Jawapan Kertas Model SPM (PT SPM Kimia Tingkatan 5) (22-23)
Diunggah oleh
hazif emyrHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Jawapan Kertas Model SPM (PT SPM Kimia Tingkatan 5) (22-23)
Diunggah oleh
hazif emyrHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
JAWAPAN
(b) (i) Sebagai mangkin/ As catalyst
KERTAS MODEL SPM
(ii) H O H H H
KERTAS 1
H—C—C—O—C—C—C—H
1 D 2 C 3 B 4 B 5 C 6 C
7 B 8 B 9 A 10 C 11 D 12 A H H H H
13 D 14 A 15 B 16 A 17 D 18 D
19 A 20 B 21 C 22 A 23 C 24 A (iii) Karboksilat/ Carboxylate
25 C 26 C 27 C 28 A 29 D 30 D (iv) Berbau wangi/ Sweet smell
31 D 32 D 33 C 34 A 35 C 36 D 6 (a) (i) Kuprum(II) oksida/ Copper(II) oxide/
37 B 38 C 39 D 40 C (ii) Panaskan kuprum(II) karbonat dengan kuat
Heat copper(II) carbonate strongly
KERTAS 2 (iii) Pepejal hijau menjadi hitam/ Green solid becomes black
(iv) Air kapur/ Lime water
BAHAGIAN A
(b) (i)Untuk memastikan asid sulfurik telah bertindak
1 (a) Molekul berantai panjang yang terbentuk daripada balas dengan lengkap
gabungan banyak ulangan unit asas. To ensure that sulphuric acid is reacted completely
Long-chain molecules formed from the combination of many (ii) CuO + H2SO4 → CuSO4 + H2O
repeating basic units.
(c) Panaskan larutan sehingga menjadi tepu. Biarkan larutan
(b) Karbohidrat/ Carbohydrate tepu menyejuk dan kemudian turaskan hablur garam.
(c) Pempolimeran kondensasi/ Condensation polymerisation Heat the solution until it becomes saturated. Allow it to cool down
(d) Molekul air dihasilkan/ Water molecules are produced and then filter off the salt crystals.
(e) Politena/ Polyethene 7 (a) Titian garam
2 (a) Asid lemak tepu/ Saturated fatty acid Salt bridge
Asid lemak tak tepu/ Unsaturated fatty acid G
(b) X mempunyai hanya ikatan tunggal antara atom karbon,
manakala Y mempunyai satu ikatan ganda dua antara
atom karbon Karbon X Karbon Y
X has only single bonds between carbon atoms, whereas Y has a Carbon X Carbon Y
double bond between carbon atoms. Larutan ferum(II) Air bromin
(c) Takat lebur lemak yang dihasilkan daripada asid lemak sulfat Bromine water
X lebih tinggi daripada asid lemak Y. Iron(II) sulphate Bikar A Bikar B
solution Beaker A Beaker B
The melting point of fats produced from fatty acids X is higher
than fatty acids Y. (b) Larutan kalium nitrat, KNO3/ Potassium nitrate solution, KNO3
3 (a) A (c) (i) Larutan hijau berubah menjadi perang
(b) (i) B, D, C, A Green solution turns brown
(ii) Bilangan proton semakin bertambah. Jadi, daya (ii) Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e–
tarikan antara nukleus dengan elektron valens (iii) Beberapa titik larutan kalium heksasianoferat(II)
semakin kuat./ The number of protons increases. So, the ke dalam bikar, mendakan biru tua terbentuk
forces of attraction between the nucleus and the valence menunjukkan kehadiran ion Fe3+.
electron is stronger. A few drops of potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) solution
(i) D
(c) is added into the beaker, a dark blue precipitate formed
(ii) Bertindak sebagai mangkin/ Act as catalysts indicating the presence of Fe3+ ions.
