Modul Nyeri Ekstremitas
Diunggah oleh
SabrinaQurrotaayunHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Modul Nyeri Ekstremitas
Diunggah oleh
SabrinaQurrotaayunHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Moh Adib Khumaidi, Dr , SpOT
SKENARIO 2
Seorang laki-laki berumur 39 tahun dating ke poliklinik
dengan keluhan nyeri pada bokong yang menjalar ke bagian
posterolateral paha,tungkai bawah & tumit. Hal ini
dirasakan sejak 5 hari yang lalu setelah penderita
mengangkat barang berat di kantor .Nyeri ini bertambah
berat bila penderita duduk dan berkurang bila penderita
berdiri atau berjalan.Pada pemeriksaan fisik ditemukan
penurunan sensoris pada sisi lateral tungkai bawah dan kaki
serta 3 jari lateral kaki kanan .reflex
SKENARIO 3
Laki-laki umur 36 tahun datang ke poliklinik dengan keluhan
utama nyeri pada daerah siku kanan menjalar ke lengan
bawah yang dirasakan sejak 9 bulan lalu. Keadaan ini
dirasakan semakin bertambah berat terutama bila penderita
memflexikan sikunya. Ada riwayat fraktur supracondylar
pada waktu berusia 5 tahun. Pada siku kanan terlihat valgus
deformitas, gangguan sensoris pada ujung jari kelingking.
Atrophy otot pada
-1w0eb-spaceI.
NYERI
Postoperative pain is a complex of
unpleasant sensory, emotional,
and mental experiences
associated with autonomic, psychological,
and behavioral responses
precipitated by the surgical injury
Henrik Kehlet, ACS Surgery 2003.
IASP 1979 :
Pain is
an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or
potential tissue damage,
or described in terms of such damage.
Perlu kita sadari bahwa
Pain is always subjective.
Many people report pain in the absence of tissue damage or any
likely pathopysiological cause.
If they regard their experience as pain and if they report it in the same
way as pain caused by tissue damage,
it should be accepted as pain.
Nominal
stimulus
Modulation
Modulation
Nyeri berawal dari adanya rangsang di perifer yang
disebut nociception.
Rangsang yang disebabkan antara lain oleh kerusakan
jaringan ini dihantarkan ke medula spinalis.
Jalur transmisi dari perifer ke dorsal horn (cornu posterior)
menggunakan serat A-delta dan C untuk nyeri somatik dan
serat afferent sympathetic untuk nyeri visceral
Situasi di perifer dapat diperberat oleh adanya prostaglandins,
serotonin, bradykinin, nerve growth factor, histamine dan
substance P serta aktifitas simpatetik lainnya
Peripheral
nerve
Peripheral
nociceptors
nociception
Di dorsal horn medula spinalis terjadi modulasi.
Setelah modulasi di cornu posterior, signal naik ke atas
melewati tractus spinothalamicus dan spinoreticularis ke
hipothalamus, brain stem, formatio reticularis dan cortex
cerebri. Proses pengolahan ini dapat berupa excitation atau
inhibition.
Modulasi di dorsal horn (Rexed's laminae I to IV)
mengikutsertakan substance P, enkephalins, somatostatin,
neurotensin, gamma-amino-butyric acid (GABA), glutamic acid,
angiotensin II, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP),
cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8).
Dorsal Horn
Spinothalamic
tract
Setelah modulasi di cornu posterior, signal naik ke atas melewati tractus
spinothalamicus dan spinoreticularis ke hipothalamus, brain stem,
formatio reticularis dan cortex cerebri.
Otak juga mengirim modulasi lagi melalui descending inhibitory
pathway menuju dorsal horn.
Spinothalamic
tract
Pain
Dorsal Horn
Descending
modulation
Obat anestesia umum
Obat anestesia spesifik
Opioid
Pain is always subjective
Potentiation
Reduced doses of
each analgesic
Improved pain relief
due to synergistic
or additive effects
May reduce severity
of side effects of
each drug
Benefits of Multimodal Pain Therapy
1
1
Kehlet H et al. Anesth Analog. 1993;77:1048-1056.
Morphine
NSAIDs,
acetaminophen,
nerve blocks
paracet
NSAID
COX-2 Inhib
Opioid
Anestetika
Analgesic Ladder WHO
Untuk Nyeri Kanker
Overview
Back pain affects most people at least once over their lifetime.
