Dasar Telkom 3 Modulasi Frekuensi (FM)
Diunggah oleh
Anugrah RamadhanHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Dasar Telkom 3 Modulasi Frekuensi (FM)
Diunggah oleh
Anugrah RamadhanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
MODULASI ANALOG
Frequency Modulation ( FM )
Phase Modulation (PM)
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 1
Obyektif Perkuliahan
Dapat memahami teknik modulasi frekuensi ( FM )
Dapat memahami teknik modulasi phase ( PM )
Dapat memahami indeks modulasi
Dapat memahami spektrum magnitudo dan bandwidth
Referensi :
MS Iqbal, 2001, Diktat dasar Telkom. Jurusan Teknik
Elektro FT, Unram,
Kennedy & Davis, 1993, Electronic Comm. System,
Fourth Ed, Mc Graw Hill.
Dennis Roddy & John Coolen, 1995, Electronic
Comm. System, Fourth Ed, Prentice Hall Inc.
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 2
Skema Modulasi Frekuensi
Sinyal pemodulasi em(t) digunakan untuk mengontrol
frekuensi carrier fc
Deviasi frekuensi sebanding dg tegangan pemodulasi
Notasi konstanta deviasi frekuensi adalah k
Satuan k adalah hertz / volt atau Hz / v
Frekuensi sesaat sinyal FM :
fi(t) = fc + k em(t)
i(t) = 2 fi(t)
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 3
Frequency Modulation ( FM )
Asumsi : em t Em max cos 2 f m t ec t Ec max cos 2 f c t
Notasi umum Gelombang FM : eFM t Ec max cos t
t
dengan t diperoleh dari integral : t dt
i t
0
mengingat fungsi modulator FM untuk mengubah parameter frekuensi
sesaat osilator, maka :
f i t f c k e m t t i t dt
t
sehingga
0
2 f c k e m t dt
t
0
e m t dt
t
2 fc t 2 k
0
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 4
Frequency Modulation ( FM )
Asumsi : em t Em max cos 2 f m t ec t Ec max cos 2 f c t
frekuensi osilasi sesaat FM adalah : f i t f c k e m t
Delta frek = k x Em mak f c k E m max cos (2 f m t )
diperoleh gelombang FM : f c f cos (2 f m t )
e t Ec max cos t
Ec max cos
2 f c t 2 f 0 cos ( 2 f m t ) dt
t
f
Ec max cos
2 f c t sin ( 2 f m t )
f m
Ec max cos 2 f c t sin ( 2 f m t )
Indeks modulasi beta = delta f / fm
Spektrum gelombang FM tergantung pada nilai index modulasi dan
tabel Bessel dengan jarak antar komponen sebesar fm .
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 5
Frequency Modulation ( FM )
Asumsi : em t Em max sin 2 f m t ec t Ec max cos 2 f c t
frekuensi osilasi sesaat FM adalah : f i t f c k e m t
f c k E m max sin ( 2 f m t )
diperoleh gelombang FM : f c f sin (2 f m t )
e t Ec max cos t
Ec max cos
2 f c t 2 f 0 sin ( 2 f m t ) dt
t
f
Ec max cos
2 f c t cos ( 2 f m t )
f m
Ec max cos 2 f c t cos ( 2 f m t )
Spektrum gelombang FM tergantung pada nilai index modulasi dan
tabel Bessel dengan jarak antar komponen sebesar fm .
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 6
Skema Modulasi Phase
Sinyal pemodulasi em(t) digunakan untuk mengontrol
fase carrier (t)
Deviasi fase sebanding dg tegangan pemodulasi
Notasi konstanta deviasi fase adalah K
Satuan K adalah rad / volt
Fase sesaat sinyal FM :
(t) = c + K em(t)
c tidak mempengaruhi proses modulasi
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 7
Phase Modulation ( PM )
Asumsi : em t Em max cos 2 f m t
ec t Ec max cos 2 f c t c
Perubahan fase sesaat PM adalah : t c k e m t
dengan membuat c = 0 diperoleh : t k e m t
berikutnya akan diperoleh gelombang PM :
e t Ec max cos 2 f c t t
Ec max cos 2 f c t k Em t
Ec max cos 2 f c t k Em max cos (2 f m t )
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 8
Contoh soal 1
Sinyal pemodulasi em(t) = 3 cos ( 2 103 t – 90o ) v
digunakan untuk modulasi phase pada gelombang
pembawa cosinus dengan Ec max = 10 volt dan fc = 20 kHz.
