Cheg1 - 4 Jan 2024 at 14.11
Diunggah oleh
Diana WalesHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Cheg1 - 4 Jan 2024 at 14.11
Diunggah oleh
Diana WalesHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Search
Seorang peneliti ingin menyelidiki performansi kinerja seseorang
setelah mengalami kekurangan tidur, dengan dua macam tipe
orang yang kekurangan tidur. Di Grup 1, 40 orang diperbolehkan
tidur selama lima jam. Di Grup 2, 35 orang diizinkan tidur selama
tiga jam. Kemudian performansi kinerja diukur dengan cara
melakukan tes memori dengan standar deviasi populasi adalah 6
orang di setiap kelompok dan diasumsikan berdistribusi normal.
Rata − rata skor tes memori pada kelompok yang tidur tiga jam
adalah 58; dalam kelompok yang tidur lima jam, itu adalah 62 .
a) Jika peneliti tertarik untuk menguji apakah kinerja memori
memiliki perbedaan yang signi!kan pada kedua kelompok tersebut,
jelaskan hipotesis nol dan hipotesis alternatifnya dan Lakukan uji
hipotesis dengan tingkat alpha 0, 01 . Apakah kesimpulan peneliti?
b) Jika peneliti tertarik untuk meneliti apakah lebih banyak tidur
dapat memberikan performansi kinerja yang lebih baik? Lakukan uji
hipotesis dengan tingkat alpha 0, 05 . Apakah kesimpulan peneliti?
There are 2 steps to solve this one.
Expert-verified 100% (1 rating) Share
1st step All steps Answer only
Step 1
a) Hypothesis Testing for Group Differences:
Null Hypothesis (H0): There is no signi!cant
difference in memory performance between the two
groups (μ1 - μ2 = 0).
Alternative Hypothesis (H1): There is a signi!cant
difference in memory performance between the two
groups (μ1 - μ2 ≠ 0).
- Given:
-x–1 = 62, x
–2 = 58
- n1 = 40, n2 = 35
- σ=6
- α = 0.01
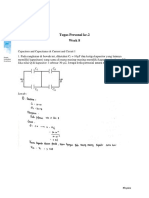
- Test Statistic:
(62−58)
t=
√ 62 + 62
40 35
- Degrees of Freedom (df):
df = n1 + n2 − 2 = 40 + 35 − 2 = 73
- Critical Value:
- Using a t-table or statistical software, !nd the tcritical
for a two-tailed test with df = 73 at α2 = 0.005.
- Calculation:
4
t≈
√ 0.36
40
.36
+ 035
4
t≈ √0.009+0.01029
4
t≈ √0.01929
4
t≈ 0.1388
t ≈ 28.85
- Conclusion:
|t| = 28.85 > tcritical
- Reject the null hypothesis.
- There is a signi!cant difference in memory
performance between the two groups.
Explanation:
a) Testing Group Differences:
- Objective:
- Determine if there's a signi!cant difference in
memory performance between two groups with
different sleep durations.
- Hypotheses:
- H0 : No difference in memory performance
(µ1 − µ2 = 0)
- H1: Signi!cant difference in memory
performance(µ1 − µ2 ≠ 0)
- Test Statistic:
- Two-sample t-test(t) comparing the means of
the two groups.
- Decision Rule:
- Reject H0 if |t| exceeds critical value.
- Conclusion:
- Reject H0, indicating a signi!cant difference in
memory performance between the two groups.
Step 2
b) Hypothesis Testing for Sleep Duration Effect:
- Given:
- Same as in part (a).
- α = 0.05
- Test Statistic:
- Same as in part (a).
- Degrees of Freedom (df):
- Same as in part (a).
- Critical Value:
- Using a t-table or statistical software, !nd the tcritical
for a one-tailed test with df = 73 at α = 0.05.
- Calculation:
- Same as in part (a).
- Conclusion:
- p (calculated using the test statistic) is compared
with α.
- If p < α , reject the null hypothesis.
