Session 02 - Physical & Thermal Properties
Diunggah oleh
Harid Luthfi Pratama0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
82 tayangan20 halamanA
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniA
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
82 tayangan20 halamanSession 02 - Physical & Thermal Properties
Diunggah oleh
Harid Luthfi PratamaA
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 20
SIFAT FISIK PLASTIK
Untuk mengukur perilaku proses dari plastik:
perlu mengetahui sifat rheologi plastik
(sifat kemampuan dideformasi dan
mengalir)
SIFAT FISIK PLASTIK:
Densitas (berat jenis)
Thermal expansion
Thermal conductivity
Specific heat capacity
Sifat alir/rheology
DENSITAS
Plastik memiliki low density (0.9 2.3 g/cm3
Polyethylene (PE) dan Polypropylene (PP)
lowest density plastics (< 1)
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) 2 g/cm3
Fiber-reinforced plastics 2.3 g/cm3
Foam 0.01 g/cm3
THERMAL EXPANSION
Plastik memiliki coefficient of thermal
expansion lebih besar dari material lain
PE & PP (200.10-6 K-1)
Besi (12.10-6 K-1)
Aluminium (24.10-6 K-1)
Untuk mengurangi koefisien thermal
plastik dengan menambahkan filler ke
dalam plastik
THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY
Plastik memiliki very low coefficient of
thermal & electrical conductivity
insulator/isolator
Thermal conductivity dari plastik : 300-
1000 lebih rendah dari logam
Untuk pure resin, thermal conductivity
0.15-1.5 W/mK
SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY
Specific heat capacity dari plastik: 0.4
2.7 kJ/kg K
Alat ukur specific heat capacity DSC
(differential scanning calorimetry),
perilaku melting dan crystallization dari
plastik
Informasi yang diperoleh dari DSC :
Melting temperature (Tm)
Crystallization temperature (Tc)
degree of crystallinity (XC)
SKEMA UJI DSC
DATA DSC
SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY
Contoh data DSC dari nanokomposit yang
terdiri dari matrik 70% Polyamide 6
(PA6), 30% Polypropylene (PP), + clay
Informasi yang diperoleh dari DSC :
Melting temperature (Tm)
Crystallization temperature (Tc)
degree of crystallinity (XC)
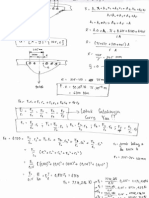
DEGREE OF CRYSTALLINITY (XC)
Di mana :
Hf (PP) : fusion enthalpy dari komponen PP
Hf0 (PP): fusion enthalpy dari PP dengan 100% crystallines = 209.2 J/g
Hf (PA6) : fusion enthalpy dari komponen PA6
Hf0 (PA6): fusion enthalpy dari PA6 dengan 100% crystallines = 190.8 J/g
wPP and wPA6 are the weight fractions of PP and PA6
DSC HEATING SCANS OF PA6/PP/CLAY NANOCOMPOSITES
DSC COOLING SCANS OF PA6/PP/CLAY NANOCOMPOSITES
DEGREE OF CRYSTALLINITY OF PA6/PP/CLAY NANOCOMPOSITES
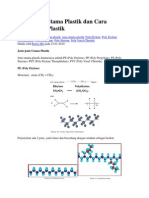
POLYMER CRYSTALLINITY
POLYMER CRYSTALLINITY
PEMBEKUAN TERMOPLASTIK SEMI-CRYSTALLINE
Ketika pembekuan
Spherulitic yang terdiri dari
crystalline dan amorphous
regions tumbuh di sekitar
inti kristalisasi
Kristalisasi terdiri 3 tahap:
Nucletion
SPHERULITIC
Crystal growth (primary
crystallization
Recrystallization (secondary
crystallization)
SIFAT ALIR PLASTIK
Plastik bersifat viscoelastic (viscous =
kental) + elastic
Teknologi yang mengukur perilaku alir
dari plastik RHEOMETRY
Alat ukur untuk mengukur sifat alir plastik
viscometer, rheometers, dan melt flow
indexer
SIFAT ALIR PLASTIK
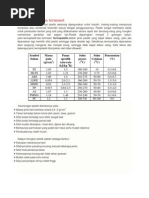
Shrinkage
Reduction in linear size during cooling from
molding to room temperature
Polymers have high thermal expansion coefficients, so
significant shrinkage occurs during cooling in mold
Typical shrinkage values for selected polymers:
Plastic Shrinkage, mm/mm (in/in)
Nylon-6,6 0.020
Polyethylene 0.025
Polystyrene 0.004
PVC 0.005
Compensation for Shrinkage
