INTERAKSI ZAT BESI & PROTEIN (Hitam Putih)
INTERAKSI ZAT BESI & PROTEIN (Hitam Putih)
Diunggah oleh
fayzaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
INTERAKSI ZAT BESI & PROTEIN (Hitam Putih)
INTERAKSI ZAT BESI & PROTEIN (Hitam Putih)
Diunggah oleh
fayzaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
INTERAKSI ZAT BESI
dengan PROTEIN
Deddy Muchtadi
Dep. Ilmu dan Teknologi Pangan
Institut Pertanian Bogor
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 1
Deddy Muchtadi
ZAT BESI (Fe)
Jumlah zat besi dalam tubuh = 3-5 g, bervariasi menurut umur, jenis
kelamin,status gizi, status kesehatan & jumlah zat besi cadangan
Semua zat besi terdapat berkombinasi dengan protein mampu
menerima/melepaskan O2 dan CO2 reaksi yang esensial bagi
kehidupan
Tubuh Distribusi Zat Besi dalam Tubuh
tidak
Jumlah Jumlah (+ mg)
memp. Zat/Senyawa Total (%) Laki-laki Wanita
saluran
untuk Hemoglobin 60-75 2100 1750
exkresi Fe
Mioglobin 3 100 100
regulasi
Fe Cadangan (Hati, Limfe, Tulang)* 0-30 1000 400
dilakukan
selama Fe Jaringan (Enzim) 5-15 350 300
absorpsi Fe Transpor (Ferritin) 1 4 4
dlm usus Ferritin Serum 1 0,3 0,3
Jumlah 3554,3 2554,3
* sbg soluble iron complex (ferrtin) & insoluble iron complex (hemosiderin)
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 2
Deddy Muchtadi
Distribusi Zat Besi dalam Tubuh
60 kg F 70 kg M
Functional compounds
Hemoglobin 1750 mg 2300 mg
Myoglobin 290 mg 320 mg
Enzymes 160 mg 180 mg
Transferrin 2.5 mg 3 mg
Storage compounds
Ferritin & hemosiderin 300 mg 1000 mg
Total 2500 mg 3800 mg
Iron Requirements
• Males 0.5-1mg per day An adequate diet
• Menstruating females 1-2mg per day contains 15mg of
iron, 10% of
• Pregnant females 1.5-2.5mg per day
which is absorbed
• Children 1mg per day
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 3
Deddy Muchtadi
Fungsi Zat Besi
(1) Carrier O2 dan CO2 : Fe terdapat dlm hemoglobin dan mioglobin
secara tdk langsung esensial untuk metabolisme energi
(2) Pembentukan sel darah merah
(3) Fungsi lainnya :
(a) Sebagian kecil Fe terdapat dalam enzim jaringan bila
defisiensi Fe jumlah enzim ini berkurang sebelum jumlah
Hb menurun
(b) Mengkatalisis konversi beta-karoten vitamin A
(c) Sintesis Purin bagian integral as. Nukleat (RNA, DNA)
(d) Penghilangan lipid dari darah
(e) Sintesis kolagen
(f) Produksi antibodi
(g) Detoksifikasi zat racun dalam hati
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 4
Deddy Muchtadi
Penyerapan (Absorpsi) Zat Besi
Dua kondisi harus terdapat
sebelum dilakukan
penyerapan oleh usus :
(1) Fe harus terpisah dari
bahan organik (mis.
protein)
(2) Fe+++ harus direduksi
menjadi Fe++ (oleh HCl
lambung atau oleh
vitamin C)
Penyerapan terjadi dalam
Duodenum regulasi :
tergantung dari kebutuhan
tubuh
Penyerapan Fe memerlukan
“protein carrier”
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 5
Deddy
Muchtadi
Penyerapan Zat Besi (Fe)
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 6
Deddy Muchtadi
Normal Iron Storage and Distribution
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 7
Deddy Muchtadi
In a normal balanced state, 1-2 mg of iron enters and leaves the
body every day. Dietary iron is absorbed in the duodenum by
enterocytes and circulates in the plasma. There it is bound by
transferrin, and becomes available for uptake throughout the body
by any tissue with transferrin receptors.