It can be a cause for lost wages & productivity
Most people will become better in 6 weeks
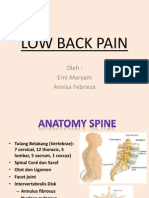
Anatomy
The back is composed of
vertebrae, muscles,
ligaments, intervertebral
disc,& nerves.
There are 7 cervical, 12
thoracic, 5 lumbar & 5
coccygeal vertebrae
Spinal cord has cervical
lordosis, Thoracic kyphosis,
& lumbar lordosis
Assessment of Low Back Pain
History & Physical: Nocturnal exacerbation occurs w tumors or inf, w
benign causes like herniated disc pain improves w bed rest
Limitation of spinal motion correlates with the presence of lower back
disability
Palpation: Gentle & systemic palpation of the back, coccyx, sacrum,
levator ani, coccygeus, & piriformis ms, & associated ligament done
Muscle spasm: has localized tenderness, & increase in ms tone
Assessment of Back Pain
Pain on percussion occurs with metastases or inf, does not occur w disc
protrusion & spasm
Radiological test: Plain Xrays show degenrative disc ds, spondylitis,
compression fx, metabolic bone disorder, bone tumors, congenital
anomalies & transitional vertebrae
Oblique view of lumbosacral level is used to visualize facet & sacroiliac
joint
Flexion-extension view is added when ever spinal instability suspected
Straight leg raising test
Straight leg raising test
should be performed to
detect nerve root irritation
Even with a soft tissue pain
source, SLR can be used
as an index of improvement
A +ve crossed SLR test has
the highest correlation w
myelographic finding of a
herniated disc
Causes of back pain
Pain sensitive structures are the supporting bone, articulations,
meninges, nerves, muscles, & aponeuroses
Vertebral body despite being short is actually a long bone with end plates
of hard bone & a center of cancellous bone
It is innervated by dorsal roots
Periosteum is pain sensitive as is facet joint which have a capsule &
meniscus richly innervated w nociceptors
Muscular Pain
Most back pains are
caused by sprain or
strain of the back
muscles & ligaments
Pain will be in discrete
area & tender to touch
It is of aching quality &
may involve muscle
spasm
Pain not involved
shooting pain
Spinal causes
Osteoporosis
Osteomylitis
Herniated Disc
Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolysis
Facet hypertrophy
Ischemia of the spinal
cord
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is painful due
to microfracture
Absence of wt bearing due
to bed ridden leads to
demineralization & fx upon
wt bearing
Postmenopause & pt Rx
with corticosteroid is at risk
Other cond r/o w serum
protein electrophoresis, sed
rate, alkaline phosphatase,
ca, x-rays.Rx
Biphosphonate, raloxifene
Osteomyelitis
Vertebral osteomyelitis
presents as subacute back
pain that increases over
days to weeks
Pain in low back if unRx
focal weakness, bowel &
bladder problem results
Most common in lumbar
spine in men over 50
With AIDS younger men &
cervical spine affected
Osteomyelitis
In immunocompetent hosts, Staphylococcus aureus inf most common
Inf involves vertebral bodies, endplates, & disc spaces, spares post
elements
In rare cases actinomycosis or coccidiodomycosis, posterior elements
involved & spine becomes unstable
Vertebral metastases
Vertebral metastasis presents as localized, deep, aching, back pain
If nerves are involved, pain occurs in neural distribution
Thoracic spine is most commonly affected
Epidural spinal cord compression is a medical emergency & pt may present
with paraparesis, sensory loss, bowl & bladder involvement
Vertebral metastases
On plain film earliest sign of
spinal metastasis is erosion of
pedicle
Over time vertebral body
begins to lose height
MRI reveals change in signal
intensity in vertebral body
As tumor progresses, it may
be seen invading epidural
space & compressing spinal
cord
Facet joint pain
The vertebral bodies have
4 facet joint, 1 pair above
& 1pair below
Synovial joints mean they
have fluid with in them
Back pain caused by
arthritis of the facet joints
is mostly midline & may
spread to the back & to
the flanks
Gets worse with bending
backward & side to side
Herniated Disc
Intervertebral disc consists of an outer fibrous body called the annulus
fibrosus & an inner gel like substance called the nucleus pulposus
It acts as a shock absorber & spacer for the spine giving room for the
intervertebral neural foramina which are portals for the exit of the spinal
nerves
The nucleus pulposus contains noxious chemicals which can be irritating to
nerves
Herniated disc-cont-
The intervertebral discs lie between the vertebral bodies. In front is the ant.
longitudinal ligament & behind the post. longitudinal ligament & behind that
is spinal cord.