Konstanta perubahan fase K = 2 rad / volt.
Tentukan pers gelombang termodulasinya.
Jawab
Fungsi fase gelombang termodulasinya :
m(t) = k em(t)
= 2 x 3 cos ( 2 103 t – 90o ) rad
= 6 sin ( 2 103 t ) rad
Fungsi gelombang termodulasinya :
e(t) = 10 cos ( 4 104 t + 6 sin ( 2 103 t ))
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 9
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 10
Contoh soal 2
Sinyal pemodulasi em(t) = 3 cos ( 2 103 t ) volt
digunakan untuk modulasi frekuensi pada gelombang
pembawa cosinus dengan Ec max = 10 volt dan fc = 20 kHz.
Konstanta perubahan frekuensi k = 2000 Hz / volt.
Tentukan pers gelombang termodulasinya.
Jawab
Deviasi maks f = 2000 x 3 = 6000 Hz
Indeks modulasi = f / fm = 6000 / 1000 = 6
Pers FM :
e(t) = Ec max cos ( 2 fc t + sin ( 2 fm t ))
e(t) = 10 cos ( 4 104 t + 6 sin ( 2 103 t ))
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 11
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 12
Prinsip Dasar Rangkaian Modulator FM
+ Vcc
RFC
C3
Tuning
adj. FM Output
Cc
L1
RFC C2
+ Amplitudo FM
tetap, tetapi
V mod Cd C1 Frekuensi osc
Cby berubah sebesar
-
1
f
Kapasitansi Cd berubah 2 L1 C Total
tergantung Vmod
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 13
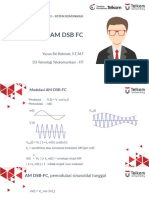
• % Contoh grafik sinyal FM
• %
• Fs = 1440;
• t = 0 : 1/Fs :2 ;
• x = 0.4*sin (2*pi*1*t);
• %
• %
• car = cos (2*pi*15*t);
• FM = cos (2*pi*15*t - 10*cos(2*pi*1*t));
• %
• figure, plot(t,FM,t,x,'r--');
• xlabel(' detik ')
• ylabel(' Amplitudo ( volt ) ')
• title(' Gelombang termodulasi Frekuensi Modulasi ')
• grid on;
• % hold on;
• % end
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 14
Frek maks pada teg maks
Frek min pada teg min
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 15
• % Contoh grafik sinyal FM
• %
• Fs = 1440;
• t = 0 : 1/Fs :2 ;
• x = 0.4*sin (2*pi*1*t) + 0.5*sin (2*pi*2*t);
• %
• %
• car = cos (2*pi*15*t);
• FM = cos (2*pi*15*t - 4*cos(2*pi*1*t) - 3*cos(2*pi*2*t));
• %
• figure, plot(t,FM,t,x,'r--');
• xlabel(' detik ')
• ylabel(' Amplitudo ( volt ) ')
• title(' Gelombang termodulasi Frekuensi Modulasi ')
• grid on;
• % hold on;
• % end
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 16
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 17
• % Contoh grafik sinyal FM untuk masukan diskrit
• clear all
• Fs = 1000; Fc = 20;
• t = [0 : Fs ]‘ / Fs ; % Sampling times
• x(1:100) = -10*ones(100,1) ; x(101:200) = zeros(100,1) ;
• x(201:500) = 30*ones(300,1); x(501:700) = -10*ones(200,1);
x(701:800) = zeros(100,1); x(801:900) = 30*ones(100,1);
• x(901:1001) = -10*ones(101,1);
• dev = 1; % Frequency deviation in modulated signal
• %
• y = fmmod(x,Fc,Fs,dev); % Modulate.
