Aplikasi Pembezaan
Diunggah oleh
Wan HamidahJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Aplikasi Pembezaan
Diunggah oleh
Wan HamidahHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
ISI KANDUNGAN 1. 2. 3. Perubahan Kadar (Rate of Change) Pergerakan Pada Garis Lurus (Rectilinear Motion) Nilai Maksimum & Minimum
OBJEKTIF PEMBELAJARAN Pelajar boleh .. Menggunakan Petua Rantai untuk mendapatkan kadar perubahan sesuatu perkara terhadap masa. Menghubung kait topik geometri (pengiraan luas dan isipadu) pelbagai bentuk umum dengan konsep perubahan kadar. Memahami dan dapat mengaitkan sebutan-sebutan seperti halaju dan pecutan melalui proses pembezaan. Mengira halaju dan pecutan pergerakan pada garis lurus melalui pembezaan. Memahami konsep maksimum dan minimum (melalui graf kuadratik) dan mengaplikasikannya ke dalam penyelesaian masalah praktikal kalkulus.
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 1
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
ULANGKAJI GEOMETRI (LUAS & ISIPADU) Planes Formula Rectangle: Area = Length x Width A = l w
Parallelogram: Area = Length x Height A = l h
Triangle: Area = 1/2 of the base length x Height 1 A = (l )(h ) 2
Trapezium: Area = 1/2 of the sum of parallel sides x Height
A=
1 (a + b )(h ) 2
Circle: Circumference = 2r Area, A = r 2
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 2
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
Solids
Formula Rectangular Solid: Volume = Length x Width x Height V = l w h
Prisms: Volume = Base Area x Height V = B h
Cylinder: Volume = r 2 x Height V = r 2 h Surface Area = 2 radius x Height A = 2r 2 + 2rh Pyramid: Volume = 1/3 of the Base Area x Height 1 V = (B )(h ) 3
Cone: Volume = 1/3 r2 x Height 1 V = r 2h 3 Surface Area A = r 2 + rs
(s = r 2 + h 2 )
Sphere: Volume = 4/3 r3 4 V = r 3 3 Surface Area A = 4r 2
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 3
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
PERUBAHAN KADAR (RATE OF CHANGE)
Pembezaan
dy y = lim juga digelar perubahan kadar y terhadap x . Dalam dx x 0 x
kebanyakan situasi praktikal, aplikasi pembezaan melibatkan pembezaan sesuatu perkara terhadap masa. Perubahan kadar bagi sesuatu perkara terhadap masa, t boleh didapati menggunakan Petua Rantai:
dy dy dx = dt dx dt
Perubahan kadar yang positif bermakna pertambahan kadar. Perubahan kadar yang negatif bermakna penurunan kadar.
Contoh 1:
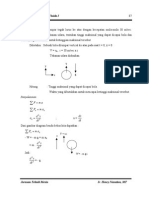
The diagram shows a circular iron sheet. When the iron sheet is heated, given that the radius is increasing at the constant rate of 0.1 cms-1, find the rate of change of the area at the instant radius of 10 cm.
Rajah menunjukkan sebuah kepingan besi berbentuk bulat. Apabila ia dipanaskan, radius besi itu mengembang dengan kadar tetap 0.1 cms-1. Cari kadar perubahan luas kepingan besi itu pada ketika radiusnya 10 cm.
Penyelesaian:
Dalam menjawab soalan yang mempunyai masalah panjang seperti di atas, pelajar disyorkan supaya menggunakan kaedah yang berperingkat seperti berikut: Kaedah 1: Baca soalan dengan teliti. Lukis dan labelkan rajah supaya faham kehendak soalan.
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 4
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
Kaedah 2:
Tuliskan semua sebutan, formula, anu dan maklumat yang diberikan ke dalam bentuk symbol matematik yang difahami. Tuliskan formula yang perlu untuk menyelesaikan masalah tersebut menggunakan Petua Rantai dan maklumat yang ada. Selesaikan masalah.
Kaedah 3:
Kaedah 4:
Kaedah 1: Telahpun diberikan bersama soalan.
