Makalah Smps
Diunggah oleh
Telekomunikasi Engineering PNJMakalah Smps
Diunggah oleh
Telekomunikasi Engineering PNJCommon questions
Didukung oleh AIThe boost converter in an SMPS serves as a power factor correction (PFC) unit. It increases the output voltage from a lower DC input voltage to a higher DC output voltage. The boost converter works in a discontinuous mode, which prevents the reverse recovery current in diodes, allowing for the use of cheaper diodes. It also reduces I2R losses and minimizes ripple current in the inductor core, lowering core losses . This design not only aids in efficiency but also allows for cheaper construction without compromising performance .
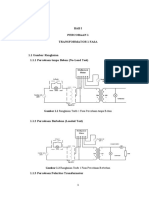
Employing a buck converter alongside a boost converter in an SMPS design offers the flexibility to efficiently handle a wide range of output voltage requirements. The boost converter elevates the voltage to a desired level, which is then precisely stepped down by the buck converter to match the specific voltage and power requirements of the load . This dual converter approach enhances the SMPS's efficiency and adaptability, allowing for optimized performance across varying loads and input conditions, while also simplifying the power management for devices that require multiple voltage outputs .
Operating the boost converter in a discontinuous mode within an SMPS is beneficial because it eliminates reverse recovery current (IRR) in diodes, allowing the use of less expensive diodes while also reducing I2R losses and ripple in the inductor . These factors contribute to reduced losses and lower electromagnetic interference, leading to improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, it simplifies the design and reduces thermal stress on components, enhancing the longevity and reliability of the SMPS .
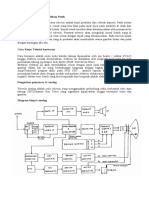
In an SMPS, the rectification process converts AC input voltage into DC voltage using a diode bridge and filtering capacitors. The filtered DC voltage is then switched at high frequencies to produce AC signals that pass through a transformer for voltage adjustment . This step is essential as it facilitates the initial conversion from AC to DC, enabling the SMPS to supply stable and regulated DC output required for electronic devices . The process is crucial as it preconditions the voltage for subsequent stages of switching and transformation .
The feedback loop in an SMPS plays a critical role in ensuring that the output voltage remains stable despite variations in input voltage or load conditions. It involves a feedback circuit that detects any deviation in the output voltage and generates a control signal for the pulse width modulation (PWM) circuit . This control signal adjusts the duty cycle of the PWM, thereby modulating the on-off times of the power switches to bring the output voltage back to its set reference level . Through real-time adjustments, the feedback loop maintains consistent output power, enhancing the overall performance reliability of the SMPS .
The integration of low loss components, such as capacitors, inductors, and transformers, significantly enhances the performance and efficiency of an SMPS by minimizing power dissipation. These components exhibit lower resistive losses (I2R losses), which increases the efficiency of power conversion, allowing the SMPS to achieve efficiency ratings as high as 91% . By reducing wasted energy, the SMPS offers higher output power relative to input power, making it more effective in applications requiring reliable power delivery in a compact form factor .
SMPS ensures safety and reliability through several methods. It includes isolation of the secondary from the primary side to prevent electrical shock from the chassis . Additionally, SMPS uses protective measures such as over-voltage protection to safeguard equipment from output voltage spikes, and feedback control to maintain stable output voltage despite input or load variations . Furthermore, error detection mechanisms are equipped with comparator circuits for real-time voltage adjustments . These features collectively enhance the SMPS’s reliability and safety in electronic applications .
The primary challenges addressed by the isolation technique in SMPS design include preventing electric shock and promoting safety by ensuring that the secondary side's chassis remains safe to touch. Isolation is achieved by using transformers or opto-couplers to separate the electrical continuity between the primary and secondary circuits . This separation prevents high-voltage input from affecting the low-voltage output and minimizes the risk of electrical faults propagating across the system. This technique is critical for user safety and for protecting sensitive circuits connected to the SMPS .
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) in an SMPS is crucial for controlling the switch mode operation of the power supply. It generates pulse signals that control the on-and-off states of the power switches within the SMPS circuit . By modulating the pulse width, PWM adjusts the energy transferred to the output, hence controlling the output voltage levels. This modulation is key for the efficient functioning and stabilization of the SMPS output .
The primary benefits of using a Switch-Mode Power Supply (SMPS) include high efficiency and minimal power leakage. SMPS utilizes low-loss components like capacitors, inductors, and transformers, and employs switches that are always on or off to maximize power conversion efficiency, reaching up to 91% . This efficiency means that the output power can be a significant portion of the input power, minimizing wasted energy, making them suitable for various electronic devices such as VCD players, TVs, and mobile phones .