Kebutuhan Dasar Manusia
Diunggah oleh
Chaerul Amin RuslyTopik yang dibahas
- kebutuhan fisiologis,
- kesehatan individu,
- kesejahteraan,
- harga diri,
- kebutuhan emosional,
- komunikasi keluarga,
- nutrisi,
- konflik keluarga,
- tujuan keluarga,
- keluarga
Kebutuhan Dasar Manusia
Diunggah oleh
Chaerul Amin RuslyTopik yang dibahas
- kebutuhan fisiologis,
- kesehatan individu,
- kesejahteraan,
- harga diri,
- kebutuhan emosional,
- komunikasi keluarga,
- nutrisi,
- konflik keluarga,
- tujuan keluarga,
- keluarga
Common questions
Didukung oleh AIFamily structures and dynamics are crucial in the context of healthcare as they directly influence individual health behaviors and outcomes. An effective family unit exercises control over its environment and positively impacts health behaviors, promoting preventive measures and healthy lifestyles . The family's role in healthcare is emphasized as they provide the primary social environment for health promotion. Healthcare providers must therefore consider the family as an essential context for individual health, recognizing its influence on health behaviors and decisions .
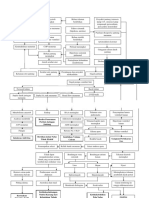
Maslow's hierarchy of needs suggests that individuals prioritize their basic requirements in a hierarchy, starting from physiological needs, which are fundamental for survival, such as oxygen, water, and food . However, safety needs, which include physical and psychological security, sometimes take precedence over these physiological needs. This is because the immediate need for safety from environmental risks or psychological threats might be critical for survival in certain contexts. For instance, in a situation of imminent danger, the individual's focus may shift from seeking food or water to ensuring personal safety .
Cultural and social backgrounds significantly shape individuals' sexual needs and behaviors by influencing values, ethics, self-esteem, and overall well-being . These factors affect how individuals perceive and express their sexuality, which can vary greatly across cultures. For healthcare providers, understanding these cultural nuances is crucial for delivering competent and respectful care. Providers must consider these differences to address sexual health and needs effectively, ensuring that care plans are appropriate and sensitive to the cultural context of the patient . This cultural competence enhances the therapeutic relationship and supports patient-centered care .
In Maslow's hierarchy of needs, self-actualization represents the highest level of psychological development, where an individual realizes their fullest potential. Once all lower-level needs, such as physiological, safety, love, and esteem are met, individuals focus on personal growth and self-fulfillment . During hospitalization, the need for privacy becomes significant as part of self-actualization, yet it is often compromised due to the hospital environment. This impacts the individual's sense of autonomy and personal space, which are critical for maintaining self-actualization . Therefore, efforts should be made to respect patient privacy to facilitate their overall well-being and alignment with their intrinsic goals .
Prolonged deprivation of physiological needs such as oxygen or water has severe implications for human health. Oxygen deprivation can lead to critical health failures within minutes, since every cell requires oxygen for metabolic processes that produce energy . Water deprivation results in dehydration, impairing metabolic processes, and can be fatal within days. Without adequate hydration, cellular functions deteriorate, causing systemic imbalance and potential organ failure . Thus, meeting these needs is vital for maintaining cellular integrity and overall health .
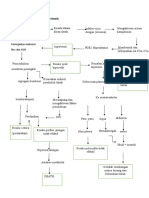
A decline in health of a primary caregiver significantly shifts family dynamics and roles. Other family members may assume additional responsibilities, altering established roles, and decision-making processes. This shift can place stress on the family system, affecting emotional, financial, and logistical aspects. The reallocation of tasks might lead to role conflict, reduced family support, and increased caregiving burden on other members. Consequently, the family must adapt through reorganization and redistribution of care-tasks, while maintaining family function and health . These changes require effective communication and conflict resolution to sustain family cohesion and functionality .
Healthcare professionals can adopt several strategies to manage pain and discomfort in patients effectively. Preemptive pain management involves anticipating the patient's need for pain relief and applying interventions proactively. This can include administering medication at scheduled intervals and employing non-pharmacological techniques such as relaxation exercises, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and using heat or cold applications . Additionally, personalized care is crucial, where treatments are tailored to the individual's pain threshold and preferences, and patient education is provided on pain management to involve them in their care plan .
Environmental control plays a pivotal role as a family function in maintaining health. Families that effectively control their environment can create safe, supportive, and health-promoting settings, mitigating risks of disease and promoting well-being . By regulating factors such as clean air, safe housing, nutrition, and stress levels, families help prevent health issues and encourage healthy behaviors among members. The effectiveness of this control is heavily linked to the familial communication and collective decision-making processes, which shape the family’s capability to adapt to external influences and challenges . Better control over environmental factors ensures that the family maintains its health integrity and resilience .
Exploration and manipulation activities are fundamental for childhood development as they provide new experiences that are essential for learning and cognitive growth. Children engage with their environment through these activities, which helps them understand and interact with the world around them . These activities support the development of problem-solving skills, stimulate curiosity, and foster creativity. The manipulation of objects allows children to learn about cause and effect, and the exploration of their environment encourages empirical learning and adaptation .
External and internal stimuli play a significant role in triggering and prioritizing human basic needs. External stimuli might include environmental changes, social interactions, or physical conditions, while internal stimuli include physiological or emotional states . The failure to meet these needs, such as through inadequate response to these stimuli, can lead to adverse outcomes including stress, illness, or psychological distress . Specifically, unmet needs like oxygen or water deprivation can lead to immediate physical harm, whereas failing to respond to emotional needs can lead to psychological impacts .