PAPER 2 Cakna Kelantan
PAPER 2 Cakna Kelantan
Diunggah oleh
cikguwanismktsl-1Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
PAPER 2 Cakna Kelantan
PAPER 2 Cakna Kelantan
Diunggah oleh
cikguwanismktsl-1Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
PAPER 2 / SET 2
SECTION A
CONSTRUCT CONCEPTUALISATION
1.
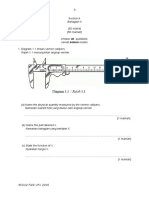
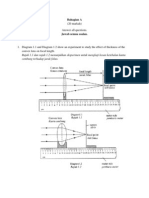
Diagram 1.1 and Diagram 1.2 show two measuring instruments used to
measure the diameter of an object.
Rajah 1.1 dan Rajah 1.2 menunjukkan dua alat pengukur yang digunakan
untuk mengukur diameter bagi satu objek.
Diagram 1.1
Rajah 1.1
0
Diagram 1.2
Rajah 1.2
a.
What is the meaning of sensitivity ?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan kepekaan ?
(1 Mark )
4531/2 @SET 2
10
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
b.
PAPER 2 / SET 2
Based on Diagram 1.1 and Diagram 1.2,
Berdasarkan Rajah 1.1 dan Rajah 1.2,
i.
compare the sensitivities of these two measuring instruments
bandingkan kepekaan bagi kedua alat pengukur
.....
(1 Mark )
ii.
compare the accuracy of the readings of these two measuring
instruments
bandingkan kejituan bacaan bagi kedua alat pengukur
(1 Mark )
c.
Relate the the sensitivity of the instrument with the accuracy of the
reading.
Hubungkaitkan kepekaan alat pengukur dengan kejituan bacaan.
(1 Mark )
d.
Diagram 1.3 shows the process to determine the diameter of a ball
bearing using a metre rule. Five identical ball bearings were placed
side by side to measure the total diameters.
Rajah 1.3 menunjukkan proses untuk menentukan diameter satu alas
bebola dengan menggunakan pembaris meter. Lima alas bebola
diletakkan bersebelahan untuk mengukur jumlah diameter semua alas
bebola itu.
3 cm
4 cm
5 cm
Diagram 1.3
Rajah 1.3
4531/2 @SET 2
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
PAPER 2 / SET 2
Based on Diagram 1.3;
Berdasarkan Rajah 1.3;
i.
ii.
What is the total diameters of the five ball bearings?
Berapakah jumlah diameter bagi kesemua lima alas bebola
itu?
...
[1 mark]
What is the diameter of one ball bearing?
Berapakah diameter bagi satu alas bebola?
[2 marks]
e)
Among the three measuring instruments shown in Diagrams 1.1, 1.2
and 1.3, which gives the least accurate reading?
Antara tiga alat pengukur yang ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 5.1, 5.2 dan
5.3, yang manakah memberikan bacaan yang paling kurang jitu?
[1 mark]
4531/2 @SET 2
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
2.
PAPER 2 / SET 2
Table 2.1 and Table 2.2 show an equation of a reaction and the total atomic
mass before and after a nuclear fission and nuclear fusion respectively.
Jadual 2.1 dan Jadual 2.2 menujukkan persamaan tindak balas dan jumlah
jisim atom sebelum dan selepas tindak balas pembelahan nukleus dan
pelakuran nukleus masing-masing.
Nuclear Fission
Pembelahan Nukleus
Before reaction
After reaction
Sebelum tindak balas
Selepas tindak balas
Equation
Persamaan
Total atomic
mass
Jumlah jisim
atom
240.06082 a.m.u
240.06082 u.j.a
239.85830 a.m.u
239.85830 u.j.a
Table 2.1
Jadual 2.1
Nuclear Fusion
Pelakuran Nukleus
Before reaction
After reaction
Sebelum tindak balas
Selepas tindak balas
Equation
Persamaan
Total atomic
mass
Jumlah jisim
atom
5.03013 a.m.u
5.03013 u.j.a
5.01043 a.m.u
5.01043 u.j.a
Table 2.2
Jadual 2.2
a.
