RPP Pertemuan 1 English Version
Diunggah oleh
echa_iqbalHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
RPP Pertemuan 1 English Version
Diunggah oleh
echa_iqbalHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
RPP - 1
LESSON PLAN
1. IDENTITY a. School Name b. Class c. Semester d. Subject Matters e. Meetings : SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB :X :2 : Kimia : 3 times meeting
2. STANDAR OF COMPETENCE To understand about characteristics of electrolyte and non-electrolyte and oxidation-reduction reaction.
3. KOMPETENSI DASAR Menjelaskan perkembangan Konsep Reaksi OksidasiReduksi dan hubungannnya dengan tata nama senyawa serta penerapannya.
4. INDIKATOR PENCAPAIAN KOMPETENSI a. Membedakan konsep Oksidasi Reduksi ditinjau dari penggabungan dan pelepasan Oksigen, pelepasan dan penerimaan elekrton serta peningkatan dan penurunan Bilangan oksidasi. b. Menentukan Bilangan Oksidasi atom dalam senyawa atau ion. c. Menentukan Oksidator dan Reduktor dalam Reaksi Redoks.
5. TUJUAN PEMBELAJARAN a. Siswa dapat membedakan konsep Oksidasi Reduksi ditinjau dari penggabungan dan pelepasan Oksigen, pelepasan dan penerimaan elekrton serta peningkatan dan penurunan Bilangan oksidasi. b. Siswa dapat menentukan Bilangan Oksidasi atom dalam senyawa atau ion. c. Siswa dapat menentukan Oksidator dan Reduktor dalam Reaksi Redoks. 6. MATERI AJAR
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 2
Reaksi redoks merupakan penggabungan antara dua reaksi yakni Reaksi Oksidasi dan Reaksi Reduksi yang dimana keduanya terjadi bersamaan. Dalam menjelaskan pengertian reduksi dan oksidasi, ada tiga konsep yang digunakan yakni : pengikatan pelepasan Oksigen, perpindahan elektron dan perubahan biloks.
3. BASIC COMPETENCE
Explain the concept of the development of Oxidation-Reduction Reactions and hubungannnya with compound nomenclature and its application.
4.
INDICATORS
OF
ACHIEVEMENT
OF
COMPETENCE
a. Oxidation Reduction distinguish the concept of merger review and release of oxygen, release and acceptance elekrton as well as increased and decreased oxidation. b. c. Determining Determining Oxidation Numbers and of atoms Reductor in the in compound Redox or ion.
oxidising
Reactions.
5.
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
a. Students can distinguish Oxidation Reduction concept in terms of the merger and the release of oxygen, release and acceptance elekrton as well as increased and decreased oxidation. b. Students can determine the oxidation numbers of atoms in the compound or ion. c. Students can determine the oxidising and Reductor in Redox Reactions. 6. TEACHING MATERIALS
Redox reaction is a reaction to the merger between the two oxidation reactions and reduction reactions that where both occur together. In explaining the notion of
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 3
reduction and oxidation, there are three concepts that are used namely: binding - the release of oxygen, electron transfer and oxidation state changes.
a. Konsep pengikatan dan Pelepasan Oksigen Pengikatan dan pelepasan oksigen adalah konsep awal pada definisi redoks. Hal ini didasarkan pada kemampuan gas oksigen untuk beraksi dengan berbagai unsure membentuk suatu oksida. Menurut konsep ini, suatu zat dikatakan mengalami oksidasi jika dalam reaksinya zat ini mengikat oksigen. Sementara itu, suatu zat dikatakan mengalami reduksi jika dalam reaksinya melepaskan oksigen. Berikut contoh reduksi dan oksidasi :
C12H22O16 + 12O2
12CO2 + 11H2O
(Oksidasi)
2KClO3
2KCl + 3O2
(Reduksi)
b. Konsep Perpindahan Elektron Perkembangan ilmu kimia memperlihatkan banyak reaksi yang terjadi tanpa melibatkan oksigen. Misalnya unsur tembaga (Cu) yang bisa bereaksi tidak hanya dengan O2 tapi juga bereaksi dengan Cl2. Amati persamaan reaksi di bawah ini
2Cu(s) + O2(g)
2CuO(s)
Cu(s) + Cl2(g)
CuCl2(s)
Reaksi antara Cu dan O2 serta reaksi antara Cu dan Cl2 memiliki persamaan yakni sama sama menerima elektron dari atom Cu. Fakta tersebut menjadi dasar pengembangan konsep redoks. Berdasarkan konsep perpindahan
2Cu O2 + 4e-
2Cu2+ + 4e2O22CuO(s)
(oksidasi) (reduksi)
Cu Cl2 + 2e-
Cu2+ + e2ClCuCl2(s)
(oksidasi) (reduksi)
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
2Cu(s) + O2(g)
Cu(s) + Cl2(g)
RPP - 4
elektron, reduksi adalah reaksi penerimaan elektron dan oksidasi merupakan reaksi pelepasan elektron. Reaksi antara Cu dan O2 atau Cu dengan Cl2 sebagai berikut :
c. Konsep perubahan Biloks Pengertian redoks selanjutnya yakni zat tersebut dikatakan mengalami oksidasi jika terjadi kenaikan biloks. Sementara itu, jika zat tersebut mengalami penurunan biloks maka zat tersebut mengalami reduksi. Munculnya pengertian redoks berdasarkan perubahan biloks ini didasarkan pada reaksi berikut :
C(s) + O2(g)
CO2(g)
Berdasarkan konsep pengikatan dengan Oksigen dan pelepasan oksigen, reaksi di atas adalah reaksi oksidasi. Akan tetapi, berdasarkan konsep perpindahan elektron, reaksi tersebut bukan reaksi oksidasi. Hal tersebut dikarenakan, menurut teori ikatan kimia, senyawa CO2 merupakan senyawa kovalen dan dalam pembentukan senyawa kovalen tidak ada serah terima elektron antara atom atom penyusunnya. Untuk menjelaskan hal tersebut, muncullah konsep ketiga ini yakni Konsep berdasarkan Perubahan Bilangan Oksidasi (Biloks).
