Nota Bab 2 PDF
Nota Bab 2 PDF
Diunggah oleh
lalisaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Nota Bab 2 PDF
Nota Bab 2 PDF
Diunggah oleh
lalisaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Sains Tingkatan 3
Nota Bab 2
Bab 2 Respirasi
2.1 Sistem Respirasi 4. Kandungan oksigen dalam udara sedutan adalah lebih
tinggi berbanding dalam udara hembusan.
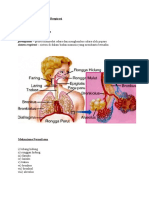
1. Struktur sistem respirasi manusia:
5. Kandungan karbon dioksida dalam udara sedutan adalah
lebih rendah berbanding dalam udara hembusan.
Bronkus Rongga nasal
2.2 Pergerakan dan Pertukaran Gas dalam
Bronkiol Trakea
Badan Manusia
Alveolus
Otot interkosta 1. Oksigen diangkut ke sel-sel oleh sel darah merah dalam
Bronkus bentuk oksihemoglobin.
Kapilari Tulang rusuk
Bronkiol 2. Darah yang mengandungi oksihemoglobin kemudian
Peparu kiri diangkut ke jantung untuk diagihkan ke seluruh sel badan.
Diafragma
3. Pada masa yang sama, karbon dioksida diserap dari
dalam sel ke kapilari darah dan seterusnya ke alveolus.
2. Laluan oksigen ketika menarik nafas: Pergerakan udara
Dinding alveolus
Rongga nasal Trakea Bronkus (setebal satu sel)
Darah
masuk Darah keluar
Rongga
Alveolus Bronkiol alveolus Lapisan lembap
yang nipis
Kapilari Sel darah merah
3. Mekanisme pernafasan manusia:
(a) Menarik nafas
Udara masuk 4. Ciri-ciri alveolus yang membantu dalam pertukaran gas:
• Mempunyai dinding nipis yang lembap
• Mempunyai luas permukaan besar yang terdedah
Sangkar rusuk kepada udara
bergerak ke atas • Kapilari darah yang banyak
dan luar
Isi padu
rongga 2.3 Kesihatan Sistem Respirasi Manusia
toraks
bertambah 1. Penyakit sistem respirasi ialah bronkitis, asma,
Diafragma pneumonia, emfisema, tuberkulosis, kanser peparu dan
mengecut
penyakit peparu obstruktif kronik.
dan mendatar
2. Bahan-bahan berbahaya dalam asap rokok dan kesan
(a) Menarik nafas negatifnya:
(b) Menghembus nafas
Udara keluar Bahan Kesan
Tar Melekat dan menyumbatkan laluan
udara
Sangkar rusuk
ke bawah dan Karbon Mengurangkan pengangkutan oksigen
ke dalam Isi padu rongga
toraks berkurangan
monoksida oleh sel darah merah
Nikotina Mengakibatkan ketagihan dan
merangsang pertumbuhan sel kanser
Diafragma
mengendur dan Karsinogen Merangsang pertumbuhan sel kanser
melengkung ke
atas
(b) Menghembus nafas
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Sains Tingkatan 3
2.4 Adaptasi dalam Sistem Respirasi 2.5 Pertukaran Gas dalam Tumbuhan
1. Haiwan amfibia bernafas melalui peparu (semasa di darat) 1. Sama seperti haiwan, tumbuhan juga menjalankan proses
dan kulit lembap (semasa di dalam air). respirasi dengan menyerap oksigen dan membebaskan
karbon dioksida.
2. Ikan bernafas di dalam air melalui insang.
2. Tumbuhan menyerap oksigen dan membebaskan karbon
3. Serangga seperti belalang melakukan pertukaran gas
dioksida melalui daun, batang dan akar.
melalui sistem trakea.
3. Pertukaran gas antara sel tumbuhan dan persekitaran
4. Manusia memerlukan bekalan oksigen yang tinggi
berlaku melalui stoma secara resapan.
semasa berada di altitud tinggi, bersukan atau mengalami
penyakit seperti anemia dan sel sabit. 4. Setiap stoma dikelilingi sepasang sel pengawal yang
mengawal pembukaan dan penutupan stoma.
5. Oleh itu, sistem respirasi manusia perlu beradaptasi bagi
membolehkan pergerakan dan pertukaran gas dalam 5. Stoma terbuka apabila air memasuki sel pengawal melalui
badan berlaku dengan lancar. proses osmosis.