What is meant by nuclear energy ?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan tenaga nukleur ?
[1 mark]
4531/2 @SET 2
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
b.
PAPER 2 / SET 2
Using the information given in Table 2.1 and Table 2.2,
Menggunakan maklumat yang diberi dalam Jadual 2.1 dan Jadual 2.2,
i.
compare the total atomic mass of nucleuses before and after the
nuclear fission and nuclear fusion
bandingkan jumlah jisim atom nukleus sebelum dan selepas
tindakan pembelahan nukleus dan pelakuran nukleusi.
......................................................................................................
[2 mark]
ii.
compare the total atomic mass before and after reaction
bandingkan jumlah jisim atom sebelum dan selepas tindak
balas
......................................................................................................
[1 mark]
iii.
compare the number of neutron produce
bandingkan bilangan neutron yang dihasilkan.
......................................................................................................
[1 mark]
c.
State the relationship between lost mass and energy released of nucleus
and number of neutron produced with the energy released.
Nyatakan hubungan antara kehilangan jisim dan tenaga dibebaskan
nukleus dan bilangan neutron yang dihasilkan dengan tenaga yang
dibebaskan
..................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
d.
Based on your answer in 2(b(ii)), explain the relationship between
energy released withlost mass.
Berdasarkan jawapan anda di 2(b(ii)), terangkan hubungan antara
tenaga yang dibebaskan dengan kehilangan jisim.
[2 marks]
4531/2 @SET 2
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
e.
PAPER 2 / SET 2
State the principle involved.
Nyatakan prinsip yang terlibat.
[1 mark]
CONSTRUCT PROBLEM SOLVING / MODIFICATION OF THE PROBLEM
3.
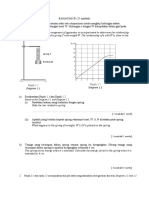
Diagram 3.1 and Diagram 3.2 show a weightlifter is lifting aload of 60 kg
using two differerent method .
Rajah 3.1 dan Rajah 3.2 menunjukkan seorang ahli angkat berat sedang
mengangkat beban seberat 60kg menggunakan dua kaedah yang berlainan.
Diagram 3.1
Rajah 3.1
a.
b.
Diagram 3.2
Rajah 3.2
What is meant by equilibrium state?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan keadaan keseimbangan ?
..............................................................................................................
[1 mark]
What is the weight of the load ?
Berapakah berat beban ?
...............................................................................................................
[1 marks]
4531/2 @SET 2
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
c.
PAPER 2 / SET 2
T1 and T2 are the tensions of the weightlifters arms that act on the load
in Diagram 3.1 and Diagram 3.2 respectively.
T1 dan T2 adalah ketegangan pada lengan ahli angkat berat yang
bertindak ke atas beban dalam Rajah 3.1 dan Rajah 3.2 masingmasing.
i.
In the space below, draw a diagram of the triangle of forces to
determine the value of T1.
[Use the scale 1 cm : 10N]
Pada ruang di bawah, lukis rajah segitiga daya-daya yang
bertindak untuk menentukan nilai T1 .
[Guna skala 1 cm : 10N]
[2 marks]
i.
Determine the value of T2
Tentukan nilai T2
[2 marks]
d.
i.
Based on the answers in 3c(i) and 3c(ii), state the suitable
method to lift the load for a long time.
Berdasarkan jawapan dalam 3c(i) and 3c(ii), nyatakan kaedah
yang sesuai untuk mengangkat beban bagi tempoh masa yang
lama.
......................................................................................................
[1 mark]
ii.
4531/2 @SET 2
Give one reason for your answer in 3d(i).
Beri satu sebab untuk jawapan anda dalam 3d(i).
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
PAPER 2 / SET 2
......................................................................................................
[1 mark ]
f.