Kaedah 2:
Diberi
dr = 0.1 cm/s , r = 10 cm . dt dA = 2r . dr
Luas bulatan diberi oleh A = r 2 . Maka,
Kaedah 3:
Kita dikehendaki mencari
dA dA dA dr , maka petua rantai yang tepat ialah = . dt dt dr dt
Kaedah 4:
dA dA dr = dt dr dt dA = 2r 0.1 = 2 (10)(0.1) = 6.283 cm 2 /s dt
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 5
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
Contoh 2:
A 13 feet ladder is leaning against a wall. Suppose that the base of the ladder slides away from the wall at the constant rate of 3 ft/sec. Find the rate at which the top of the ladder is moving down the wall at 1 sec.
Sebuah tangga 13 kaki disandarkan pada dinding seperti rajah berikut. Angin kuat menyebabkan bahagian bawah tangga itu bergerak menjauhi dinding pada kadar tetap 3 kaki / saat. Cari kadar apabila bahagian atas tangga itu bergerak jatuh ke bawah pada 1 saat.
Maklumat penting: 1. 2. 3.
x dan y adalah pembolehubah (variables) manakala tinggi tangga adalah
tetap (constant). Diberi t = 1s ,
dx = 3ft/s x = 3ft dt
dx adalah kadar positif kerana ia semakin tinggi (tangga bergerak menjauhi dt
dinding)
4. 5.
dy akan menjadi negatif kerana tangga jatuh ke bawah ( y menurun). dt
Persamaan yang perlu diketahui adalah Teorem Pythagoras (segitiga yang terlibat) iaitu x 2 + y 2 = 13 2
Penyelesaian:
Kita perlu mendapatkan kadar bahagian atas tangga yang jatuh ke bawah, Melalui Petua Rantai (Chain Rule), Diketahui
dy . dt
dy dy dx = dt dx dt
dx =3 dt dy , kita perlu membezakan x 2 + y 2 = 13 2 . dx
Untuk mendapatkan
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 6
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
Opsyen 1 (Pembezaan menggunakan penggantian (Substitution Method))
x 2 + y 2 = 13 2 y = 169 x 2 = (169 x 2 )2
1 1
u = 169 x 2
y =u2
1
dy 1 2 du = 2x ; = u du 2 dx 1 x dy 1 2 = u ( 2x ) = dx 2
Maka,
(169 x )
1 2 2
dy = = 3 = 0.712ft/s dt 160 169 x 2
dy dy dx = dt dx dt 3 x
Opsyen 2 (Pembezaan menggunakan Implicit Differentiation)
x 2 + y 2 = 13 2 dy =0 2 x + 2y dx dy 2y = 2 x dx dy 2x = dx 2y
Apabila x = 3 3 2 + y 2 = 13 2
y 2 = 160 y = 160 dy 2x x = = 2y dx 160
Maka,
dy = = 3 = 0.712ft/s dt 160 169 x 2
dy dy dx = dt dx dt 3 x
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 7
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
WORKSHEET
The volume of a cone decreases at the rate of 20 cm3/s. Find the rate of change in height of the cone if the radius of its base is fixed at 4cm. 1 (Formula of volume of cone, V = r 2 h ) 3 15 [Answer: cm/s ] 4
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 8
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
GERAKAN PADA GARIS LURUS (HALAJU & PECUTAN)
Gerakan suatu partikel P pada satu garis lurus boleh dinyatakan sebagai s = f (t ) , yang mana t adalah masa, dan s adalah jaraknya daripada suatu titik tetap O .
Halaju (Velocity) bagi P pada sesuatu masa adalah v =
ds dt
Jika v > 0 , P bergerak dalam arah s yang bertambah Jika v < 0 , P bergerak dalam arah s yang berkurangan Jika v = 0 , P dalam keadaan rehat (instantaneously at rest)
dv d 2 s Pecutan (Acceleration) bagi P pada sesuatu masa adalah a = = dt dt 2
Jika a > 0 , v bertambah, tetapi jika a < 0 , v berkurangan Jika v dan a serupa, kelajuan (speed) P bertambah Jika v dan a bertentangan, kelajuan P berkurangan Jika sesuatu partikel melalui suatu jarak, s meter dalam masa, t saat, maka:
Distance:
s = f (t )
Velocity:
v = f ' (t ) =
ds dt
Acceleration:
a = f ' ' (t ) =
d 2s dt 2
Distance travelled in n seconds:
s n s n 1
Average velocity over n seconds:
sn s0 n (0 )
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 9
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
Contoh:
1. A body moves along a straight line according to the law s = Determine its velocity and acceleration at 2 seconds. 1 3 t 2t . 2
s =
1 3 t 2t 2
3 ds =v = t 2 2 2 dt
v =
3 2 (2) 2 = 3 (4 ) 2 = 4 m/s 2 2
dv = a = 3t dt v = 3(2) = 6 m/s 2
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 10
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
2.