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 5
Biloks merupakan bilangan yang menyatakan banyaknya elektron yang dilepaskan atau diterima oleh atom dalam suatu senyawa. Biloks diberi tanda (+) jika melepaskan elektron dan tanda (-) jika menerima elektron. Perhatikan deret unsur berikut :
a. The concept of binding and release of oxygen
Binding and release of oxygen is the initial concept in a redox definition. This is based on the ability of oxygen gas to react with various elements to form an oxide. According to this concept, a substance said to suffer from oxidation when the oxygen binding reaction of this substance. Meanwhile, a substance said to suffer from the reduction if the reaction releasing oxygen. Here's an example of reduction and oxidation: (Oxidation) (Reduction)
b.
Electron
Transfer
Concept
The development of chemical science shows many reactions that occur without involving oxygen. For example, the element copper (Cu) which can react not just with O2 but also reacts with Cl2. Observe the reaction equation below
The reaction between Cu and O2 and the reaction between Cu and Cl2 has the same equation - together receive electrons from Cu atoms. Facts are the basis on the development of the concept of redox. Based on the concept of electron transfer, reduction is the acceptance of electrons and the oxidation reaction is a reaction to the release of electrons. The reaction between Cu and O2 or Cu with Cl2 as follows:
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 6
c.
The
concept
of
oxidation
state
changes
Understanding the subsequent redox substance is said to be oxidized, if there is an increase oxidation state. In the meantime, if these substances decreased the oxidation state of the substance is reduced. The emergence of understanding based on the change in oxidation state redox is based on the following reaction:
Based on the concept of binding with oxygen and release oxygen, the above reactions are oxidation reactions. However, based on electron transfer concept, the reaction is not the oxidation reaction. That is because, according to the theory of chemical bond, the compound is a compound of CO2 in the formation of covalent and covalent compounds there is no handing over of electrons between atoms - the constituent atoms. To explain this, comes the third concept is the concept based on Oxidation Numbers Changes (oxidation state).
Oxidation state is a number stating the number of electrons that are released or received by the atoms in a compound. Oxidation state is marked (+) if the release of electrons and the sign (-) if it receives electrons. Consider the following sequence elements:
Logam H P C S I Br Cl N O F Jika unsur tersebut membentuk senyawa maka unsur dengan posisi paling kiri akan membentuk biloks (+) dan unsur dengan posisi paling kanan bernilai (-).
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 7
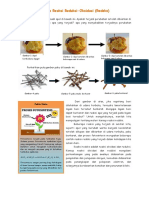
Aturan dalam penentuan nilai Biloks suatu unsur yakni sebagai berikut : a) Bilangan oksidasi unsur bebas adalah 0 (contoh: N2, Cl2, O2, C, P8, dll). b) Bilangan Oksidasi untuk ion monoatomik sama dengan jumlah muatannya (contoh: Na+ = +1, Mg2+ = 2+, Cl- = -1, dll). c) Jumlah bilangan oksidasi untuk semua atom dalam senyawa = 0 (jumlah biloks Cu dan O dalam CuO = 0). d) Bilangan Oksidasi untuk ion poliatomik sama dengan jumlah muatannya (contoh: NH4+ = +1, SO42- = -2, OH- = -1, dll). e) Bilangan oksidasi unsur unsur golongan IA dalam senyawa = +1 dan unsur unsur golongan IIA dalam senyawa = +2 (contoh: K = +1, Na = +1, Ca = +2, Mg = +2, dll). f) Bilangan oksidasi unsur golongan VIIA dalam senyawa = -1. g) Bilangan oksidasi Hidrogen dalam senyawanya = +1 kecuali dalam senyawa Hidrida = -1 h) Bilangan oksidasi Oksigen dalam senyawanya = -2 kecuali dalam senyawa peroksida = -1 dan senyawa biner dengan Flour = +2. Contoh reaksi redoks berdasarkan konsep perubahan biloks adalah reaksi antara logam seng (Zn) dengan larutan CuSO4. Jika logam seng dicelupkan ke dalam larutan CuSO4 yang berwarna biru maka akan berubah menjadi bening dan menghasilkan endapan hitam. Hal itu disebabkan karena perubahan Zn menjadi Zn2+ (biru menjadi bening) dan Cu2+ menjadi Cu (endapan hitam). Adapun reaksi yang terjadi yakni :
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 8
Cu2+ + Zn
+2 0 Oksidasi Reduksi
Cu + Zn2+
0 +2 Bilangan Oksidasi
Oksidator : yang mengalami reduksi Reduktor : yang mengalami oksidasi
7. ALOKASI WAKTU 3 Kali pertemuan (3 x 45 menit)