Wear & tear can cause annulus fibrosus to weaken allowing bulges of
nucleous pulposis
These bulges may protrude out enough to touch the spinal cord causing
irritation to nerves
These large disc bulges are called herniation
Herniated Disc
With extreme forces these disc
bulges may tear the annulus
fibrosus & allow leakage of
nucleus pulposus
This is observed as sudden sharp
pain radiating down the leg
The chemicals of nucleus
pulposus can cause swelling of
nerves resulting in constant
burning pain termed lumbar
radiculopathy or sciatica, pain
radiating down the leg & feet
Types of Herniate Disc
Disc degeneration
Disc prolapse
Disc extrusion
Disc seqestration
Radiographic herniated disc
Spondylosis
It can be described as
arthritis of the spine
The bony surfaces may
become roughened & bony
spurs may develop & intrude
upon the spinal canal
Spondylolisthesis
It is a slippage of the
vertebra upon one
another
The vertebra are
usually aligned so that
each one is stacked like
legos so that the
spinal canal is a fairly
straight tube
Spondylolithesis
If there is a slippage,
the spinal canal has a
kink & is a smaller in
that area
When spinal stenosis
occurs, it squeezes
upon the spinal cord
This may cause
irritation or ischemia of
the spinal cord & lead
to cramping or aching
of the legs
Grades of Spondylolisthesis
Piriformis Syndrome
It is a syndrome of low
back & leg pain due to ch.
Contracture of the
piriformis muscle that
causes irritation of sciatic n
Gluteal pain radiates to
sciatic nerve
It occurs by compression of
nerve between ms. Or ms
& pelvis
Buttock pain
Common causes are
Piriformis syndrome
Ischial tuberosity inj.
Rupture of gluteal ms.
Piriformis Syndrome
It is also called hip pocket
neuropathy or wallet neuritis
Piriformis ms is flat, pyramidal ms
that originates from ant surface of
sacrum from S2-S4 & sacrotuberous
lig passes through the upper part of
greater sciatic notch, & inserts on
superior surface of great trochanter
Treatment of Back Pain
Walking is best exercise
Physical therapy for core stabilization
Spinal manipulation & manual therapy
Analgesics like acetaminophen, NSAIDS, antidepressants
Application of heat or ice
Acupuncture
Corticosteroid injections
Treatment of Chronic Back Pain
Treat the cause like in osteomylitis, surgery with antibiotics is used
Vertebral metastasis will respond to high doses of dexamethasone,
definitive treatment with radiation & surgery
Osteoporosis treated with Biphosphonate, Robaxifene
Muscle spasms may respond to ms relaxants
Back Exercises
Ankle pump
Heel slides
Abdominal contraction
Wall squats
Heel raises
Straight leg raises
Knee to chest stretch
Hamstring stretch
Exercises with swiss ball
Epidural steroid injection
Epidural space
identified w loss of
resistance tech or
fluroscopy
60-80 mg of triamcilone
with 0.25% bupivacaine
injected
Intradiscal electrothermic therapy
IDET is done using fluoroscopy,
a hollow needle containing
flexible tube & heating element
is inserted into spinal disc
The catheter placed in a circle
in the annular layer of disc &
slowly heated to 194 deg.
The heat is meant to destroy the
nerve fibers & toughen the disc
tissue, sealing any small tear
Vertebroplasty
Under fluoroscopy, a
hollow needle is inserted
& a cement is injected to
restore the vertebra
Kyphoplasty
In kyphoplasty a ballon
is inserted through the
hollow needle into the
fractured bone to restore
the height & shape of the
vertebra.
Once the ballon is
removed, the cement
mixture is injected.