Liver parenchymal tissue is especially rich in transferrin receptors,
and stores large quantities of iron. Most of the circulating iron is
used by the bone marrow to generate hemoglobin for red blood
cells, while around 10-15% is utilized by muscle fibers to generate
myoglobin.
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 8
Deddy Muchtadi
Circulating red blood cells normally comprise the largest iron storage
pool. When they become senescent, red blood cells are engulfed by
retoculo-endotelial macrophages, which make their iron available for
redistribution to other tissues using transferrin. Traces of iron are lost
each day by sloughing of mucosal cells, loss of epithelial cells, and
blood loss.
Since the human body has not evolved a mechanism to clear excess
iron, disorders of iron balance, such as iron overload and iron
deficiency, are among the most common diseases in humans.
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 9
Deddy Muchtadi
Iron Metabolism: Key to Hemoglobin O2 Transport
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 10
Deddy Muchtadi
Interkonversi Fe++ Fe+++ dalam Tubuh
Ferrous Iron Ferric Iron
(dlm makanan) (dlm makanan)
L a m b u n g
Ferrous Iron
Dinding Usus
Ferrous Iron Ferric Iron
(Chelate) (Ferritin)
Aliran Darah
Liver, Spleen (ferric iron)
Bone Marrow (ferric iron)
Ferrous Iron Body Tissues (ferric iron)
(Transport Iron) Muscle (ferric iron)
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 11
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 12
Deddy Muchtadi
Faktor yang Mempengaruhi Penyerapan Fe
(1) Kebutuhan tubuh akan Fe
Direfleksikan oleh transferrin dalam darah atau “chelated
iron” dalam sel mukosa dinding usus (messenger)
Peningkatan TIBC (total iron binding capacity) darah
(disebabkan oleh unsaturated transferrin)
menunjukkan bahwa Fe telah ditransportasikan ke
jaringan atau tempat penyimpanan (hati, limfa)
absorpsi meningkat
Bila sepertiga transferrin telah jenuh penyerapan menurun lagi
Penyerapan pada orang dengan Hb normal : Fe non-heme :
2 – 10 %, Fe heme : 23 %
Pada kondisi defisien Fe non-heme : 20 %, Fe heme : 33 %
Kebutuhan Fe meningkat bila berolahraga produksi sel darah
merah meningkat
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 13
Deddy Muchtadi
HEME-IRON
Zat Besi dalam bahan pangan :
Non-heme iron : sebagian
besar bentuk ferri
(Fe+++), sedikit bentuk
ferro
Heme iron : dalam daging
(bagian dari HB dan Mb)
• In the cell, iron is frequently
found in a sequestered state as
part of a complex with
protoporhyrin IX.
• Protoporphyrin IX containing a
bound iron atom is called a
heme.
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 14
Deddy Muchtadi
• The iron within the heme
prosthetic group is referred to
as heme iron.
• The iron atoms of hemes typically
exist in two different
oxidation states (+2, or +3).
• Oxygen will bind only to the +2
oxidation state.
• When oxygen binds to free
heme, it oxidizes the iron by one
electron, resulting in superoxide
and ferric heme (+3 oxidation
state).
• The ferric form of heme that is
free in solution is called
hematin.