8. METODE PEMBELAJARAN a. Metode Pemecahan Masalah b. Latihan c. Penugasan d. Diskusi kelompok
If these elements form a compound of the element with the left-most position will form an oxidation state (+) and elements for the position at the right value (-). The rules in determining the value of oxidation state of an element that is as follows: a) The oxidation number of the free element is 0 (eg, N2, Cl2, O2, C, P8, etc.). b) Oxidation Numbers for monatomic ion equals the number of charges (eg, Na + = +1, Mg2 + = 2 +, Cl-= -1, etc.). c) The number of oxidation states for all atoms in a compound = 0 (the number of oxidation states of Cu and O in CuO = 0). d) Oxidation Numbers for polyatomic ion equals the number of charges (eg, NH4 + = +1, SO42-= -2, OH-= -1, etc.). e) The oxidation number of elements - elements in a compound class IA = +1 and element - the element in the compound group IIA = +2 (example: K = +1, Na = +1, Ca = +2, Mg = +2, etc.) . f) The oxidation number of elements in the compound group VIIA = -1. g) Hydrogen oxidation number = +1 in its compounds except in the compound hydrides = -1
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 9
h) The oxidation number of Oxygen in their compounds = -2 except in peroxides compound = -1 and binary compounds with Flour = +2. Examples of redox reactions on the historical changes in metal oxidation state is the reaction between zinc (Zn) with a solution of CuSO4. If the zinc metal is dipped into a solution of CuSO4 in the blue it will turn into clear and produce a black precipitate. That's because the change of Zn into Zn2 + (blue to clear) and Cu2 + to Cu (black precipitate). The reactions that occur are:
7. TIME ALLOCATION 3 time attendance (3 x 45 minutes) 8. LEARNING METHOD a. Problem Solving Method b. Exercise c. Assignment d. Discussion groups 9. KEGIATAN PEMBELAJARAN Pertemuan 1 (2 x 45 menit) KegiatanBelajar 1. Pendahuluan (15 menit) a. Menyiapkan peserta didik. Membagi siswa dalam beberapa kelompok yang beranggotakan 4 5 orang / kelompok. Menginformasikan tata cara berdiskusi serta kelengkapannya. Membagi instrument tiap kelompok b. Memberi motivasi siswa tentang pentingnya bekerja sama dalam kelompok untuk memaksimalkan proses diskusi.
2. Kegiatan Inti (65 menit) a. Menampilkan slide yang berisi pemahaman awal yang digunakan sebagai informasi untuk mengerjakan permasalahan yang diajukan: Oksidasi terdiri dari kata Oksi : Oksigen dan Isasi : menunjukkan proses (pengikatan oksigen) sedangkan reduksi : berarti pengurangan oksigen
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 10
b. Menampilkan slide yang berisi beberapa reaksi kimia yang kemudian siswa ditugaskan untuk menggolongkannya berdasarkan ikatannya dengan oksigen. tentukan mana yang mengikat oksigen dan melepas oksigen? 4Fe + 3O2 2Fe2O3 2Mn + O2 2MnO 2HgO + Hg + O2 . c. Memberikan arahan atau tuntunan mengenai jalannya diskusi. Arahan tersebut berupa tata cara mengisi format penilaian yang dibagikan serta hal hal yang akan dilakukan pada tahap selanjutnya. d. Memberikan waktu kepada tiap kelompok untuk berdiskusi mengenai reaksi yang ditampilkan kemudian menyimpulkannya. e. Mengontrol jalannya diskusi dengan cara berjalan ke semua kelompok untuk melihat bagaimana perkembangan diskusi pada tiap kelompoknya. f. Menampilkan slide selanjutnya : perhatikan konfigurasi elektron dan ikatan dalam senyawa MgCl2. Ingat bahwa: atom yang lebih bermuatan negative akan suka menarik elektron dari atom yang lebih bermuatan positif g. Menampilkan slide berisi beberapa reaksi : 2Cu + O2 CuO 2Na + Cl2 2NaCl N2 + 3H2 2NH3 lalu diskusikan kembali mengenai ikatan di dalamnya h. Menampilkan kembali slide untuk bahan diskusi selanjutnya yakni konsep III: ada beberapa ketentuan dalam rangka penentuan biloks yakni diantaranya: (1) biloks unsure Gol. IA = +1, IIA = +2, (2) biloks unsure Gol. VIIA = -1, (3) jumlah biloks untuk semua unsur dalam senyawa adalah 0. Untuk ketentuan lainnya coba analisis dari contoh berikut :
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 11
Biloks H dalam H2O, H2O2, NaH, CaH Biloks Fe dalam Fe2O3 dan FeCl3 .. i. Memberikan kesempatan kepada perwakilan tiap kelompok untuk mengemukakan hasil diskusinya berupa kesimpulan sementara. j. Memberikan tugas kepada tiap kelompok untuk mencari sumber informasi lainnya mengenai hasil diskusi dan menghubungkannya dengan hasil diskusi. k. Memberikan beberapa masalah yang berhubungan dengan redoks yang kemudian memberitahukan siswa untuk menyiapkan kelompoknya untuk melakukan diskusi minggu depan dengan masalah tersebut.