6. Stoma tertutup apabila air keluar dari sel pengawal
melalui proses osmosis.
7. Persekitaran yang tercemar mengandungi debu yang
melekap pada daun tumbuhan dan menutup liang stoma.
Keadaan ini menyebabkan kadar respirasi tumbuhan
menurun, sekali gus mengganggu tumbesaran pokok.
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Sains Tingkatan 3
Notes Chapter 2
Chapter 2 Respiration
2.1 Respiratory System 4. Oxygen content in inhaled air is higher than in exhaled
air.
1. Structures in the human respiratory system:
5. Carbon dioxide content in inhaled air is lower then in
exhaled air.
Bronchus Nasal cavity
2.2 Movement and Exchange of Gas in the
Bronchiole Trachea Human Body
Alveolus Intercostal 1. Oxygen is transported to cells by the red blood cells in
muscles
the form of oxyhaemoglobin.
Bronchus
Capillary Ribs
2. Blood containing oxyhaemoglobin is then transported to
Bronchiole
the heart to be distributed to all of the body cells.
Left lung
Diaphragm
3. At the same time, carbon dioxide is absorbed from inside
of cell to blood capillary and then to alveolus.
2. Pathway of oxygen during inhalation:
Air movement
Alveolus wall
Nasal cavity Trachea Bronchus (one cell thick)
Blood enter
Blood out
Alveolus Bronchiole Alveolus
cavity A thin layer of moist
3. Mechanism of human breathing: Capillary Red blood cell
(a) Inhalation
Air goes in 4. Characteristic of an alveolus for supporting the gas
exchanges:
• Has a thin moist wall
Ribcage moves • A large surface area in contact with the air
upwards and
outwards • A lot of blood capillaries
Volume of
thoracic cavity
increases 2.3 The Health of Human Respiratory
Diaphragm System
contracts
and flattened 1. Diseases of the respiratory system are bronchitis, asthma,
pneumonia, emphysema, tuberculosis, lung cancer and
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
(b) Exhalation (a) Inhalation
2. Harmful substances in cigarettes smoke and the negative
Air comes out effects:
Substance Effect
Rib cage moves
downwards Tar Stick and block the air passage
and inwards Volume of thoracic
cavity decreases Carbon Reduce transport of oxygen by the red
monoxide blood cells
Nicotine Causes addiction and stimulate the
Diaphragm relaxes growth of cancerous cell
and curved
Carcinogen Stimulate the growth of cancerous cell
(b) Exhalation
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Sains Tingkatan 3
2.4 Adaptation in Respiratory System 2.5 Exchange of Gas in Plants
1. Amphibians breathe through the lungs (while on land) 1. Just like animals, plants also carry out respiration
and moist skin (while in the water). processes by absorbing oxygen and releasing carbon
dioxide.
2. Fish breathe in water through the gills.
2. The plant absorbs oxygen and releases carbon dioxide
3. Insects such as grasshoppers carry out gas exchange
through leaves, stems and roots.
through the tracheal system.
3. The exchange of gases between plant cells and the
4. Humans need high oxygen supply while in high altitude,
environment occurs through the stoma by diffusion.
sports or suffer from diseases such as anaemia and sickle
cells. 4. Each stoma is surrounded by a pair of guard cells that
control the opening and closing of the stoma.
5. Hence, human respiratory systems need to be adapted
to enable movement and exchange of gas in the body 5. Stoma opens when the water enters the guard cell
to occur efficiently. through the osmosis process.
6. Stoma is closed when the water comes out of the guard
cell through the osmosis process.
7. The polluted environment contains dust that is attached
to the leaves of the plant and closes the stoma. This
causes the rate of plant respiration to decrease, thereby
disrupting the growth of the plant.
