Deformasi Strain Stress
Diunggah oleh
Sai RootsHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Deformasi Strain Stress
Diunggah oleh
Sai RootsHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
KARAKTERISTIK DEFORMASI
Strain dan Stress
HERI ANDREAS
Mahasiswa Program Doktor
Prodi Geodesi dan Geomatika ITB
E-mail : heri@gd.itb.ac.id
September 2007
1. Pengertian Deformasi
Deformasi adalah perubahan bentuk, dimensi dan posisi dari
suatu materi baik merupakan bagian dari alam ataupun buatan
manusia dalam skala waktu dan ruang
2. Penyebab Deformasi
Bila dikenai Gaya (Force) maka benda/ materi akan terdeformasi
3. Objek dari Deformasi
tektonik lempeng
pasut
atmosferik
proses hidrologi
ocean loading
proses geologi lokal
rotasi bumi
Alam
Manusia
pelapukan
erosi
abrasi
subsidence
longsoran
tsunami
Fenomena lain
D. Sarsito, 2006
3. Objek dari Deformasi
S AMP No rt h
-25
-20
-15
-10
-5
0
5
10
15
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
35.000
35.040
35.080
35.120
35.160
35.200
35.240
35.280
35.320
35.360
35.400
35.440
35.480
35.520
35.560
35.600
35.640
35.680
35.720
35.760
35.800
35.840
35.880
35.920
35.960
36.000
36.040
36.080
36.120
36.160
36.200
36.240
36.280
36.320
36.360
36.400
36.440
36.480
36.520
36.560
22 /9/ 06 -1 24 /9/ 06 -13 26 /9/ 06 -1 27 /9/ 06 -13 29 /9/ 06 -1 30 /9/ 06 -13 2/10 / 06 -1 3/10 / 06 -13 5/10 / 06 -1 6/10 / 06 -13 8/10 / 06 -1 9/10 / 06 -13 11 /10 /06 -1 12 /10 /06 -13 13 /10 /06 -19 15 /10 /06 -7 16 /10 /06 -16 18 /10 /06 -4 19 /10 /06 -16 21 /10 /06 -4 22 /10 /06 -16 24 /10 /06 -4 25 /10 /06 -16 27 /10 /06 -4 28 /10 /06 -16 30 /10 /06 -4 31 /10 /06 -16 2/11 / 06 -4 3/11 / 06 -16 5/11 / 06 -4 6/11 / 06 -16 8/11 / 06 -4 9/11 / 06 -16 11 /11 /06 -4 12 /11 /06 -16 14 /11 /06 -4 15 /11 /06 -16 17 /11 /06 -4 18 /11 /06 -16 20 /11 /06 -4 21 /11 /06 -16 23 /11 /06 -4 24 /11 /06 -16
Tgl/Bln/Thn-Jam
Height (m)
4. Jenis dari Deformasi
Deformasi dapat dibagi menjadi 2 jenis yaitu Deformasi Statik dan
Deformasi sesaat
Deformasi statik bersifat permanen
Deformasi sesaat bersifat sementara / dinamis
5. Parameter Deformasi
Deformasi dari suatu benda/ materi dapat digambarkan secara
penuh dalam bentuk tiga dimensi apabila diketahui 6 parameter
regangan (normal-shear) dan 3 parameter komponen rotasi
Parameter deformasi ini dapat dihitung apabila diketahui fungsi
pergeseran dari benda tersebut persatuan waktu
Normal strain Shear strain
6. Model dan pengamatan Deformasi
Secara praktis survey deformasi akan terpaut pada titik-titik yang
bersifat diskrit, dengan demikian deformasi dari benda harus
didekati dengan model.