• figure, subplot(3,1,1); plot(t,x);
• title(' Gelombang Termodulasi FM dengan masukan diskrit ' )
• grid on ;
• subplot(3,1,[2:3]); plot(t,y)
• axis([0 1 -1.2 1.2])
• grid on ;
• % end
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 18
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 19
• % Contoh grafik sinyal FM untuk masukan biner bipolar
• clear all
• Fs = 1000; Fc = 20;
• t = [0 : Fs]‘ / Fs; % Sampling times
• x1(1:200) = -10*ones(200,1); x1(201:500) = 10*ones(300,1);
• x1(501:700) = -10*ones(200,1); x1(701:800) = 10*ones(100,1);
x1(801:900) = -10*ones(100,1); x1(901:1001) = 10*ones(101,1);
• dev = 1; % Frequency deviation in modulated signal
• %
• y1 = fmmod(x1,Fc,Fs,dev); % Modulate
• figure, subplot(3,1,1); plot(t,x1); axis([0 1 -12 12])
• title(' Gelombang Termodulasi FM dengan masukan biner
bipolar ' )
• grid on ;
• subplot(3,1,[2:3]); plot(t,y1)
• axis([0 1 -1.2 1.2])
• grid on ;
• % end
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 20
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 21
Spektrum Frekuensi FM & PM
• Spektrum amplitudo sinyal FM dan PM
tergantung pada indeks modulasi
• Amplitudo kurang dari 1 % diabaikan
• Komponen j n fungsi bessel menyatakan
amplitudo untuk harga yang ditinjau
• J0 bersesuaian dengan amplitudo carrier
• Jk bersesuaian dengan amplitudo pada
frek fc ± k fm
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 22
Tabel fungsi Bessel dengan amplitudo ternormalisasi 1 Volt
x n atau order
( β) J0 J1 J2 J3 J4 J5 J6 J7 J8 J9 J 10 J 11
0.00 1.00 - - - - - - - - - - -
0.25 0.98 0.12 - - - - - - - - - -
0.50 0.94 0.24 0.03 - - - - - - - - -
1.00 0.77 0.44 0.11 0.02 - - - - - - - -
1.50 0.51 0.56 0.23 0.06 0.01 - - - - - - -
2.00 0.22 0.58 0.35 0.13 0.03 - - - - - - -
2.50 - 0.05 0.50 0.45 0.22 0.07 0.02 - - - - - -
3.00 - 0.26 0.34 0.49 0.31 0.13 0.04 0.01 - - - - -
4.00 - 0.40 - 0.07 0.36 0.43 0.28 0.13 0.05 0.02 - - - -
5.00 - 0.18 - 0.33 0.05 0.36 0.39 0.26 0.13 0.05 0.02 - - -
6.00 0.15 - 0.28 - 0.24 0.11 0.36 0.36 0.25 0.13 0.06 0.02 - -
7.00 0.30 0.00 - 0.30 - 0.17 0.16 0.35 0.34 0.23 0.13 0.06 0.02 -
8.00 0.17 0.23 - 0.11 - 0.29 - 0.10 0.19 0.34 0.32 0.22 0.13 0.06 0.03
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 23
Contoh penggunaan tabel Bessel
• Misalnya nilai = 0,5 maka komponen
spektrum amplitudonya :
• Carrier ( fc ) J0(0,5) = 0,94
• Side band 1 ( fc ± fm ) J1(0,5) = 0,24
• Side band 2 ( fc ± 2 fm ) J2(0,5) = 0,03
• Dari komponen terlihat lebar bandwidth
BFM = 2 n fm = 4 fm
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 24
Spektrum untuk = 0,5
0,94
0,24 0,24
0,03 0,03
fc - 2 fc - fm fc fc + fm fc + 2 fm
fm Bandwidth = 4 fm
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 25
Frequency Modulation ( FM )
Contoh : em t 0,4 sin 2 100 t ec t cos 2 800 t
dengan k = 750 Hz/volt , maka : f i t f c k e m t
Omega/kec sudut = 2x pi x frek 800 750 x 0,4 sin ( 2 100 t )
diperoleh gelombang FM : 800 300 sin (2 100 t )
fm = 100 Hz e t cos t
fc = 800 Hz
cos 2 800 t 2 300 sin (2 100 t ) dt
t
0
300
cos 2 800 t cos (2 100 t )
100
cos 2 800 t 3 cos (2 100 t )
