Bab 1 Akl
Diunggah oleh
Arby DirgaDinataJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Bab 1 Akl
Diunggah oleh
Arby DirgaDinataHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 1: Business Combinations
by Jeanne M. David, Ph.D., Univ. of Detroit Mercy
to accompany
Advanced Accounting, 10th edition
by Floyd A. Beams, Robin P. Clement,
Joseph H. Anthony, and Suzanne Lowensohn
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-1
Business Combinations: Objectives
1. Memahami motivasi ekonomi mengenai
kombinasi bisnis.
2. Memahami bentuk alternatif kombinasi bisnis,
dilihat dari segi hukum dan perspektif akuntansi.
3. Memperkenalkan konsep akuntansi untuk
kombinasi bisnis, menekankan pada metode
akuisisi.
4. Melihat bagaimana perusahaan melakukan
alokasi biaya dalam metode akuisisi.
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-2
Business Combinations
1: Economic Motivations
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-3
Types of Business Combinations
Kombinasi bisnis sebelum digabungkan adalah
entitas bisnis yang terpisah.
• Horizontal integration – lini bisnis dan pasar
yang sama.
• Vertical integration – penggabungan perusahaan
dengan operasi pada tahap produksi dan
distribusi berbeda, tapi berurutan.
• Conglomeration – tidak berhubungan dan
produk serta jasa yang beragam.
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-4
Reasons for Combinations
• Keuntungan biaya
• Resiko lebih rendah
• Memperkecil keterlambatan operasi
• Menghindari pengambilalihan
• Akuisisi aktiva tak berwujud
• Alasan lain, seperti: bisnis dan keuntungan
pajak atau alasan personal lainnya.
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-5
Business Combinations
2: Forms of Business Combinations
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-6
Legal Form of Combination
• Merger
– Terjadi ketika suatu perusahaan mengambil
alih semua operasi entitas bisnis lain dan
bisnis lain tersebut dibubarkan.
• Consolidation
– Terjadi ketika perusahaan baru dibentuk
dari semua aset dan operasi dua atau lebih
entitas bisnis, kemudian entitas bisnis
sebelumnya dibubarkan.
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-7
Mergers: A + B = A
1) Perusahaan A membeli aset perusahaan B
dengan kas, aktiva lainnya, sekuritas
hutang/ekuitas perusahaan A. Perusahaan B
dibubarkan, perusahaan A menjalankan aset
dan kewajiban perusahan B.
2) Perusahaan A membeli saham perusahaan B
dari pemegang sahamnya berupa kas, aktiva
lain, sekuritas hutang/ekuitas perusahaan A.
Perusahaan B dibubarkan, perusahaan A
menjalankan aset dan kewajiban perusahaan B.
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-8
Consolidations: E + F = “D”
1) Perusahaan D dibentuk dan memperoleh aset
perusahaan E dan F dengan menerbitkan saham
perusahan D. Perusahaan E dan F dibubarkan.
Perusahaan D tetap hidup, dengan aset dan kewajiban
dari dua perusaaan yang telah dibubarkan.
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-9
Business Combinations
3: Accounting for Business
Combinations
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-10
Recording Guidelines (1 of 2)
• Untuk mencatat aset dan kewajiban yang diperoleh, asumsi
yang digunakan adalah prinsip fair value.
• Jika sekuritas ekuitas diterbitkan oleh “acquirer” (pembeli),
biaya yang berhubungan dengan penerbitan sekuritas
menentang prinsip fair value, biasanya menggurangi
tambahan modal disetor saja (reduction in additional paid-
in-capital)
• Biaya lain langsung yang disebabkan karena kombinasi
((e.g., legal fees, finders’ fees) dan indirect combination costs
(e.g., management salaries) diakui sebagai biaya investasi dan
nantinya akan mengurangi laba ditahan.
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-11
Recording Guidelines (2 of 2)
• Ketika perusahaan yang diperoleh mentransfer asetnya
selain kas untuk kombinasi bisnis, maka gain atau loss
karena penghapusan aset tersebut dicatat sebagai
current income.
• Kelebihan kas, aset lainnya, dan sekuritas ekuitas yang
ditransfer melebihi fair value dari net asset (A-L) yang
diperoleh dicatat sebagai goodwill.
