force exists (F ≠ 0)
JUMLAH 4
2 (a) Daya yang melawan arah pergerakan 1 1
Force that oppose the acted force forward
(b) (i) W = mg
= 43 3 10
= 430 N 1 1
(ii) F = W sin 20° − 147.1 N
= 147.1 N – 147.1 N 1
= 0 N 1 2
(c) Pegun 1
Kerana daya dalam keseimbangan//daya bertindak = daya geseran 1 2
Stationary
Because balance force/ force in equilibrium//acted force = frictional force
JUMLAH 6
3 (a) Hukum Hooke/Hooke’s law 1 1
(b) (i) Rajah 3.1 mempunyai tenaga keupayaan kenyal lebih besar daripada dalam Rajah 3.2. 1 1
Diagram 3.1 has greater elastic potential energy than in Diagram 3.2
(ii) Halaju bola yang dilepaskan dalam Rajah 3.1 lebih besar berbanding dalam Rajah 3.2 1 1
The velocity of the ball ejected in Diagram 3.1 is greater than in Diagram 3.2
(iii) Jarak yang dilalui oleh bola itu selepas dilepaskan dalam Rajah 3.1 lebih jauh daripada 1 1
dalam Rajah 3.2
The distance travelled by the ball after ejection in Diagram 3.1 is further than in Diagram 3.2
(c) (i) Semakin besar mampatan spring, semakin laju halaju bola itu selepas dilepaskan 1 1
The greater the spring compression, the faster the velocity of the ball after being ejected
(ii) Semakin besar mampatan spring, semakin jauh jarak yang dilalui oleh bola itu selepas 1 1
dilepaskan
The greater the spring compression, the further the distance travelled by the ball after ejection
(d) • Gunakan spring lebih tebal 1
Use thicker spring
• Untuk tingkatkan kekerasan spring//pemalar spring 1
To increase the stiffness of the spring//spring constant
• Gunakan spring yang mempunyai diameter kecil 1
Use smaller diameter of a spring
• Tenaga keupayaan kenyal dan tenaga kinetik lebih besar 1 4
Greater elastic potential energy and kinetic energy
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 10
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 10 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
(e) Ciri-ciri Huraian
Characteristics Explanation
Diameter spring yang lebih kecil Pemalar spring lebih besar, maka dapat 2
Small diameter of the spring membawa muatan berat
Higher spring constant, thus be able to
carry heavier load
Tayar yang lebar Menambah luas//Mengurangkan tekanan 2
Wider tyres Increase contact area//Reduce pressure
Bahan tempat duduk yang lembut Menambah masa impak// 2
Soft materials of the seat Mengurangkan daya impuls
Increase impact time//Decrease impulsive force
Bahan untuk rangka motosikal mempunyai Mengurangkan berat motosikal
ketumpatan rendah Reduce weight of the motorcycle 2
Low density materials for the motorcycle frame
Pola bunga tayar yang kasar Menambah cengkaman geseran
Rough thread patterns on the tyres Increase frictional grip 2 10
JUMLAH 20
Bab 2 Tekanan
Pressure
FIZIK
KERTAS 2
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
1 (a) (i) Prinsip Bernoulli/Bernoulli’s principle 1 1
(ii) Y 1 1
(b) Gas yang mengalir keluar daripada muncung yang sempit pada kelajuan paling tinggi 1 1
Gas flows out the nozzle at the highest speed
(c) Udara daripada luar ditolak (disedut) ke dalam lubang 1
Air from the outside is pushed (sucked) into the hole
Menghasilkan pembakaran lengkap/Resulting in complete combustion 1 2
JUMLAH 5
2 (a) (i) Tekanan yang dikenakan ke atas bendalir tertutup akan dipindahkan secara seragam ke 1 1
semua arah dalam bendalir itu
The pressure applied on an enclosed fluid is transmitted uniformly in all directions in the fluid
(ii) • Daya dikenakan pada omboh kecil menghasilkan tekanan 1
The force applied to the small piston produces pressure
• Tekanan dipindahkan secara seragam melalui cecair 1
Pressure transmitted equally throughout the liquid
• F2 dihasilkan apabila tekanan bertindak ke atas A2; F2 = PA2 1
F2 is produced when pressure acts on A2; F2 = PA2
• A2 > A1//Nisbah A2 : A1 lebih besar daripada 1 dan F2 > F1 1 4
A2 > A1//Ratio A2 : A1 is greater than 1 and F2 > F1
(b) Ciri-ciri Huraian
Characteristics Explanation
Jenis bendalir brek yang tidak boleh Tekanan boleh dipindahkan melalui bendalir 2
dimampatkan brek ke semua arah dengan seragam
Type of brake fluid is incompressable Pressure can be transferred through the brake
fluid equally to all direction
Takat didih bendalir brek yang tinggi Tidak mudah tersejat 2
High boiling point of brake fluid Not easily to evaporate
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 11
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 11 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
Ciri-ciri Huraian
Characteristics Explanation
Pemalar spring bagi spring adalah tinggi Boleh menahan daya yang besar 2
High spring constant of the spring Can withstand large force
Nisbah luas keratan rentas omboh di Daya yang lebih besar dikenakan ke atas 2
dalam silinder induk kepada silinder omboh
gelendung brek rendah Larger force exerted on the piston
Low ratio of cross-section of pistons in the
master cylinder to the brake drum cylinder
Brek hidraulik yang paling berkesan ialah L kerana mempunyai jenis bendalir brek
2 10
yang tidak boleh dimampatkan, takat didih bendalir brek yang tinggi, pemalar spring
bagi spring adalah tinggi dan nisbah luas keratan rentas omboh di dalam silinder induk
kepada silinder gelendung brek rendah.
