Invko Mat2 3
Diunggah oleh
nazainJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Invko Mat2 3
Diunggah oleh
nazainHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
MAT 2
materi78.co.nr
Invers dan Komposisi Fungsi
A.
Fungsi kuadrat: f(x) = x2 6x 7, x 3
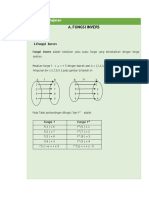
INVERS FUNGSI
Invers fungsi (f-1(x)) adalah kebalikan dari fungsi
f(x) yang juga merupakan sebuah fungsi.
f-1(x2 6x 7) = x
Syarat agar suatu fungsi memiliki invers:
(x -3)2 9 = y + 7
a.
x 3 = y+16
f(x) harus merupakan fungsi bijektif.
x2 6x = y + 7
b. Grafik fungsi tidak boleh membalik.
x = 3 y+16
Contoh invers fungsi
penyajian fungsi:
karena x 3, maka
dari berbagai cara
Dapat dilakukan dengan membalik arah
panah.
Contoh:
1
2
3
4
f-1(x3 +2) = x
y = x3 +2
x3 = 2 - y
x = 32 - y
f-1(x) = 2 - x
Fungsi akar: f(x) = 2x - 5
B
h
f-1(x) = 3 + x+16
Fungsi polinomial: f(x) = x3 +2
1) Diagram panah
y = x2 6x 7
f-1(2x - 5) = x
a
b
c
d
y = 2x - 5
y2 = 2x 5
2x = y2 + 5
x=
y2 + 5
2
f-1(x) =
x2 + 5
2
Fungsi logaritma: f(x) = 2log(x-3) 4
A
h-1
1
2
3
4
f-1(2log(x -3) 4) = x
y = 2log(x -3) 4
a
b
c
d
y + 4 = 2log(x -3)
2y + 4 = x 3
x = 2y + 4 + 3
Fungsi eksponen: f(x) = 3x+1 5
2) Pasangan berurutan
Berlaku:
f-1(3x+1 5) = x
Df = Rf-1
log(y + 5) = x + 1
Contoh:
x = 3log(y + 5) 1
f = {(1, 5)(2, 8)(3, 10)(4, 13)}
3) Rumus fungsi
f(x) = a, maka inversnya:
f-1(a) = x
Contoh:
Tentukan invers dari fungsi berikut!
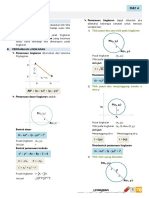
Invers f-1(x) pada grafik adalah sebuah garis
yang simetris terhadap f(x) pada cermin y =
x.
Grafik yang memiliki invers fungsi adalah
grafik yang jika dibuat garis mendatar hanya
memotong satu titik saja.
Fungsi linear : f(x) = 2x + 1
x=
y-1
2
, maka
Fungsi pecahan: f(x) =
f-1(
3-x
2x + 5
)=x
f-1
y = 2x + 1
f-1(x) =
3-x
f-1(x) = 3log(x + 5) 1
4) Grafik
f-1 = {(5, 1)(8, 2)(10, 3)(13, 4)}
f-1(2x +1) = x
y = 3x+1 5
y + 5 = 3x+1
Rf = Df-1
Berlaku:
f-1(x) = 2x + 4 + 3
y=x
x-1
2
, x - 5/2
2x + 5
3-x
y=
2x + 5
2xy + 5y = 3 x
2xy + x = 3 - 5y
x(2y + 1) = 3 5y
x=
3 - 5y
2y + 1
f-1(x) =
3 - 5x
2x + 1
FUNGSI
MAT 2
materi78.co.nr
B.
KOMPOSISI FUNGSI
b. gfg(3)
= g(f(g(3)))
Komposisi fungsi (o) adalah kejadian dimana
fungsi f yang memetakan anggota x ke y,
dilanjutkan oleh fungsi g yang memetakan y ke z.
x
1
2
3
a
b
c
= g(f(2(3) + 2)) = g(f(8))
= g(8 - 4) = g(2)
= 2(2) + 2 = 6
C.
d
e
SIFAT DAN ALJABAR FUNGSI
Sifat-sifat invers dan komposisi fungsi:
Involusi
(f-1)-1 = f
fI = If = f
Identitas
gf
f(x) = y
atau
f = {(x, y)}
g(y) = z
atau
g = {(y, z)}
sehingga, gf(x) = g(f(x)).
atau gf = {(x, z)}
Tidak
komutatif
fg gf
Asosiatif
(fgh) = ((fg)h) = (f(gh))
Penulisan komposisi fungsi:
gf(x)
dibaca f dilanjutkan g
dapat ditulis gf(x) atau g(f(x)).