• Jika net asset yang diperoleh melebihi kas, aset lainnya
dan ekuitas sekuritas yang ditransfer, laba yang
diperoleh pada bargain purchase dicatat pada current
income.
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-12
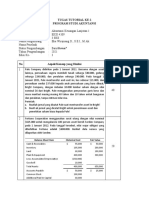
Example: Poppy Corp. (1 of 3)
Poppy Corp. menerbitkan 100,000 saham dengan nilai
par value nya $10 saham biasa untuk Sunny Corp.
saham Poppy dinilai $16 per lembar (dalam ribuan)
Investment in Sunny Corp. 1,600
Common stock, $10 par 1,000
Additional paid-in-capital 600
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-13
Example: Poppy Corp. (2 of 3)
Poppy Corp. membayar kas sebesar $80,000 untuk biaya
pendirian dan biaya konsultan dan biaya $40,000 untuk
mendaftarkan dan menerbitkan saham biasa (Dalam ribuan)
Investment expense 80
Additional paid-in-capital 40
Cash 120
Sunny Corp. diasumsikan akan dibubarkan. Jadi Poppy Corp.
akan mengalokasikan biaya investasi kedalam nilai wajar
untuk mengidentifikasu aset yang diperoleh dan kewajiban
yang diasumsikan. Kelebihan biaya dihitung sebagi goodwill.
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-14
Example: Poppy Corp. (3 of 3)
Receivables XXX
Inventories XXX
Plant assets XXX
Goodwill XXX
Accounts payable XXX
Notes payable XXX
Investment in Sunny Corp. 1,600
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-15
Business Combinations
4: Cost Allocations Using the
Acquisition Method
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-16
Identify the Net Assets Acquired
Identify:
1. Tangible assets acquired,
2. Intangible assets acquired, and
3. Liabilities assumed
Include:
• Identifikasi aset tidak berwujud yang berasal
dari hak legal dan kontraktual, atau yang
terpisah dari entitas.
• Penelitian dan pengembangan dalam proses
• Beberapa perjanjian nonkontraktual
(noncontractual contingencies)
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-17
Assign Fair Values to Net Assets
Gunakan nilai wajar yang ditentukan dengan
cara:
1. Nilai pasar yang ada
2. Present value yang diestimasi dengan aliran
kas masa depan (estimated future cash
flows) didiskontokan berdasarkan ukuran
yang dapat diobservasi.
3. Estimasi internal lainnya.
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-18
Example – Pitt Co. Data
Pitt Co. acquires the net assets of Seed Co. in a
combination consummated on 12/27/2008. The
assets and liabilities of Seed Co. on this date, at
their book values and fair values, are as follows
(in thousands):
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-19
Book Val. Fair Val.
Cash $ 50 $ 50
Net receivables 150 140
Inventory 200 250
Land 50 100
Buildings, net 300 500
Equipment, net 250 350
Patents 0 50
Total assets $1,000 $1,440
Accounts payable $ 60 $ 60
Notes payable 150 135
Other liabilities 40 45
Total liabilities $ 250 $ 240
Net assets $ 750 $1,200
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-20
Acquisition with Goodwill
Pitt Co. pays $400,000 cash and issues 50,000
shares of Pitt Co. $10 par common stock with a
market value of $20 per share for the net assets
of Seed Co.
Total consideration at fair value (in thousands):
$400 + (50 shares x $20) $1,400
Fair value of net assets acquired: $1,200
Goodwill $ 200
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-21
Entries with Goodwill
The entry to record the acquisition of the net
assets:
Investment in Seed Co. 1,400
Cash 400
Common stock, $10 par 500
Additional paid-in-capital 500
The entry to record Seed’s assets directly on Pitt’s
books:
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-22
Cash 50
Net receivables 140
Inventories 250
Land 100
Buildings 500
Equipment 350
Patents 50
Goodwill 200
Accounts payable 60
Notes payable 135
Other liabilities 45
Investment in Seed Co. 1,400
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-23
Acquisition with Bargain Purchase
Pitt Co. issues 40,000 shares of its $10 par
common stock with a market value of $20 per
share, and it also gives a 10%, five-year note
payable for $200,000 for the net assets of Seed
Co.