The most effective hydraulic brake is L because it contains type of brake fluid is incompressable,
high boiling point of brake fluid, high spring constant of the spring and low ratio of cross-section
of pistons in the master cylinder to the brake drum cylinder.
(c) (i) F 1
P=
A
50
=
2
= 25 N cm-2 1 2
(ii) F2 = P 3 A2 1
= 25 3 6 1
= 150 N 1 3
JUMLAH 20
Bab 3 Elektrik
Electricity
KERTAS 2
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
1 (a) Cerek elektrik menghasilkan 2000 J tenaga sesaat apabila disambungkan kepada bekalan 1 1
240 V
The electric kettle will produce 2000 J energy per second when connect with 240 V
(b) P = IV
P
I=
V
2000
= 1
240
= 8.33 A 1 2
(c) (i) 9 A/10 A 1 1
(ii) Nilai fius mesti sedikit lebih besar daripada arus yang mengalir dalam cerek 1 1
Fuse value must be slightly more than the current flow through the kettle
(d) V = IR
V
R=
I
240
= 1
8.33
= 28.8 Ω 1 2
2 (a) Tenaga elektrik → Tenaga cahaya + Tenaga haba 1 1
Electrical energy → Light energy + Heat energy
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 12
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 12 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
(b) (i) P = I 2R
P
I2 =
R
20
=
120 1
I = 0.41 A 1 2
(ii) E = I2Rt
= (0.41)2 (120) (2 3 60 3 60) 1
= 1.45 3 105 J 1 2
(c) (i) Kuasa rendah/Low power 1
Sebab: Kadar penggunaan tenaga rendah//kos rendah 1 2
Reason: Low energy consumption rate//low cost
(ii) Jangka hayat lama//Long lifespan 1
Sebab: Tahan lama//kos rendah 1 2
Reason: Durable//low cost
(iii) Penghasilan tenaga haba rendah/Low heat energy production 1
Sebab: Kurang tenaga terbazir 1 2
Reason: Less energy wasted
(iv) LED 1 1
3 (a) Tungsten 1 1
(b) (i) P=VI
1 000 = 240 (I) 1
I = 4.17 A 1 2
V=IR
FIZIK
(ii)
240 = 4.17 R 1
R = 57.6 Ω 1 2
(c) (i) Tenaga elektrik → Tenaga haba 1 1
Electrical energy → Heat Energy
(ii) EP = V I t
= 240 (6.0) (8.0 3 60)
= 6.912 3 105 J 1
EQ = V I t
= 240 (5.0) (10.0 3 60)
= 7.200 3 105 J 1
ER = V I t
= 240 (4.0) (9.0 3 60) 1
= 5.184 3 105 J 1 4
(iii) R sebab menggunakan tenaga yang kurang/R because it used less energy 1,1 2
JUMLAH 12
4 (a) Arus/Current 1 1
(b) (i) 1 1 1 1
= +
R 2 2
R=1Ω 1 2
(ii) • Bacaan ammeter meningkat/Ammeter reading increases 1
• Rintangan berkesan berkurang/Effective resistance decreases 1 2
V2 1
(c) (i) R=
P
= 6
2
20
= 1.8 Ω 1 2
(ii) 1 = 1
+
1 + 1
R R1 R2 R3
1 1 1 1
= +
R 1.8 1.8 + 1.8
R = 0.6 1 1
(iii) E = Pt 1
= 3(20 3 180)
= 10 800 J 1 2
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 13
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 13 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
(d) Ciri-ciri Huraian
Characteristics Explanation
Dawai tebal Rintangan rendah 2
Thick wire Low resistance
Voltan/Voltage = 240 V Voltan bekalan kuasa sama dengan spesifikasi
alat-alat elektrik//Alat-alat elektrik bekerja 2
secara normal
Voltage same appliances rating//Appliances
normal work
Litar selari Rintangan berkesan adalah rendah//Arus
Parallel circuit tinggi//Jika satu peralatan tidak berfungsi, 2
peralatan lain masih berfungsi
Effective resistance is lower//High current//If one of
appliances is not function, the others still function
Fius/Fuse = 20 A Arus mengalir ialah 17.5 A 2
Total current flows is 17.5 A
Litar yang paling sesuai ialah litar K kerana mempunyai dawai tebal, nilai voltan ialah
240 V, litar selari dan mempunyai nilai fius 20 A. 2 10
The most suitable circuit is K because it contains thick wire, voltage values is 240 V, parallel circuit
and fuse value is 20 A.
