Chapter 3
Diunggah oleh
Nalynhi lynhi0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
27 tayangan4 halamanJudul Asli
Chapter 3.docx
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
27 tayangan4 halamanChapter 3
Diunggah oleh
Nalynhi lynhiHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 4
Chapter 3: Electromagnetism
Electromagnet
Elektromagnet
An electromagnet is a temporary magnet in which its magnetic field is
produced by the flow of electric current in a conductor.
Suatu electromagnet merupakan magnet sementera yang mana medan magnetnya
dihasilkan oleh pengaliran arus elaktrik di dalam sebuah konduktor.
Coiled wire The iron nail becomes a magnet
Gegelung dawai because of the magnetic field
produced around the wire when an
electrical current flows through it.
The coil of wire increases the
Iron nail magnetic field.
Paku besi Paku besi menjadi sebuah magnet
disebabkan oleh medan magnet yang
Wire terhasil di sekeliling dawai apabila
dawai arus elektrik mengalir melalui dawai
itu. Dawai yang bergegelung
meningkatkan medan magnet.
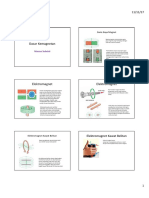
Magnetic Fields
Medan Magnet
The direction of the magnetic field in an electromagnet can be determined by
using the right-hand grip rule.
Arah medan magnet dalam suatu electromagnet dapat ditentukan dengan menggunakan
peraturan genggaman tangan kanan.
Thumb poiting in the direction of the
electric current, l.
Ibu jari menunjuk arah arus elektrik, l.
Thumb poiting in the direction of the
magnetic field, B.
Jari menunjuk arah medan magnet, B
Magnetic field due to a current in a straight wire.
Medan magnet yang disebabkan oleh arus dalam suatu dawai lurus.
Direction of current Wire
Arah arus dawai
Compass
Kompas
Magnetic field pattern
Corak medan magnet
Magnetic field due to a current in circular coil
Medan magnet yang disebabkan oleh arus dalam suatu gegelung bulat.
Direction of current
Arah arus
Magnetic field pattern
Corak medan magnet
Magnetic field due to a current in a solenoid
Medan magnet yang disebabkan oleh arus dalam suatu solenoid.
Solenoid
solenoid Magnet bar
Magnet bar
Similar to
Serupa dengan
Magnetic field pattern Direction of current
Corak medan magnet Arah arus
Number of turns of coil The greater the
Bilangan lilitan gegelung current, the higher the
Magnitude of current strength of the
Magnitud arus
The more the number electromagnet.
of turns of coil, the Semakin besar arus,
higher the strength of semakin tinggi kekuatan
the electromagnet. Factors that affect the electromagnet.
Semakin banyak strength of an
bilangan lilitan gegelung, electromagnet
semakin tinggi kekuatan Faktor-faktor yang Type of material of
electromagnet. mempengaruhi core
Jenis bahan teras
kekuatan suatu
elektromagnet The use of an iron core
Diameter of wire produces a stronger
Jenis bahan dawai electromagnet.
Penggunaan teras besi
The bigger the diameter of
Lower resistance menghasilkan
wire, the higher the
materials produce electromagnet yang lebih
strength of the
stronger kuat.
electromagnet.
Semakin besar diameter electromagnets.
dawai, semakin tinggi Bahan dengan rintangan
Type of material of
kekuatan electromagnet. lebih rendah
wire
menghasilkan Jenis bahan dawai
electromagnet yang lebih
kuat.
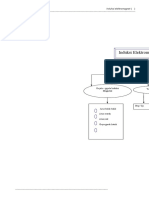
An Application of Electromagnets
Aplikasi Elektromagnet
Electric bell
Loceng elektrik
suis
2 As the hammer moves
1 The springtowards thethe
returns gong, the armature
soft-iron
circuit position
to its original is broken.
which reconnect
Electricity
the circuit stops
and so electricity flows again. 3 The soft-iron armature is attracted
Spring mengembalikan
flowing causes angkerthebesi lembut ke to the electromagnet and the
kedudukan asal yang menyambung
electromagnet loses its 4 When
semula the switch
hammerisstrikes the gong.
elektrik kembali mengalir. pressed,
litar dan magnetism. a Angker
currentbesi lembut ditarik pada
flows through electromagnet
the dan penukul mengetuk
Semasa pemukul
gong.
electromagnet coils.
bergerak kea rah gong,
litar diputuskan. Elekrik Apabila suis ditekan,
berhenti mengalir arus mengalir melalui
menyebabkan gegelung electromagnet.