Fair value of net assets acquired (in thousands):
$1,200
Total consideration at fair value:
(40 shares x $20) + $200 $1,000
Gain from bargain purchase $ 200
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-24
Entries with Bargain Purchase
The entry to record the acquisition of the net
assets:
Investment in Seed Co. 1,000
10% Note payable 200
Common stock, $10 par 400
Additional paid-in-capital 400
The entry to record Seed’s assets directly on Pitt’s
books:
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-25
Cash 50
Net receivables 140
Inventories 250
Land 100
Buildings 500
Equipment 350
Patents 50
Accounts payable 60
Notes payable 135
Other liabilities 45
Investment in Seed Co. 1,000
Gain from bargain purchase 200
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-26
Impairments
• Perusahaan harus menilai secara tahunan tentang
penurunan nilai goodwill untuk pelaporan.
– Jika nilai buku unit melebihi fair value nya,
penilaian tambahan perlu dilakukan untuk
menentukan penurunan nilai goodwill atau aset
lainnya.
• Test / penilaian lebih sering perlu dilakukan
untuk penurunan nilai ini jika dibutuhkan (e.g.,
loss of key personnel, unanticipated competition,
goodwill impairment of subsidiary).
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-27
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any
means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or
otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher.
Printed in the United States of America.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Publishing as Prentice Hall
© Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 1-28
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Kombinasi Bisnis - IN MateriDokumen15 halamanKombinasi Bisnis - IN MateriNurlatifahBelum ada peringkat
- Business - Combinations - 15 September 2021.en - IdDokumen22 halamanBusiness - Combinations - 15 September 2021.en - IdNABILAH KHANSA 1911000089Belum ada peringkat
- Bab 1 (B - Com)Dokumen20 halamanBab 1 (B - Com)Yoan TunggalBelum ada peringkat
- BAB 1 - Pengantar Kombinasi BisnisDokumen28 halamanBAB 1 - Pengantar Kombinasi BisnisF.X. LEONARDOBelum ada peringkat
- Mhs-Pert 2 - Akuisisi Antar Perusahaan Dan PenggabunganDokumen26 halamanMhs-Pert 2 - Akuisisi Antar Perusahaan Dan PenggabunganHellyana dewiBelum ada peringkat
- AKL 1 - Materi Mingu 1 - Penggabungan UsahaDokumen6 halamanAKL 1 - Materi Mingu 1 - Penggabungan UsahaVettyBelum ada peringkat
- Business Combination Beams IDN KSDokumen42 halamanBusiness Combination Beams IDN KSdewi0% (1)
- Business CombinationDokumen43 halamanBusiness CombinationaruminawatiBelum ada peringkat
- Business Combinations 56abe0849dfc0Dokumen47 halamanBusiness Combinations 56abe0849dfc0NIWAYANRADHABelum ada peringkat
- Pert 3 - Latihan Soal Akuisisi Antar Perusahaan Dan PenggabunganDokumen19 halamanPert 3 - Latihan Soal Akuisisi Antar Perusahaan Dan PenggabunganHellyana dewiBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 1 AklDokumen5 halamanBab 1 AklNaomi NovelinBelum ada peringkat
- Cover AKUNTANSI LANJUTANDokumen17 halamanCover AKUNTANSI LANJUTANTheresa MettaBelum ada peringkat
- Penggabungan UsahaDokumen10 halamanPenggabungan UsahaSyfa SyifaurohmahBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas AKL 1 Pert.1Dokumen4 halamanTugas AKL 1 Pert.1Riska auliaBelum ada peringkat
- Persekutuan Pertemuan 1-3Dokumen39 halamanPersekutuan Pertemuan 1-3bahan Kuliah RikkyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Dan 3Dokumen60 halamanChapter 1 Dan 3astridBelum ada peringkat
- RMK AKL Kelompok 6 - Chapter 1Dokumen12 halamanRMK AKL Kelompok 6 - Chapter 1Asia MotorBelum ada peringkat
- 2017 SESI 1 AKL Advance Accounting Beams11 - Ppt01.en - IdDokumen42 halaman2017 SESI 1 AKL Advance Accounting Beams11 - Ppt01.en - IdjokerrggBelum ada peringkat