JUMLAH 20
5 (a) (i) Apabila disambung kepada bekalan 240 V, tenaga dihasilkan ialah 150 J sesaat 1 1
When the voltage is 240 V, the energy produced is 150 J per second
(ii) Kuasa output
• Kecekapan = 3 100%
Kuasa input
Output power
Efficiency = 3 100%
Input power
Mentol dan lampu pendarfluor mempunyai kuasa input yang sama iaitu 150 W 1
Bulb and pendarfluor lamp have same input power which are 150 W
• Mentol memberikan kuasa output yang rendah kerana terdapat tenaga hilang dalam
bentuk haba 1
Bulb gives low output power because more electrical energy lost in the form of heat
• Lampu pendarfluor memberikan kuasa output yang lebih tinggi kerana kebanyakan
tenaga elektrik ditukarkan kepada bentuk tenaga cahaya yang berguna 1
Pendarfluor lamp gives high output power because more electrical energy convert to useful
energy that is light energy
• Lampu pendarfluor lebih cekap daripada mentol kerana tenaga elektrik yang dibekalkan
lebih banyak ditukarkan kepada tenaga yang berguna 1 4
Pendarfluor lamp is more efficient rather than bulb because more electrical energy convert to
light energy (useful energy)
(b) Ciri-ciri Huraian
Characteristics Explanation
Kerintangan yang tinggi Rintangan tinggi, lebih banyak haba
High resistivity dihasilkan 2
High resistance, more heat is produced
Takat lebur yang tinggi Tidak mudah melebur 2
High melting point Not easy to melt
Kekuatan yang tinggi Tidak putus 2
High strength Not snap
Ketahanan terhadap pengaratan yang tinggi Tidak mudah berkarat 2
Resistance to rusting is high Not easy to rust
Dawai yang paling sesuai ialah dawai Z kerana mempunyai kerintangan yang tinggi, takat 2 10
lebur yang tinggi, kekuatan yang tinggi dan ketahanan terhadap pengaratan yang tinggi.
The most suitable wire is wire Z because it contains high resistivity, high melting point, high strength
ans resistance to rusting is high.
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 14
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 14 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
(c) (i) E = Pt 1
= 150 3 10 800 1
= 1.62 3 106 J 1 3
V2
(ii) R=
P 1
2402
=
150
= 384 Ω 1 2
JUMLAH 20
Bab 4 Keelektromagnetan
Electromagnetism
KERTAS 2
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
1 (a) Aruhan elektromagnet ialah penghasilan d.g.e. aruhan merentasi suatu konduktor apabila 1 1
terdapat gerakan relatif antara konduktor itu dengan suatu medan magnet
Electromagnetic induction is the production of an induced e.m.f in a conductor when there is relative
motion between theconductor and a magnetic field.
(b) (i) Solenoid mengalami perubahan medan magnet. Arus aruhan dihasilkan. 1 1
The solenoid experiences a change in the magnetic field. An induced current is produced.
(ii) A: Kutub utara/ North pole 1
FIZIK
B: Kutub selatan/ South pole 1 2
(c) Meningkat/Increases 1 1
(d) Magnitud arus aruhan meningkat. 1 1
The magnitude of the induced current increases.
JUMLAH 6
2 (a) Transformer injak naik/Step-up transformer 1 1
(b) (i) Kuprum/Copper 1 1
(ii) Untuk mengurangkan kehilangan tenaga akibat rintangan gegelung 1 1
To reduce the energy loss due to the resistance of the coils
NS V
(c) = S
NP VP
NS 1200
=
200 240 1
NS = 1000 1 2
(d) (i) Pinput = IP 3 VP
= 240 V 3 0.2 A 1
= 48 W 1
Poutput = 48 W 3 80%
= 38.4 W 1 3
(ii) Poutput = IS 3 VS
38.4 = IS 3 1200 1
IS = 0.032 A 1 2
(e) (i) Kipas itu tidak berfungsi. 1 1
The fan does not function.
(ii) Voltan output ialah arus ulang-alik. 1 1
Output voltage is an alternating current.