4 (a) (i) Ammonia/ Ammonia (d)(i) Agen pengoksidaan/ Oxidation agent
(ii) Kerana ammonia kehilangan hidrogen (ii) Larutan kalium manganat(VII) berasid
Because ammonia loses hydrogen Acidified potassium manganate(VII) solution
(iii) CuO, kerana kuprum(II) oksida mengalami (e) 2Fe2+ + Br2 → 2Fe3+ + 2Br–
penurunan dengan kehilangan oksigen untuk 8 (a) (i) Larutan kuprum(II) sulfat/ Copper(II) sulphate solution
membentuk atom kuprum (ii) Sebagai mangkin/ As a catalyst
CuO, because copper(II) oxide undergoes reduction by (b) Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
losing oxygen to form copper atom (c) (i) Set II mempunyai kadar tindak balas yang lebih
(b) (i) Kerana ion kuprum(II) menerima elektron dan tinggi daripada Set I
bertukar menjadi atom kuprum. Set II has a higher rate of reaction than Set I
Because copper(II) ions receive electrons and converted to (ii) Mangkin menyediakan laluan alternatif dengan
copper atoms. tenaga pengaktifan yang lebih rendah. Frekuensi
(ii) Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu perlanggaran antara ion hidrogen dengan atom
5 (a) (i) Kalsium etanoat/ Calcium ethanoate zink tetap sama, tetapi lebih banyak zarah-zarah
Karbon dioksida/ Carbon dioxide mencapai tenaga pengaktifan yang lebih rendah
(ii) Alirkan gas Y ke dalam air kapur, air kapur menjadi yang menyebabkan frekuensi perlanggaran
keruh.
Flow gas Y into lime water, lime water turns chalky. berkesan lebih tinggi.
J1 Praktis Topikal SPM: Kimia Tingkatan 5 – Jawapan
The catalyst provides an alternative pathway with a lower 6.
Ulang langkah 1 hingga 5 dengan menggantikan
activation energy. The frequency of collisions between naftalena dengan serbuk plumbum(II) bromida.
hydrogen ions and zinc atoms is the same but more Repeat steps 1 to 5 by replacing naphthalene with lead(II)
particles reach the lower activation energy resulting in a bromide powder. [4]
higher frequency of effective collisions. Pemerhatian/ Observation:
(d)
Naftalena lebur: Jarum ammeter tidak terpesong
Tenaga/ Energy Molten naphthalene: Ammeter needle does not deflect [1]
Plumbum(II) bromida lebur: Jarum ammeter
Ea terpesong
– Ea’ Molten lead(II) bromide: Ammeter needle deflects [1]
2H + Zn
Kesimpulan/ Conclusion:
H2 + Zn Leburan PbBr2 boleh mengkonduksikan arus
elektrik, manakala leburan naftalena tidak boleh
Lintasan tindak balas
Reaction pathway mengkonduksikan arus elektrik.
Molten PbBr2 can conduct electric current while the molten
BAHAGIAN B naphthalene cannot conduct electric current. [2]
9 (a) (i) – Susunan elektron atom A ialah 2.4 dan atom B 10 (a) (i) Set I: Tindak balas peneutralan antara HCl
ialah 2.6. dengan NaOH
The electron arrangement of atom A is 2.4 and atom B Set I: Neutralisation reaction between HCl and NaOH [1]
is 2.6. [2] Set II: Penguraian CaCO3
– Untuk mencapai susunan elektron oktet, atom
Set II: Decomposition of CaCO3 [1]
A menyumbangkan empat elektron, manakala (ii)
atom B menyumbangkan dua elektron apabila Set I Set II
bertindak balas.
Tindak balas eksotermik Tindak balas endotermik
To achieve the octet electron arrangement, atom A
Exothermic reaction Endothermic reaction
contributes four electrons while atom B
contributes two electrons when reacting. [2] Suhu persekitaran meningkat Suhu persekitaran menurun
– Atom A berkongsi empat pasang elektron Temperature of surroundings Temperature of surroundings
dengan dua atom B untuk membentuk dua increases decreases
ikatan kovalen ganda dua. Jumlah kandungan tenaga Jumlah kandungan tenaga
Atom A shares four pairs of electrons with two atom B bahan tindak balas lebih tinggi bahan tindak balas lebih
to form two double covalent bonds. [2] daripada hasil tindak balas rendah daripada hasil tindak
– Sebatian kovalen, AB2 terbentuk. Total energy content of reactants is balas
A covalent compound, AB2 is formed. [1] higher than products Total energy content of reactants is
(ii) – Sebatian C mempunyai takat didih yang lebih lower than products
rendah daripada suhu bilik.