9. LEARNING ACTIVITIES Meeting 1 (2 x 45 minutes) KegiatanBelajar 1. Introduction (15 minutes) a. Preparing learners. Divide students into groups consisting of 4-5 persons / group. Inform discuss ordinances and completeness. Divide each group of instruments b. Motivate students about the importance of working together in groups to maximize the process of discussion. 2. Core Activities (65 minutes) a. Showing a slide that contains the initial understanding that is used as information for working on the problem posed: "... Oxidation of oxy words: Oxygen and ization: shows the process (oxygen binding) while the reduction: mean reduction of oxygen ..." b. Showing a slide that contains some chemical reaction which is then assigned students to categorize it based on its binding with oxygen. "... Specify which binds oxygen and release oxygen? 4Fe + 3O2 2Fe2O3 2Mn + O2 2MnO 2HgO + Hg + O2 .... " c. Provide direction or guidance on the discussion. Referrals are a good way to fill the assessment form is distributed and things - things that will be done at a later stage. d. Allow time for each group to discuss the reaction shown later concluded. e. Controlling the discussion in a way to walk to all the groups to see how the
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 12
development of discussions in each group. f. Showing slide further: "Note the electron configuration and bonding in the compound MgCl2. Remember that: atoms are more negatively charged would like to draw electrons from the positively charged atoms are more ... " g. Showing a slide containing a few reactions: "2Cu + O 2 CuO 2Na + Cl2 2NaCl N2 + 3H2 2NH3 ... then discuss the return of the bonds in it " h. Showing slide back for further discussion of the concept III: "There are several provisions in order to determine the oxidation states which are: (1) oxidation state of elements of Gol. IA = +1, IIA = +2, (2) oxidation state of elements of Gol. VIIA = -1, (3) the amount of oxidation states for all elements in the compound is 0. For other provisions of analysis try the following example: The oxidation state of H in H2O, H2O2, well, CAH The oxidation state of Fe in Fe2O3 and FeCl3 ... .. " i. Provide opportunities for representatives of each group to put forward the results of their discussion of tentative conclusions. j. Giving tasks to each group to seek other sources of information about the results of the discussion and connect with the discussion. k. Providing some of the problems associated with redox who then notify the student to prepare the group for discussion next week with the problem. 3. Kegiatan Penutup (10 menit) a. Memberikan penegasan pemahaman yang telah dibahas sebelumnya untuk mempertajam pemahaman siswa dengan memberikan tugas. b. Siswa diminta mengisi angket dalam rangka Umpan balik siswa dalam pelaksanaan PBL sehingga akan memberikan koreksi untuk proses selanjutnya. c. Membuat rangkuman/simpulan d. Memberikan tugas kembali guna menguji pemahaman siswa. e. Menyampaikan rencana pembelajaran untuk pertemuan selanjutnya
10. INSTRUMEN PENILAIAN HASIL BELAJAR
3. Concluding Activity (10 minutes) a. Confirm understanding of previously discussed to sharpen students'
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 13
understanding by giving the task. b. Students are asked to fill out questionnaires in the context of student feedback in the implementation of PBL that will provide corrections for the next process. c. Creating a summary / conclusion d. Giving the task back in order to test student understanding. e. Delivering the lesson plan for next meeting 10. ASSESSMENT INSTRUMENT OF LEARNING 1) Senyawa yang mengandung vanadium dengan bilangan oksidasi +4 adalah. a. NH4VO2 d. VOSO4 b. K4[V(CN)6] e. VCl3 c. VSO4 2) Persamaan reaksi yang menunjukkan spesi yang digarisbawahi mengalami reduksi adalah. 2MnSO4 + 10CO2 + 8H2O. Zat yang berperan sebagai reduktor adalah. a. H2SO4 d. KMnO4 b. MnSO4 e. H2C2O4 c. H2O
5) Reduksi satu mol ion MnO4- menjadi Mn2+ memerlukan elektron sebanyak. a. Mg + 2H+ Mg2+ + H2 a. 3 mol d. 6 mol b. 2Fe2+ + Cl2 2Fe3+ + 2Clb. 4 mol e. 7 mol c. CO32- + 2H+ CO2 + H2O c. 5 mol 6) Dari reaksi 2Na + H2 2NaH. d. Br2 + 2I 2Br + I2 + Manakah pernyataan berikut ini yang e. 2Na + 2H2O 2Na + 2OH + salah . H2 a. Unsur Na memiliki biloks 0 3) Berikut ini yang merupakan reaksi b. Na bertindak sebagai Reduktor autoredoks adalah. c. Biloks Hidrogen berubah dari 0 a. NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) menjadi +1 NaNO3(aq) + AgCl(s) d. Dalam reaksi redoks tersebut b. KIO3(aq) + 6HCl(aq) 3I2(s) + melibatkan 4e6KCl(aq) + 3H2O(aq) e. Hidrogen bertindak sebagai c. MnO2(s) + 2NaI(aq) + 2H2SO4(aq) oksidator MnSO4(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) + I2(aq) 7) Unsur dengan bilangan Oksidasi +5 + 2H2O(l) dalam senyawa berikut adalah. d. Cl2(g) + 2NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + a. HClO4 d. HCl NaClO(aq) + H2O(l) b. HClO3 e. H3PO3 e. Cu(s) + 4HNO3(aq) Cu(NO3)2(aq) c. H2SO4 + 2NO2(g) + 2H2O(l) 4) Pada persamaan reaksi: 2KMnO4 + 8) Reduksi dipandang sebagai peristiwa 5H2C2O4 + 3H2SO4 K2SO4 + ..