JUMLAH 12
3 (a) (i) Aruhan elektromagnet 1 1
Electromagnetic induction
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 15
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 15 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
(b) Ciri-ciri Huraian
Characteristics Explanation
Bahan teras besi lembut Senang dimagnetkan dan dinyahmagnetkan
Soft iron core material Easy to magnetise and demagnitise
2
Pembinaan teras berlamina Kurangkan kehilangan tenaga akibat arus
2
Laminated construction of the core pusar
Reduce the energy loss due to Eddy current
Jenis transformer ialah transformer injak Meningkatkan voltan output
naik Increase the output voltage 2
Type of transformer is step-up transformer
Jenis dawai untuk gegelung ialah kuprum Rintangan rendah
Type of wire for coil is copper Low resistance 2
Transformer yang paling sesuai ialah transformer R kerana ia mempunyai bahan teras
2 10
besi lembut, pembinaan teras berlamina, jenis transformer ialah transformer injak naik
dan jenis dawai untuk gegelung ialah kuprum.
The most suitable transformer is transformer R because it contains soft iron core material,
laminated construction of the core, type of transformer is step-up transformer and type of wire for
coil is copper.
(c) (i) A: Transformer injak naik/Step-up transformer 1
B: Transformer injak turun/Step-down transformer 1
C: Transformer injak turun/Step-down transformer 1 3
(ii) • Penghantaran pada voltan yang tinggi menghasilkan penghantaran pada arus yang kecil 1
Transmission at high voltage produces transmission in small current
1 2
• Mengurangkan kehilangan kuasa semasa proses penghantaran elektrik
Helps to reduce the power loss in the transmission process
(d) (i) P
I=
V
2 3 106
I= 1
40 3 103
= 50 A 1 2
(ii) P = I 2R
= 502 3 2 1
= 5 kW 1 2
JUMLAH 20
Bab 5 Elektronik
Electronics
KERTAS 2
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
1 (a) Diod/Diode 1 1
(b) p n
2 2
(c) (i) Ya, mentol menyala. 1 1
Yes ,the bulb will light up.
(ii) Bekalan arus ulang-alik mengalir dalam dua arah. Maka, terdapat arus mengalir melalui 2 2
diod semasa pincang kedepan dan menyalakan mentol
The alternating current supply will moves in two directions. So, there is current moves in forward-
biased through the diode and the bulb will light up.
JUMLAH 6
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 16
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 16 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
2 (a) Alur elektron berhalaju tinggi/Beam of electron moving at high speed 1 1
(b) Cahaya dari filament dihalang oleh palang//Sinar katod dihalang oleh palang 1 1
Light from the filament is blocked by the cross//Cathode ray is blocked by the cross
(c) 1 mv2 = eV
2
√
v = 2 eV
m
= √ 2 (1.6 3 10-19) (3000)
9 3 10-31
= 3.27 3 107 m s-1
1
1 2
(d) (i) N
1 1
N
S
(ii) Peraturan tangan kiri Fleming/Fleming’s left- hand rule 1 1
JUMLAH 6
3 (a) Pendopan ialah proses menambahkan bendasing kepada semikonduktor untuk 1 1
menambahkan kekonduksian
FIZIK
Doping is a process of adding a certain amount of specific impurities to a semiconductor to increase
the conductivity
(b) • Pada Rajah 3.1, diod jenis-p disambungkan kepada terminal negatif sel kering 1
manakala pada Rajah 3.2, diod jenis-n disambungkan kepada terminal positif sel
kering
In Diagram 3.1, p-type diode is connected to negative terminal of dry cell while in Diagram 3.2,
n-type diode is connected to positive terminal of dry cell
• Mentol pada Rajah 3.1 tidak menyala, manakala mentol pada Rajah 3.2 menyala 1
The bulb in Diagram 3.1 is not light up, while the bulb in Diagram 3.2 is light up
• Tiada bacaan ammeter pada Rajah 3.1 berbanding pada Rajah 3.2. Ini menunjukkan 1
tiada arus mengalir dalam Rajah 3.1
There is no ammeter reading in Diagram 3.1 compared to Diagram 3.2. This is shown that there
is no current flow in Diagram 3.1
• Mentol akan menyala apabila diod jenis-p disambungkan kepada terminal positif 1
sel kering
The bulb will light up when p-type diode is connected to positive terminal of dry cell
• Arus akan mengalir apabila diod jenis-p disambung kepada terminal positif sel 1 5
kering atau pincang ke depan
The current will flow when p-type diode is connected to the positive terminal of dry cell or in
forward bias
(c) (i)
Kotak Y
Box Y
1 1
Lukis simbol dan arah yang betul
Draw correct symbol and direction
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 17
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 17 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
(ii) • Lukis bentuk gelombang licin 1
Draw smooth waveform
• Kapasitor menyimpan cas apabila arus mengalir 1
Capacitors store charge when current flow
• Kapasitor dinyahcaskan apabila tiada arus mengalir 1 3
Capacitor discharged when current does not flow
(d) Ciri-ciri Huraian
Characteristics Explanation
PPC diganti dengan termistor Rintangan berkurang apabila suhu 2
LDR is replaced by thermistor meningkat
Resistance decreases when temperature
increases
Tukarkan kedudukan termistor dan R1 V merentasi R1 meningkat apabila suhu 2
Change position of thermistor and R1 bilik panas
V across R1 increases when the room is hot
Suis geganti menggantikan LED Untuk menghidupkan litar sekunder// 2
Relay switch replace LED Menghidupkan suis kipas
To switch on secondary circuit//To switch on
the fan
Kipas disambung secara selari Semua kipas menerima voltan sebanyak 2
Fans are arranged in parallel 240 V//Semua kipas berfungsi walaupun
satu kipas rosak
All fans received 240 V voltage//Other fans
still functioning eventhough one fan did not
function
Perintang disambungkan pada litar tapak Mengurangkan arus ke pemancar 10
2
transistor Limit the current to the transmitter
Resistor is connected to the base of transistor
JUMLAH 20
Bab 6 Fizik Nuklear
Nuclear Physics
KERTAS 2
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
1 (a) (i) Pelakuran nuklear/Nuclear fusion 1 1
(ii) Suhu tinggi dan tekanan tinggi/High temperature and high pressure 1 1
(b) (i) Positif/Positive 1 1
(ii) 2 1 1
JUMLAH 4
2 (a) Keradioaktifan ialah reputan secara spontan nukleus yang tidak stabil dengan 1 1
memancarkan zarah bertenaga atau foton.
Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of unstable nucleus with the emission of energetic
particles or photons.
(b) (i) X –Zarah alfa/Alpha particle 1 1
Z – Zarah beta/Beta particle
(ii) Z lebih ringan daripada X/Z is lighter than X 1 1
(c) (i) Pembelahan nuklear/Nuclear fission 1 1
(ii) 56 1 1
(iii) E = mc2
= (2.988 3 10-11)(3 3 108)2 1
= 2.67 3 10-11 J 1 2
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 18
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 18 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
(d) (i) Bagi bahan radioaktif yang kuat, pengendalian menggunakan lengan mekanikal kawalan 1 1
jauh//Bagi bahan radioaktif yang lemah, pengendalian menggunakan forsep//Pekerja
memakai plat fotografi//menggunakan sarung tangan//cermin mata pelindung
strong radioactive substances are handled using remote controlled mechanical arms from a safe
distance//weak radioactive substance can be handled by forceps//Workers should wear a special
badge//wearing protective suits and gears such as gloves//eye glasses
(ii) Elakkan persentuhan terus//Mengesan jumlah radiasi yang terdedah 1 1
To avoid direct contact//Detect the amount of radiation they are exposed to
[Alasan hendaklah berkaitan dengan jawapan di d(i)]
[Reason must be related to answer in d(i)]
JUMLAH 9
3 (a) Isotop dengan nukleus tidak stabil yang boleh memancarkan sinaran radioaktif 1 1
Isotopes with unstable nuclei that can emit radioactive radiation
(b) • Apabila paras air tinggi, sinar radioaktif melalui air 1
When the water level is high, radioactive rays pass through the water
• Air menyerap sebahagian sinaran 1
Water absorbs part of the radiation
• Pengesan menunjukkan bacaan berkurang 1
Detector shows the reading is decreases
• Pengesan mengaktifkan pengawal injap keluar untuk membuka injap keluar 1 4
Detector activates the outlet valve controller to open the outlet valve
(c) Ciri-ciri Huraian
Characteristics Explanation
FIZIK
Keaktifan awal adalah tinggi Lebih tinggi daripada sinaran latar 2
Initial activity is high Much higher than the background radiation
Sinaran radioaktif ialah beta Kuasa penembusan dan kurang bahaya
Radioactive emission is beta kepada pengguna 2
High penetrating power and less dangerous
to the user
Setengah hayat yang panjang Tahan lama//Tidak perlu diganti selalu 2
Long half-life Can last longer//No need to change often
Keadaan fizikal radioisotop ialah pepejal Lebih mudah dikendalikan 2
The physical state of the radioisotope is solid Easier to handle
Radioisotop yang paling sesuai ialah jenis R (Iron-60) kerana mempunyai keaktifan 2 10
awal yang tinggi, sinaran radioaktif ialah beta, setengah hayat yang panjang dan keadaan
fizikal radioisotop ialah pepejal.
The most suitable radioisotope is type R (Iron-60) because it contains high initial activity, radioactive
emission is beta, long half-life and the physical state of the radioisotope is solid.