Fungsi dari deformasi dinyatakan oleh persamaan dalam bentuk
matrik :
d = B c
Dimana :
B, adalah matrik deformasi yang elemennya merupakan fungsi dari
posisi dari titik yang diamati, serta waktu
C, vektor yang koefisiennya akan diketahui
6. Model dan pengamatan Deformasi
Survey deformasi: penentuan perubahan posisi, jarak, sudut,
regangan : teknik geodetik, geofisika, dan lain-lain
7. Analisis Deformasi
Analisis Geometrik :
Bila kita hanya tertarik pada status geometrik (ukuran dan
dimensi) dari benda yang terdeformasi
Analisis Fisis :
Bila kita bermaksud untuk menentukan status fisis dari benda yang
terdeformasi, regangan, dan hubungan antara gaya dengan
deformasi yang terjadi
8. Analisis Deformasi aspek fisis
Dalam analisis fisis deformasi, hubungan antara gaya dan
deformasi dapat dimodelkan dengan menggunakan metoda
empiris (statistik), yaitu melalui korelasi antara pengamatan
deformasi dan pengamatan gaya
Metoda lain dalam analisis fisis yaitu metoda deterministik, yang
memanfaatkan informasi dari gaya, jenis material dari benda, dan
hubungan fisis antara regangan (strain) dan tegangan (stress)
pada benda
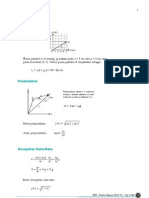
9. Normal strain :perubahan panjang
- Change of length proportional to length
- cxx, cyy, czz are normal component of strain
nb : If deformation is small, change of volume is cxx + cyy + czz (neglecting quadratic terms)
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
10. Shear Strain : perubahan sudut
cxy = -
1
/
2
(u1 + u2) =
1
/
2
(
de
y
/
dx
+
de
x
/
dy
)
cxy = cyx (obvious)
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
11. Stress dalam 2 Dimensi
- Force = ox surface
- no rotation =>
oxy = oyx
- only 3 independent
.components :
..oxx , oyy , oxy
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
12. Applied Forces
Normal forces on x axis :
= oxx
(x)
.
oy
oxx
(x+ox)
.
oy
=
oy
|oxx
(x)
. oxx
(x+ox)
|
=
oy
do
xx
/
d
x
. ox (1)
Shear forces on x axis :
= oyx
(y)
.
ox
oyx
(y+oy)
.
ox
=
ox
do
yx
/
d
y
. oy (2)
Total on x axis = (1)+(2)
|
do
xx
/
d
x
+
do
yx
/
d
y
|
ox oy
=
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
13. Forces Equilibrium
Total on x axis = |
do
xx
/
d
x
+
do
yx
/
d
y
|
ox oy
Total on y axis = |
do
yy
/
d
y
+
do
yx
/
d
x
|
oy ox
|
do
yy
/
d
y
+
do
yx
/
d
x
|
= 0
|
do
xx
/
d
x
+
do
yx
/
d
y
|
= 0
Equilibrium =>
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
14. Solid elastic deformation
Stresses are proportional to strains
No preferred orientations
oxx = (+2G) cxx + cyy + czz
oyy = cxx + (+2G) cyy + czz
ozz = cxx + cyy + (+2G) czz
and G are Lam parameters
The material properties are such that a principal strain component c
produces a stress (+2G)c in the same direction
and stresses c in mutually perpendicular directions
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
Inversing stresses and strains give :
cxx =
1
/
E
oxx -
v
/
E
oyy -
v
/
E
ozz
cyy = -
v
/
E
oxx +
1
/
E
oyy -
v
/
E
ozz
czz = -
v
/
E
oxx -
v
/
E
oyy +
1
/
E
ozz
E and vare Youngs modulus and Poissons ratio
a principal stress component oproduces
a strain
1
/
E
o in the same direction and
strains
v
/
E
oin mutually perpendicular directions
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
14. Solid elastic deformation
15. Elastic deformation across a locked fault
What is the shape of the accumulated deformation ?
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
Formula matematis
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
Formula matematis
Symetry => all derivative with y = 0
cyy = 0
No gravity => ozz = 0
What is the displacement field U in the elastic layer ?