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Nota Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 2 (2.1) RespirasiDokumen6 halamanNota Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 2 (2.1) RespirasinusaibahBelum ada peringkat
- Mind Map Sistem RespirasiDokumen1 halamanMind Map Sistem RespirasiNada Alfi40% (5)
- Skema Modul Geografi Tingkatan 2 Bab 4 PDFDokumen4 halamanSkema Modul Geografi Tingkatan 2 Bab 4 PDFAngah YusBelum ada peringkat
- Ujian Setara 1 Sains Tingkatan 3 2018Dokumen6 halamanUjian Setara 1 Sains Tingkatan 3 2018Diana Ahmad100% (2)
- Sejarah Tingkatan 1 (Bab 2 Dan Bab3)Dokumen3 halamanSejarah Tingkatan 1 (Bab 2 Dan Bab3)Kye Xen TeohBelum ada peringkat
- Sejarah Tingkatan 1 Bab 2Dokumen3 halamanSejarah Tingkatan 1 Bab 2Iamtheuser ZilaBelum ada peringkat
- Sains t3 Bab 1 - Respirasi (Nota Ringkas)Dokumen9 halamanSains t3 Bab 1 - Respirasi (Nota Ringkas)Daniel Barnes67% (3)
- Sejarah Tingkatan 2 Bab 2 Sistem Pemerintahan & Kegiatan EkonomiDokumen58 halamanSejarah Tingkatan 2 Bab 2 Sistem Pemerintahan & Kegiatan EkonomiEyza Jimat100% (1)
- Folio Sejarah Tingkatan 1-EditedDokumen46 halamanFolio Sejarah Tingkatan 1-EditedHARIDH KUMAR NAIR A/L JAYA CHANDRAN MANIYANI Moe100% (1)
- Nota Geografi Tingkatan 1,2 Dan 3 (PMR)Dokumen40 halamanNota Geografi Tingkatan 1,2 Dan 3 (PMR)Ajwad Hashim67% (3)
- Ujian 1 Sejarah T3Dokumen10 halamanUjian 1 Sejarah T3Lienda LynBelum ada peringkat
- Sejarah Tingkatan 2 Bab 6Dokumen6 halamanSejarah Tingkatan 2 Bab 6Teng Pei ErBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 5 Tamadun Awal DuniaDokumen17 halamanBab 5 Tamadun Awal DunianajihahBelum ada peringkat
- Sejarah Tingkatan 1-126-147Dokumen22 halamanSejarah Tingkatan 1-126-147Praveena MoganBelum ada peringkat
- Jadual KerjaDokumen2 halamanJadual Kerjanur_1202Belum ada peringkat
- Perjanjian LondonDokumen3 halamanPerjanjian LondonbbshafaBelum ada peringkat
- Kajian Kes Bab 6 Kegemilangan Kerajaan Johor RiauDokumen1 halamanKajian Kes Bab 6 Kegemilangan Kerajaan Johor Riauzaliha zainal33% (3)
- Sumbangan Tamadun Mesir & MesopotamiaDokumen6 halamanSumbangan Tamadun Mesir & MesopotamiaMohaspa Mohd HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Esei SejarahDokumen3 halamanContoh Esei SejarahDaniel Weeyz100% (2)
- Skema Jawapan Sejarah Kertas 3 Tingkatan 4 2Dokumen9 halamanSkema Jawapan Sejarah Kertas 3 Tingkatan 4 2Caferatte OngBelum ada peringkat
- Skema Jawapan Soalan 2Dokumen2 halamanSkema Jawapan Soalan 2Jia Xun Tu0% (1)
- Nota Sej Bab 8Dokumen5 halamanNota Sej Bab 8zharfanadlyBelum ada peringkat
- JawapanDokumen22 halamanJawapanmasdBelum ada peringkat
- S13 Dan S14 E3Dokumen7 halamanS13 Dan S14 E3Evelyn YingBelum ada peringkat
- Soalan Sejarah Tingkatan 2 Bab 8Dokumen15 halamanSoalan Sejarah Tingkatan 2 Bab 8NAZIEFAH ABDUL AZIZ100% (2)
- Tingkatan 2Dokumen8 halamanTingkatan 2Ting 후아힌 쌰Belum ada peringkat
- Contoh Kerja Kursus Sejarah PT3 Bangunan BersejarahDokumen8 halamanContoh Kerja Kursus Sejarah PT3 Bangunan BersejarahBintang Sukan75% (8)
- Cabaran Ke Arah KegemilanganDokumen1 halamanCabaran Ke Arah Kegemilangansmart guysBelum ada peringkat
- Sejarah Tingkatan 3 Bab 2 Pentadbiran NegeriDokumen5 halamanSejarah Tingkatan 3 Bab 2 Pentadbiran NegeriAdriana HismiBelum ada peringkat
- Sinopsis Hempasan OmbakDokumen5 halamanSinopsis Hempasan OmbakNorfazlieyna FazlieBelum ada peringkat