(d) (i) 83 −35 = 48 1 1
(ii) Kripton/Krypton 1 1
83 83 0
(iii) 35
Br → Kr + e
36 −1
1 1
(iv) Bilangan sepatruh hayat dalam 9.6 jam
Number of half-life in 9.6 hours
9.6
=
2.4
= 4 separuh hayat/half-life 1
Keaktifan/Activity
1 1 1 1
2 2 2 2
= 384 → 192 → 96 → 48 → 24
\ 24 bilangan per minit/counts per minute 1 2
JUMLAH 20
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 19
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 19 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Bab 7 Fizik Kuantum
Quantum Physics
KERTAS 2
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
1 (a) Kesan fotoelektrik/Photoelectric effect 1 1
(b) (i) Kesan fotoelektrik tidak berlaku kerana frekuensi cahaya merah rendah 1 1
The photoelectric effect does not occur because of the low frequency of red light
(ii) Kesan fotoelektrik berlaku kerana frekuensi cahaya ultraungu tinggi 1 1
The photoelectric effect occurs due to the high frequency of ultraviolet light
(iii) Kesan fotoelektrik berlaku kerana frekuensi cahaya ultraungu tinggi 1 1
The photoelectric effect occurs due to the high frequency of ultraviolet light
(iv) Kesan fotoelektrik tidak berlaku kerana fotoelektron bercas negatif, ia akan ditarik oleh 1 1
plat zink yang bercas positif
The photoelectric effect does not occur because the photoelectron is negatively charged, it will be
attracted by the positively charged zinc plate
(c) P = nhf = nh ( λc )
3 3 108
0.30 3 10-3 = n 3 6.63 3 10-34 3 1
6.35 3 10-9
n = 9.58 3 1014 foton sesaat/photons per second 1 2
JUMLAH 7
2 (a) (i) Kesan fotoelektrik ialah pemancaran elektron daripada permukaan logam yang disinari 1 1
dengan gelombang elektromagnet
Photoelectric effect is phenomenon of electron emission from a metal surface when it is illuminated
by an electromagnetic waves
(ii) Mengumpul dan menerima pancaran elektron daripada katod 1 1
Collects or receives electron beam from the cathode
(b) (i) λ= h
mv
= 6.63 3 -10
10-34 1
5.0 3 10 (0.4)
= 3.32 3 10–24 m 1 2
(ii) Tidak. Panjang gelombang de Broglie pasir terlalu pendek (10–24 m) dibandingkan 1,1 2
dengan ukuran lubang (1 mm). Sekiranya ukurannya lubang itu dikurangkan lebih jauh
untuk mendekati urutan panjang gelombang de Broglie, pasir tidak akan dapat dilalui
melaluinya kerana diameter pasir adalah 0.07 mm.
No. The de Broglie wavelength of the sand is too short (10–24 m) compared to the size of the hole (1 mm).
If the size of the hole is further reduced to approximate the order of the de Broglie wavelength, the sand
will not be able to pass through it because the diameter of the sand is 0.07 mm
JUMLAH 6
c
4 (a) (i) E = nh ( )
λ
n = Eλ
hc
= (10-18) 3 (550 3 10-9)
1
(6.63 3 10-34) 3 (3.00 3 108)
= 2.77 = 3 (nombor bulat/ whole number) 1 2
(ii) Tenaga cahaya dipindah dalam bentuk paket tenaga yang diskrit 1 1
Light energy is transferred in the form of discrete energy packets
(iii) Jika panjang gelombang ambang bagi had penglihatan manusia adalah 550 nm, tenaga foton:
If the threshold wavelength for the limit of human vision is 550 nm, the photon energy:
E=h ( cλ )
= (6.63 3 10-34) 3 ( 3.00
550 3 10 )
3 10 8
-9
= 3.62 × 10-19 J
1 eV = 1.60 3 10-19 J
E = 2.3 eV 1
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 20
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 20 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Sub Jumlah
Soalan Cadangan jawapan
markah markah
Kuprum dan besi mempunyai nilai fungsi kerja lebih tinggi dari 2.3 eV, maka tidak 1 2
memancar elektron apabila disinari dengan cahaya nampak
Copper and iron have a working function value higher than 2.3 eV, thus they do not emit electrons
when irradiated with visible light
(b) Ciri-ciri Huraian
Characteristics Explanation
Keamatan sumber cahaya yang rendah Menjimatkan tenaga
Low light source intensity Save energy 2
Jenis bahan sel foto ialah semikonduktor Saiz kecil dan penggunaan tenaga elektrik
Type of photocell material is semiconductor yang sedikit 2
Small size and low electrical energy consumption
Fungsi kerja yang rendah Kecekapan sistem pintu automatik yang
Low work function lebih tinggi 2
High efficiency of automatic door system
Sumber cahaya inframerah Tidak boleh tampak dan lebih selamat 2
Infrared light source Invisible and safer
Sel foto yang paling sesuai ialah R kerana mempunyai keamatan sumber cahaya yang
rendah, jenis bahan sel foto ialah semikonduktor, fungsi kerja yang rendah dan sumber 2 10
cahaya inframerah.
The most suitable photo cell is R because it contains low light source intensity, type of photocell
material is semiconductor, low work function and infrared light source.