Invers
komposisi
Pada komposisi fungsi:
(fg)-1 = g-1f-1
(fgh)-1 = h-1g-1f-1
Jika fg = h, maka:
1) Irisan daerah hasil fungsi f dengan daerah
asal fungsi g bukan himpunan kosong.
2) Daerah asal fungsi komposisi gf adalah
daerah asal fungsi f.
ff-1 = f-1f = I = x
f = hg-1
Lain-lain
g = f-1h
Jika fgh = k, maka:
f = k(gh)-1
3) Daerah hasil fungsi komposisi gf adalah
daerah hasil fungsi g.
h = (fg)-1k
Komposisi fungsi dalam berbagai penyajian
data:
Sifat-sifat aljabar fungsi:
1) Pasangan berurutan
Jika diketahui:
f = {(1, 2)(2, 3)(3, 4)(4, 1)}
g = {(1, 3)(2, 2)(3, 1)(4, 4)}
Maka Rg = Df. Tentukan:
fg = {(1, 4)(2, 3)(3, 2)(4, 1)}
gf = {(1, 2)(2, 1)(3, 4)(4, 3)}
fgf = {(1, 3)(2, 2)(3, 1)(4, 4)}
2) Rumus fungsi
Jika diketahui:
x + 2, jika x < -1
f(x) = x2 3, jika -1 x < 4
x - 4, jika x 4
g(x) = 2x + 2
Tentukan:
a. ffff(5)
= f(f(f(f(5))))
g = f-1kh-1
1) Penjumlahan
(f+g)(x)= f(x)+g(x)
Df Dg= Df+g
2) Pengurangan
(f-g)(x)= f(x)-g(x)
Df Dg= Df-g
3) Perkalian
(f.g)(x)= f(x).g(x)
Df Dg= Dfg
4) Pembagian
f
(g)(x)=
f(x)
g(x)
Df Dg = Df/g
g(x) 0
= f(f(f(5 - 4))) = f(f(f(1)))
= f(f(12 3)) = f(f(-2))
= f(-2 + 2) = f(0)
= 02 3 = 3
FUNGSI
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- .PPT MTK Wajib Kel. 1Dokumen13 halaman.PPT MTK Wajib Kel. 1ridh eggBelum ada peringkat
- Fungsi Komposisi Dan Fungsi InversDokumen15 halamanFungsi Komposisi Dan Fungsi Inversnining karlinaBelum ada peringkat
- Fungsi Komposisi Dan Fungsi InversDokumen10 halamanFungsi Komposisi Dan Fungsi InversHendraBelum ada peringkat
- Komposisi Dua FungsiDokumen12 halamanKomposisi Dua FungsiDevy 'autissm' NoviandhitaBelum ada peringkat
- Operasi Pada FungsiDokumen32 halamanOperasi Pada Fungsiamelia mambrasar100% (1)
- BAB 3 Modul Fungsi-DikonversiDokumen12 halamanBAB 3 Modul Fungsi-DikonversiAndi WiedhBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Fungsi - SPDokumen95 halaman2 Fungsi - SPEdma Nadhif Oktariani100% (2)
- Hand Out (2) Matematika 1 (Fungsi)Dokumen35 halamanHand Out (2) Matematika 1 (Fungsi)Hardianti KamaluddinBelum ada peringkat
- Kegiatan Pembelajaran 2 Operasi Aljabar FungsiDokumen7 halamanKegiatan Pembelajaran 2 Operasi Aljabar FungsiDhiniBelum ada peringkat
- Fungsi SongsangDokumen17 halamanFungsi SongsangjesslynBelum ada peringkat
- FungsiDokumen37 halamanFungsiIndosat OoredooBelum ada peringkat
- Matematika DasarDokumen22 halamanMatematika DasarAhmad MukhlisBelum ada peringkat
- Matdas - Course 1 Fungsi Invers, KomposisiDokumen49 halamanMatdas - Course 1 Fungsi Invers, KomposisizalfaBelum ada peringkat
- Matematika ArsitekturDokumen80 halamanMatematika ArsitekturNon Aktif81% (16)
- Matematika IPA - 12 SMA PTN Worksheet 20 (Komposisi Fungsi Invers) (Layout) TA 21-22. Nasywa Cs 27-01Dokumen5 halamanMatematika IPA - 12 SMA PTN Worksheet 20 (Komposisi Fungsi Invers) (Layout) TA 21-22. Nasywa Cs 27-01Rizky AgungBelum ada peringkat
- PJJ Matematika Wajib Kelas X 5-6Dokumen3 halamanPJJ Matematika Wajib Kelas X 5-6Puput NoviantiBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan Ajar Fungsi Invers Dan Fungsi KomposisiDokumen6 halamanBahan Ajar Fungsi Invers Dan Fungsi KomposisiBambang SenoBelum ada peringkat