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 14
a. Penambahan biloks 12) Reaksi berikut ini yang termasuk reaksi autoredoks adalah b. Pelepasan oksigen c. Penambahan proton a. Br2 + NaOH NaBrO3 + NaBr d. Penangkapan oksigen + H2 O e. Transfer elektron b. CuO + CO Cu2O + CO2 9) Berikut ini merupakan pernyataan c. SnCl2 + I2 + HCl SnCl4 + HI yang benar mengenai reduktor d. I2 + H2S2O3 2I- + H2S4O6 kecuali . e. Cu + HNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + NO2 + a. Zat yang melepas elektron H2O b. Zat yang menarik oksigen 13) Unsur Mn yang mempunyai biloks c. Zat yang mengalami kenaikan sama dengan biloks Cr dalam K2Cr2O7 bilangan oksidasi adalah d. Zat yang mengalami oksidasi a. KMnO4 d. MnO b. K2MnO4 e. MnO2 e. Zat yang mengalami reduksi 10) Sebagaian dari daur Nitrogen di alam c. MnSO4 melibatkan berbagai macam senyawa 14) Pada persamaan reaksi : Cu2O + C Nitrogen yakni N2, NO, NO2 dan 2Cu + CO, yang bertindak sebagai NO3 . Urutan biloks dari yang oksidator adalah terkecil a. C d. O b. Cu e. Cu2O a. 0, +2, +4, +5 b. 0, +3, +5, +7 c. CO c. 0, +2, +3, +4 15) Perkembangan pengertian reaksi d. 0, +1, +2, +3 redoks dinyatakan dalam tiga konsep 11) Diantara reaksi berikut ini, yang berikut : bukan merupakan reaksi redoks 1) Penangkapan elektron adalah 2) Pelepasan oksigen a. SnCl2 + I2 + 2HCl SnCl4 + 3) Pengurangan biloks 2HI Urutan pengertian redoks yang b. H2 + Cl2 2HCl benar adalah c. Cu2O + C 2Cu + CO a. (1), (2), (3) d. (2), (1), (3) b. (1), (3), (2) e. (3), (1), (2) d. Cu2O + 2HCl CuCl2 + H2O e. MnO2 + 4HCl MnCl2 + 2H2O + c. (2), (3), (1) Cl2 1) Compounds containing vanadium with oxidation state +4 is. ... a. NH4VO2 d. VOSO4 b. K4 [V (CN) 6] e. VCl3 c. VSO4 2) The equation showing the reaction of the underlined species are reduced. ... a. Mg + 2H + Mg2 + + H2 b. 2Fe2 + + Cl2 2Fe3 + + 2Clc. CO32-+ 2H + CO2 + H2O
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 15
d. Br2 + 2I- 2Br-+ I2 e. 2Na + 2H2O 2Na + + 2OH-+ H2 3) Here's what is autoredoks reaction is. ... a. NaCl (aq) + AgNO3 (aq) NaNO3 (aq) + AgCl (s) b. KIO3 (aq) + 6HCl (aq) 3I2 (s) + 6KCl (aq) + 3H2O (aq) c. MnO2 (s) + 2NaI (aq) + 2H2SO4 (aq) MnSO4 (aq) + Na2SO4 (aq) + I2 (aq) + 2H2O (l) d. Cl2 (g) + 2NaOH (aq) NaCl (aq) + NaClO (aq) + H2O (L) e. Cu (s) + 4HNO3 (aq) Cu (NO3) 2 (aq) + 2NO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) 4) In the reaction equation: 2KMnO4 + 5H2C2O4 + 3H2SO4 K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 10CO2 + 8H2O. Substances that act as a reducing agent is. ... a. D. H2SO4 KMnO4 b. MnSO4 e. H2C2O4 c. H2O
5) Reduction of one mole of ion MnO4 be Mn2 +-electron requires as much. ... a. 3 mol d. 6 mol b. 4 mol e. 7 mol c. 5 moles 6) From the reaction 2Na + H2 2NaH. Which of the following statements are wrong .... a. The element has an oxidation state 0 Na b. Na acts as Reductor c. Hydrogen oxidation state changes from 0 to +1 d. In these redox reactions involving 4ee. Hydrogen acts as an oxidant 7) The element with oxidation number +5 in the following compounds are. ... a. HClO4 d. HCl b. HClO3 e. H3PO3 c. H2SO4 8) The reduction is seen as an event .. a. The addition of oxidation state b. The release of oxygen c. Addition of proton d. Arrest oxygen e. Electron transfer 9) The following is a true statement about reducing agent unless. ... a. Substances which release electrons b. Substances that attract oxygen c. Substances that increased oxidation d. Substances that oxidize e. Substance that is reduced 10) Part of the nitrogen cycle in nature involve a variety of nitrogen compounds namely N2, NO, NO2 and NO3-. The order of the oxidation states of the smallest ...