If the weightlifter feleased the load, calculate the final velocity of the
load before it touches the surface of the ground.
Jika ahli angkat berat itu melepaskan beban, hitung halaju akhir
beban sejurus sebelum ia menyentuh permukaan bumi.
[ 2 marks ]
CONSTRUCT MAKING DECISION
4.
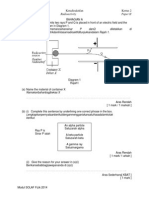
Diagram 4.1 shows two transformers P and Q.
Rajah 4.1 menunjukkan 2 tranformer P dan Q
Diagram 4.1
Rajah 4.1
a.
i..
What is meant by transformer?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan transformer ?
..................................................................................................
[1 mark]
ii.
4531/2 @SET 2
Np
Based on Diagram 4.1, which transformer is a step-up
Np
Ns
transformer?
Ns
240V
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
PAPER 2 / SET 2
Give one reason for your choice.
Berdasarkan Rajah 4.1, yang manakah merupakan transformer
injak naik?
Beri satu sebab atas pilihan anda.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
[ 2 marks ]
b.
Calculate the output voltage of
Hitung voltan output bagi
i.
transformer P
ii.
transformer Q
[ 2 marks ]
b.
The transmission of electricity over the National Grid Network uses
high voltage cables. You are assigned to study the characteristics of
cables which could be used as transmission cable. Table 4.1 shows the
characteristics of three transmission cables.
Penghantaran tenaga elektrik melalui Rangkaian Grid Nasional
menggunakan kabel yang mempunyai voltan yang tinggi. Anda
diminta unuk mengkaji ciri-ciri kabel yang sesuai digunakan sebagai
kabel penghantaran.. Jadual 4.1 menunjukkan ciri-ciri bagi 3 jenis
kabel penghantaran.
Cable
Kabe
l
4531/2 @SET 2
Resistivity
/m-1
Kerintangan
/m-1
Density /
kg m-3
Ketumpatan /
kg m-3
Rate of thermal
expansion
Kadar
pengembangan
termal
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
10
PAPER 2 / SET 2
3.0 x l0-7
5 x l05
High
Tinggi
1.8 x l0-8
2 x l03
Low
Rendah
7.5 x l0-7
8 x l02
Medium
Sederhana
7.0 x l0-8
4 x l03
High
Tinggi
Based on Table 4.1, state the suitable characteristics of the cables to be
used as transmission cable.
Give reason for the suitability of the characteristics.
Berdasarkan Jadual 4.1, nyatakan ciri-ciri kabel yang sesuai untuk
dijadikan kabel penghantaran.
Beri sebab mengapa sifat-sifat itu sesuai.
i.
Resistivity
Kerintangan
.....................................................................................................
Reason
Sebab
.....................................................................................................
[ 2 marks ]
ii.
Density
Ketumpatan
.....................................................................................................
Reason
Sebab
iii.
.....................................................................................................
[ 2 marks ]
Rate of thermal expansion
Kadar pengembangan termal
.....................................................................................................
4531/2 @SET 2
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
11
PAPER 2 / SET 2
Reason
Sebab
.....................................................................................................
[ 2 marks ]
e.
Based on the answers in 4(d), determine the most suitable cable in
Table 4.1 to be used as a transmission cable.
Berdasarkan jawapan di 4(d), tentukan kabel dalam Jadual 4.1 yang
paling sesuai digunakan sebagai kabel penghantaran.
..................................................................................................................
.
[ 1 mark ]
SECTION B
CONSTRUCT KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING
a)
4531/2 @SET 2
Diagram 5.1 shows a ray of light directed perpendicularly at a side
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
12
PAPER 2 / SET 2
of the semi circular glass block. The ray passes through the glass
block to a point O before leaving the glass block. The angle of
incidence in the glass block is 30 .