Jumlah haba yang dibebaskan Jumlah haba yang dibebaskan
Compound C has a lower boiling point than the room
semasa pembentukan ikatan semasa pembentukan ikatan
temperature. [1]
dalam hasil tindak balas dalam hasil tindak balas lebih
– Molekul sebatian C ditarik oleh daya van der
lebih tinggi daripada jumlah rendah daripada jumlah
Waals yang lemah//Daya tarikan yang lemah
haba yang diserap semasa haba yang diserap semasa
antara molekul.
memutuskan ikatan dalam memutuskan ikatan dalam
The molecules of compound C are pulled by the weak
van der Waals force//Weak attraction force between bahan tindak balas bahan tindak balas
the molecules. [1] Total heat released during the Total heat released during the
formation of bonds in products is formation of bonds in products
– Kurang tenaga haba diperlukan untuk mengatasi
higher than total heat absorbed is lower than total heat absorbed
daya tarikan ini. during the breaking of bonds in during the breaking of bonds in
Less heat energy is needed to overcome the attraction force. reactants reactants
[1]
[8]
(b) Sebatian kovalen: Serbuk naftalena
Covalent compound: Naphthalene powder [1] (b) (i)
Purata suhu awal/ Average initial temperature
Sebatian ion: Serbuk plumbum(II) bromida = 28.5 °C
Ionic compound: Lead(II) bromide powder [1] Perubahan suhu/ Change in temperature [1]
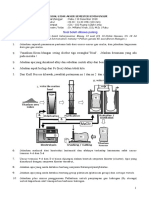
Prosedur/ Procedure: = 30.5 – 28.5 = 2.0 °C
1. Letakkan serbuk naftalena ke dalam mangkuk Q = mcθ
pijar sehingga penuh. = 100 × 4.2 × 2
Put naphthalene powder into a crucible until half full. = 840 J
1 × 50
2.
Sambungkan dua elektrod karbon kepada bateri Bil. mol/ No. of moles of Pb(NO3)2 =
1 000
dan ammeter dengan wayar penyambung. = 0.005 mol
Connect two carbon electrodes to the battery and the 1 × 50
ammeter with the connecting wires. Bil. mol/ No. of moles of Na2SO4 = 1 000
3. Panaskan mangkuk pijar sehingga naftalena = 0.005 mol [2]
melebur. Pb2+ + SO42– → PbSO4
Heat the crucible until naphthalene melts. Daripada persamaan/ From the equation,
4. Celupkan kedua-dua elektrod karbon ke dalam 1 mol Pb2+ bertindak balas dengan 1 mol SO42–
naftalena lebur. menghasilkan 1 mol PbSO4.
Dip both carbon electrodes into the molten naphthalene. 1 mole of Pb2+ reacts with 1 mole of SO42– to produce 1 mole
5. Rekodkan pemerhatian. of PbSO4. [1]
Record the observation.
Penerbit Ilmu Bakti Sdn. Bhd. (732516-M) 2023 J2
\ 0.005 mol Pb2+ bertindak balas dengan 0.005 –
Mg mengalami pengoksidaan kerana atom Mg
mol SO42– menghasilkan 0.005 mol PbSO4 dan membebaskan elektron untuk menghasilkan ion
membebaskan haba sebanyak 840 J. Mg2+.
0.005 mole of Pb2+ reacts with 0.005 mole of SO42– to Mg undergoes oxidation because it releases electrons to
produce 0.005 mole of PbSO4 and releases 840 J of heat. form Mg2+ ions. [2]
[1] – Setengah persamaan penurunan:
840 J
ΔH = Reduction half equation:
0.005 mol
O2 + 4e– → 2O2–
= 168 000 J mol–1
– Molekul O2 mengalami penurunan kerana
= 168 kJ mol–1 [1]
menerima elektron untuk membentuk ion oksida.
Andaian yang dibuat/ Assumptions made:
O2 molecules undergo reduction because they received
1. Muatan haba tentu larutan sama dengan muatan electrons to form oxide ions.
haba tentu air. –Mg ialah agen penurunan manakala O2 ialah
Specific heat capacity of solution is the same as specific agen pengoksidaan.
heat capacity of water.
Mg is a reducing agent, while O2 is an oxidising agent. [2]
2. Tiada haba yang terbebas ke persekitaran//Tiada
(c) Bahan: Larutan ferum(II) sulfat, air bromin, asid sulfurik
haba diserap oleh radas cair
No heat released to the surroundings//No heat absorbed
Materials: Iron(II) sulphate solution, bromine water, dilute
by the apparatus [2]
sulphuric acid [1]
(ii) Perubahan suhu adalah sama = 3.5 °C
Prosedur/ Procedure:
Change in temperature is the same = 3.5 °C
Mendakan yang terhasil masih sama iaitu PbSO4. G
Oleh itu, haba pemendakan masih sama.