- Kelompok 1B Penggabungan Usaha Dengan Metode Pembelian Aset NetoDokumen10 halamanKelompok 1B Penggabungan Usaha Dengan Metode Pembelian Aset NetoNurul MaghfirahBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan 2 Partnership Beams10e - ch15Dokumen40 halamanPertemuan 2 Partnership Beams10e - ch15Hasim kunBelum ada peringkat
- Bandi: Advanced Accounting (Beams Et Al. 2012)Dokumen40 halamanBandi: Advanced Accounting (Beams Et Al. 2012)ELTIN YULI ASTUTIBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Soal Akl Sap 11Dokumen3 halamanContoh Soal Akl Sap 11Wika Noya100% (1)
- Beams10e Ch07 Intercompany Profit Transactions BondsDokumen26 halamanBeams10e Ch07 Intercompany Profit Transactions BondsnathasaviBelum ada peringkat
- Akl 1Dokumen36 halamanAkl 1segararilo100% (5)
- Akl 1Dokumen36 halamanAkl 1segararilo100% (1)
- Universitas Tanjungpura Pontianak TAHUN 2014Dokumen36 halamanUniversitas Tanjungpura Pontianak TAHUN 2014Ishyara Nuur Safana0% (1)
- Chapter 3introduksi - Penyusunan Lap Keu KonsolidasianDokumen54 halamanChapter 3introduksi - Penyusunan Lap Keu KonsolidasianKirani WahyuningBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 1 IndoDokumen39 halamanBab 1 IndoNurcahyonoBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan 123 Ch15 PersekutuanDokumen39 halamanPertemuan 123 Ch15 PersekutuanIrham PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Uts AklDokumen15 halamanUts AklAnonymous Jpy3HVg0Belum ada peringkat
- Akuntansi Keuangan Lanjutan 2 Pertemuan 2Dokumen30 halamanAkuntansi Keuangan Lanjutan 2 Pertemuan 2mitaBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 4 BakerDokumen41 halamanBab 4 BakerMerta WigunaBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 4 BakerDokumen43 halamanBab 4 BakerSherly Haekase-TseBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Soal Penggabungan UsahaDokumen8 halamanContoh Soal Penggabungan UsahaWenni AmeliaBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Keuangan Konsolidasi Suatu PengantarDokumen44 halamanLaporan Keuangan Konsolidasi Suatu PengantarRai Sugih RaharjaBelum ada peringkat
- Akuntansi Keuangan LanjutanDokumen57 halamanAkuntansi Keuangan LanjutanLorensius GintingBelum ada peringkat
- QUIZ 1 Soal Dan Jawaban Penggabungan Usaha Dan Investasi SahamDokumen8 halamanQUIZ 1 Soal Dan Jawaban Penggabungan Usaha Dan Investasi SahamCepi Juniar PrayogaBelum ada peringkat
- Si330 091053 991 1Dokumen32 halamanSi330 091053 991 1Winni DepariBelum ada peringkat
- Persamaan AkuntansiDokumen10 halamanPersamaan AkuntansiPresly Kore DjuBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan 2Dokumen28 halamanPertemuan 2Amirul AdilBelum ada peringkat
- Materi An Introduction To Consolidated Financial StatementDokumen12 halamanMateri An Introduction To Consolidated Financial StatementChatya RezateBelum ada peringkat
- AKL II - Partnerships-Formation, Operations, and Changes in OwnershipDokumen20 halamanAKL II - Partnerships-Formation, Operations, and Changes in Ownershipoktaviani 52418012 oktavianiBelum ada peringkat
- Penggabungan Badan UsahaDokumen37 halamanPenggabungan Badan UsahaMaryana YanaBelum ada peringkat
- Bab - 4 - Baker (2) .PPTX - 20240318 - 094339 - 0000-1Dokumen51 halamanBab - 4 - Baker (2) .PPTX - 20240318 - 094339 - 0000-1Okta SaputriBelum ada peringkat
- Akuisisi Antarperusahaan Dan Investasi PDokumen12 halamanAkuisisi Antarperusahaan Dan Investasi PArtha FahrezaBelum ada peringkat
- Akuntansi Keuangan Lanjutan 1 Tugas 1Dokumen6 halamanAkuntansi Keuangan Lanjutan 1 Tugas 1Alya NuralizaBelum ada peringkat
- #5 Penggabungan Badan UsahaDokumen39 halaman#5 Penggabungan Badan UsahaharisBelum ada peringkat
- Lembar Jawab - EKSI4309 - Tugas2 - MAS'UDI - AK LanjutanDokumen6 halamanLembar Jawab - EKSI4309 - Tugas2 - MAS'UDI - AK LanjutanFahmut TaajuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas 1Dokumen2 halamanTugas 1Andhy Arya Ekaputra0% (2)
- Tugas 1Dokumen2 halamanTugas 1sigit75% (4)
- Akl Bisnis Kombinasi LengkapDokumen28 halamanAkl Bisnis Kombinasi LengkapFitrah SiregarBelum ada peringkat