Rajah 5.1 menunjukkan satu bongkah kaca semi bulatan. Satu sinar
cahaya ditujukan secara tegak ke suatu sisi blok kaca itu. Sinar itu
kemudiannya memasuki bongkah kaca itu dan menuju ke titik O
sebelum keluar semula. Sudut tuju sinar itu di dalam kaca adalah 30.
Diagram 5.1
Rajah 5.1
i)
W
h
a
t
semi circular glass block
blok kaca semi bulatan
is meant by angle of incidence?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan sudut tuju?
[ 1mark]
ii)
Explain how you can produce total internal reflection using the above
set-up diagram?
Terangkan bagaimana anda boleh menghasilkan pantulan dalam
penuh menggunakan rajah di atas?
[4 marks]
CONSTRUCT CONCEPTUALISATION
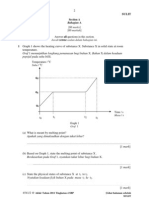
5
b)
4531/2 @SET 2
Diagram 5.2 and Diagram 5.3 show two rectangular glass blocks with
different optical density and refractive index. Ray of light is directed
toward the glass blocks with the same angle of incidence 30.
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
13
PAPER 2 / SET 2
Rajah 5.2 dan Rajah 5.3 menunjukkan dua buah bongkah kaca yang
berlainan ketumpatan dan indeks biasannya. Sinar cahaya ditujukan
kepada kedua-dua bongkah kaca itu dengan sudut tuju 30.
air/udara
air/udara
glass/kacaa
Density = 2600 kgm-3
Ketumpatan = 2600 kgm-3
n = 1.52
glass/kacaa
Density = 2670 kgm-3
ketumpatan = 2670 kgm-3
n = 1.58
Diagram 9.2
Rajah 9.2
Diagram 9.3
Rajah 9.3
Based on Diagram 9.2 and Diagram 9.3,
Berdasarkan Rajah 9.2 dan Rajah 9.3,
(i)
compare the density of the glass blocks.
bandingkan ketumpatan bongkah kaca itu.
(ii)
compare the refractive index of the glass blocks
bandingkan indeks biasan bongkah kaca itu.
(iii)
compare the angle of refraction of the glass blocks
bandingkan sudut tuju pembiasan bongkah kaca itu.
(iii)
relate the angle of refraction, r and the density of the glass
blocks.
hubungkaitkan sudut pembiasan,r dengan ketumpatan blok
kaca.
(iv)
relate the angle of refraction, r and the refractive index of the
glass blocks
hubungkaitkan sudut pembiasan,r dengan indeks biasan kaca.
4531/2 @SET 2
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
14
PAPER 2 / SET 2
[5 marks]
CONSTRUCT PROBLEM SOLVING / MODIFICATION OF THE PROBLEM
5.
(c)
Diagram 5.4 shows a fibre optic.
Rajah 5 .4 menunjukkan gentian optik.
You are
required to give
suggestions to
design a fibre
optics which
can
works efficiently. Using your knowledge on light, and the properties of
material, explain the suggestion based on the following aspects;
Anda diminta untuk memberikan cadangan untuk mereka bentuk satu
gentian optik yang dapat berfungsi dengan cekap. Menggunakan
pengetahuan anda tentang cahaya dan sifat bahan, terangkan
cadangan anda berdasarkan aspek berikut;
(i)
the refractive index of outer and inner layer
indeks biasan lapisan luar dan dalam
(ii)
flexibility
kelenturan
(iii)
strength
kekuatan
(iv)
4531/2 @SET 2
thickness
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
15
PAPER 2 / SET 2
ketebalan
(v)
density of the glass
ketumpatan kaca
CONSTRUCT KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING
6.
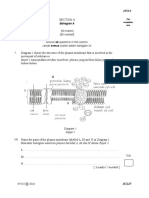
Diagram 6.1 and Diagram 6.2 show a copper wire carrying current is placed in
a permanent magnetic field. The magnetic field produced is called catapult
field.