The produced precipitate is still the same which is PbSO4. Elektrod karbon Elektrod karbon
Therefore, the heat of precipitate is the same. [2] Carbon electrode Carbon electrode
BAHAGIAN C
Air bromin Larutan ferum(II) sulfat
11 (a) Pengoksidaan: Apabila sesuatu bahan kehilangan Bromine water Iron(II) sulphate solution
elektron semasa tindak balas berlaku. Asid sulfurik cair
Dilute sulphuric acid
Oxidation: When a substance loses electrons during a reaction.
[1] [2]
Penurunan: Apabila sesuatu bahan menerima elektron
semasa tindak balas berlaku. 1. Tuangkan 50 cm asid sulfurik cair ke dalam tiub U.
3
Reduction: When a substance gains electrons during a reaction. Pour 50 cm3 dilute sulphuric acid into a U-tube.
[1] 2. Apitkan tiub U kepada kaki retort.
(b) (i)
Penyesaran logam kuprum daripada larutan Clamp the U-tube to the retort stand.
CuSO4 oleh zink 3. Masukkan 10 cm3 larutan ferum(II) sulfat 1.0 mol
Displacement of copper metal from CuSO4 solution by dm–3 ke dalam satu lengan tiub U.
zinc Add 10 cm3 of iron(II) sulphate solution 1.0 mol dm–3 into one
– Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Zn arm of the U-tube.
– Setengah persamaan pengoksidaan: 4. Masukkan 10 cm3 air bromin ke dalam satu lagi
Oxidation half-equation: lengan tiub U.
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e– Add 10 cm3 of bromine water into another arm of the U-tube.
– Zn mengalami pengoksidaan kerana atom 5. Sambungkan dua elektrod karbon kepada
Zn telah membebaskan elektron untuk galvanometer. Celupkan elektrod karbon masing-
menghasilkan ion Zn2+. masing ke dalam setiap larutan.
Zn undergoes oxidation because it releases electrons Connect the two carbon electrodes to the galvanometer. Dip
to form Zn2+ ions. [2] the carbon electrodes into each solution. [4]
– Setengah persamaan penurunan: Pemerhatian/ Observation:
Reduction half-equation: 1. Jarum galvanometer terpesong dari arah larutan
Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu ferum(II) sulfat ke arah air bromin menunjukkan
– Ion Cu2+ mengalami penurunan kerana telah ada pemindahan elektron.
menerima elektron untuk membentuk atom Galvanometer needle is deflected from iron(II) sulphate
Cu. solution to the direction of bromine water to show transfer of
Cu2+ ions undergo reduction because they received electrons.
electrons to form Cu atoms. 2. Warna larutan ferum(II) sulfat bertukar daripada
– Zn ialah agen penurunan, manakala ion Cu2+ hijau kepada perang, manakala warna air bromin
ialah agen pengoksidaan. [2] berubah daripada perang kepada tidak berwarna.
Zn is a reducing agent, while Cu2+ ion is an oxidising agent. The colour of iron(II) sulphate solution turns from green to
(ii) Pembakaran pita magnesium brown, while the colour of bromine water turns from brown
Combustion of magnesium ribbon to colourless.