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
Elastic equations :
(3) + ozz = 0 => cxx + czz = -2G czz
and (2) => oyy = cxx + czz = -2 G czz
(1) oxx = (+2G) cxx + czz
(2) oyy = cxx + czz
(3) ozz = cxx + (+2G) czz
oxy = 2G cxy oxz = 2G cxz
oyz = 2G cyz
=> cxx = - (2G + )/ czz
and (1) => oxx = [-
(
+2G)
2
/
+ ] czz
_________________________
Formula matematis
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
Force equilibrium along the 3 axis
(x) doxx / dx + doyx / dy + doxz / dz = 0
_________________________
(y) doxy / dx + doyy / dy + doyz / dz = 0
(z) doxz / dx + doyz / dy + dozz / dz = 0
x
x
x x
Derivation of eq. 1 with x and eq. 3 give :
d
2
oxx / dx
2
= 0
equation 2 becomes : doxy / dx + doyz / dz = 0
Formula matematis
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
Formula matematis
relations between
stress (o) and displacement vector (U)
oxy = 2G cxy = 2G [dUx / dy + dUy / dx] .
1
/
2
_________________________
oyz = 2G cyz = 2G [dUz / dy + dUy / dz] .
1
/
2
x
d/dx[dUx/dy + dUy/dx] + d/dz[dUz/dy + dUy/dz] = 0
d
2
Uy / dx
2
+ d
2
Uy / dz
2
= 0
Using doxy / dx + doyz / dz = 0 we obtain :
x
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
Formula matematis
What is U
y
, function of x and z, solution of this equation ?
d
2
Uy / dx
2
+ d
2
Uy / dz
2
= 0
Guess : U
y
= K arctang (
x
/
z
) works fine !
Nb.
d
atan(o)
/
do
=
1
/
(1+o2 )
dUy/dx=
K
/z(1+x
2
/z
2
) =>
d
2
Uy/dx
2
= -2Kxz/(z
2
+x
2
)
dUy/dz=
-Kx
/z
2
(1+x
2
/z
2
) =>
d
2
Uy/dz
2
= 2Kxz/(x
2
+z
2
)
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
Formula matematis
Boundary condition at the base of the crust (z=0)
U
y
= K arctang (
x
/
z
)
U
y
= K . H/2 if x > 0 = K . H/2 if x < 0
=> K = 2.
V
0 /
H
And also :
U
y
= +V
0
if x > 0 = V
0
if x < 0
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
Formula matematis
at the surface (z=h)
U
y
= K arctang (
x
/
z
)
U
y
= 2.
V
0 /
H
arctang (
x
/
h
)
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
16. Arctang Profiles
U
y
= 2.
V
0 /
H
arctang (
x
/
h
)
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
17. Deeping Fault
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
18. Elastic Dislocation (Okada, 1985)
Surface deformation due to shear and tensile faults in a half space, BSSA vol75, n4, 1135-1154, 1985.
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
The displacement field u
i
(x
1
,x
2
,x
3
)
due to a dislocation A u
j
(
1
,
2
,
3
)
across a surface E in an isotropic
medium is given by :
Where o
jk
is the Kronecker delta,
and are Lams parameters, v
k
is
the direction cosine of the normal to
the surface element dE.
u
i
j
is the i
th
component of the
displacement at (x
1
,x
2
,x
3
) due to the
j
th
direction point force of magnitude
F at (
1
,
2
,
3
)
18. Elastic Dislocation (Okada, 1985)
(1) displacements
For strike-slip For dip-slip For tensile fault
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
18. Elastic Dislocation (Okada, 1985)
Where :
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
19. Case : Sagaing Fault Nyanmar
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
20. Case : Palu Koro Fault
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
20. Case : Palu Koro Fault (more complex)
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
21. Case : Sumatra subduction zone
Triyoso, 2005
Natawijaya, 2007
Segmen Mentawai-Pagai belum sepenuhnya terpatahkan ??? !!!