- Provide the actual p value for a more accurate
conclusion.
Please note that the exact critical value and p-value would
depend on the degrees of freedom. You may use
statistical software or a t-table to obtain precise values.
Explanation:
In both cases, the t-tests help assess if observed
differences are statistically signi!cant. The decision
to reject the null hypothesis is made based on the
calculated test statistic or p-value, providing
insights into whether there are meaningful
distinctions in memory performance or sleep
duration effects.
Answer
The Final Answers are :
a) Testing Group Differences:
- Conclusion: There is a signi!cant difference in memory
performance between the two groups (3 hours vs. 5 hours
of sleep) at a signi!cance level of 0.01.
b) Testing Sleep Duration Effect:
- Conclusion: More sleep duration (5 hours vs. 3 hours)
signi!cantly improves memory performance at a
signi!cance level of 0.05.
"If you found my answer helpful, I would greatly
appreciate it if you could take a moment to like it."
Was this solution helpful?
What would you like to do next?
Send my question to an expert
Academic Integrity / Feedback / Help Center / Manage Subscription
Cookie Notice Your Privacy Choices Do Not Sell My Info
General Policies Privacy Policy Honor Code IP Rights
© 2003-2023 Chegg Inc. All rights reserved.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Cheg2 - 4 Jan 2024 at 14.11Dokumen1 halamanCheg2 - 4 Jan 2024 at 14.11Diana WalesBelum ada peringkat
- rev2-STAT TP1Dokumen3 halamanrev2-STAT TP1Viva AlieBelum ada peringkat
- Cheg3 - 4 Jan 2024 at 14.12Dokumen1 halamanCheg3 - 4 Jan 2024 at 14.12Diana WalesBelum ada peringkat
- 2121 Isye6187037 Lkda TK4-W9-S13-R1 Team8Dokumen8 halaman2121 Isye6187037 Lkda TK4-W9-S13-R1 Team8Manik RetnoBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan FisikaDokumen16 halamanLaporan FisikaTasy WijayaBelum ada peringkat
- 2112 Isye6187037 Tkda TK1-W3-S4-R1 Team4Dokumen3 halaman2112 Isye6187037 Tkda TK1-W3-S4-R1 Team4valdi sBelum ada peringkat
- 2111 Scie6056037 Ljda TK4 W9 S24 R0 Team4 PDFDokumen6 halaman2111 Scie6056037 Ljda TK4 W9 S24 R0 Team4 PDFdiffa sajaBelum ada peringkat
- 2122 Isye6189037 Loda TK2-W4-S5-R0Dokumen6 halaman2122 Isye6189037 Loda TK2-W4-S5-R0Golem MonterBelum ada peringkat
- TP 2 ProbabilityDokumen3 halamanTP 2 ProbabilityMarta ManggalaBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Kelompok Ke-1 (Minggu 3/ Sesi 4)Dokumen2 halamanTugas Kelompok Ke-1 (Minggu 3/ Sesi 4)yolandavmsBelum ada peringkat
- 2311 Isye6187037 Exda TK4-W9-S13-R3 Team4Dokumen6 halaman2311 Isye6187037 Exda TK4-W9-S13-R3 Team4mifta fajarBelum ada peringkat
- LWDA STAT6174037 ProbabilityTheoryandAppliedStatistics-QuestionDokumen19 halamanLWDA STAT6174037 ProbabilityTheoryandAppliedStatistics-QuestionLuthfiBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Percobaan 1 Genap 1819Dokumen13 halamanPhysics Percobaan 1 Genap 1819tasyawijayaBelum ada peringkat
- TK 2 PhysicsDokumen9 halamanTK 2 PhysicsFadhil MuhammadBelum ada peringkat