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 16
a. 0, +2, +4, +5 b. 0, +3, +5, +7 c. 0, +2, +3, +4 d. 0, +1, +2, +3 11) Among the following reaction, which is not a redox reaction is ... a. SnCl2 + I2 + 2HCl SnCl4 + 2HI b. H2 + Cl 2 2HCl c. Cu2O + C 2Cu + CO d. Cu2O + 2HCl CuCl2 + H2O e. MnO2 + 4HCl MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2 12) the following reactions which include autoredoks reaction is ... a. Br2 + NaOH NaBrO3 + NaBr + H2O b. CuO + CO Cu2O + CO2 c. SnCl2 + I2 + HCl SnCl4 + HI d. H2S2O3 I2 + 2I-+ H2S4O6 e. Cu + HNO3 Cu (NO3) 2 + NO2 + H2O 13) The element Mn has an oxidation state equal to the oxidation state of Cr in K2Cr2O7 is ... a. KMnO4 d. MnO b. K2MnO4 e. MnO2 c. MnSO4 14) In reaction equation: Cu2O + C 2Cu + CO, which acts as an oxidant is ... a. C d. O b. E. Cu Cu2O c. CO 15) The development of understanding of redox reactions expressed in the following three concepts: 1) The arrest of electron 2) The release of oxygen 3) Reduction of oxidation state The order is the true understanding of redox ... a. (1), (2), (3) d. (2), (1), (3) b. (1), (3), (2) e. (3), (1), (2) c. (2), (3), (1) 11. KUNCI JAWABAN 1) D 2) B 3) D 4) E 5) C 6) D 7) B 8) B 9) E 10) A 11) D 12) A 13) B 14) E 15) D
12. PENILAIAN HASIL BELAJAR
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 17
KISI-KISI PENILAIAN KOGNITIF/PSIKOMOTORIK
Satuan Pendidikan Kelas/Semester Alokasi Waktu Mata Pelajaran Bentuk soal Jumlah Soal Standar Kompetensi
: SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB : X-1 / Genap : 2 x 45 Menit : Kimia : Pilihan Ganda : 15 Butir : Memahami sifat-sifat larutan elektrolit serta reaksi oksidasi-reduksi.
Kompetensi Dasar
: Menjelaskan perkembangan konsep reaksi oksidasireduksi dan hubungannya dengan tata nama serta penerapannya.
Grid ASSESSMENT OF COGNITIVE / psychomotor Education Unit: SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB Class / Semester: X-1 / Even Allocation of Time: 2 x 45 Minutes Subject: Chemistry The question: Multiple Choice Number of Questions: 15 Minutes Competency Standards: Understand the properties of electrolyte solution and the oxidation-reduction reaction. Basic Competency: Explain the development of the concept of oxidation-reduction reaction and its relationship with the nomenclature and its application. No. Soal 3 2 5 6 Level Kognitif 4 C2 C3 C2 6
No 1
Indikator 2 Menjelaskan pengertian redoks berdasarkan
Jumlah Soal 5
pelepasan oksigen dan perubahan biloks, perpindahan elektron, dan perubahan bilangan
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 18
oksidasi
8 10 15
C1 C2 C1 4 C2 C2 C2 C2 C1 C2 C3 C2 C3 3 3 3 5
2 Menentukan bilangan oksidasi unsur dalam senyawanya
3 1 7 13 4 9 14 3
Menentukan perubahan bilangan oksidasi dalam redoks (tanpa penyetaraan reaksi)
Menentukan oksidator dan reduktor suatu reaksi
11 12
13. PEDOMAN PENSKORAN
Satuan Pendidikan Mata Pelajaran TahunAjaran Kelas / Semester
: SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB : Kimia : 2011-2012 : X-1 / genap
Kriteria Jika jawaban benar Jika jawaban salah ( )
Skor 1 0
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
RPP - 19
14. SUMBER BELAJAR a. Susilowati, Endang. 2007. Sains Kimia Prinsip dan Terapannya. Jakarta : Tiga Serangkai b. Sunardi. 2009. Bank Soal Kimia SMA edisi ke-5. Bandung : M2S Bandung. c. Johari. 2006. Buku Kerja Kimia 2A. Jakarta : Erlangga. d. Rahmawati. 2005. Kimia SMA Bilingual. Jakarta : Esis Erlangga.