22. Strain rate and rotation rate tensors
2. Compute strain rate and rotation rate tensors
1. Look at station velocity residuals
Velocity mm/yr
Strain =
_______
=
_____
= % / yr
Distance km
Matrix tensor notation : S
i
j
= d(V
i
) / d(x
j
) =
d(V
x
) / d(x) d(V
x
) / d(y)
d(V
y
) / d(x) d(V
y
) / d(y)
Theory says : [S] = [E] + [W]
Symetrical Antisymetrical
Strain rate rotation rate
To asses plate deformation :
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
22. Strain rate and rotation rate tensors
[E] has 2 Eigen values : c
1
, c
2
c
1
and c
2
are extension/compression along principal direction defined
by angle u (defined as angle between c
2
direction and north)
[E] =
([S] + [S]
T
) =
E
11
E
12
E
12
E
22
[W] =
([S] - [S]
T
) =
0 W
-W 0
c
1
= E
11
cos
2
u + E
22
sin
2
u 2 E
12
sinu cosu
c
2
= E
11
sin
2
u + E
22
cos
2
u 2 E
12
sinu cosu
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
22. Strain rate and rotation rate tensors
Therefore we can compute strain rate and rotation rate within any
polygon, the minimum polygon being a triangle
Minimum requirement to compute strain and rotation rates is :
3 velocities (to allow to determine 3 values c
1
, c
2
, and W)
No deformation compression rotation
Strain and rotations are unsensitive to reference frame
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
23. Case : Strain & Rotation on GEODYSSEA network
Strains :
extension/compression/strike-slip
Rotations :
Anti-clockwise/clockwise
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
24. Case : intensity of strain in GEODYSSEA network
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
25. Case : Strain & Rotation in Nyanmar
SEAMERGES GPS COURSE, 2005
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Praktikum Fisika Dasar Gerak Jatuh BebasDokumen22 halamanPraktikum Fisika Dasar Gerak Jatuh Bebasadiar_warisan83% (36)
- MEKBANDokumen82 halamanMEKBANDjunaidi SyalatBelum ada peringkat
- Elastisitas Kelompok 2 FixDokumen13 halamanElastisitas Kelompok 2 FixfaitulBelum ada peringkat
- 4.vibrasi (Kuliah)Dokumen42 halaman4.vibrasi (Kuliah)Intan Mustika NspBelum ada peringkat
- 03 Kunci Jawaban Dan Pembahasan PR Fisika 11A PDFDokumen52 halaman03 Kunci Jawaban Dan Pembahasan PR Fisika 11A PDFNur Mahmudah100% (1)
- Tugas Kelompok GelombangDokumen12 halamanTugas Kelompok GelombangJhoni Prasetyo K. OberlinBelum ada peringkat
- Gerak Dua BendaDokumen72 halamanGerak Dua BendaThareeq Alfiqar TindaonBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 3 - 1 - Variabel Terregional - Deterministik PDFDokumen12 halamanBab 3 - 1 - Variabel Terregional - Deterministik PDFArif Rahman HakimBelum ada peringkat
- 2 AnplasDokumen12 halaman2 AnplasResa MuliadiBelum ada peringkat
- 02 Getaran Bebas SDOFDokumen14 halaman02 Getaran Bebas SDOFpriscaregitaBelum ada peringkat
- Pengantar Anstruk MatriksDokumen25 halamanPengantar Anstruk MatriksDwie OktavianaBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas DimstrukDokumen3 halamanTugas DimstrukMuhammad YunusBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Praktikum Mekanika Fluida H.02 Tekanan HidrostatisDokumen15 halamanLaporan Praktikum Mekanika Fluida H.02 Tekanan HidrostatisZohansyah MulyadiBelum ada peringkat
- Pesongan Rasuk (JJ310)Dokumen57 halamanPesongan Rasuk (JJ310)Khairul Anuar Bin Halik100% (2)
- 10 Hukum Dasar Orbit SateltDokumen14 halaman10 Hukum Dasar Orbit SateltRetnoPratiwi11Belum ada peringkat