– 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO 3. Setengah persamaan penurunan
– Setengah persamaan pengoksidaan: Reduction half equation: Br2 + 2e– → 2Br–
Oxidation half equation: Setengah persamaan pengoksidaan
Mg → Mg2+ + 2e– Oxidation half equation: Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e– [3]
J3 Praktis Topikal SPM: Kimia Tingkatan 5 – Jawapan
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Latihan GaramDokumen3 halamanLatihan GaramAnis Wahida MohamadBelum ada peringkat
- Kimia Skema SPM Kimia k2 Set 3Dokumen8 halamanKimia Skema SPM Kimia k2 Set 3api-3841296Belum ada peringkat
- Kimia Skema SPM Kimia k2 Set 1Dokumen7 halamanKimia Skema SPM Kimia k2 Set 1api-38412960% (1)
- MODUL 2 SKEMA e AKADEMIK 2021Dokumen5 halamanMODUL 2 SKEMA e AKADEMIK 2021Yusa YusufBelum ada peringkat
- Jawapan Pat Kimia t4 2021 Modul 2Dokumen11 halamanJawapan Pat Kimia t4 2021 Modul 2Nur Farhana Binti Mohamad Mokhtar100% (1)
- Anorganik 3Dokumen10 halamanAnorganik 3ilhamBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Kuis GolonganDokumen1 halamanSoal Kuis GolonganAna FitrianaBelum ada peringkat
- Soal PAT K13 Kimia Kelas 10Dokumen10 halamanSoal PAT K13 Kimia Kelas 1003I Gede Bagus Eka WicaksanaBelum ada peringkat
- Share LKPD Hidrokarbon 1Dokumen9 halamanShare LKPD Hidrokarbon 1farza mahsaranaBelum ada peringkat
- Skema Set 7 Paper 2Dokumen8 halamanSkema Set 7 Paper 2Miesya87Belum ada peringkat
- CobaltDokumen50 halamanCobaltNoerman YusufBelum ada peringkat
- Kimia Pas Semester 1Dokumen3 halamanKimia Pas Semester 1Cicilia NatalieBelum ada peringkat
- Kuis 1 Superintensif - OkeDokumen2 halamanKuis 1 Superintensif - OkeAryo WicaksonoBelum ada peringkat
- Jawaban Soal-Soal Tugas Matakuliah Kimia Anorganik 2Dokumen4 halamanJawaban Soal-Soal Tugas Matakuliah Kimia Anorganik 2Rulia Susialis100% (1)
- Latihan Kimia UnsurDokumen2 halamanLatihan Kimia UnsurBundaBelum ada peringkat
- Pembahasan Soal Set 4Dokumen2 halamanPembahasan Soal Set 4princessBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Responsi Kimia 12 IPA - 1 (K13R)Dokumen3 halamanSoal Responsi Kimia 12 IPA - 1 (K13R)31. Nadia Anasthasia X MIPA 1Belum ada peringkat
- 2018 Soal UAS OBj Dan Essay RabuDokumen6 halaman2018 Soal UAS OBj Dan Essay RabuHidayati KardenaBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Latihan Kimia UnsurDokumen4 halamanSoal Latihan Kimia UnsurArdhi OmenBelum ada peringkat
- 068 Modul t2v Kimia Tingkatan 4-223-236Dokumen14 halaman068 Modul t2v Kimia Tingkatan 4-223-236maznah omarBelum ada peringkat
- SNMPTN Kimia Wilayah I 2009Dokumen5 halamanSNMPTN Kimia Wilayah I 2009wahyuBelum ada peringkat
- BP (Buku Pegangan) KIMIA PAKET HALAMAN 164-172Dokumen15 halamanBP (Buku Pegangan) KIMIA PAKET HALAMAN 164-172Syahra raraaBelum ada peringkat
- PKSM f5Dokumen9 halamanPKSM f5NurImanBelum ada peringkat
- Reaksi Reaksi CobaltDokumen5 halamanReaksi Reaksi Cobaltdellad16Belum ada peringkat
- Tugas Kimia Analisis 2Dokumen14 halamanTugas Kimia Analisis 2NvitaaBelum ada peringkat
- Pas Genap - Kimia - Kisi Kisi - Kelas 10Dokumen4 halamanPas Genap - Kimia - Kisi Kisi - Kelas 10Mr CreeperBelum ada peringkat
- Persentase Golongan 9Dokumen42 halamanPersentase Golongan 9rosiBelum ada peringkat
- Soal SBMPTN KimiaDokumen2 halamanSoal SBMPTN KimiaAis Amalia Tsani100% (3)
- Cara Pembuatan Unsur Periode 3Dokumen22 halamanCara Pembuatan Unsur Periode 3Ahmat FauziBelum ada peringkat
- 2021 Kedah Chemistry K2 Set - 1 JawapanDokumen12 halaman2021 Kedah Chemistry K2 Set - 1 JawapanNychang DinieBelum ada peringkat