Spektrum gelombang FM tergantung pada nilai index modulasi = 3 dan
tabel Bessel dengan jarak antar komponen sebesar 100 Hz
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 26
Contoh penggunaan tabel Bessel
• Tabel Bessel nilai = 3 maka komponen spektrum
amplitudonya :
• Carrier (800) J0(3) = 0,26
• Side band 1 ( 800 ± 100 ) J1(3) = 0,34
• Side band 2 ( 800 ± 200) J2(3) = 0,49
• Side band 3 ( 800 ± 300) J3(3) = 0,31
• Side band 4 ( 800 ± 400) J4(3) = 0,13
• Side band 5 ( 800 ± 500) J5(3) = 0,04
• Side band 6 ( 800 ± 600) J6(3) = 0,01
• Dari komponen terlihat lebar bandwidth
BFM = 2 n fm = 2 x 6 x 100 = 1200 Hz
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 27
Spektrum untuk = 3
0,49 0,49
0,34 0,34
0,31 0,31
0,26
0,13 0,13
0,04 0,04
0,01 0,01
Hz
200 500 800 1100 1400
Bandwidth = 12 x 100 = 1200 Hz
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 28
Bila E cmax = 2 volt, maka amplitudo dikali 2
0,98 0,98
0,68 0,68
0,62 0,62
0,52
0,26 0,26
0,08 0,08
0,02 0,02
Hz
200 500 800 1100 1400
Bandwidth = 12 x 100 = 1200 Hz
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 29
• % Contoh grafik SPEKTRUM AMPLITUDO sinyal FM
• %
• Fs = 1600*2 ;
• t = 0 : 1/Fs :2 ;
• x = 0.4*sin (2*pi*100*t); % frekuensi pemodulasi 100 Hz
• car = cos (2*pi*800*t); % frekuensi carrier 800 Hz
• FM = cos (2*pi*800*t - 3*cos(2*pi*100*t)); %=3
• %
• % untuk fft gelombang FM
• dataFM = fft(FM,512) ;
•
• % The power spectrum, a measurement of the power at various frequencies, is
• Pyy_FM = abs(dataFM) / 256 ;
•
• % Graph the first 257 points
• f_FM = Fs*(0:256)/512 ;
• figure, plot(f_FM,Pyy_FM(1:257))
• title(‘ Spektrum Frequency dari sinyal FM dengan beta = 3 ')
• xlabel(‘ Frequency (Hz) ')
• ylabel(‘ Amplitudo ternormalisasi pada 1 Volt ‘)
• grid on:
• % end
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 30
fc
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 31
• % Contoh grafik SPEKTRUM AMPLITUDO sinyal FM
• %
• Fs = 1600*2 ;
• t = 0 : 1/Fs :2 ;
• x = 0.4*sin (2*pi*100*t)+0.5*sin (2*pi*200*t);
• car = cos (2*pi*800*t);
• FM = cos (2*pi*800*t - 3*cos(2*pi*100*t) - 1*cos(2*pi*200*t));
• %
• % untuk fft gelombang FM
• dataFM = fft(FM,512) ;
•
• Pyy_FM = abs(dataFM) / 256 ;
•
• % Graph the first 257 points
• f_FM = Fs*(0:256)/512;
• figure, plot(f_FM,Pyy_FM(1:257))
• title(‘ Spektrum Frequency dari sinyal FM dengan beta 3 & 1 ')
• ylabel(‘ Amplitudo ternormalisasi pada 1 Volt ‘)
• xlabel(‘ Frequency (Hz) ')
• % end
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 32
fc
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 33
Bandwidth Aturan Carson
• Amplitudo kurang dari 5 % diabaikan
• Komponen j n fungsi bessel (berdasarkan
tabel) maks bersesuaian dengan n = +1
• J0 bersesuaian dengan amplitudo carrier
• Jk bersesuaian dengan amplitudo pada
frek fc ± k fm
• Maka : BFM = 2 ( + 1) fm
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 34
Contoh soal 3
Regulasi untuk siaran FM menyatakan deviasi frekuensi
maksimum yang diijinkan 75 kHz, dan frek pemodulasi
maksimum yang diijinkan adalah 15 kHz. Hitunglah
bandwidth maksimum yang diperlukan.