Rajah 6.1 dan Rajah 6.2 menunjukkan satu dawai kuprum yang membawa
arus diletakkan dalam medan magnet kekal. Medan magnet yang terhasil
dipanggil medan lastik.
galvanometer
Diagram 6.1
Rajah 6.1
(a)
galvanometer
Diagram 6.2
Rajah 6.2
What is meant by catapult field ?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan medan lastik ?
[1 mark]
] (b)
CONSTRUCT CONCEPTUALISATION
6.
(b) Using Diagram 6.1 and Diagram 6.2, compare the number of magnet
used, the angle of deflection of the cooper wire and the angle of
deflection of Galvanometer
Menggunakan Rajah 6.1 dan Rajah 6.2, bandingkan bilangan magnet
yang digunakan, sudut pesongan dawai kuprum dan sudut pesongan
Galvanometer.
[3 marks]
(c)
State the relationship between the strength of the catapult field
produced with
Nyatakan hubungan antara kekuatan medan magnet lastik yang
terhasil dengan
(i)
number of magnet used
bilangan magnet yang digunakan
4531/2 @SET 2
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
(ii)
16
PAPER 2 / SET 2
angle of deflection of copper wire
sudut pesongan dawai kuprum
[2 marks]
CONSTRUCT KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING AND PROBLEM
SOLVING
6
(d)
Diagram 6.3 shows a set up used to study the effects of magnetic field
of a current-carrying copper rod
Rajah 6.3 menunjukkan susunan radas yang digunakan untuk
mengkaji kesan medan magnet terhadap rod kuprum yang membawa
arus elektrik.
(i)
Diagram 6.3
Rajah 6.3
Explain what happens to the copper rod when the switch is turned on.
Terangkan apa yang berlaku kepada rod kuprum apabila suis
dihidupkan.
[2 marks]
(ii)
The dry cells are replaced with 12 V a.c. Explain what happens to
copper rod when the switch is turned on.
Sel bateri ditukarkan dengan 12 V a.u .Terangkan apa yang berlaku
kepada rod kuprum apabila suis dihidupkan.
[2 marks]
(e)
Diagram 6.4 shows a d.c. electric motor .
Rajah 6.4 menunjukkan sebuah motor elektrik a.t.
4531/2 @SET 2
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
17
PAPER 2 / SET 2
Diagram 6.4
Rajah 6.4
(i)
Explain how the motor is able to rotate.
Terangkan bagaimana motor tersebut boleh berputar.
[4 marks]
(ii)
Suggest three modifications that need to be done on the d.c electric
motor to increase the speed of rotation of the motor. Give an
explanation for each suggestion given.
Cadangkan tiga pengubahsuaian yang perlu dilakukan terhadap
motor elektrik a.t itu untuk menambah kelajuan putaran motor
tersebut. Berikan penjelasan untuk setiap cadangan yang diberikan.
[6 marks]
SECTION C
CONSTRUCT KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING
7.
(a)
Archimedes principle states that:
An object that is totally or partially submerged in fluid experiences a
buoyant force equal to the weight of fluid displaced
Prinsip Archimedes menyatakan bahawa:
Object yang terendam separa atau sepenuhnya mengalami daya
apungan yang sama dengan berat bendalir yang tersesar
(i)
What is meant by buoyant force?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan daya apungan?
[1 mark]
4531/2 @SET 2
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
(iii)
18
PAPER 2 / SET 2
Diagram 7.1 shows a wooden block is submerged in a liquid.
Rajah 7.1 menunjukkan satu bongkah terendam di dalam
cecair.
Liquid surface
Permukaan cecair
h1
h2
P1
A
P2
Keys: [Petunjuk:]
h1 : depth of upper surface
kedalaman permukaan atas
h2 : depth of bottom surface
kedalaman permukaan bawah
Diagram 7.1
Rajah 7.1
Using the idea of difference in pressure P1 and P2 for different
depth, h1 and h2 , explain how a buoyant force is produced due
to difference in pressure
Dengan menggunakan idea tekanan yang berbeza, P1 dan P2,
pada kedalaman yang berbeza, h1 dan h2 terangkan
bagaimana suatu daya apungan dihasilkan kerana perbezaan
tekanan.