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 15
Deddy Muchtadi
Kebutuhan Tubuh akan Fe
Fe diperlukan untuk mempertahankan jumlah Hb, storage
iron dan untuk pertumbuhan (di luar dari 20 mg yang di-recycle
tiap hari) :
(1) Laki-laki dewasa : 0,9 – 1,2 mg/hari
(2) Wanita dewasa : 1,4 – 2,2 mg/hari
(3) Wanita hamil : 1,9 – 2,2 mg/hari
(4) Anak-anak : 1,1 – 1,4 mg/hari
(5) Gadis remaja : 1,9 – 2,7 mg/hari
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 16
Deddy Muchtadi
KEHILANGAN DARI TUBUH :
Meskipun tidak ada mekanisme exkresi Fe dari tubuh sejumlah kecil
Fe akan hilang melalui keringat, urine dan “permukaan tubuh”
(sel-sel kulit, rambut dan kuku) bervariasi 0,2 – 0,5 mg/hari
Loss Fe dalam feces (dari sel-sel permukaan usus) : 0,7 mg/hari
Untuk wanita terjadi kehilangan Fe selama menstruasi : 0,5 – 1 g/hari
IRON LOSS IN PREGNANCY
• Obligatory iron loss 150-200 mg
• Fetal iron 200-370 mg
• Iron in placenta and cord 30-170 mg
• Iron in blood lost at delivery 90-310 mg
• Total iron loss 470-1050mg
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 17
Deddy
Muchtadi
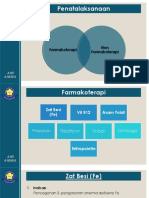
(2) Bentuk zat besi bentuk Fe tereduksi (ferro) lebih mudah diserap
dibandingkan ferri vitamin C sebaiknya ditambahkan pada
pangan yang difortifikasi dengan Fe
(3) Komposisi Makanan :
Daging akan meningkatkan (2-3 X) penyerapan Fe dari bahan
pangan nabati mungkin terbentuk chelate antara AA (dr
daging) dgn Fe
Bila 25 – 75 mg vit C dan 30 – 90 g daging (sapi,
ayam atau ikan) terdapat dlm makanan heme iron
: 23 % available non-heme iron : 5 % available
Bila > 75 mg vit C dan > 90 g daging (sapi, ayam atau
ikan) terdapat dalam makanan : heme iron : 23 %
available non-heme iron : 8 % available
(4) Serat (Dietary Fiber) selulosa & lignin dapat mengganggu
penyerapan Fe (sekitar 1 – 3 %)
(5) Dosis :
Konsumsi 0,25 mg/kg BB : penyerapan 32 %
Konsumsi 4 mg/kg BB : penyerapan 4,1 %
lebih baik dosis rendah dan diberikan 2-3 kali sehari
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 18
Deddy Muchtadi
Faktor Lainnya :
(a) Asam fitat dapat membentuk kompleks tidak larut dengan Fe
tidak dapat diserap
Dalam serealia, asam fitat terikat pada protein tidak
berpengaruh, tetapi yang terdapat dalam dedak (gandum)
berpengaruh negatif
(b) Excess P dapat menghambat penyerapan Fe
(c) Minuman kopi/teh dapat menurunkan penyerapan Fe (polifenol/tanin)
(d) Steatorrhea menunjukkan menurunnya penyerapan Fe
(e) Orang yang tinggal di tempat tinggi (pegunungan) menyerap lebih
banyak Fe
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 19
Deddy Muchtadi
Non-Heme Iron Absorption
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 20
Deddy Muchtadi
Pengaruh Protein thd Penyerapan Zat Besi
Egg albumen strongly inhibited absorption of non-heme iron
(Monsen & Cook, 1979)
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 21
Deddy Muchtadi
Pengaruh Protein thd Penyerapan Zat Besi
Other non-cellular animal proteins (milk, cheese, egg) are
also inhibitory to the absorption of non-heme iron
(Cook & Monsen, 1976)
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 22
Deddy Muchtadi
PENGARUH PROTEIN KEDELAI
Soy protein has an exceptionally inhibitory effect:
- Non-heme iron was absorbed at only 20 % of the reference level,
when soy protein was substituted for egg albumen
- The addition of 100 mg ascorbic acid to the soy protein meals
increased absorption of non-heme iron the soy inhibition seemed
to be modulated more by ascorbic acid than by the addition of meat
to the isolated soy protein meals
iron in soybean flour is bound to phytoferritin poor
absorption in human
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 23
Deddy Muchtadi
Pengaruh Protein thd Penyerapan Zat Besi
Cellular animal proteins appear to enhance the absorption of
non-heme iron
(Cooke & Monsen, 1976)
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 24
Deddy Muchtadi
Pengaruh Protein thd Penyerapan Zat Besi
The enhancing effect of cellular animal protein to the absorption of
non-heme iron is dose-related
(Cook & Monsen, 1975; Bjorn-Rasmussen & Hallberg, 1979)
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 25
Deddy Muchtadi
PEMBENTUKAN SEL DARAH MERAH :
Hb merupakan komponen esensial sel darah merah (erythrocyte)
Sel darah merah dibentuk dalam tulang (bone marrow) bila juml.