FIZIK
(c) (i) P = nhf = nh c ( )
λ
Pλ 1
n =
hc
(7.5 3 10-3) 3 (700 3 10-9)
= (6.63 3 10-34) 3 (3.0 3 108) 1
= 2.6 3 1016 s-1 1 3
h
(ii) p =
λ
(6.63 3 10-34)
=
(700 3 10-9)
= 9.47 3 10-28 kg m s-1 1
= 2.5 3 10-11 kg m s-1 1 2
JUMLAH 20
© Hak cipta SBP Zon Utara 21
Ans Platinum Fizik.indd 21 10/12/21 11:53 AM
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Tingkatan 4: Bab 1 PengukuranDokumen28 halamanTingkatan 4: Bab 1 PengukuranIceStrong 123Belum ada peringkat
- Skema PPT F4 Physics P2 2022Dokumen9 halamanSkema PPT F4 Physics P2 2022Srikanth SagardevanBelum ada peringkat
- Ee Jembatan KamanDokumen148 halamanEe Jembatan KamanagusBelum ada peringkat
- Jawapan Ujian Amali SBPDokumen24 halamanJawapan Ujian Amali SBPAlexandra Chieng100% (1)
- Rks Tajab AyuuuDokumen257 halamanRks Tajab Ayuuuvirga septa hadiBelum ada peringkat
- Ee Jembatan LutipDokumen115 halamanEe Jembatan LutipagusBelum ada peringkat
- Boq KosongDokumen10 halamanBoq KosongrianBelum ada peringkat
- Ee Jembatan MuyuDokumen125 halamanEe Jembatan MuyuagusBelum ada peringkat
- Perhitungan RAB Jembatan 6 MDokumen3 halamanPerhitungan RAB Jembatan 6 Mluthfi qolbi100% (1)
- Scalar Quantity Tendency of An Object To Resist Change in Initial Motion. Mass Q. The Load Has Inertia. P. Tension at P Is Larger Than QDokumen5 halamanScalar Quantity Tendency of An Object To Resist Change in Initial Motion. Mass Q. The Load Has Inertia. P. Tension at P Is Larger Than QKRISTA SEMA ANAK EDWIN MEREKA MoeBelum ada peringkat
- Skema Fizik Tingkatan 4 PPT 2021Dokumen3 halamanSkema Fizik Tingkatan 4 PPT 2021Roszana SelamatBelum ada peringkat
- S Fiz2 PHG 2015Dokumen10 halamanS Fiz2 PHG 2015nusaibahBelum ada peringkat
- Analisa Stabilitas Struktur Dinding Penahan Tanah Mansahang OkDokumen14 halamanAnalisa Stabilitas Struktur Dinding Penahan Tanah Mansahang Oksarilytha1Belum ada peringkat
- Daftar Kuantitas Dan HargaDokumen4 halamanDaftar Kuantitas Dan Hargajupz_freeBelum ada peringkat
- Draft Soal Quiz Pondasi 230621 - R3Dokumen4 halamanDraft Soal Quiz Pondasi 230621 - R3StuergeonBelum ada peringkat
- HPS REFOCUSING PAKET RATE RATE 2020-Rehab PDFDokumen3 halamanHPS REFOCUSING PAKET RATE RATE 2020-Rehab PDFTri Sunanda FathanahBelum ada peringkat
- Answer P2 Mid Year F4Dokumen10 halamanAnswer P2 Mid Year F4EVELYN WONG KHE XIN MoeBelum ada peringkat
- B344 ÙyýDokumen1 halamanB344 Ùyýyudhi engineerBelum ada peringkat
- Ujian Tengah Semester-SlametDokumen8 halamanUjian Tengah Semester-SlametSlamet PrabowoBelum ada peringkat
- Mk. M.proyek Contoh RabDokumen2 halamanMk. M.proyek Contoh RabRandicivilBelum ada peringkat
- 2.daftar Kuantitas Dan HargaDokumen2 halaman2.daftar Kuantitas Dan Hargafazri 488Belum ada peringkat
- Rab Laston Ac BCDokumen10 halamanRab Laston Ac BCerichen15Belum ada peringkat
- Skema Trial Fizik Kedah k2Dokumen10 halamanSkema Trial Fizik Kedah k2Muhd RazlanBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan GLB Dan GLBBDokumen13 halamanLaporan GLB Dan GLBBFadhila Putri50% (2)
- Skema K2 Bab 1 - 2Dokumen3 halamanSkema K2 Bab 1 - 2Hakim IsamudinBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar Kuantitas Dan Harga Spesifikasi Umum 2018Dokumen2 halamanDaftar Kuantitas Dan Harga Spesifikasi Umum 2018Josh Fereira PBelum ada peringkat
- CCO Jembatan TPU Sarimulya (Rev2 08-11-2021)Dokumen31 halamanCCO Jembatan TPU Sarimulya (Rev2 08-11-2021)Kiu NugrohoBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Pratikum GLB Dan GLBBDokumen14 halamanLaporan Pratikum GLB Dan GLBBM. Aizri Fadillah100% (1)