Takalar , Februari 2010 Mengetahui : Kepala Sekolah, Guru Mata Pelajaran,
( NIP.
Hadriadi Nim. 071304151
SMAN 3 Takalar Model SKM PBKL PSB @2010, by Hadriadi
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- REDOKSDokumen9 halamanREDOKSNURHANIPAHBelum ada peringkat
- Modul Kimia Semester 2Dokumen39 halamanModul Kimia Semester 2Rika HermawatiBelum ada peringkat
- Pramesti Putri Cahyani - Tgs KhususDokumen14 halamanPramesti Putri Cahyani - Tgs KhususTri Indri LestariBelum ada peringkat
- Materi RedoksDokumen7 halamanMateri RedoksAguz PrayitnoBelum ada peringkat
- Modul Reaksi Reduksi Oksidasi (Redoks)Dokumen7 halamanModul Reaksi Reduksi Oksidasi (Redoks)DorkasBelum ada peringkat
- LKM Redoks Dan Elektrokimia (P-9) - Adipa - 015Dokumen15 halamanLKM Redoks Dan Elektrokimia (P-9) - Adipa - 015I Putu Adi Payana PutraBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Kimsel RedoksDokumen40 halamanMakalah Kimsel RedoksCintia PebriBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan Ajar Reaksi RedoksDokumen10 halamanBahan Ajar Reaksi RedoksKalsum SujainiBelum ada peringkat
- 4 PembahasanDokumen22 halaman4 PembahasanRisma Aprilli SimarmataBelum ada peringkat
- RPP AnggaDokumen19 halamanRPP AnggaRidhaAyu UtamiBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Reaksi Redoks Dan Elektrokimia SukrisnoDokumen24 halamanMakalah Reaksi Redoks Dan Elektrokimia SukrisnoSukrisno SyukriBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan Ajar 3.7Dokumen6 halamanBahan Ajar 3.7Kurniawan EkaBelum ada peringkat
- Reaksi Oksidasi Reduksi: Rencana Pelaksanaan Pembelajaran (RPP) Model Pembelajaran IntegratifDokumen11 halamanReaksi Oksidasi Reduksi: Rencana Pelaksanaan Pembelajaran (RPP) Model Pembelajaran IntegratifNur Mahiyatus SholikhahBelum ada peringkat
- Modul Reaksi Oksidasi Reduksi Dan Tata Nama SenyawaDokumen24 halamanModul Reaksi Oksidasi Reduksi Dan Tata Nama SenyawaIsni NuraniBelum ada peringkat
- Peer Teaching/Bahan Ajar KD 3.9 Kelas X TerbaruDokumen10 halamanPeer Teaching/Bahan Ajar KD 3.9 Kelas X Terbarusuci hadi rahmawatiBelum ada peringkat
- 2.kegiatan 1 (Penyetaraan Reaksi Redoks)Dokumen17 halaman2.kegiatan 1 (Penyetaraan Reaksi Redoks)anang7100% (2)
- Ringkasan Materi Reaksi RedoksDokumen10 halamanRingkasan Materi Reaksi RedoksTya arstBelum ada peringkat
- KIMIA X - REVISI BAB 7 Redoks RevDokumen11 halamanKIMIA X - REVISI BAB 7 Redoks RevwaginoosmondBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan Ajar Reaksi RedoksDokumen5 halamanBahan Ajar Reaksi RedoksKhariya ArthannaBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Kimia Dasar II RedoksDokumen117 halamanLaporan Kimia Dasar II RedoksAgnes Retania Marpaung100% (1)
- 09 LKPD Reaksi Reduksi Dan OksidasiDokumen2 halaman09 LKPD Reaksi Reduksi Dan Oksidasigereja getsemani tarus timurBelum ada peringkat
- Perkembangan Konsep RedoksDokumen4 halamanPerkembangan Konsep Redoksmutiara khanzaBelum ada peringkat
- Reaksi Reduksi Dan Oksidasi Serta Tata Nama SenyawaDokumen62 halamanReaksi Reduksi Dan Oksidasi Serta Tata Nama SenyawaHesti Elsa PramauditaBelum ada peringkat
- Reaksi RedoksDokumen14 halamanReaksi RedoksTRI GOESEMA PUTRA M.Pd100% (4)
- Konsep Redoks Berdasarkan Pelepasan Dan Pengikatan OksigenDokumen5 halamanKonsep Redoks Berdasarkan Pelepasan Dan Pengikatan OksigenA'Yu P. Larasati100% (2)
- BAHAN AJAR (Hand Out) KD 3.9-4.9 Redok-Tata NamaDokumen19 halamanBAHAN AJAR (Hand Out) KD 3.9-4.9 Redok-Tata NamaDersani la PattajangBelum ada peringkat
- LKPDDokumen17 halamanLKPDNur Mahiyatus SholikhahBelum ada peringkat
- ELEKTROKIMIA DAN REAKSI REDOK Utk KulDokumen40 halamanELEKTROKIMIA DAN REAKSI REDOK Utk KulElfrida Ruman100% (1)
- Falachul Mufid (LKS Reaksi Redoks)Dokumen10 halamanFalachul Mufid (LKS Reaksi Redoks)elsyakuro270377Belum ada peringkat
- Laporan PraktikumDokumen12 halamanLaporan PraktikumNur Mahiyatus SholikhahBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Kimia Dasar II RedoksDokumen116 halamanLaporan Kimia Dasar II RedoksAgnes Retania Marpaung100% (1)