A particle P moves in a straight line so that its distance, s meter, from a fixed point O , t seconds after passing O is given by s = 12t t 3 . Calculate: i) ii) iii) The distance travelled by P in the fourth second. The value of s , when P comes instantaneously to rest. The velocity of P when the acceleration is zero.
ds = v = 12 3t 2 dt dv = a = 6t dt
i) The distance travelled by P in the fourth second means when s at t = 4 minus s at t = 3 . So,
s 4 = 12(4 ) (4 ) = 48 64 = 16
3
s 3 = 12(3) (27 ) = 36 27 = 9
3
Hence, s 4 s 3 = 16 9 = 25 . Distance travelled by P in the fourth second is 25 m.
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 11
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
ii)
When particle comes to rest means that its velocity is zero.
v = 12 3t 2
0 = 12 3t 2
t2 =
12 =4 3
t =2
When t = 2s , s = 12(2 ) (2 ) = 24 8 = 16 .
3
When P comes instantaneously to rest, the distance is 16 m.
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 12
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
iii)
When acceleration is zero:
a = 6t = 0 t =0
So, v = 12 3(0 ) = 12 0 = 12 .
2
When the acceleration is zero, the velocity is 12 m/s.
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 13
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
WORKSHEET
The distance, x meters moved by a body in t seconds is given by 11 x = 3t 3 t 2 + 2t + 5 . Find: 2 i) ii) iii) iv) v) vi) vii) Its velocity after t seconds [v = 9t 2 11t + 2 ] Its velocity at the start, and also after 4 seconds [v = 2 m/s ; v = 102 m/s ] The value of t , when the body comes to rest [ t = 1 s ; t = 0.22 s ] Its acceleration after t seconds [ a = 18t 11 ] Its acceleration after 2 seconds [ a = 25 m 2 /s ] The value of t , when the acceleration is 16 m/s2 [ t = 1.5 s ] The average velocity over the third seconds [v = 34 m/s ]
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 14
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
NILAI MAKSIMUM & MINIMUM
Suatu titik pada lengkung yang mempunyai kecerunan 0 atau apabila
dy =0 dx
dipanggil stationary point. Pada titik ini, tangent yang melaluinya adalah mendatar, atau kita boleh katakan lengkung tersebut leper (flat). Terdapat 3 jenis stationary point: i) Titik Minimum P Dalam kes ini, kecerunan lengkung adalah negatif pada belah kiri titik P tetapi kecerunannya positif pada belah kanan titik P.
Kiri P
Pada P
Kanan P
dy <0 dx d 2y >0 dx 2
dy =0 dx
dy >0 dx
Walau bagaimanapun, pada titik minimum P, pembezaan keduanya bernilai positif
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 15
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
ii)
Titik Maksimum P Dalam kes ini, kecerunan lengkung adalah positif pada belah kiri titik P tetapi kecerunannya negatif pada belah kanan titik P.
Kiri P
Pada P
Kanan P
dy >0 dx
dy =0 dx
dy <0 dx
Walau bagaimanapun, pada titik maksimum P, pembezaan keduanya bernilai negatif
d 2y <0 dx 2
iii)
Point of inflexion Dalam kes ini, kecerunan pada belah kiri dan kanan titik P serupa. Suatu point of inflexion yang mempunyai kecerunan 0 dipanggil saddle point.
Pada titik P, pembezaan keduanya bernilai 0
d 2y = 0. dx 2
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 16
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
MASALAH PRAKTIKAL MAKSIMUM & MINIMUM Contoh 1:
In the right-angled triangle ABC shown, the lengths of AB and BC vary such that their sum is always 6 cm. Find the maximum area of the triangle.
Penyelesaian:
Diberi maklumat bahawa AB + BC = 6 :
x + BC = 6 BC = 6 x
Luas untuk segitiga ialah A =
2 1 (x )(6 x ) = 3x x 2 2
1 (AB )(BC ) 2
A=
Luas maksimum adalah apabila 1 2 dA =3x x ; 2 dx
dA =0 dx
A = 3x
0 =3x
x =3
Jadi, apabila x = 3 ,
A = 3x
1 2 1 x = 3(3) (9 ) 2 2
A=
9 = 4.5 cm 2 2
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 17
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
Contoh 2:
A closed circular cylinder with radius r cm, and height h cm, has a volume of 54 108 cm3. Show that the total surface area is given by S = + 2r 2 . Then find the
values of r and h so that the area is minimum. Given cylinder area is S = 2rh + 2r 2 and its volume is V = r 2 h .