Kyphoplasty / Vertebroplasty
Spondylolithesis
Discectomy
A scope is inserted
through a small cannula
to inspect disc surface
Peri-annular fat is
removed & small
capillaries are
cauterized
Small nerves in the
annular fat can be
removed with peri-
annular tissue
WHO Pain ladder
Step 3: Opioids for
moderate-to-severe
pain +/- non-opioid
+/-adjuvant therapy
Step 2: Opioids for
mild- to-moderate
pain +/- non-opioid
+/- adjuvant therapy
Step 1: Non-opioid
+/- adjuvant therapy
STEP 1
STEP 2
STEP 3
GOAL:
Freedom From Pain
Pain Persists
Pain Persists
WHO Pain Ladder
Step 1 Mild (pain rating 1-3)
Non opioid + co-analgesics
e.g. NSAID+TCA/membrane stabilizer/ms.relax.
Step 2 Moderate (pain rating 4-6)
Opioid + Non opioid + co-analgesics
Lorcet + NSAID+TCA/memb. Stab./ms. Relax.
Step 3 Severe ( pain rating 7-10)
Pure opioids + non-opioids + co-analgesics
e.g. Morphine SR + NSAID + above.
Opioid combination products
Drug Opioid Non-opioid Doses
Lortab (vicodin) Hydrocodone
5 mg
APAP 500 mg 1-2 q 4 hrs.
Max. 8 tabs/day
Lorcet Hydrocodone
10 mg
APAP 650 mg 1 q 4 hrs.
Max. 6 tabs/day
Tylenol # 3 Codeine 30 mg APAP 300 mg 1-2 q 4 hrs.
Max. 13 tabs/day
Norco Hydrocodone 10
mg
APAP 325 mg 1-2 q 4 hrs.
Max. 12 tabs/day
Percocet Oxycodone 5 mg APAP 325 mg 1-2 q 4 hrs.
Max. 12 tabs/day
Tylox 5/500 Oxycodone 5 mg APAP 500 mg 1-2 q 4-6 hrs.
Max. 8 tabs/day
Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
MoA: Cox-3 inhibter of PG in the CNS & peripheral pain impulse
Pain indication: Use alone for mild pain
Do not exceed 4 gms / day
Lorcet 6 tabs/day= 60 mgs morphine
Lortab- 8 tabs / day=40 mgs morphine
Adverse effects:
-Lightheadedness, dizziness, hepatotoxicity
with high doses & chronic use
NSAIDS
Indications: anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, analgesic
Acetylsalicylic acid ( ASA ) irreversibly inhibits platelet
Side effects: Reversible antiplatelet effect, minimal
w/ non-acetylated salicylates ( eg Disalcid, Dolobid )
- GI ulceration, less w ibuprofen, etodolac, salsalate,
nabumentone
- Nephrotoxity caution in CHF, dehydratation, elderly
- Hepatotoxicity: caution in elderly & alcoholics
- Avoid in asthmatics & nasal polyps
Mechanism of Action
Phospholipids, released from cell membrane are cenverted
to Arachidonic acid by phospholipase A2
Arachidonic acid is acted by lipo-oxygenase to be converted
to Leukotrienes
Cyclo-oxygenase acts on Arachidonic acid to form
Prostaglandin endoperoxides which are converted to
Prostaglandin G & by isomerase into Prostaglandin E2,
Prostaglandin D2, & F2 alpha
Prostaglandin H is formed from prostaglandin endoperoxides
& converted by Thromboxane to Thromboxane A2 &
Thromboxane B2.
Prostacyclin synthetase converts prostaglandin
endoperoxides to Prostacyclin ( PGI )
Co-analgesic Pain Medications
Antiepileptics
Antidepressants
Muscle Relaxants
Anesthetics
Corticosteroids
Psychostimulants
Substance P
inhibitors
Alpha-2 agonists
Neuroleptics
Antiarryhmics
Benzodiazepines
Antiepileptics
MOA: Block Na+ & Ca+ channels>>inhibits release of
glutamate>> stabilizes neural memb.
Uses: Trigeminal neuralgia, peripheral neuropathies,
herpetic neuralgia, phantom limb pain, migraines.
Aniepileptics: Gabapentin, Carbamazepines,
topiramate, phenytoin, oxycarbamazepine, pregabalin
Comared to TCAs:
-equally efficacious in painful DN
-some AED may be more expensive
- differences in safty profile
- synergy with AED plus TCA
Gabapentin (Neurontin)
MOA: a 2-delta ca+ channel subunit modulator
Uses: Peripheral neuropathic pain, phantom limb pain,
CRPS, post herptic & trigeminal neuralgia.