- Sap 10 AklDokumen5 halamanSap 10 AklnindyaBelum ada peringkat
- Persamaan Dasar Akuntansi 1Dokumen6 halamanPersamaan Dasar Akuntansi 1Yopi Dika Saputra SaputraBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas 2 AKLDokumen5 halamanTugas 2 AKLDavidIsnaini ChannelBelum ada peringkat
- Lembar Jawab - EKSI4309 - Tugas1 - MAS'UDI - AK LanjutanDokumen4 halamanLembar Jawab - EKSI4309 - Tugas1 - MAS'UDI - AK LanjutanFahmut TaajuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Renova Ramadina - 2101036251 - Akuntansi Persekutuan&perusahaan Kewajiban Terbatas.Dokumen8 halamanRenova Ramadina - 2101036251 - Akuntansi Persekutuan&perusahaan Kewajiban Terbatas.Renova RamadinaBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Pigp Wira SilviantiDokumen39 halamanLaporan Pigp Wira SilviantiArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Cover GeotekDokumen1 halamanCover GeotekArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- LAPORAN PIPG AFRIYANI, S.PD SisaDokumen24 halamanLAPORAN PIPG AFRIYANI, S.PD SisaArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Candle PantulanDokumen1 halamanCandle PantulanArby DirgaDinata100% (1)
- Daftar TabelDokumen1 halamanDaftar TabelArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Susunan Panitia Praktek Ekplorasi Ke TikuDokumen1 halamanSusunan Panitia Praktek Ekplorasi Ke TikuArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Soal TpaiDokumen1 halamanSoal TpaiArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Pendahuluan GeoteknikDokumen7 halaman1 Pendahuluan GeoteknikNudi HairullahBelum ada peringkat
- Vocabulary PPU InggrisDokumen4 halamanVocabulary PPU Inggrisgbriel ch100% (5)
- Asistensi Latihan Soal IDokumen14 halamanAsistensi Latihan Soal IGun AwanBelum ada peringkat
- KepemimpinanDokumen8 halamanKepemimpinanYolla TrimeilaniBelum ada peringkat
- Bab IiDokumen2 halamanBab IiArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Pasar ModalDokumen30 halamanPasar ModalArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Mengelola Perubahan Dan Kendala Yang Dihadapi ManajerDokumen9 halamanMengelola Perubahan Dan Kendala Yang Dihadapi ManajerArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Pengumuman Mahasiswa Daring Ut 2020Dokumen1 halamanPengumuman Mahasiswa Daring Ut 2020Septi Putri DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Modul Pratikum 3Dokumen4 halamanModul Pratikum 3Arby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Soal TpaiDokumen1 halamanSoal TpaiArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- KewirausahaanDokumen9 halamanKewirausahaanArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas ResumeDokumen20 halamanTugas ResumeArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Ujian Akhir Semester V Perencanaan TambangDokumen21 halamanLaporan Ujian Akhir Semester V Perencanaan TambangArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Menyelesaikan Pengujian Dalam Siklus Akuisisi Dan PembayaranDokumen33 halamanMenyelesaikan Pengujian Dalam Siklus Akuisisi Dan PembayaranArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Bab IiDokumen2 halamanBab IiArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas ResumeDokumen20 halamanTugas ResumeArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Lapangan UsahaDokumen16 halamanLapangan UsahaArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar GambarDokumen6 halamanDaftar GambarArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Susunan Panitia Praktek Ekplorasi Ke TikuDokumen1 halamanSusunan Panitia Praktek Ekplorasi Ke TikuArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Hasil RapatDokumen2 halamanHasil RapatArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar TabelDokumen1 halamanDaftar TabelArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat
- Jawaban Kelompok MMDokumen2 halamanJawaban Kelompok MMArby DirgaDinataBelum ada peringkat