Jawab
Deviasi maks f = 75 kHz
Indeks modulasi = f / fm = 75 / 15 = 5
maka :
Bmaks = 2 (+1) fm = 2 (5+1) 15 kHz
= 180 kHz BW FM standarnya 200 kHz
berarti ada guard band sebesar
20 kHz antar kanal
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 35
Problem
Suatu sinyal pemodulasi diberikan oleh
em(t) = 9 cos (6 103 t + 27o ) volt
digunakan memodulasi frekuensi dari sinyal
carrier berbentuk sinus yang mempunyai
Ec max = 3 Volt, dan frekuensi carrier 80 kHz.
Bila konstanta perubahan frekuensi adalah
2,2 kHz / volt, tentukan sinyal FM, spektrum
FM dan lebar bandwidthnya.
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 36
Problem
Suatu sinyal pemodulasi diberikan oleh
em(t) = 9 cos (6 103 t + 27o ) volt
digunakan untuk memodulasi phase dari
sinyal carrier yang mempunyai ec max = 12
Volt, dan frekuensi carrier 40 kHz. Bila
konstanta perubahan phase adalah 0,7
rad / volt, tentukan lebar bandwidthnya.
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 37
THANK’S
NOW
REST TIME
Dasar Telkom SM Sasongko Pertemuan ke 3 38
Diketahui :
fm = 3000 Hz ; fc = 80000 Hz ; Ec mak = 3 volt ; Em mak = 9 volt ; k = 2,2 kHz / volt
Sinyal carrier Ec(t) = 3 Sin ( 2x pi x 80000x t ) volt
Bentuk sinyal FM(t) = 3 Sin ( Ɵ (t))
= 3 Sin ( 1,6 105 pi t – (2 x pi x 2,2 103 x 9) /( 6 x pi x 103 ) sin (6 x pi x 103 t + 27o))
= 3 Sin ( 1,6 105 pi t – 6,6 sin (6 x pi x 103 t + 27o))
Diperoleh beta = 6,6
Lebar Bandwidth = 2 x 10 x fm = 2 x 10 x 3000 = 60 kHz
Gambar Spektrum :
0,93 v 0,93 v
0,81 v
V
0,36 v 0,36 v
dst dst
0,03 v
0,03 v
50 kHz 74 kHz 77 kHz 80 kHz 83 kHz 86 kHz 110 kHz
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Dasar Telkom 2 Amplitudo Modulasi Dan DSBDokumen31 halamanDasar Telkom 2 Amplitudo Modulasi Dan DSBAnugrah RamadhanBelum ada peringkat
- BAB IIb Modulasi FrekwensiDokumen43 halamanBAB IIb Modulasi FrekwensiDeby AinunBelum ada peringkat
- Modulasi Analog FM PMDokumen35 halamanModulasi Analog FM PMPadlul BaturglemBelum ada peringkat
- Modulasi FMDokumen33 halamanModulasi FMSophie Dwivita Evans AnthenBelum ada peringkat
- 3.1 Dasar Sistem Komunikasi Analog Rev 1Dokumen45 halaman3.1 Dasar Sistem Komunikasi Analog Rev 1Aan JuniorBelum ada peringkat
- 3.1 Dasar Sistem Komunikasi Analog Rev 1Dokumen45 halaman3.1 Dasar Sistem Komunikasi Analog Rev 1Aan JuniorBelum ada peringkat
- Pengertian ModulasiDokumen9 halamanPengertian ModulasiBarito Siregar SiloBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem AMDokumen46 halamanSistem AMhahaaBelum ada peringkat
- Modulasi AnadigDokumen44 halamanModulasi AnadigAbdul Hafidz 1Belum ada peringkat