Doses: adjust for elderly & renal failure
-range 300- 3600 mg /day divided in 3-4 doses
Somnolance, dizziness, constipation, fatigue,
peripheral edema, difficulty concentrating
Pregabalin (Lyrica)
MoA: a 2 delta Ca+ channel subunit modulator
Pain uses: Diabetic & post herpetic neuropathic pain
at doses 300-600 mgs/day divided 2-3 X.
Other neuropathic pain conditions, fibromyalgia,
generalized anxiety disorder.
Compared to gabapentin:
- Bioavailability remains 90% at all doses
- Time to effective dose (150-300mg/day) is 1-3days
- Class v schedules drug.
Carbamazepine ( Tegretol)
MoA: Na+ & Ca+ channel blockade
Pain uses: trigeminal neuralgia, glossopharyngeal neuralgia, DPN
Dosing: 200-1000mg divided 2-3X (with food)
Side effects: N & V, dizziness, sedation, transient leukopenia, hepatic
toxicity, thrombocytopenia, diplopia, hyponatremia, rash, Steven-
Johnsons syndrome.
Tricyclic antidepressants
MoA: inhibits re-uptake of NE, SE,
antihistamine
Pain indications: Painful neuropathies,
Phantom limb pain, migraine prevention
Dose: start low & adjust every 2- 3 days
Drug interactions
- caution with other
anticholinergics/serotonergics
- CYP2D6 substrate ( all TCAs)
- CYP3A4 substrate ( Elavil )
Choice of A TCA
Amitriptyline ( Elavil)
- most widely studied
- more side effects- hang over effect.
Doxepin ( Sinequan )
- similar to Elavil, but shorter duration of sedation
Desipramine ( Norpramin ), Nortriptyline ( Pamelor)
- may cause insomnia
- less anticholinergic effect
- Desipramine may cause orthostatic hypotension
TCA Side Effects
Side effects
Blurred vision
Cognitine changes
Constipation
Dry mouth
Orthostatic hypotention
Sexual dysfunction
Tachcardia
Urinary retention
Desipramine
Nortriptyline
Doxapin
Amitriptyline
Duloxetine ( Cymbalta )
MoA : Dual reuptake inhibitor ( NE & SE )
Indications : Neuropathic pain, depression
Dosage : 30 mgs PO qd to 60 mgs PO bid
Side effects : nausea, dry mouth, constipation
decreased appetite, dizziness, insomnia
Drug interaction : CYPIA2 & 2D6 substrate
SSRIs , quinidine, cimetidine, quinolenes, may
increase duloxitine levels.
- mod. Inhibitor of CYP2D6 increases TCAs,
phenothiazine, type 1C antiarrythmias
Muscle Relaxants
Heterogenous group of medications:
- Spasticity from upper motor neuron syndrome
- Muscular pain & / or spasm from peripheral musculoskeletal condition.
- Dose : may dose 6-8 hrs ATC or give more hs if daytime drowsiness does not
resolve ( e.g. Flexaril 10-30 mg po qhs )
Side effects:Drowsiness,dizziness,blurred vision
Drug interaction: Other CNS depressants
Muscle Relaxants
Spasticity:
- Baclofen ( Lioresal )
- Tizanidine ( Zanaflex)
- Dantrolene ( Dantrium )
- Diazepam ( Valium )
Muscular pain & spasm
- Methcarbamol (Robaxin)
- Cylobenzaprine(Flexaril)
- Carisoprodal ( Soma )
- Baclofen ( Lioresal )
- Tizanidine ( Zanaflex )
Muscle Relaxants
Spasticity:
- Baclofen ( Lioresal )
- Tizanidine ( Zanaflex)
- Dantrolene ( Dantrium )
- Diazepam ( Valium )
Muscular pain & spasm
- Methcarbamol (Robaxin)
- Cylobenzaprine(Flexaril)
- Carisoprodal ( Soma )
- Baclofen ( Lioresal )
- Tizanidine ( Zanaflex )
Baclofen ( Lioresal )
Baclofen ( Lioresal ) gaba b agonist
Indications : Neuropathic pain, spasticity
Side effects : less sedating, ms weakness
With drawl syndrome: spasticity, hallucination,
anxiety,seizure when doses 80 mgs/ day or intrathecal
baclofen are stopped abruptly
Flexeril ( Cyclobenzaprine )
Indications : muscle spasms, neuropathic pain
Side effects : CNS & anticholinergic effect
Drug interactions : w/TCAs additive anticholinergic side
effects, CYPIA2 substrate
Systemic / Topical anesth.