- Perencanaan Turap Baja SheeppelDokumen8 halamanPerencanaan Turap Baja SheeppelYoga Abdhi Negara100% (1)
- Rekayasa PondasiDokumen12 halamanRekayasa PondasiDjunaidi SyalatBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan Ke-4 Kinematika GLB Dan GLBB (Atwood)Dokumen4 halamanPertemuan Ke-4 Kinematika GLB Dan GLBB (Atwood)Alya Shafira DewantiBelum ada peringkat
- Komputasi Navier Stokes Orde 3Dokumen41 halamanKomputasi Navier Stokes Orde 3Agus Madatama PujaBelum ada peringkat
- AR11FIS0201Dokumen7 halamanAR11FIS0201putriajah23Belum ada peringkat
- Desain Perkuatan Lereng Dengan GeosintetikDokumen8 halamanDesain Perkuatan Lereng Dengan GeosintetikHardianto SumanBelum ada peringkat
- Ringkasan Fisika SMA Kelas XI Semester 1Dokumen21 halamanRingkasan Fisika SMA Kelas XI Semester 1Dea Tita HastikaBelum ada peringkat
- Ringkasan Fisika SMA Kelas XI Semester 1Dokumen21 halamanRingkasan Fisika SMA Kelas XI Semester 1blogq91% (23)
- Laporan Fisika - Tetapan Pegas FixDokumen11 halamanLaporan Fisika - Tetapan Pegas Fixputribintaang100% (1)
- Laporan Praktikum Gesek - AishaDokumen17 halamanLaporan Praktikum Gesek - AishaAisha NursaniBelum ada peringkat
- SOAL Analisa Dinamika StrukturDokumen22 halamanSOAL Analisa Dinamika StrukturNa Ja MaBelum ada peringkat
- Pemodelan Fondasi Pelat Dengan Matriks Menggunakan Metode Elemen HinggaDokumen11 halamanPemodelan Fondasi Pelat Dengan Matriks Menggunakan Metode Elemen HinggaArais AisahBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Soal Fisika 1Dokumen22 halamanContoh Soal Fisika 1Yulian SyahBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Soal Fisika 1Dokumen8 halamanContoh Soal Fisika 1Fatur RohmanBelum ada peringkat
- Bandul MatematisDokumen11 halamanBandul MatematisLamborighini-man Gallardo100% (2)
- Triaxial IrwinDokumen19 halamanTriaxial IrwinMuhammadAkhyarBelum ada peringkat
- BanjirDokumen56 halamanBanjirannisawldrBelum ada peringkat
- Gerak Dalam Bidang DatarDokumen21 halamanGerak Dalam Bidang DatarferdikaandrizaBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 2 Gerak LurusDokumen77 halamanBab 2 Gerak LurusAnnisa WulandariBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal Pesawat AtwoodDokumen20 halamanJurnal Pesawat AtwoodDea Febrian Wiliardi50% (2)
- Laporan Akhir PraktikumDokumen21 halamanLaporan Akhir Praktikum'Asifatun Nufus100% (2)
- Laporan Praktikum Fisika Modul 2Dokumen28 halamanLaporan Praktikum Fisika Modul 2'Adinda Mulyani100% (1)
- Contoh Soal FisikaDokumen31 halamanContoh Soal FisikaDzz Zeet Oonn100% (1)
- Solusi Modul Tutorial 1 - 4 Sks 2013-2014Dokumen6 halamanSolusi Modul Tutorial 1 - 4 Sks 2013-2014Rahma Dhani Prasetiyawati100% (1)
- Solusi Soal Bab I Bab II Bab IIIDokumen43 halamanSolusi Soal Bab I Bab II Bab IIIFakhrurrazi100% (1)
- Panduan Menulis PaperDokumen8 halamanPanduan Menulis PaperRiyanz SaBelum ada peringkat
- Sejarah Kabupaten CilacapDokumen2 halamanSejarah Kabupaten CilacapLoren 'olend' SalsabillaBelum ada peringkat
- PANDUAN MAWAPRES Sarjana 2014Dokumen34 halamanPANDUAN MAWAPRES Sarjana 2014Himapemia Fkip UnjaBelum ada peringkat
- Perumusan MasalahDokumen6 halamanPerumusan MasalahLoren 'olend' SalsabillaBelum ada peringkat
- Terapi RokokDokumen1 halamanTerapi RokokLoren 'olend' SalsabillaBelum ada peringkat
- Struktur Baja Metode LRFDDokumen352 halamanStruktur Baja Metode LRFDZulham Afani100% (8)
- DeformasiDokumen43 halamanDeformasiLoren 'olend' Salsabilla100% (1)