electromagnet hilang
kemagnetannya.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Laporan Praktikum Fisika Dasar II Medan MagnetikDokumen16 halamanLaporan Praktikum Fisika Dasar II Medan MagnetikSeptiani Luxitaa25% (4)
- PPT: MagnetDokumen50 halamanPPT: Magnetimanuelsukarno84% (19)
- 7 6 EmagnetDokumen12 halaman7 6 Emagnetslokkro100% (16)
- Nota Fizik Tingkatan 5 Bab 3 KeelektromagnetanDokumen71 halamanNota Fizik Tingkatan 5 Bab 3 KeelektromagnetanAnis HassimBelum ada peringkat
- 9b196 p12 MagnetDokumen13 halaman9b196 p12 MagnetChristinaBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 3 KeelektromagnetanDokumen71 halamanBab 3 KeelektromagnetanhildaBelum ada peringkat
- 26 Magnet-01Dokumen32 halaman26 Magnet-01tri agustiningsihBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 3 KeelektromagnetanDokumen30 halamanBab 3 Keelektromagnetannfaizah1Belum ada peringkat
- 8 Elektromagnet G April2016Dokumen69 halaman8 Elektromagnet G April2016nfaizah1100% (5)
- KD 4.2 Pemanfaatan KemagnetanDokumen22 halamanKD 4.2 Pemanfaatan KemagnetanSepty Reski FadilahBelum ada peringkat
- Medan MagnetDokumen21 halamanMedan MagnetBunga WangiBelum ada peringkat
- 5.LKPD 2. Medan Magnet ListrikDokumen3 halaman5.LKPD 2. Medan Magnet Listrikjustmine96Belum ada peringkat
- MaghnetDokumen11 halamanMaghnetNurul FajriahBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Project Fisika DasarDokumen14 halamanLaporan Project Fisika DasarCelia FaradhibaBelum ada peringkat
- Elektromagnetik Part 2 Kelas 9Dokumen19 halamanElektromagnetik Part 2 Kelas 9Satrio SayaBelum ada peringkat
- Elektromagnet Adalah Magnet Yang Terhasil Apabila Satu Teras BesiDokumen3 halamanElektromagnet Adalah Magnet Yang Terhasil Apabila Satu Teras BesiZune LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 3 Keelektromagnetan Edisi Guru 2016Dokumen37 halamanBab 3 Keelektromagnetan Edisi Guru 2016zularisBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 3 Keelektromagnetan Edisi Guru 2017Dokumen37 halamanBab 3 Keelektromagnetan Edisi Guru 2017Aisha SyafikaBelum ada peringkat
- Pengertian Gaya LorentzDokumen4 halamanPengertian Gaya LorentzReddya FanadaBelum ada peringkat
- Mind Map FisikaDokumen5 halamanMind Map FisikaGitaBelum ada peringkat
- Gambar, Definisi & Pengertian ElektromagnetDokumen6 halamanGambar, Definisi & Pengertian ElektromagnetJihad Mufry AnnahlBelum ada peringkat
- MagnetikDokumen18 halamanMagnetikKhusniaBelum ada peringkat
- Teori Kemagnetan BumiDokumen2 halamanTeori Kemagnetan BumiDiva EdeniaBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 6 Kemagnetan Dan Induksi ElektromagnetikDokumen26 halamanBab 6 Kemagnetan Dan Induksi Elektromagnetikahmadin Gr100% (2)
- 01 Dasar Kemagnetan - 5Dokumen5 halaman01 Dasar Kemagnetan - 5Desi AzmariantyBelum ada peringkat
- LKPD Induksi ElektromagnetikDokumen13 halamanLKPD Induksi ElektromagnetikAlia Rizki Fatiah67% (3)
- Induksi ElektromagnetikDokumen15 halamanInduksi ElektromagnetikSALWA PUDJABelum ada peringkat
- Nota AlatubahDokumen17 halamanNota Alatubahakiey_0577Belum ada peringkat
- ELEKTROMAGNETDokumen32 halamanELEKTROMAGNETMarko VrancicBelum ada peringkat
- Diktat Mesin-Mesin ListrikDokumen30 halamanDiktat Mesin-Mesin Listriksuka kepoBelum ada peringkat
- PPT ImDokumen20 halamanPPT ImMuhammad FikriBelum ada peringkat
- Ipa Fisika Magnet Ix SMPDokumen8 halamanIpa Fisika Magnet Ix SMPSenny Ummu AlMuharromBelum ada peringkat