Lidocaine 5% patch apply to intact skin at most
painful site, 1- 3 patches for 12 hrs
Indications : Post-herpetic neuralgia, post
thoracotomy, mastectomy, pain syndrome.
Side effects : site irritation, dizziness, arrythmias
Lidocaine cream 5% apply to affected area 3-4 X /
day for short term use.
Mexileteine 150 mg po bid adjust q 2-3 days upto
400 mgs / day
- Indications : resistant neuropathic pain
- Side effects : dizziness, tremor, GI upset, arrythmias
Tramadol ( Ultram )
MoA : mu opioid receptors, NE & SE reuptake inhibitors
Mixed mild to moderate pain
Side effects: dizziness, nausea, constipation, somnolence, sweating,
pruritus, sz, serotonergic syndrome
Maximum dose: 400 mg / day
10-20% pt. lack CYP2D6 needed to form MI ( metabolite ) impact or
efficacy & safety
Dose conversion: 50 mg = codeine 30 mg.
Botulinum Toxin A ( Botox )
MoA : direct antinociceptive effects, prolonged ms relaxation by inhibition of
acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction
Indications : Blephrospasm, facial wrinkles, ms spasm
Duration of effect : 3 4 months
Side effects:
Opioids
MoA : agonist on mu, kappa, & delta receptors
Methadone: also NMDA receptor antagonist & NE/SE reuptake inhibitor
Indications: Acute & ch Moderate to severe pain
For most type of pain with limited use in
- Neuropathic pain
- Spinal cord compression
- Bone pain
JEPITAN NERVUS ULNARIS PADA SENDI SIKU
Disebut juga Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
Karena tekanan pd bagian belakang epikondilus medial
Tersering kedua setelah carpal tunnel syndrome
Etiologi
Valgus sendi siku
Fraktur kondilus lateral humeri
Traksi yg berulang
Osteoartritis
osteofit
Gambaran klinis
Rasa tebal dan nyeri pd distribusi n. ulnaris
Gangguan gerakan halus pd jari
Hilangnya persarafan sensoris
Atrofi dan kelemahan otot yg dipersarafi
Kulit yg dipersarafi menjadi kering
Tinels sign positif
Paralisis/tardy paralisis (lanjut)
Atrofi m. interossea dorsalis
Tinels sign
Kelemahan otot
Pengobatan
Operatif dg pembebasan atau tranposisi n. ulnaris
Transposisi n. ulnaris
Transposisi n. ulnaris
JEPITAN NERVUS ULNARIS PD CABANG
PALMAR BAGIAN PROKSIMAL
Nama lain Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome
Jepitan pd Guyons canal yg dibentuk :
- os hamatum
- os pisiformis
- lig pisohamatum
Banyak pd laki-laki umur 40 thn
Guyons canal
Etiologi
Adanya riwayat trauma tangan
Biasanya ditemukan adanya ganglion/lipoma
Aneurisma
Hipertrofi m. palmaris brevis
Lipoma
Gambaran klinis
Kelemahan otot hipotenar
Atrofi otot hipotenar
Gangguan sensoris pd 1 mdial jari tangan
Area sensoris n. ulnaris
pd volar
Area sensoris
n. ulnaris pd
dorsum manus
Area persarafan n. ulnaris
Diagnosis
Gambaran klinis
EMG (electromyografi)
EMG
Pengobatan
Konservatif
- imobilisasi
- menghindarkan dari trauma
Operatif untuk dekompresi
Dekompressi pd Guyons canal
What is the name of our galaxy?
How many planets in the solar system have
rings?
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune all
have rings.
What is inertia?