sel darah merah berkurang hormon erythropoietin
(diproduksi oleh ginjal) akan menstimulir pembentukan sel
darah merah baru (proses : erythropoiesis)
Erythrocyte dibentuk dalam tulang sebagai “immature cells”
(erythroblast) yang mengandung inti sel (nucleus) pada
waktu menjadi dewasa mensintesis Heme (iron
containing protein) dari glisin + Fe (dibantu oleh vitamin B12
atau pyridoxine)
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 26
Deddy Muchtadi
Pada waktu yang sama disintesis juga protein Globin Heme +
Globin = Hemoglobin yang mengandung immature red blood cell
(retyculocyte) dalam aliran darah akan melepaskan inti sel
menjadi “mature non-nucleated red blood cell” (erythrocyte)
Karena sel darah merah tidak mempunyai inti sel tidak dapat
mensintesis enzim untuk kelangsungan hidupnya sel darah
merah masa hidupnya hanya selama enzim masih terdapat dan sel
darah merah masih berfungsi sebagai carrier O 2 dan CO2 (umumnya
4 bulan atau 120 hari)
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 27
Deddy Muchtadi
TULANG Fe Glisin
Erythroblast Heme Globin
ALIRAN DARAH
Reticulocyte Hemoglobin
Erythrocyte
Bila sel darah merah mati dipindahlan dari darah ke hati, tulang
dan limfa dalam limfa, Fe dan AA dari hemoglobin diambil
kembali Fe disimpan dalam hati atau limfa sebagai ferritin
atau hemosiderin atau dikembalikan ke dalam tulang untuk
digabungkan dengan molekul Hb baru; dan AA dikembalikan
ke darah untuk sintesis protein tubuh
Bagian lain (struktur sel) dari erythrocyte dixkresikan melalui asam/
garam empedu
Kecepatan penghancuran sel darah merah meningkat bila defisiensi
vitamin C, E atau B12
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 28
Deddy Muchtadi
Sel Darah Merah
Struktur Sel Hemoglobin
As. Empedu Protein Fe
As. Amino Storage Fe
Urea
(Urine) Energi
Kadar Hb dalam darah : laki-laki dewasa = 15 g Hb/ dl darah
wanita dewasa = 13,6 g Hb/dl darah
Jumlah Hb dalam 5 liter darah laki-laki dewasa = 750 g
Karena hidupnya erythrocyte hanya sekitar 120 hari 1/120 sel-sel
erythrocyte harus diganti setiap hari diperlukan 20 mg Fe/
hari karena tidak mungkin menyerap Fe sebanyak 20 mg/
hari dari makanan konservasi Fe dalam tubuh (dari
erythrocyte) sangat penting
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 29
Deddy Muchtadi
Myoglobin is a compact globular
protein. It is a single polypeptide
chain of 153 amino acids, having a
molecular weight of 16,700. It contains
a covalently bound heme group.
In contrast, Hemoglobin is a tetramer.
Each polypeptide chain is structurally
similar to the polypeptide chain of
myoglobin, and each contains a heme,
which like in myoglobin, is where
oxygen binds. The overall structure of
hemoglobin is an a2b2 tetramer. The a
subunit is about 141 amino acids,
while the b subunit is about 146 amino
acids.