- IPA Kelas 9 BAB 6Dokumen33 halamanIPA Kelas 9 BAB 6Aga WNIBelum ada peringkat
- IPA Kelas 9 BAB 6Dokumen27 halamanIPA Kelas 9 BAB 6nema endahBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Induksi MagnetikDokumen11 halaman3 Induksi MagnetikRafikatul MunaBelum ada peringkat
- 7.9 Electromagnetism (BM)Dokumen17 halaman7.9 Electromagnetism (BM)Siti Hajar Abd HamidBelum ada peringkat
- Ke Magnet AnDokumen29 halamanKe Magnet AnZiniaBelum ada peringkat
- Rumusan Bab 10 ElektromagnetDokumen17 halamanRumusan Bab 10 ElektromagnetBENNY LAU XUE ZHENG MoeBelum ada peringkat
- Kemagnetan Dan Induksi ElektromagnetikDokumen27 halamanKemagnetan Dan Induksi ElektromagnetikJochieBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan - Nabeel Ragheed - 101121010 - GP-02 - Modul3Dokumen11 halamanLaporan - Nabeel Ragheed - 101121010 - GP-02 - Modul3Nabeel RagheedBelum ada peringkat
- Induksi Elektromagnetik2Dokumen9 halamanInduksi Elektromagnetik2hamangkhullafahBelum ada peringkat
- IPA Kelas 9 BAB 6Dokumen26 halamanIPA Kelas 9 BAB 6ipukBelum ada peringkat
- Kemagnetan Listrik (Elektromagnetik)Dokumen31 halamanKemagnetan Listrik (Elektromagnetik)Diva Mustika Takhiyah divamustika.2021Belum ada peringkat
- MATERI PERT. 4. Dasar-Medan-MagnetDokumen23 halamanMATERI PERT. 4. Dasar-Medan-MagnetSurya NugrahaBelum ada peringkat
- KEMAGNETANDokumen28 halamanKEMAGNETANandrea septiadiBelum ada peringkat
- 5.3 Elektromagnet PDFDokumen8 halaman5.3 Elektromagnet PDFhildaBelum ada peringkat
- MODUL IPA 1 (Part 2) Kls 9 KemagnetanDokumen4 halamanMODUL IPA 1 (Part 2) Kls 9 KemagnetanSseungminxBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan Ajar Mesin Listrik Bab IDokumen15 halamanBahan Ajar Mesin Listrik Bab IRachmat Evan HutabaratBelum ada peringkat
- Jawaban IPA KeisyaDokumen2 halamanJawaban IPA KeisyaDoniSetiawanBelum ada peringkat
- Ta Billy TgsDokumen47 halamanTa Billy TgsBillyBelum ada peringkat
- KemagnetanDokumen30 halamanKemagnetanareta wiratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan RBL - Kelompok 2 - TPB 15ADokumen4 halamanLaporan RBL - Kelompok 2 - TPB 15AFardita Ode josanBelum ada peringkat
- Rangkaian Bel Listrik SederhanaDokumen12 halamanRangkaian Bel Listrik SederhanaMichael LevyBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan Ajar Medan Magnet Dan Gaya Lorentz RevisiDokumen15 halamanBahan Ajar Medan Magnet Dan Gaya Lorentz RevisiYogaswara AdiputraBelum ada peringkat
- Elek Tro MagnetDokumen8 halamanElek Tro Magnetibonk kasepBelum ada peringkat
- ApitanDokumen19 halamanApitanNalynhi lynhiBelum ada peringkat
- SisipanDokumen22 halamanSisipanNalynhi lynhiBelum ada peringkat
- RPH Pend Kesenian THN 3 2019Dokumen37 halamanRPH Pend Kesenian THN 3 2019Siti Syariah Nabila100% (2)
- Skrip Hari Guru 2019Dokumen5 halamanSkrip Hari Guru 2019Nalynhi lynhiBelum ada peringkat
- Litupan BadanDokumen3 halamanLitupan BadanNalynhi lynhiBelum ada peringkat
- KERTAS KERJA IntervensiDokumen3 halamanKERTAS KERJA IntervensiNalynhi lynhiBelum ada peringkat
- Kumpulan 5Dokumen1 halamanKumpulan 5Nalynhi lynhiBelum ada peringkat
- Skrip Hari Guru 2019Dokumen5 halamanSkrip Hari Guru 2019Nalynhi lynhiBelum ada peringkat
- KERTAS KERJA IntervensiDokumen3 halamanKERTAS KERJA IntervensiNalynhi lynhiBelum ada peringkat
- Arnab DGN KambingDokumen8 halamanArnab DGN KambingErnieyanti BakriBelum ada peringkat