- FM PDFDokumen31 halamanFM PDFMuhammad ArsalBelum ada peringkat
- 3.1 Dasar Sistem Komunikasi Analog Rev 1Dokumen40 halaman3.1 Dasar Sistem Komunikasi Analog Rev 1Padlul BaturglemBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem FMDokumen54 halamanSistem FMRama SeptianBelum ada peringkat
- Modul - 04 Siskom1 - FMDokumen44 halamanModul - 04 Siskom1 - FMMohammed Awaluddin Al-islamiBelum ada peringkat
- Slide Persentation Celoe - Modul 1 Siskom - Dth2e3-Kode DosenDokumen32 halamanSlide Persentation Celoe - Modul 1 Siskom - Dth2e3-Kode Dosenhermas ngapungBelum ada peringkat
- Modul 6 Teknik Elektro Dasar Telekomunikasi RevBDokumen19 halamanModul 6 Teknik Elektro Dasar Telekomunikasi RevBRizki AdzBelum ada peringkat
- Slide Persentation Celoe - Modul 3 Siskom - Dth2e3-Kode DosenDokumen32 halamanSlide Persentation Celoe - Modul 3 Siskom - Dth2e3-Kode Dosenhermas ngapungBelum ada peringkat
- Slide Persentation Celoe - Modul 2 Siskom - Dth2e3-Kode DosenDokumen8 halamanSlide Persentation Celoe - Modul 2 Siskom - Dth2e3-Kode Dosenhermas ngapungBelum ada peringkat
- Modulasi SudutDokumen26 halamanModulasi SudutBudiSetiawanBelum ada peringkat
- 03 Modulasi AmplitudoDokumen13 halaman03 Modulasi AmplitudoAdam SmithBelum ada peringkat
- Modul 3-Modulasi-Am DSBSC SSB VSBDokumen37 halamanModul 3-Modulasi-Am DSBSC SSB VSBluthfiBelum ada peringkat
- ANALISA 5 FeliDokumen6 halamanANALISA 5 Felifeli ramasariBelum ada peringkat
- Prima Yogaswara - Laporan Modul 1Dokumen12 halamanPrima Yogaswara - Laporan Modul 1PRIMA YOGASWARABelum ada peringkat
- 3.1.1 Cara Gambar Sinyal AMDokumen56 halaman3.1.1 Cara Gambar Sinyal AMAan Junior100% (2)
- Bab 8 Isi Modulasi Frekuensi (FM)Dokumen25 halamanBab 8 Isi Modulasi Frekuensi (FM)Fahrur RadziBelum ada peringkat
- BAB-3.2. Modulasi Frekuensi Pertemuan Ke-10Dokumen17 halamanBAB-3.2. Modulasi Frekuensi Pertemuan Ke-10SHAFFANAH GHANIYAH MIRANDABelum ada peringkat
- 04 Modulasi Sudut 2003Dokumen34 halaman04 Modulasi Sudut 2003celvin sinagaBelum ada peringkat
- GTRN 02Dokumen51 halamanGTRN 02Amir udinBelum ada peringkat
- Dasar Telkom 4 Single Side BandDokumen35 halamanDasar Telkom 4 Single Side BandAnugrah RamadhanBelum ada peringkat
- 8 WaveletDokumen9 halaman8 WaveletHominem BonumBelum ada peringkat
- Modulasi EksponensialDokumen27 halamanModulasi EksponensialWahyu HPBelum ada peringkat
- BAB 5 Sistem Telekomunikasi Sistem Modulasi FrekuensiDokumen9 halamanBAB 5 Sistem Telekomunikasi Sistem Modulasi FrekuensiAljira AmaralBelum ada peringkat
- Bab II Modulasi AmplitudoDokumen19 halamanBab II Modulasi AmplitudoAnisa Ulya DarajatBelum ada peringkat