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 30
Deddy Muchtadi
Hemoglobin
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 31
Deddy Muchtadi
Blood
Components
• Erythrocytes
– Red Blood
Cells (RBC)
– O2 & CO2
transport
• White Blood Cells
(WBC)
– Immune defense
– Phagocytosis
• Platelets: clotting
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 32
Deddy Muchtadi
Hematopoiesis:
Blood Cell
Formation
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 33
Deddy Muchtadi
Blood Components: Platelets
• Coagulate, form plug, prevent blood loss
• Formed by fragmentation from megakaryoctyes
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 34
FAKTOR PEMBEKU (KOAGULASI) DARAH
Faktor Nama Zat/Senyawa
I Fibrinogen
II Prothrombin
III Thromboplastin
IV Kalsium (Ca)
V Faktor labil/Proakselerin/Globulin/Akselerator (Ac globulin)
VI Prokonvertin/Akselerator KonversiProthrombin Serum (SPCA)/Ko-
thromboplastin/Antoprothrombin I
VII Faktor Antihemolitik/Globulin Anti Hemolitik (AHG)
VIII Komponen Thromboplastin Plasma (PTC)/ Faktor Christmas
IX Faktor Stuart-Power
X Antesedan Thromboplastin Plasma (PTS)
XI Faktor Hageman
XII Faktor Laki-Lorand (LLF)
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 35
Deddy Muchtadi
Hemostasis:
Coagulation &
Clot Stabilization
• Prothrombin
• Ca++
• Fibrinogen
• Fibrin
• Polymerization
7/27/21 Interaksi Fe & Protein 36
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Metabolisme BesiDokumen10 halamanMetabolisme BesiAn'umillah Arini ZidnaBelum ada peringkat
- Farmakologi Obat AnemiaDokumen18 halamanFarmakologi Obat AnemiaratnawatiBelum ada peringkat
- Metabolisme Zat BesiDokumen6 halamanMetabolisme Zat BesiSelvia RahayuBelum ada peringkat
- Metabolisme Zat Besi FixDokumen18 halamanMetabolisme Zat Besi FixKholifatul Khasanah100% (1)
- Metabolisme BesiDokumen13 halamanMetabolisme BesiAli Ahmad KhameiniBelum ada peringkat
- Anemia Defisiensi Besi Pada AnakDokumen12 halamanAnemia Defisiensi Besi Pada AnakRifka WidianingrumBelum ada peringkat
- (K3) Farmakologi Hematinik (Dr. Ufah)Dokumen66 halaman(K3) Farmakologi Hematinik (Dr. Ufah)Puti Callistha IchsanBelum ada peringkat
- METABOLISME ZAT BESI FeDokumen31 halamanMETABOLISME ZAT BESI Fegracia daraBelum ada peringkat
- Metabolisme Besi Saat HamilDokumen8 halamanMetabolisme Besi Saat HamilRESSABelum ada peringkat
- Metabolisme Besi Dan Pembentukan HemoglobinDokumen11 halamanMetabolisme Besi Dan Pembentukan Hemoglobinamirnu100% (7)
- Makalah FerritinDokumen11 halamanMakalah FerritinMaulana S SidikBelum ada peringkat
- Besi Dan Radikal BebasDokumen22 halamanBesi Dan Radikal BebasPramasanti HeraBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Hematologi Metabolisme Zat BesiDokumen14 halamanMakalah Hematologi Metabolisme Zat BesiArvan SagalaBelum ada peringkat
- Metabolisme BesiDokumen6 halamanMetabolisme BesiHagi WibawaBelum ada peringkat
- BAB II (FIN) Tablet Zat BesiDokumen22 halamanBAB II (FIN) Tablet Zat BesiDofi Pebriadi100% (1)
- 11 - 235hepcidin Dan Anemia Defisiensi BesiDokumen8 halaman11 - 235hepcidin Dan Anemia Defisiensi BesiAnonymous ZbhBxeEVBelum ada peringkat
- FebbbkbkbkDokumen13 halamanFebbbkbkbkMutia DwisaBelum ada peringkat