- Lap - Tetap Perc.3 HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHDokumen17 halamanLap - Tetap Perc.3 HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHAnonymous mAAISKPBelum ada peringkat
- Cara Saya Meremidial Siswa Yang Kesulitan Dalam Memahami Perkembangan Konsep Redoks YaituDokumen12 halamanCara Saya Meremidial Siswa Yang Kesulitan Dalam Memahami Perkembangan Konsep Redoks YaituA'Yu P. LarasatiBelum ada peringkat
- Tessa Togatorop - Tugas KhususDokumen11 halamanTessa Togatorop - Tugas KhususTri Indri LestariBelum ada peringkat
- Konsep Reaksi RedoksDokumen9 halamanKonsep Reaksi Redoksgabriel tonceBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan AjarDokumen14 halamanBahan AjarBrigittaBelum ada peringkat
- KD 3.5 (Redoks)Dokumen15 halamanKD 3.5 (Redoks)visti100% (2)
- OksidatorDokumen10 halamanOksidatorNova Liliyani SihotangBelum ada peringkat
- Shintia Friska Wulandari - Reaksi Oksidasi Reduksi (2) Pengaruh Asam Dan Basa Terhadap LogamDokumen25 halamanShintia Friska Wulandari - Reaksi Oksidasi Reduksi (2) Pengaruh Asam Dan Basa Terhadap LogamShintia FriskaBelum ada peringkat
- Materi PembelajaranDokumen5 halamanMateri PembelajaranNurjayaBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan Ajar Reaksi Redoks Dan Tatanama SenyawaDokumen23 halamanBahan Ajar Reaksi Redoks Dan Tatanama SenyawaNur Mahiyatus Sholikhah100% (1)
- RedoksDokumen12 halamanRedoksAdineBelum ada peringkat
- 09 LKPD Reaksi Reduksi Dan OksidasiDokumen2 halaman09 LKPD Reaksi Reduksi Dan Oksidasigereja getsemani tarus timurBelum ada peringkat
- Ringkasan Materi Reaksi RedoksDokumen3 halamanRingkasan Materi Reaksi RedoksJan Soepadmo100% (1)
- Reaksi Redoks (Siswa)Dokumen18 halamanReaksi Redoks (Siswa)kimia smagraBelum ada peringkat
- Kimia 2Dokumen32 halamanKimia 2Vi AnBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas KuDokumen6 halamanTugas Kuwahyu ajipBelum ada peringkat
- Soal BiloksDokumen6 halamanSoal BiloksWulan MollyBelum ada peringkat
- RPP RedoksDokumen15 halamanRPP RedoksDevi Amiratul AsviaBelum ada peringkat
- BAB VII Reaksi Oksidasi-ReduksiDokumen16 halamanBAB VII Reaksi Oksidasi-ReduksiYUNUSBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan Ajar 3.9Dokumen10 halamanBahan Ajar 3.9SariBelum ada peringkat
- Redoks-Kelas 10Dokumen6 halamanRedoks-Kelas 10Abu HilmanBelum ada peringkat
- RedoksDokumen19 halamanRedoksMardianto Ra'bangBelum ada peringkat
- Modul Kimia Oksidasi Dan ReduksiDokumen13 halamanModul Kimia Oksidasi Dan ReduksiDwikurniawnBelum ada peringkat
- BAB 7 REAKSI REDOKS. Proses Perkaratan BesiDokumen23 halamanBAB 7 REAKSI REDOKS. Proses Perkaratan BesiMelly Tri RahmiBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan Ajar Reaksi Redoks 1Dokumen5 halamanBahan Ajar Reaksi Redoks 1Sri KurniatiBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan Ajar Reaksi Redoks 1Dokumen5 halamanBahan Ajar Reaksi Redoks 1Sri KurniatiBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 3 StoikiometriDokumen11 halamanBab 3 Stoikiometriecha_iqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Asam Dan Basa KuliahDokumen41 halamanAsam Dan Basa Kuliahecha_iqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 1 Struktur Atom Dan Sifat PeriodikDokumen19 halamanBab 1 Struktur Atom Dan Sifat Periodikecha_iqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Kim - Analis KLPK AasDokumen17 halamanMakalah Kim - Analis KLPK Aasecha_iqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Handout KoloidDokumen20 halamanHandout Koloidecha_iqbalBelum ada peringkat
- RPP IonDokumen3 halamanRPP Ionecha_iqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Penerapan ElektrolisisDokumen18 halamanMakalah Penerapan Elektrolisisecha_iqbal50% (2)
- RPP Bahan Kimia Rumah TanggaDokumen7 halamanRPP Bahan Kimia Rumah TanggaFawnia D'Genkbellzz Ezzar FluorinAnindyaBelum ada peringkat