- FM Pak RifkyDokumen10 halamanFM Pak RifkyFia FianiBelum ada peringkat
- ModulasiDokumen33 halamanModulasiMr. SatyaSBelum ada peringkat
- Modulasi AnalogDokumen17 halamanModulasi AnalogAfdal TahirBelum ada peringkat
- Percobaan I: Modulasi AmplitudoDokumen56 halamanPercobaan I: Modulasi AmplitudoAgusl09Belum ada peringkat
- Transformasi FourierDokumen29 halamanTransformasi FourierStepanus18Belum ada peringkat
- 3.2 Modulasi Analog FM PM Rev 1Dokumen38 halaman3.2 Modulasi Analog FM PM Rev 1Aan JuniorBelum ada peringkat
- TP Siskom Modul 2Dokumen2 halamanTP Siskom Modul 2lalanfajjrinBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 2 Gelombang Mekanik BaruDokumen45 halamanBab 2 Gelombang Mekanik BaruBaiqUlfaPutriBelum ada peringkat
- GelombangDokumen12 halamanGelombangDheaa AmbarwatiBelum ada peringkat
- Analisis FrekuensiDokumen104 halamanAnalisis Frekuensidaniel gonjaloBelum ada peringkat
- Modulasi FrekuensiDokumen3 halamanModulasi FrekuensiMuhammad Najmul Fadli100% (1)
- Kuliah 4 Modulasi FrekuensiDokumen13 halamanKuliah 4 Modulasi FrekuensiOwe EwoBelum ada peringkat
- 03 Modulasi Amplitudo 2003Dokumen71 halaman03 Modulasi Amplitudo 2003Aditya WardhanaBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Sistem Modulasi Analog 1Dokumen30 halaman5 Sistem Modulasi Analog 1Bin BunBelum ada peringkat
- Modulasi AM, FM - (1) (2) ... Okt 2018Dokumen37 halamanModulasi AM, FM - (1) (2) ... Okt 2018NanagpartyBelum ada peringkat
- 175 215 1 PB PDFDokumen7 halaman175 215 1 PB PDFHendy AlvianBelum ada peringkat
- Solusi Tutorial Fisika DINAMIKADokumen6 halamanSolusi Tutorial Fisika DINAMIKADesti RiandianiBelum ada peringkat
- Dasar Telkom 4 Single Side BandDokumen35 halamanDasar Telkom 4 Single Side BandAnugrah RamadhanBelum ada peringkat
- Dasar Telkom Pert Ke 11 Dan 12 Dasar Sistem Komunikasi DigitalDokumen45 halamanDasar Telkom Pert Ke 11 Dan 12 Dasar Sistem Komunikasi DigitalAnugrah RamadhanBelum ada peringkat
- Algoritma Dan Struktur DataDokumen20 halamanAlgoritma Dan Struktur DataAnugrah RamadhanBelum ada peringkat
- Desain Sistem Kontrol Penggerak Pintu Pagar Otomatis Di Politeknik JambiDokumen7 halamanDesain Sistem Kontrol Penggerak Pintu Pagar Otomatis Di Politeknik JambiAnugrah RamadhanBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal Elektronika, Listrik Dan Teknologi Informasi Terapan: Volume 3, Terbitan 1, Desember 2021 (8 - 11)Dokumen4 halamanJurnal Elektronika, Listrik Dan Teknologi Informasi Terapan: Volume 3, Terbitan 1, Desember 2021 (8 - 11)Anugrah RamadhanBelum ada peringkat