All of the above
The speed at which an object falls
Measurement of electrical resistance
A ratio between mass and velocity
Resistance to motion or change
Match the device to what it measures:
Stop Watch
Scale
Thermometer
Speedometer
Odometer
Distance
Temperature
Elapsed Time
Weight
Rate of Travel
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Pembedahan Skoliosis Lengkap Buku Panduan bagi Para Pasien: Melihat Secara Mendalam dan Tak Memihak ke dalam Apa yang Diharapkan Sebelum dan Selama Pembedahan SkoliosisDari EverandPembedahan Skoliosis Lengkap Buku Panduan bagi Para Pasien: Melihat Secara Mendalam dan Tak Memihak ke dalam Apa yang Diharapkan Sebelum dan Selama Pembedahan SkoliosisPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (13)
- Jurnal Perawatan Skoliosis Natural Anda: Petunjuk per hari selama 12 minggu untuk tulang belakang yang lebih lurus dan kuat!Dari EverandJurnal Perawatan Skoliosis Natural Anda: Petunjuk per hari selama 12 minggu untuk tulang belakang yang lebih lurus dan kuat!Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (7)
- Referat HNPDokumen31 halamanReferat HNPRezkina Azizah PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Referat HNPDokumen15 halamanReferat HNPStreet Fhigteer AgitatorBelum ada peringkat
- HNPDokumen34 halamanHNPChanvira Aria Candrayana100% (2)
- Bab 8 Gangguan Degeneratif MuskuloskeletalDokumen78 halamanBab 8 Gangguan Degeneratif MuskuloskeletalSam WitwickyBelum ada peringkat
- Modul Saraf Tepi 2 KhansaDokumen26 halamanModul Saraf Tepi 2 KhansaKhansa SalsabilaBelum ada peringkat
- Referat BronkiolitisDokumen13 halamanReferat BronkiolitisSabrinaQurrotaayun0% (1)
- ISCIALGIADokumen19 halamanISCIALGIAAsma FiraniBelum ada peringkat
- Hernia Nukleus PulposusDokumen28 halamanHernia Nukleus PulposusTiara GussyofnitriaBelum ada peringkat
- Power Point Referat HNPDokumen22 halamanPower Point Referat HNPwindyani hardiBelum ada peringkat
- LaporanIndividu Modul 2Dokumen26 halamanLaporanIndividu Modul 2Dewi SartikaBelum ada peringkat
- LBPDokumen20 halamanLBPAdi Saputra IIBelum ada peringkat
- Hernia Nucleus PulposusDokumen26 halamanHernia Nucleus Pulposusjesika ita niomiBelum ada peringkat
- LBPDokumen20 halamanLBPAdi Saputra IIBelum ada peringkat
- Persentasi Jurnal - KMBDokumen37 halamanPersentasi Jurnal - KMBimmanuelBelum ada peringkat
- Hernia Nukleus Pulposus (HNP)Dokumen18 halamanHernia Nukleus Pulposus (HNP)Yukimura SanadaBelum ada peringkat
- Dr. Ken Wirastuti, M Kes, SP.S, KIC Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Saraf FK. UnissulaDokumen49 halamanDr. Ken Wirastuti, M Kes, SP.S, KIC Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Saraf FK. UnissulaRidhaBelum ada peringkat
- Hernia Nukleus Pulposus: Oleh: Fithri Wulandhani Pembimbing: Dr. Novi Irawan, SP.SDokumen23 halamanHernia Nukleus Pulposus: Oleh: Fithri Wulandhani Pembimbing: Dr. Novi Irawan, SP.SHeinz CpBelum ada peringkat
- HNP YantiDokumen33 halamanHNP YantiAnonymous hKqoqrJCSrBelum ada peringkat
- Lapkas Iki HNPDokumen33 halamanLapkas Iki HNPMisrul Rahmi UtamiBelum ada peringkat
- Tentiran LBP CODDokumen60 halamanTentiran LBP COD6130020068 NOVANTHY NUR ROHMADHANI SUBAGYOBelum ada peringkat
- HNPDokumen23 halamanHNPRayza Swan ABelum ada peringkat
- Kelompok 13 - RPS10 - Tugas Kelompok Patofisiologi MuskuloskeletalDokumen25 halamanKelompok 13 - RPS10 - Tugas Kelompok Patofisiologi MuskuloskeletalAz Zahra FitrianiBelum ada peringkat
- LBP E.C HNPDokumen23 halamanLBP E.C HNPErviani MaulidyaBelum ada peringkat