Dimensions of mold cavity must be larger
than specified part dimensions:
Dc = Dp + DpS + DpS2
where Dc = dimension of cavity;
Dp = molded part dimension, and
S = shrinkage value
Shrinkage Compensation Factors
Fillers in the plastic tend to reduce shrinkage
Injection pressure as pressure is increased, it forces
more material into the mold cavity, and shrinkage is
reduced
Compaction time - similar effect - forces more material
into cavity during shrinkage
Molding temperature - higher temperature lowers the
polymer melt viscosity, allowing more material to be
packed into mold and reducing shrinkage
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 2Dokumen19 halaman2angel vandelanBelum ada peringkat
- Sifat Karakteristik Material Plastik PDFDokumen9 halamanSifat Karakteristik Material Plastik PDFArifBelum ada peringkat
- Sifat Dan Karakteristik Material Plastik Dan Bahan Aditif-With-Cover-Page-V2Dokumen10 halamanSifat Dan Karakteristik Material Plastik Dan Bahan Aditif-With-Cover-Page-V2Febri Muhamad RoziBelum ada peringkat
- Polimer 5Dokumen55 halamanPolimer 5Muhammad Afnan MBelum ada peringkat
- ThermoplastDokumen13 halamanThermoplastpiyust titaBelum ada peringkat
- Pelapisan PlastikDokumen9 halamanPelapisan PlastikMarshel DanielBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan PlastikDokumen19 halamanLaporan PlastikAgathaPutri0% (1)
- Uji Kinerja Rancangan Alat Pirolisis Pengolahan Sampah PlastikDokumen36 halamanUji Kinerja Rancangan Alat Pirolisis Pengolahan Sampah PlastikAfrina NuratikaBelum ada peringkat
- Muhammad Nur Achmad Shandy - Laporan Kuliah Lapangan InstrumentasiDokumen11 halamanMuhammad Nur Achmad Shandy - Laporan Kuliah Lapangan InstrumentasiachmadBelum ada peringkat
- Ilmu Bahan Bab Vii - PolimerDokumen25 halamanIlmu Bahan Bab Vii - PolimerFany Dwi KristantiBelum ada peringkat
- Termoplastik Dan TermosetDokumen6 halamanTermoplastik Dan Termosetseptiani wulandariBelum ada peringkat
- Sifat Dan Karakteristik Material Plastik Dan BahanDokumen8 halamanSifat Dan Karakteristik Material Plastik Dan BahanDicky SepriantoBelum ada peringkat
- Muhammad Nur Achmad Shandy - Laporan Kuliah Lapangan InstrumentasiDokumen11 halamanMuhammad Nur Achmad Shandy - Laporan Kuliah Lapangan InstrumentasiachmadBelum ada peringkat
- Artikel KIMIA (PLASTIK)Dokumen5 halamanArtikel KIMIA (PLASTIK)Nisa Alaicia Rachmanda0% (1)
- Kel 1 - Rita Purnamasari - 444418002 - Laporan 2 TPPDokumen13 halamanKel 1 - Rita Purnamasari - 444418002 - Laporan 2 TPPRian SopianBelum ada peringkat
- Otomatisasi Pengolahan Sampah PlastikDokumen35 halamanOtomatisasi Pengolahan Sampah PlastikJamatul FirdausBelum ada peringkat
- Rizka Riani & Berliana Sitompul PPT TermoplastikDokumen23 halamanRizka Riani & Berliana Sitompul PPT Termoplastikrizka rianiBelum ada peringkat
- TekberDokumen10 halamanTekberWahyudiBelum ada peringkat
- Plastik Anni N AlbaDokumen11 halamanPlastik Anni N Albaizzonk1773Belum ada peringkat
- Jenis Jenis PlastikDokumen21 halamanJenis Jenis PlastikYaritsu ZyBelum ada peringkat
- Ciri Termoplastik Dan TermosetDokumen10 halamanCiri Termoplastik Dan TermosetStephanieRawi100% (2)
- Tugas Material PolimerDokumen51 halamanTugas Material PolimerMukhlisah YunusBelum ada peringkat
- Modul 3Dokumen4 halamanModul 3Afifah SBelum ada peringkat
- ThermoformingDokumen27 halamanThermoformingherfianaemaBelum ada peringkat
- ID NoneDokumen8 halamanID NoneAdam CrystalpasBelum ada peringkat
- Print PetroDokumen8 halamanPrint Petroerdila putriBelum ada peringkat
- Pom - PBT Indonesia (PP)Dokumen32 halamanPom - PBT Indonesia (PP)Rizqy Fadry LazimBelum ada peringkat
- PlastikDokumen3 halamanPlastikMaudy FaradilaBelum ada peringkat