- Unsur Transisi 5CDokumen38 halamanUnsur Transisi 5CisamanhanafiBelum ada peringkat
- Latihan UAS 1 Kelas XiiDokumen3 halamanLatihan UAS 1 Kelas XiiPrimaazkaBelum ada peringkat
- Kelantan - Skema Kimia K2 Trial SPM 2020Dokumen12 halamanKelantan - Skema Kimia K2 Trial SPM 2020Su Ling ThungBelum ada peringkat
- Soal UTS Kimdas Fisika 2016Dokumen4 halamanSoal UTS Kimdas Fisika 2016Tubagus PutraBelum ada peringkat
- Kelantan - Skema Kimia K2 Trial SPM 2020Dokumen12 halamanKelantan - Skema Kimia K2 Trial SPM 2020Iqmal RosliBelum ada peringkat
- Kumpulan Soal Kimia UnsurDokumen12 halamanKumpulan Soal Kimia Unsuraufa laili muhtarinaBelum ada peringkat
- Reaksi Kimia KobaltDokumen6 halamanReaksi Kimia KobalthahahaBelum ada peringkat
- Persamaan Reaksi Dan Tata Nama KimiaDokumen3 halamanPersamaan Reaksi Dan Tata Nama KimiaairiBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Latihan Persiapan PTS Kimia Kelas XDokumen3 halamanSoal Latihan Persiapan PTS Kimia Kelas XMohamad HuseinBelum ada peringkat
- Febrianti Harahap - V3720023 - P2 - KimsisDokumen31 halamanFebrianti Harahap - V3720023 - P2 - KimsisFebrianti HarahapBelum ada peringkat
- (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 6.: Informasi Berikut Digunakan Untuk Menjawab Soal Nomor 1 Dan 2Dokumen2 halaman(A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 6.: Informasi Berikut Digunakan Untuk Menjawab Soal Nomor 1 Dan 2Muhammad Bimo RamadhanBelum ada peringkat
- Latihan Pts Kimia Kelas X/IiDokumen3 halamanLatihan Pts Kimia Kelas X/IiFadhil A MBelum ada peringkat
- SOAL ALJABAR KIMIA-3 OkDokumen3 halamanSOAL ALJABAR KIMIA-3 OkAliyyah FarhanaBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Un Kimia Kls Xii Ipa (Lat 12)Dokumen9 halamanSoal Un Kimia Kls Xii Ipa (Lat 12)hasanlina2007Belum ada peringkat
- Mandiri Kim 2Dokumen4 halamanMandiri Kim 2Keisya InnayahBelum ada peringkat
- Mandiri K-4Dokumen2 halamanMandiri K-4Ayik SevenfoldBelum ada peringkat
- 10IPA3 Latihan Soal PAT Kimia X 2022Dokumen5 halaman10IPA3 Latihan Soal PAT Kimia X 2022pelajarkeempat4Belum ada peringkat
- Soal SulitDokumen6 halamanSoal Sulitnora santiBelum ada peringkat
- Anor Kobalt NikelDokumen20 halamanAnor Kobalt NikelLiyaAlBrhBelum ada peringkat
- F5c3-Tindak Balas RedoksDokumen14 halamanF5c3-Tindak Balas RedoksNUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -Belum ada peringkat
- SOAL - LATIHAN - KIMIA - UNSUR Kelas XIIDokumen3 halamanSOAL - LATIHAN - KIMIA - UNSUR Kelas XIIdinirahayu820Belum ada peringkat
- Pembahasan Reaksi RedoksDokumen11 halamanPembahasan Reaksi RedoksZAHRA ULHAQBelum ada peringkat
- BesiDokumen26 halamanBesiWinona Wahyusasi AnggraeniBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Kimia Unsur Dok PriDokumen2 halamanSoal Kimia Unsur Dok PriYusri Dwi NuryantiBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Remed Kimia UnsurDokumen3 halamanSoal Remed Kimia UnsurAlma TsabitaBelum ada peringkat
- Skema Kimia K2 Putrajaya 2022Dokumen12 halamanSkema Kimia K2 Putrajaya 2022Jing Yun NgBelum ada peringkat
- Praktikum Kation Golongan 1Dokumen18 halamanPraktikum Kation Golongan 1Anonymous KNnsXtzLDBelum ada peringkat
- SOAL - Kimia - Try Out 08 (Kode 543) - Superintensif 2019Dokumen3 halamanSOAL - Kimia - Try Out 08 (Kode 543) - Superintensif 2019Naurah NazhifahBelum ada peringkat
- Mpdca - Kimia (t5 Bab 3 Pengoksidaan Dan Penurunan)Dokumen4 halamanMpdca - Kimia (t5 Bab 3 Pengoksidaan Dan Penurunan)NUR DAMIA MOHAMAD AZIZIBelum ada peringkat