Penyelesaian:
Daripada maklumat yang diberikan, V = r 2 h = 54
r 2 h = 54
h =
54
r 2
Letakkan nilai h yang diperolehi ke dalam formula luas untuk mendapat:
S = 2rh + 2r 2 S = 2r
54 + 2r 2 2 r + 2r 2
S =
108
(Terbukti)
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 18
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
Untuk mendapat luas silinder yang minimum, kita tahu bahawa:
dS = 108r 2 + 4r = 0 dr
108 + 4r = 0
r2
4r =
108
r2
r3 =
108 = 27 4
r =3
Apabila r = 3 , h = 54
(3)
= 6.
Maka, luas permukaan silinder adalah minimum apabila r = 3 cm , dan h = 6 cm .
Untuk membuktikan bahawa luas permukaan adalah minimum, kita semak pembezaan keduanya, iaitu suatu nilai yang positif.
d 2S = 216r 3 + 4 > 0 2 dr
216r
3
+ 4 =
216
(3)3
+ 4 = 12 nilai positif
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 19
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
WORKSHEET
A rectangular fence is formed from a 40 m wire with a long wall forming on one side of the fence as figure shown.
Given that the width of the rectangle is x meters, find: i) ii) iii) The length of the other unknown side, in terms of x . [ y = 40 2x ] Value of x [10 m] The maximum area possible formed by the fence. [200 m2]
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 20
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
INTENSIVE EXERCISE
1. 1 3 x + 2x , and the value of x changes at the rate of 0.1 unit s-1. 3 Find the rate of change of y when x = 2 units. [0.6 unit/s] Given y =
A spherical balloon is inflated at the rate of 3 cm3/s. Find the rate of increase of the radius when the instant radius is r = 2 cm . 4 (Formula of volume of sphere, V = r 3 ) 3 3 [ cm/s ] 16 A circular ink blot spreads at the rate of 1 cm 2 /s . Find the rate of increase in 3 1 the circumference of the ink blot when its radius is cm . 3 (Formula of perimeter of circle, P = 2r ) 2 [ cm/s ] 3
2.
3.
4.
The side of a square is increasing at the rate of 5 cms 1 . Find the rate of increase of the area when the length of a side is 10 cm. [ 100 cm 2 /s ] A missile fired from the ground level rises s meters in t seconds, and s = 75t 12.5t 2 . Determine: i) The initial velocity of the missile [v 0 = 75 m/s ] ii) The time when the height (distance) of the missile is a maximum [t = 3 s ] The maximum height reached [ s = 112.5 m ] iv) The velocity when the missile strikes the ground [v = 75 m/s ]
5.
iii)
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 21
APLIKASI PEMBEZAAN
6.
An open metal tank of square base has a volume of 108 m3. Given that the square base has sides of x meters each, find in terms of x , the: i) Height of the tank [ h = 108x 2 ] ii) Surface area of the tank [ A = 432x 1 + x 2 ] iii) Value of x , when the area is minimum [6 m]
7.