- Cabaran Minda A For ScienceDokumen9 halamanCabaran Minda A For ScienceAisyah BatrisyiaBelum ada peringkat
- T3 SN Modul Nilam Bab 5Dokumen9 halamanT3 SN Modul Nilam Bab 5Saridah Mohamad100% (1)
- Sejarah T3Dokumen24 halamanSejarah T3ayacomelBelum ada peringkat
- (Tingkatan 2) Sajak Pada Sekuntum MawarDokumen2 halaman(Tingkatan 2) Sajak Pada Sekuntum MawarErin Brown0% (1)
- JWPN Pat Ask t1Dokumen11 halamanJWPN Pat Ask t1intan iyenBelum ada peringkat
- Kajian Sejarah Tajuk: Perjuangan Tokoh Tempatan: Sekolah Kebangsaan Pusat JertehDokumen75 halamanKajian Sejarah Tajuk: Perjuangan Tokoh Tempatan: Sekolah Kebangsaan Pusat JertehYusniza YahyaBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 9 Cuaca Angkasa LepasDokumen41 halamanBab 9 Cuaca Angkasa Lepaslalisa100% (1)
- Bangunan Sultan Abdul SamadDokumen26 halamanBangunan Sultan Abdul Samadmuazz100% (10)
- Geografi Tingkatan 2 Bab 10 Teknologi HijauDokumen2 halamanGeografi Tingkatan 2 Bab 10 Teknologi Hijaufatin100% (1)
- Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun PJPK Form 2Dokumen14 halamanPeperiksaan Akhir Tahun PJPK Form 2Nor Zana Ithnin100% (1)
- Bab 3 Tingkatan 1Dokumen3 halamanBab 3 Tingkatan 1Hafs An AsimBelum ada peringkat
- PKL21 Bacaan Ting.3 Guru (BM)Dokumen27 halamanPKL21 Bacaan Ting.3 Guru (BM)SITI NORHAYANI MISNANBelum ada peringkat
- Senarai Contoh Ulasan PT3 Dan Tips TerbaikDokumen8 halamanSenarai Contoh Ulasan PT3 Dan Tips TerbaikFasihah LiewBelum ada peringkat
- Nota Revisi Sejarah f3 Chekgu AnasDokumen32 halamanNota Revisi Sejarah f3 Chekgu AnasEirfanEirfan100% (1)
- Puteri Buluh BetungDokumen10 halamanPuteri Buluh Betungwise_conan1412100% (3)
- Jawapan Sejarah Ting 2 2021Dokumen20 halamanJawapan Sejarah Ting 2 2021Mohd HazifBelum ada peringkat
- Nota Ringkas BAB 1Dokumen3 halamanNota Ringkas BAB 1polarisBelum ada peringkat
- Soalan 1Dokumen3 halamanSoalan 1atiqnadzirahBelum ada peringkat
- Mengapakah Hubungan Diplomatik Penting Bagi SesebuDokumen2 halamanMengapakah Hubungan Diplomatik Penting Bagi SesebuShane ClaireBelum ada peringkat
- Perjanjian London 1824 Dan Kesannya Terhadap Alam Melayu SejarahDokumen17 halamanPerjanjian London 1824 Dan Kesannya Terhadap Alam Melayu Sejarahfarah nadhirahBelum ada peringkat
- Dalam Persekitaran Kata"Dokumen11 halamanDalam Persekitaran Kata"Nurin EmelinBelum ada peringkat
- Pengenalan ColosseumDokumen1 halamanPengenalan ColosseumMizan Mohd Noor50% (2)
- Bab 1Dokumen5 halamanBab 1NOR HANANI BINTI AHMAD NASARUDDIN Moe100% (1)
- Jawapan Lengkap Matematik Tingkatan 2Dokumen19 halamanJawapan Lengkap Matematik Tingkatan 2liyanaBelum ada peringkat
- Sains T3 Bab 1 - Respirasi (Nota Ringkas) PDFDokumen9 halamanSains T3 Bab 1 - Respirasi (Nota Ringkas) PDFbaby shazanaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomi Fisiologi Sistem PernafasanDokumen27 halamanAnatomi Fisiologi Sistem Pernafasanulyati ulfahBelum ada peringkat
- Fungsi Sistem RespiratoriDokumen4 halamanFungsi Sistem RespiratoriammaBelum ada peringkat
- Rudy Fisiologi Anestesi Dan RespirasiDokumen42 halamanRudy Fisiologi Anestesi Dan RespirasiRudy Siahaan100% (1)
- Bab Vii RespirasiDokumen9 halamanBab Vii RespirasiNazarruddin falakhBelum ada peringkat
- Kuliah 7 Sistem RespirasiDokumen35 halamanKuliah 7 Sistem RespirasiJennie Rose KomalaBelum ada peringkat