[ 4 marks ]
CONSTRUCT MAKING DECISION
(b)
Table 7.1 shows four hot air balloons, P, Q, R and S, with different
specifications.
Jadual 7.1 menunjukkan empat belon udara panas, P, Q, R dan S,
dengan spesifikasi yang berbeza
4531/2 @SET 2
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
19
PAPER 2 / SET 2
Size of the parachute and number of burners used.
Saiz payung dan bilangan pemanas yang digunakan.
Material of
parachute
Bahan untuk
payung
Material of
basket
Bahan untuk
bakul
Canvas
Kanvas
Iron
Besi
Parachute
payung
Skirt
Burner
Pemanas
Propane tanks
Tangki propane
4531/2 @SET 2
Basket
Bakul
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
20
PAPER 2 / SET 2
Size of the parachute and number of burners used.
Saiz payung dan bilangan pemanas yang digunakan.
Material of
parachute
Bahan untuk
payung
Material of
basket
Bahan untuk
bakul
Nylon
Nilon
Rattan
Rotan
Parachute
payung
Skirt
Burner
Pemanas
Propane tanks
Tangki propane
4531/2 @SET 2
Basket
Bakul
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
21
PAPER 2 / SET 2
Size of the parachute and number of burners used.
Saiz payung dan bilangan pemanas yang digunakan.
Material of
parachute
Bahan untuk
payung
Material of
basket
Bahan untuk
bakul
Canvas
Kanvas
Iron
Besi
Parachute
payung
Skirt
Burner
Pemanas
Propane tanks
Tangki propane
4531/2 @SET 2
Basket
Bakul
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
22
PAPER 2 / SET 2
Size of the parachute and number of burners used.
Saiz payung dan bilangan pemanas yang digunakan.
Material of
parachute
Bahan untuk
payung
Material of
basket
Bahan untuk
bakul
Nylon
Nilon
Rattan
Rotan
Parachute
payung
Skirt
Burner
Pemanas
Propane tanks
Tangki propane
Basket
Bakul
Table 7.1
Jadual 7.1
You are required to determine the most suitable balloon which can be
used for the construction of a hot air balloon. Study the specifications
of all the four balloons from the following aspects:
Anda dikehendaki untuk menentukan belon yang paling sesuai untuk
digunakan untuk pembinaan sebuah belon udara panas. Kaji
spesifikasi keempat-empat belon berdasarkan aspek-aspek berikut:
4531/2 @SET 2
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
23
PAPER 2 / SET 2
the size of balloons parachute
saiz payung belon
the material of parachute
bahan untuk payung
the number of burner used
bilangan pemanas yang digunakan
the type of basket used to carry the passenger.
jenis bakul yang digunakan untuk mengangkut penumpang.
Explain the suitability of the aspects.
Terangkan kesesuian aspek-aspek itu.
Justify your choice.
Beri sebab bagi pilihan anda.
[ 10 marks ]
(c)
A hot air balloon is tied to the ground. The balloon contains 1200
m3 of hot air of density 0.8 kg m-3. The mass of the balloon (not
including the hot air) is 400 kg . The density of the surrounding air is
1.3 kg m-3.
Sebuah belon udara panas diikat ke tanah. Belon tersebut
mengandungi 1200 m3 udara panas dengan ketumpatan 0.8 kg m-3.
Jisim belon (tidak termasuk udara panas) ialah 400 kg. Ketumpatan
udara di sekitarnya ialah 1.3 kg m-3.
Calculate
Hitung
(i)
the total weight of the balloon and the hot air.
jumlah berat belon dan udara panas.
[ 2 marks ]
(ii)
the buoyant force exerted on the balloon.
daya apungan yang bertindak ke atas belon itu.
[ 1 mark ]
4531/2 @SET 2
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
(iv)
24
PAPER 2 / SET 2
the net force exerted on the ballon when it is released?
daya paduan yang bertindak ke atas belon apabila ia
dilepaskan?