- 2122 Isye6189037 Lpda TK2 W4 S5 R0 Team5 PDFDokumen7 halaman2122 Isye6189037 Lpda TK2 W4 S5 R0 Team5 PDFRahmat Rama DhoniBelum ada peringkat
- Ariella 2602303885 DNDA TP2-W8-S21-R0Dokumen5 halamanAriella 2602303885 DNDA TP2-W8-S21-R0Aayunda Ariella100% (1)
- Tugas Kelompok Ke-3 Minggu 8/ Sesi 12 Soal No 1Dokumen4 halamanTugas Kelompok Ke-3 Minggu 8/ Sesi 12 Soal No 1Luffy Albi FradanaBelum ada peringkat
- Fix His11 Agda Module03Dokumen16 halamanFix His11 Agda Module03Marlita HardiyantiBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Akhir Praktikum Fisika BOL - AKDA - Team 1Dokumen30 halamanLaporan Akhir Praktikum Fisika BOL - AKDA - Team 1Cravle StruickBelum ada peringkat
- Modul 5Dokumen3 halamanModul 5Feby LailaniBelum ada peringkat
- TP1 W2 S3 R2 Farid Aulia RahmanDokumen3 halamanTP1 W2 S3 R2 Farid Aulia RahmanRahmat Rama DhoniBelum ada peringkat
- Laprak 1 RevisiDokumen32 halamanLaprak 1 RevisiVincenzo DohertyBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Kelompok Minggu Ke-2 (Kelompok Satu)Dokumen8 halamanTugas Kelompok Minggu Ke-2 (Kelompok Satu)imam baktyBelum ada peringkat
- MATH6162037 Mathematics-2502053716Dokumen7 halamanMATH6162037 Mathematics-2502053716Dika CahyoBelum ada peringkat
- StatistikDokumen6 halamanStatistikToxic Gamers HQ100% (1)
- Tugas Kelompok Ke-1 Week 2Dokumen7 halamanTugas Kelompok Ke-1 Week 2LuthfiBelum ada peringkat
- Probabilitas PDFDokumen3 halamanProbabilitas PDFnjkjhBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Kelompok Ke-3 Week 7: PhysicsDokumen2 halamanTugas Kelompok Ke-3 Week 7: PhysicstikaBelum ada peringkat
- 2212 Isye6187037 Luda TK1-W3-S4-R2 Team1Dokumen3 halaman2212 Isye6187037 Luda TK1-W3-S4-R2 Team1Rahmat Rama DhoniBelum ada peringkat
- TK2 W4 S5 R1Dokumen6 halamanTK2 W4 S5 R1Dimas NugrahaBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Kelompok Ke 4 DeterministikDokumen4 halamanTugas Kelompok Ke 4 DeterministikBunga AfriestaBelum ada peringkat
- LKDA SCIE6057 ChemistryandBiology-QuestionDokumen2 halamanLKDA SCIE6057 ChemistryandBiology-QuestionPrasetya BaktiBelum ada peringkat
- Latihan EkotekDokumen2 halamanLatihan EkotekEmmy ItemBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Kelompok Group 4 - ProbabilityDokumen3 halamanTugas Kelompok Group 4 - ProbabilityAyub IlhamBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Personal Ke-2 Week 8: Capacitors and Capacitance & Current and Circuit 1 1Dokumen2 halamanTugas Personal Ke-2 Week 8: Capacitors and Capacitance & Current and Circuit 1 1selamat datang0% (2)
- Tugas Personal Ke-2 (Minggu 7/ Sesi 11) : Engineering Economy and System Analysis - R2Dokumen2 halamanTugas Personal Ke-2 (Minggu 7/ Sesi 11) : Engineering Economy and System Analysis - R2selamat datangBelum ada peringkat
- 2212 Stat6174037 Toda TK1-W3-S4-R1 Team4Dokumen4 halaman2212 Stat6174037 Toda TK1-W3-S4-R1 Team4Ayub IlhamBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Kelompok Ke-1 (Minggu 3/sesi 4)Dokumen6 halamanTugas Kelompok Ke-1 (Minggu 3/sesi 4)Rahmat Rama DhoniBelum ada peringkat