- Metabolisme FeDokumen4 halamanMetabolisme Feindahneesa0% (1)
- Pengecatan Prussian BlueDokumen12 halamanPengecatan Prussian BluePande Putu Rangga RadityaBelum ada peringkat
- Iom GitDokumen4 halamanIom Git2127 Risqia Maulida PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Kelainan DarahDokumen34 halamanKelainan DarahDini MayrisdayaniBelum ada peringkat
- Zat BesiDokumen4 halamanZat BesibdhBelum ada peringkat
- Metabolisme Zat BesiDokumen13 halamanMetabolisme Zat BesiNad2HeRe!Belum ada peringkat
- Ds Case 1 HistoneDokumen21 halamanDs Case 1 HistoneAlfiyya nur marhdiyyahBelum ada peringkat
- Anemia Defisiensi BesiDokumen3 halamanAnemia Defisiensi BesiCennikon PakpahanBelum ada peringkat
- Metabolisme Zat BesiDokumen13 halamanMetabolisme Zat BesiTeus FatamorganaBelum ada peringkat
- Anemia Defisiensi Besi: A. DefinisiDokumen14 halamanAnemia Defisiensi Besi: A. DefinisiemaBelum ada peringkat
- Metabolisme MikromineralDokumen36 halamanMetabolisme MikromineralSyifaa PravitasuriBelum ada peringkat
- Mineral MikroDokumen57 halamanMineral MikroMaro MendoncaBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Mandiri Fero SulfatDokumen20 halamanMakalah Mandiri Fero SulfatJoko YanBelum ada peringkat
- Bab IiDokumen25 halamanBab IiNikhen NBelum ada peringkat
- Anemia Defisiensi BesiDokumen36 halamanAnemia Defisiensi Besiawaniedream8391Belum ada peringkat
- Bioavailabilitas MineralDokumen8 halamanBioavailabilitas MineralirfanBelum ada peringkat
- Farmakologi - Anti AnemiaDokumen23 halamanFarmakologi - Anti AnemiaGraciaBelum ada peringkat
- Anemia Defisiensi Besi Dalam KehamilanDokumen5 halamanAnemia Defisiensi Besi Dalam KehamilanAndy F MonroeBelum ada peringkat
- Palacio Et Al. - 1967 - 済無No Title No Title No TitleDokumen31 halamanPalacio Et Al. - 1967 - 済無No Title No Title No TitleLENI KUSUMAWATIBelum ada peringkat
- Metabolisme BesiDokumen29 halamanMetabolisme BesiAlFi KamaliaBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal 1Dokumen22 halamanJurnal 1Irara RaBelum ada peringkat
- Bioavailabilitas MineralDokumen16 halamanBioavailabilitas MineralGilman Ali RezaBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Mineral-Kelompok 10Dokumen14 halamanMakalah Mineral-Kelompok 10Abdul HadiBelum ada peringkat
- Zat BesiDokumen9 halamanZat BesiPratiwi Raissa WindianiBelum ada peringkat
- AnemiaDokumen56 halamanAnemiamunik fajar ranyBelum ada peringkat
- Gizi SeimbangDokumen7 halamanGizi SeimbangIghlimaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter II PDFDokumen22 halamanChapter II PDFSimbaBelum ada peringkat
- Kelompok 6-Pengaruh Mineral Fe Terhadap ObatDokumen10 halamanKelompok 6-Pengaruh Mineral Fe Terhadap ObatSeptiBelum ada peringkat
- Metabolisme Asam FolatDokumen40 halamanMetabolisme Asam FolatIca Trianjani Setyaningrum67% (3)
- Metabolisme Fe Dan ZNDokumen9 halamanMetabolisme Fe Dan ZNRinday 77Belum ada peringkat
- Anemia Defisiensi BesiDokumen23 halamanAnemia Defisiensi BesiVujhia UL HaqBelum ada peringkat
- Metabolisme FeDokumen9 halamanMetabolisme FeSyahrilBelum ada peringkat
- Biokimia Pada Kasus GAKYDokumen6 halamanBiokimia Pada Kasus GAKYRukhaniBelum ada peringkat