A piece of string of 40 cm is cut into two lengths. Each length is used to form a square. Given the length of one of the square is x cm, find in terms of x : i) The length of the other square [ (10 x ) cm] [ x 2 + (10 x ) cm2]
2
ii)
The total area enclosed by the two squares
iii)
Value of x when the sum of both areas is a minimum [5 cm]
lect notes/jazz Muka surat | 22
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Tugas 1 Madas UasDokumen20 halamanTugas 1 Madas UasVhen Vhiiee50% (10)
- Turunan Materi MatematikaDokumen36 halamanTurunan Materi MatematikaBayu AjipBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Soal Fisika Dan JawabanDokumen12 halamanContoh Soal Fisika Dan JawabanMhya Thu Ulun100% (1)
- Fisika IDokumen67 halamanFisika IEllyTahaleleBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Soal Kinematika GerakDokumen9 halamanContoh Soal Kinematika GerakFuyuka ReizeiBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Soal Fisika DanDokumen8 halamanContoh Soal Fisika DanYulianti MalikBelum ada peringkat
- TurunanDokumen27 halamanTurunanErsalia ShifaBelum ada peringkat
- Sola FisikaDokumen21 halamanSola FisikaMuhammad Akram Ramadan WeroBelum ada peringkat
- Aplikasi Turunan Fungsi TrigonometriDokumen10 halamanAplikasi Turunan Fungsi TrigonometriAnchaBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Fisika Kelas XI Bab 1Dokumen7 halamanSoal Fisika Kelas XI Bab 1Rio Andika0% (1)
- Bab II KinematikaDokumen18 halamanBab II KinematikaArhim Shorinji KempoBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Dan Jawaban Turunan TrigonometriDokumen11 halamanSoal Dan Jawaban Turunan TrigonometriILhami Fahyudin67% (15)
- 2 Kinematika & DinamikaDokumen50 halaman2 Kinematika & Dinamikaputri wulandariBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Pendulum ArmanDokumen15 halamanLaporan Pendulum ArmanRobby GunawanBelum ada peringkat
- Kalkulus 1 - Turunan LanjutanDokumen6 halamanKalkulus 1 - Turunan LanjutanLeonhart Heartily100% (1)
- Bab 3 Gerak LurusDokumen33 halamanBab 3 Gerak LurusPangeran SitorusBelum ada peringkat
- Fisika Dasar KinematikaDokumen17 halamanFisika Dasar Kinematikarachmat agungBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematika Gerak Lurus XBDokumen94 halamanKinematika Gerak Lurus XBherawatiBelum ada peringkat
- Bab-2 Gerak Lurus - Fisika Kelas X - Marthen Kanginan - Erlangga - Kurtilas - SolusiWIKIDokumen40 halamanBab-2 Gerak Lurus - Fisika Kelas X - Marthen Kanginan - Erlangga - Kurtilas - SolusiWIKIInnataRevailleBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan 2. Gerak-2020Dokumen13 halamanPertemuan 2. Gerak-2020Rafqi syah alamBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Rutin 1 Fisika UmumDokumen21 halamanTugas Rutin 1 Fisika UmumEka NoviasariBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Kelompok 1 Gerak 2 DimensiDokumen23 halamanMakalah Kelompok 1 Gerak 2 DimensiFransiskus LepongBelum ada peringkat
- BAB 3 Gerak-LurusDokumen37 halamanBAB 3 Gerak-LurusChristopher Dichard MewengkangBelum ada peringkat
- 14-15-16 Derivatif - PENGGUNAANDokumen17 halaman14-15-16 Derivatif - PENGGUNAANAce AzisBelum ada peringkat
- Puji FIsDokumen10 halamanPuji FIsKurnia NiaBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan 2. GerakDokumen25 halamanPertemuan 2. GerakYulia SridewiBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematika Dengan Analisa Vektor - 2Dokumen14 halamanKinematika Dengan Analisa Vektor - 2Agastiya Aldi100% (1)
- Soal MekfluDokumen29 halamanSoal MekfluSetiawan AungBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas 8 PelabuhanDokumen5 halamanTugas 8 Pelabuhanagnes weluBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematika Satu DimensiDokumen17 halamanKinematika Satu DimensihanifahBelum ada peringkat
- Gerak Lurus Fisika Terapan Jurusan SipilDokumen15 halamanGerak Lurus Fisika Terapan Jurusan SipilRakha KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- Wahyu TR FisikaDokumen11 halamanWahyu TR FisikaMuhammad WahyuBelum ada peringkat