- Materi Fungsi KomposisiDokumen5 halamanMateri Fungsi KomposisiKdsatriyawisnuBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan 4 - FungsiDokumen29 halamanPertemuan 4 - FungsiAmalia Wulan SaputriBelum ada peringkat
- Materi 5. Relasi Dan Fungsi RiilDokumen44 halamanMateri 5. Relasi Dan Fungsi RiilUmmi Kalsum ZainuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Fungsi Linier OkeDokumen28 halamanFungsi Linier OkeAgung PodomoroBelum ada peringkat
- Fungsi Komposisi Dan Invers FungsiDokumen8 halamanFungsi Komposisi Dan Invers FungsieligatuBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Ke 7Dokumen7 halamanTugas Ke 7Ropinus Sarumaha RopinusBelum ada peringkat
- TB Bab 3Dokumen5 halamanTB Bab 3xaxaxaxa xaxaxaxaBelum ada peringkat
- FUNGSI INVERS-dikonversiDokumen5 halamanFUNGSI INVERS-dikonversiwilly darwatiBelum ada peringkat
- FungsiDokumen29 halamanFungsitati masriyatiBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 3 FungsiDokumen29 halamanBab 3 Fungsitati masriyatiBelum ada peringkat
- Bab Fungsi Komposisi Dan InversDokumen61 halamanBab Fungsi Komposisi Dan InversLi V YaBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan 3Dokumen31 halamanPertemuan 3Muhammad Aldhi PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan 1 FungsiDokumen22 halamanPertemuan 1 Fungsimuhammad iqballBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan Ajar Aljabar Dan Trigonometri PDFDokumen283 halamanBahan Ajar Aljabar Dan Trigonometri PDFTrisnawathy NasirBelum ada peringkat
- Materi Funsi InversDokumen7 halamanMateri Funsi InversAqilah ZainabBelum ada peringkat
- Fungsi & GrafikDokumen35 halamanFungsi & GrafikAhimBelum ada peringkat
- Resume Kalkulus Bab 2 Dan 3Dokumen15 halamanResume Kalkulus Bab 2 Dan 3Muhammad Iqbal0% (1)
- Bab 6 Komposisi Dua Fungsi Dan Fungsi InversDokumen15 halamanBab 6 Komposisi Dua Fungsi Dan Fungsi InversResy MonitasariBelum ada peringkat
- Jenis-Jenis FungsiDokumen18 halamanJenis-Jenis FungsiNabila50% (2)
- Fungsi KomposisiDokumen3 halamanFungsi KomposisiANDRIES ANDRIESBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Fungsi KomposisiDokumen2 halamanSoal Fungsi Komposisianon_197794120Belum ada peringkat
- Komposisi Dua FungsiDokumen16 halamanKomposisi Dua FungsiAde ErmawatiBelum ada peringkat
- FungsiDokumen12 halamanFungsiandhyi47Belum ada peringkat
- Makalah MatematikaDokumen9 halamanMakalah MatematikaMarsanda ElizaBelum ada peringkat
- Pengertian Fungsi LogaritmaDokumen28 halamanPengertian Fungsi Logaritmanabila safitriBelum ada peringkat
- FUNGSIDokumen16 halamanFUNGSIRizqy DhiniaBelum ada peringkat
- Fungsi LogaritmaDokumen17 halamanFungsi LogaritmaBang GessBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan 3Dokumen32 halamanPertemuan 3Draconic TzyBelum ada peringkat
- Fungsi Dan Grafik Fungsi - Minggu II (1 September) PDFDokumen17 halamanFungsi Dan Grafik Fungsi - Minggu II (1 September) PDFRisma Karimah PratiwiBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Fungsi Week 5Dokumen15 halamanTugas Fungsi Week 5Fery BuyaBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 3 Fungsi1Dokumen13 halamanBab 3 Fungsi1Juanita BentonBelum ada peringkat
- Kumpulan Materi Power MatDokumen21 halamanKumpulan Materi Power MatJihan Putri100% (1)