- Spondilosis, HNP CervicalDokumen33 halamanSpondilosis, HNP CervicalFaishol Reza AdiyaksaBelum ada peringkat
- Hernia Nucleus Pulposus TPDokumen38 halamanHernia Nucleus Pulposus TPEster Kapaiter BakujayBelum ada peringkat
- Askep Low Back PainDokumen13 halamanAskep Low Back PainHilda RahmatikaBelum ada peringkat
- Hernia Nukleus PulposusDokumen13 halamanHernia Nukleus Pulposus譚惠玲Belum ada peringkat
- HNPDokumen29 halamanHNPRaras MayangBelum ada peringkat
- HNP PresentasiDokumen24 halamanHNP PresentasiNimas Ajeng100% (1)
- ASKEP Low Back PainDokumen7 halamanASKEP Low Back PainFatika Berliantari CQBelum ada peringkat
- Referat HNPDokumen31 halamanReferat HNPMarcella KarauwanBelum ada peringkat
- Low Back Pain PermadiDokumen59 halamanLow Back Pain PermadiDhewie NaraliaBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 2 HNPDokumen7 halamanBab 2 HNPwiwik rahayuBelum ada peringkat
- Gambaran Penderita Hernia Nukleus PulposusDokumen50 halamanGambaran Penderita Hernia Nukleus Pulposusglenn poddalahBelum ada peringkat
- HNP BedahDokumen25 halamanHNP Bedahstephanigualagetzsa0Belum ada peringkat
- Hernia Nukleus PulposusDokumen20 halamanHernia Nukleus PulposusWahyu Sholekhuddin0% (1)
- Januari 2020 Laminectomy - En.idDokumen39 halamanJanuari 2020 Laminectomy - En.idMaulida HusnaBelum ada peringkat
- Askep HNPDokumen31 halamanAskep HNPsiska misaliBelum ada peringkat
- Spinal StenosisDokumen23 halamanSpinal StenosisBimantara Cakra AditamaBelum ada peringkat
- Fisioterapi Pada Cervical Disc HerniaDokumen25 halamanFisioterapi Pada Cervical Disc HerniaWijaya Krisna I NyomanBelum ada peringkat
- Low Back Pain-Rehab MedisDokumen45 halamanLow Back Pain-Rehab MedisAnnisa Febrieza ZulkarnaenBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah ISCHIALGIADokumen101 halamanMakalah ISCHIALGIAwisnu mayBelum ada peringkat
- Bagaimana Anatomi Dari NN - Spinales? (Tambahkan Gambar), Nucleus?Dokumen11 halamanBagaimana Anatomi Dari NN - Spinales? (Tambahkan Gambar), Nucleus?Tiahalimatusadiah 19Belum ada peringkat
- SpondilosisDokumen32 halamanSpondilosisiweBelum ada peringkat
- Hip DysplasiaDokumen26 halamanHip DysplasiaAndri SaputraBelum ada peringkat
- Askep Sakit PinggangDokumen11 halamanAskep Sakit PinggangSilaturrahman IkhlasjaBelum ada peringkat
- Askep LBPDokumen7 halamanAskep LBPHarry WibowoBelum ada peringkat
- Patologi CRSDokumen83 halamanPatologi CRSWijaya Krisna I NyomanBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Pendahuluan Nyeri Punggung BawahDokumen21 halamanLaporan Pendahuluan Nyeri Punggung Bawahsri mayuniBelum ada peringkat
- Nyeri Pinggang DenganDokumen22 halamanNyeri Pinggang Denganayam kecapBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Pendahuluan: Low Back Pain (LBP)Dokumen11 halamanLaporan Pendahuluan: Low Back Pain (LBP)Tuti alawiyah OktavianaBelum ada peringkat
- Hernia Diskus IntervertebralisDokumen11 halamanHernia Diskus IntervertebralisMaeBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah HNPDokumen25 halamanMakalah HNPArmando ReyaanBelum ada peringkat
- Referat Rehab - Joana PosumahDokumen36 halamanReferat Rehab - Joana PosumahJoana MariaBelum ada peringkat
- Ischial GiaDokumen40 halamanIschial GiaSilvia SafitriBelum ada peringkat
- Referat Radio HNPDokumen28 halamanReferat Radio HNPTeguh SetiadiBelum ada peringkat
- MyalgiaDokumen13 halamanMyalgiaditanovrianaBelum ada peringkat
- Dikamon PPT THTDokumen61 halamanDikamon PPT THTSabrinaQurrotaayunBelum ada peringkat
- TUGASDokumen11 halamanTUGASSabrinaQurrotaayunBelum ada peringkat
- Anomali RefraksiDokumen26 halamanAnomali RefraksiSabrinaQurrotaayunBelum ada peringkat