0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
233 tayangan17 halamanCatatan Muskuloskeletal
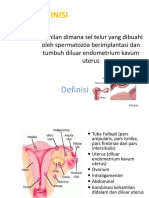
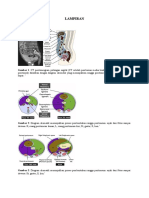
Dokumen tersebut membahas tentang anatomi sistem muskuloskeletal, yang mencakup pertumbuhan dan perkembangan tulang, jaringan tulang, proses pembentukan tulang, trauma seperti fraktur dan dislokasi, evaluasi radiologi fraktur, komplikasi fraktur, dan osteokondrosis. "
Diunggah oleh
rifalHak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Kami menangani hak cipta konten dengan serius. Jika Anda merasa konten ini milik Anda, ajukan klaim di sini.
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online di Scribd
0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
233 tayangan17 halamanCatatan Muskuloskeletal
Dokumen tersebut membahas tentang anatomi sistem muskuloskeletal, yang mencakup pertumbuhan dan perkembangan tulang, jaringan tulang, proses pembentukan tulang, trauma seperti fraktur dan dislokasi, evaluasi radiologi fraktur, komplikasi fraktur, dan osteokondrosis. "
Diunggah oleh
rifalHak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Kami menangani hak cipta konten dengan serius. Jika Anda merasa konten ini milik Anda, ajukan klaim di sini.
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online di Scribd