- Fungsi KomposisiDokumen13 halamanFungsi KomposisiRahmaBelum ada peringkat
- Fungsi 4Dokumen5 halamanFungsi 4Isabella T AnantaBelum ada peringkat
- Kalkulus I 04 FungsiDokumen29 halamanKalkulus I 04 FungsiFerdian Rafa FirdausBelum ada peringkat
- Fungsi Komposisi, Operasi Aljabar Dan Fungsi InversDokumen9 halamanFungsi Komposisi, Operasi Aljabar Dan Fungsi InversPICIS SuryaBelum ada peringkat
- Dan 6. FungsiDokumen38 halamanDan 6. FungsiTri AnggoroBelum ada peringkat
- FungsiDokumen13 halamanFungsiendahBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan 5 OPERASI PADA FUNGSIDokumen19 halamanPertemuan 5 OPERASI PADA FUNGSIKubun Ginta Ginting100% (1)
- JH, VHLHDokumen11 halamanJH, VHLHnazainBelum ada peringkat
- HrduyDokumen1 halamanHrduynazainBelum ada peringkat
- Pelajaran Gramatika Jerman: Finished MarDokumen1 halamanPelajaran Gramatika Jerman: Finished MarnazainBelum ada peringkat
- Lembar Kerja Siswa MomentumDokumen3 halamanLembar Kerja Siswa MomentumnazainBelum ada peringkat
- Io Io (Iuopu9ipo8uiDokumen1 halamanIo Io (Iuopu9ipo8uinazainBelum ada peringkat
- Wa0001Dokumen31 halamanWa0001nazainBelum ada peringkat
- Lembar Kerja Siswa MomentumDokumen3 halamanLembar Kerja Siswa MomentumnazainBelum ada peringkat
- Polin Mat4 PDFDokumen3 halamanPolin Mat4 PDFnazainBelum ada peringkat
- Baris Dan DeretDokumen2 halamanBaris Dan DeretAriati CitadewiBelum ada peringkat
- Pelajaran Gramatika Jerman: Finished MarDokumen1 halamanPelajaran Gramatika Jerman: Finished MarnazainBelum ada peringkat
- Lingk Mat4 1Dokumen3 halamanLingk Mat4 1nazainBelum ada peringkat
- Pelajaran Gramatika Jerman: Finished MarDokumen1 halamanPelajaran Gramatika Jerman: Finished MarnazainBelum ada peringkat
- Hdmol Kim1 3Dokumen4 halamanHdmol Kim1 3Hildayanti MustikasariBelum ada peringkat
- Pelajaran Gramatika Jerman: Finished MarDokumen1 halamanPelajaran Gramatika Jerman: Finished MarnazainBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Kerajaan Islam Di IndonesiaDokumen20 halaman8 Kerajaan Islam Di IndonesiaChairil VenusBelum ada peringkat
- Pelajaran Gramatika Jerman: Finished MarDokumen1 halamanPelajaran Gramatika Jerman: Finished MarnazainBelum ada peringkat
- BBM 7Dokumen30 halamanBBM 7Tyuul Clarkson MooBelum ada peringkat
- Pembahasan Soal Statistik SMADokumen30 halamanPembahasan Soal Statistik SMAWilliam LuffyBelum ada peringkat
- Xy JG DDNC DehDokumen7 halamanXy JG DDNC DehnazainBelum ada peringkat
- FunkDokumen1 halamanFunknazainBelum ada peringkat
- Peluang Kombinasi Jabat Tangan GabunganDokumen2 halamanPeluang Kombinasi Jabat Tangan GabungannazainBelum ada peringkat
- Baris Dan DeretDokumen2 halamanBaris Dan DeretAriati CitadewiBelum ada peringkat
- Hdmol Kim1 3Dokumen4 halamanHdmol Kim1 3Hildayanti MustikasariBelum ada peringkat
- Bab-1 pkn2Dokumen36 halamanBab-1 pkn2nazainBelum ada peringkat
- D H CDokumen3 halamanD H CnazainBelum ada peringkat
- Bgmol Kim1 3Dokumen4 halamanBgmol Kim1 3Fadli HmiBelum ada peringkat
- Hdmol Kim1 3Dokumen4 halamanHdmol Kim1 3Hildayanti MustikasariBelum ada peringkat
- JVF GK AdaDokumen4 halamanJVF GK AdanazainBelum ada peringkat
- 9 Kolonialisme Dan ImperialismeDokumen27 halaman9 Kolonialisme Dan Imperialismedwi marita putriBelum ada peringkat