- Print Percobaan 2Dokumen7 halamanPrint Percobaan 2Zahratul HasanahBelum ada peringkat
- KUIS Ilmu Bahan Dan KorosiDokumen7 halamanKUIS Ilmu Bahan Dan KorosiDani SetiawanBelum ada peringkat
- Plastik NiDokumen32 halamanPlastik NiAdit Fernando IIBelum ada peringkat
- Proses Manufaktur Material Dan Karakterisasi Polimer ThermoplastikDokumen4 halamanProses Manufaktur Material Dan Karakterisasi Polimer ThermoplastikFerdiansyah Iqbal Rafandi0% (1)
- Pemanfaatan Limbah Ban Bekas Sebagai Bahan Bakar Altenatif Dengan Metode PirolisisDokumen6 halamanPemanfaatan Limbah Ban Bekas Sebagai Bahan Bakar Altenatif Dengan Metode PirolisisIZAZ RAMADHAN NUR ARKHANBelum ada peringkat
- 12 - I Komang Gede Tryas Agameru PutraDokumen33 halaman12 - I Komang Gede Tryas Agameru PutrahanifBelum ada peringkat
- PolymerDokumen66 halamanPolymerMagdalena SinagaBelum ada peringkat
- Termoplastik MakalahDokumen16 halamanTermoplastik MakalahIlma Nurulita QolbiBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Paparan Campuran Beraspal Menggunakan Limbah Plastik - PKPTDokumen47 halaman1 Paparan Campuran Beraspal Menggunakan Limbah Plastik - PKPTr_massora5485Belum ada peringkat
- Kimia Polimer IIDokumen19 halamanKimia Polimer IIMuhammad FarhanBelum ada peringkat
- Bhan Korosi PlastikDokumen15 halamanBhan Korosi PlastikMuhammad AzzamBelum ada peringkat
- Electroplating PlasticDokumen5 halamanElectroplating PlastickatastropBelum ada peringkat
- Kekuatan ImpakDokumen5 halamanKekuatan ImpakPrayogo Marley100% (2)
- Termoplastik Dan TermosetDokumen10 halamanTermoplastik Dan TermosetWawanW36Belum ada peringkat
- Transition Glass TemperatureDokumen23 halamanTransition Glass TemperatureGeraldi CoolBelum ada peringkat
- Modul Pertemuan 14-Pemrosesan PlastikDokumen13 halamanModul Pertemuan 14-Pemrosesan PlastikReza KamaludinBelum ada peringkat
- Ilmu Bahan 2Dokumen147 halamanIlmu Bahan 2Bernadus PranataBelum ada peringkat
- Rizka Riani & Berliana Sitompul Makalah TermoplastikDokumen20 halamanRizka Riani & Berliana Sitompul Makalah Termoplastikrizka rianiBelum ada peringkat
- Local Wisdom Inspiring Global SolutionDokumen11 halamanLocal Wisdom Inspiring Global SolutionHarid Luthfi PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Kisi2 Kisi2 MIKDokumen14 halamanKisi2 Kisi2 MIKHarid Luthfi PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem Otomasi Isian BakpiaDokumen10 halamanSistem Otomasi Isian BakpiaHarid Luthfi PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Termodinamika Cengel Sistem TerbukaDokumen16 halamanTermodinamika Cengel Sistem TerbukaHarid Luthfi PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Peran Ilmu Kimia Dalam Bidang EnergiDokumen4 halamanPeran Ilmu Kimia Dalam Bidang EnergiHarid Luthfi Pratama0% (1)
- PR Matematika Teknik 2Dokumen1 halamanPR Matematika Teknik 2Harid Luthfi PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Implan Gigi BiomaterialDokumen3 halamanImplan Gigi BiomaterialHarid Luthfi PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Sejarah Super Semar Dan Orde BaruDokumen4 halamanSejarah Super Semar Dan Orde BaruHarid Luthfi PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Persamaan Bessel IDokumen5 halamanPersamaan Bessel IArko Alfathar TumanggorBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Kartu Ucapan Aqiqah Berwarna Versi Ms WordDokumen1 halamanContoh Kartu Ucapan Aqiqah Berwarna Versi Ms WordTijarBelum ada peringkat
- Memanfaatkan Waktu Dengan BaikDokumen1 halamanMemanfaatkan Waktu Dengan BaikHarid Luthfi PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Rangkuman Materi PKN Kelas XiiDokumen4 halamanRangkuman Materi PKN Kelas XiiHarid Luthfi PratamaBelum ada peringkat