- TP2-W8-S21-R0-sofia MailalDokumen4 halamanTP2-W8-S21-R0-sofia MailalSOFIA MAILAL IKHSANIBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Kelompok Ke-3 Minggu 8/ Sesi 12 Soal No 1Dokumen1 halamanTugas Kelompok Ke-3 Minggu 8/ Sesi 12 Soal No 1Muhammad Adi Waskito0% (1)
- TNDA ISYE6187037 EngineeringEconomyandSystemAnalysis-QuestionDokumen4 halamanTNDA ISYE6187037 EngineeringEconomyandSystemAnalysis-QuestionUttarrii AiBelum ada peringkat
- 2311 Stat6174037 Dtda TK2-W4-S5-R2 Team2Dokumen7 halaman2311 Stat6174037 Dtda TK2-W4-S5-R2 Team2klozeesamaBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Kelompok Ke-2 Week 4/ Sesi 5: Tabel 2. Alternatif PilihanDokumen3 halamanTugas Kelompok Ke-2 Week 4/ Sesi 5: Tabel 2. Alternatif PilihanUttarrii AiBelum ada peringkat
- TK1-W3-S4-R2 Kelompok 9Dokumen5 halamanTK1-W3-S4-R2 Kelompok 9SOFIA MAILAL IKHSANIBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Kelompok Ke-1 Week 2: PhysicsDokumen5 halamanTugas Kelompok Ke-1 Week 2: PhysicsBos Pil100% (1)
- Forum Diskusi 6-3 (Soal Induksi Dan Hukum Faraday)Dokumen2 halamanForum Diskusi 6-3 (Soal Induksi Dan Hukum Faraday)Reyhan Julianto PribadiBelum ada peringkat
- Jawab 20230214000247 TP1 W2 S3 UpdateDokumen5 halamanJawab 20230214000247 TP1 W2 S3 UpdateMarlita HardiyantiBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Economy BayuDokumen5 halamanEngineering Economy BayuBayu WirandanaBelum ada peringkat
- TK 3 RevDokumen7 halamanTK 3 RevBos PilBelum ada peringkat
- 04 Soal STK511 2019 Pendugaan Parameter Dan Pengujian HipotesisDokumen1 halaman04 Soal STK511 2019 Pendugaan Parameter Dan Pengujian HipotesisHijkBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Praktikum 1Dokumen20 halamanLaporan Praktikum 1Rico Giyar PionarBelum ada peringkat
- 2112 Scie6056037 Lkda TP2-W8-S21-R0Dokumen5 halaman2112 Scie6056037 Lkda TP2-W8-S21-R0ZakiBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Praktikum Pertemuan 8Dokumen20 halamanLaporan Praktikum Pertemuan 8Muhammad Rizki WijayaBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Kelompok - 3 (Minggu 8/ Sesi 12) : Team Project: Design For Usability (Human Factors)Dokumen1 halamanTugas Kelompok - 3 (Minggu 8/ Sesi 12) : Team Project: Design For Usability (Human Factors)selamat datangBelum ada peringkat
- Calvin Agasta TP2 Economy EngineeringDokumen5 halamanCalvin Agasta TP2 Economy EngineeringcalvinBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Kelompok Ke-2 Week 4/ Sesi 5: Group 9Dokumen5 halamanTugas Kelompok Ke-2 Week 4/ Sesi 5: Group 9SOFIA MAILAL IKHSANIBelum ada peringkat
- TBDA STAT6128 StochasticProcesses-QuestionDokumen4 halamanTBDA STAT6128 StochasticProcesses-Questionerni nasirBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Personal Ke-2 (Minggu 7/ Sesi 11) : Engineering Economy and System Analysis - R2Dokumen1 halamanTugas Personal Ke-2 (Minggu 7/ Sesi 11) : Engineering Economy and System Analysis - R2tikaBelum ada peringkat
- His06 Anda Module06Dokumen20 halamanHis06 Anda Module06suara menenangkanBelum ada peringkat
- Uji BedaDokumen27 halamanUji BedaDianHandianaBelum ada peringkat