- BAB 3 TurunanDokumen18 halamanBAB 3 TurunanArief RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Turunan Tingkat Tinggi&Implisit 6Dokumen8 halamanTurunan Tingkat Tinggi&Implisit 6ArBelum ada peringkat
- Ringkasan Fisika SMA Kelas XI Semester 1Dokumen21 halamanRingkasan Fisika SMA Kelas XI Semester 1Dea Tita HastikaBelum ada peringkat
- 2 KinematikaDokumen27 halaman2 Kinematikanur anisa panusuBelum ada peringkat
- 08 Teorema StokesDokumen49 halaman08 Teorema StokesHerry Siswanto100% (1)
- Ma1101 Matematika 1A: Hendra GunawanDokumen13 halamanMa1101 Matematika 1A: Hendra GunawanJaqila Hajitya PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Bab III Kinematika PartikelDokumen17 halamanBab III Kinematika Partikelode arya indranataBelum ada peringkat
- Rita Permata Sari Sitorus (4143121049)Dokumen14 halamanRita Permata Sari Sitorus (4143121049)Rita SitorusBelum ada peringkat
- Bab11 Rotasi Benda Tegar1Dokumen26 halamanBab11 Rotasi Benda Tegar1KevargaBelum ada peringkat
- Bab Ii KinematikaDokumen18 halamanBab Ii KinematikaBrandon Marcello PotuBelum ada peringkat
- Vektor Satuan Dan Vektor PosisiDokumen9 halamanVektor Satuan Dan Vektor PosisiFarisdaBelum ada peringkat
- Perpindahan Adalah Perubahan PosisiDokumen33 halamanPerpindahan Adalah Perubahan PosisiArifBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematika Gerak LurusDokumen12 halamanKinematika Gerak LurusFarhan HisyamBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Soal FisikaDokumen31 halamanContoh Soal FisikaDzz Zeet Oonn100% (1)
- Pertemuan 4 Fisdas Farmasi TeksipDokumen28 halamanPertemuan 4 Fisdas Farmasi TeksipEndra Putra RaharjaBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematika PartikelDokumen28 halamanKinematika PartikelMaura Femitri SiahaanBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Jawab Pers Gerak TranslasiDokumen2 halamanSoal Jawab Pers Gerak TranslasiwasimudinBelum ada peringkat
- Matematik Dan SeniDokumen6 halamanMatematik Dan SeniWan HamidahBelum ada peringkat
- Matematik Dan SeniDokumen6 halamanMatematik Dan SeniWan HamidahBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 5Dokumen33 halamanBab 5khoirulnizam75Belum ada peringkat
- 1 PB PDFDokumen4 halaman1 PB PDFIrmayani AmangBelum ada peringkat
- Pengujian, Pengukuran Dan PenilaianDokumen19 halamanPengujian, Pengukuran Dan PenilaianIkhwan IzamBelum ada peringkat
- Senidalammm 130816214252 Phpapp02Dokumen10 halamanSenidalammm 130816214252 Phpapp02Wan HamidahBelum ada peringkat
- Rancangan Pengajaran HarianDokumen2 halamanRancangan Pengajaran HarianWan HamidahBelum ada peringkat
- Soalan No. 2Dokumen8 halamanSoalan No. 2Wan HamidahBelum ada peringkat
- LAPORAN AKTIVITI KhemahDokumen5 halamanLAPORAN AKTIVITI KhemahWan HamidahBelum ada peringkat
- Bahasa Dan KomunikasiDokumen17 halamanBahasa Dan KomunikasiWan HamidahBelum ada peringkat
- Bahasa Dan KomunikasiDokumen17 halamanBahasa Dan KomunikasiWan HamidahBelum ada peringkat
- Kalkulus Yang Dah Bener2 JadiDokumen10 halamanKalkulus Yang Dah Bener2 JadiWan HamidahBelum ada peringkat
- Isi Perut NomborDokumen25 halamanIsi Perut NomborAhmad IdzzuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Artikel OlahragaDokumen8 halamanArtikel OlahragaWan HamidahBelum ada peringkat
- Rancangan Pengajaran HarianDokumen2 halamanRancangan Pengajaran HarianWan HamidahBelum ada peringkat
- Aplikasi Pembezaan Dalam Kehidupan HarianDokumen2 halamanAplikasi Pembezaan Dalam Kehidupan HarianPatrickAnthony100% (3)
- Sukan Permainan MarkahDokumen13 halamanSukan Permainan MarkahWan HamidahBelum ada peringkat
- 08 (A) Isi Pelajaran - Interaksi 1Dokumen29 halaman08 (A) Isi Pelajaran - Interaksi 1ismakieBelum ada peringkat
- Rumusan ArtikelDokumen15 halamanRumusan ArtikelWan HamidahBelum ada peringkat
- Artikel 1Dokumen11 halamanArtikel 1Wan HamidahBelum ada peringkat
- Kertas Kerja Sukan Tara 2Dokumen18 halamanKertas Kerja Sukan Tara 2Wan HamidahBelum ada peringkat
- Tajuk 2Dokumen14 halamanTajuk 2masazlinzBelum ada peringkat
- 08 (A) Isi Pelajaran - Interaksi 1Dokumen29 halaman08 (A) Isi Pelajaran - Interaksi 1ismakieBelum ada peringkat
- Konsep Asas KomputerDokumen3 halamanKonsep Asas KomputerWan HamidahBelum ada peringkat