- Standar Satuan Harga Pekerjaan Bina Marga 2021Dokumen37 halamanStandar Satuan Harga Pekerjaan Bina Marga 2021Sulisyanto MasbayanBelum ada peringkat
- Rab Jalan Pasar Kapar BaruDokumen2 halamanRab Jalan Pasar Kapar Barudin mahyaBelum ada peringkat
- Cadangan Skema Pemarkahan Fiizik K2 Pat F4 2022Dokumen9 halamanCadangan Skema Pemarkahan Fiizik K2 Pat F4 2022Arina IrawanBelum ada peringkat
- Dokumen MC 0% Ruas Jalan Lembasada - Bambarimi TA 2022Dokumen28 halamanDokumen MC 0% Ruas Jalan Lembasada - Bambarimi TA 2022Fandi's Classic100% (1)
- Tugas 3Dokumen4 halamanTugas 3Ganda WilsonBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh BOQ JalanDokumen1 halamanContoh BOQ Jalandarmawan.jugaBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Perhitungan Alinyemen Horizontal PDFDokumen14 halamanContoh Perhitungan Alinyemen Horizontal PDFJoko Sucahyo100% (1)
- Laporan Praktikum PFRDokumen18 halamanLaporan Praktikum PFRAwayni Husna100% (1)
- Muhammad Hardyansyah 1810611017Dokumen7 halamanMuhammad Hardyansyah 1810611017Ainiya Faida AzmiBelum ada peringkat
- AHSP Bantaeng 6Mm-BaruDokumen1 halamanAHSP Bantaeng 6Mm-BaruDaengIcalBelum ada peringkat
- Pedoman Penskoran Uh Fisika X Besaran Dan SatuanDokumen3 halamanPedoman Penskoran Uh Fisika X Besaran Dan SatuanAli Akbar Al AfghaniBelum ada peringkat
- 1 BoqDokumen29 halaman1 Boqwiwi tonoBelum ada peringkat
- BOQJL. GANTING WAGE Ok KOSONGANDokumen48 halamanBOQJL. GANTING WAGE Ok KOSONGANBenben BravoBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas 1 Ade ManikDokumen51 halamanTugas 1 Ade Manikade manikBelum ada peringkat
- Skema Pemarkahan KKPAT SBP Fizik Tg4Dokumen42 halamanSkema Pemarkahan KKPAT SBP Fizik Tg4siti nurhanimsaBelum ada peringkat
- CCO Puskeswan SumberDokumen3 halamanCCO Puskeswan SumberTeguh SantosoBelum ada peringkat
- Lembar Kerja TKDNDokumen9 halamanLembar Kerja TKDNRoy Minta MaafBelum ada peringkat
- Boq Kunduran - DoplangDokumen24 halamanBoq Kunduran - DoplangBinamarga2 dpuprBelum ada peringkat
- Matrik Triagatona 2021 RevisiDokumen691 halamanMatrik Triagatona 2021 RevisiPT LESTARI INDOMINERAL JAYABelum ada peringkat
- Mingguan - Bulanan Sui Kelik - Siduk 2 (Myc) Cek2 - Add 01 Ok (Sip) (62) MC 22 Desember 2021Dokumen1.272 halamanMingguan - Bulanan Sui Kelik - Siduk 2 (Myc) Cek2 - Add 01 Ok (Sip) (62) MC 22 Desember 2021Sofyan SuriBelum ada peringkat
- Rab Batam 2Dokumen2 halamanRab Batam 2CV AKUNINDO CITRA BINTANBelum ada peringkat
- BAB V Perencanaan Dan Perhitungan Dimensi Saluran IrigasiDokumen40 halamanBAB V Perencanaan Dan Perhitungan Dimensi Saluran IrigasiRA ThriftshopBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar KHDokumen1 halamanDaftar KHFitriyani SyahrirBelum ada peringkat
- Dimensi SaluranDokumen15 halamanDimensi Saluran04 Gneis PermataBelum ada peringkat
- Progress Jembatan Sempit Cs. (Add-02)Dokumen41 halamanProgress Jembatan Sempit Cs. (Add-02)ridjalBelum ada peringkat
- RAB Spam - OkDokumen89 halamanRAB Spam - OkMuhammad fikriBelum ada peringkat
- Boq Puro Rogdog MatotonaDokumen1 halamanBoq Puro Rogdog MatotonaarinsBelum ada peringkat
- Rab JembatanDokumen2 halamanRab JembatanRahmat AkbarBelum ada peringkat
- RAB Perhitungan Tugas (Pekerjaan Jalan)Dokumen207 halamanRAB Perhitungan Tugas (Pekerjaan Jalan)fuad tri hutomoBelum ada peringkat