[ 2 marks ]
8.
a)
Diagram 8.1 (a) shows a filament bulb labeled 240 V. 80 W.
Diagram 8.1 (b) shows a graph of potential difference against current
for two materials, Y and Z.
One of the materials will be chosen as filament in a bulb.
Rajah 8.1 (a) menunjukkan sebiji mentol berfilamen dilabelkan 240
V, 80 W.
Rajah 8.1 (b) menunjukkan graf beza keupayaan melawan arus bagi
dua bahan, Y dan Z.
Satu bahan yang sesuai akan dipilih sebagai filamen sebiji mentol.
Diagram 8
Rajah 8
(i)
What is meant by 240 V, 80 W?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan 240 V, 80 W?
[1 mark]
(ii)
Based on the graph in Diagram 8.1 (b), compare the resistance of
materials Y and Z.
Berdasarkan graf dalam Rajah 8.1 (b), bandingkan rintangan bahan
Y dan Z.
Choose the more suitable material to use as a filament of the bulb.
Explain your choice.
Pilih bahan yang sesuai untuk dijadikan filamen mentol tersebut.
Terangkan jawapan anda.
4531/2 @SET 2
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
25
PAPER 2 / SET 2
[4 marks]
b)
You are required is to study the characteristics of a material to make a
heating element of a water heater. You are given four choices of
heating elements J, K, L and M. Table 8.1 shows the characteristics of
the four heating elements.
Anda ditugaskan untuk mengkaji ciri-ciri bahan yang digunakan untuk
membuat unsur pemanas bagi pemanas air.. Anda diberikan empat
jenis unsur pemanas J, K, L dan M.. Jadual 8.1 menunjukkan ciri-ciri
logam tersebut.
Heating
Element
Unsur
pemanas
J
K
L
M
The cross
Melting point
sectional area Takat lebur
Luas keratan
rentas
Small
Kecil
Large
Besar
Small
Kecil
Large
Besar
Low
Rendah
Low
Rendah
High
Tinggi
High
Tinggi
Specific Heat
Capacity
Muatan
Haba Tentu
Length
Panjang
High
Tinggi
Low
Rendah
Low
Rendah
Low
Rendah
Long
Panjang
Short
Pendek
Long
Panjang
Short
Pendek
Table 8.1
Jadual 8.1
Determine the most suitable heating element. Study the specifications
of all the four metals based on the following aspects.
keempat-
Tentukan unsur pemanas yang paling sesuai. Kaji spesifikasi
empat logam itu berdasarkan aspek yang berikut;
-
The cross sectional area
Luas keratan rentas
Melting point
Takat lebur
Specific Heat Capacity
Muatan haba tentu
4531/2 @SET 2
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
26
PAPER 2 / SET 2
Length of the heating element
Panjang unsur pemanas
[10 marks]
(c)
Three resistors with resistance 1 , 2 , and 3 respectively are
connected to 6 V battery as shown in Diagram 8.2.
Tiga perintang 1 , 2 , dan 3 disambungkan kepada bateri 6 V
seperti dalam Rajah 8.2.
Diagram 8.2
Rajah 8.2
Based on Diagram 8.2
Berdasarkan Rajah 8.2
Calculate
Hitung
(i)
Effective resistance
Rintangan berkesan
(ii)
Power dissipated by 2 resistor
Kuasa yang lesapkan oleh perintang 2
[5 marks]
THE END
SKEMA
4531/2 @SET 2
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
NO
4531/2 @SET 2
27
SCHEMA
PAPER 2 / SET 2
MARK
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
1a
28
PAPER 2 / SET 2
The ability of the instrument to detect any small changes by
giving a big change in the measurement
1M
1 b (i)
D 5.1 is more sensitive
1M
1 b(ii)
D 5.1 is more accurate
1M
1c
1 d (i)
The more sensitive, the more accurate of the reading
6.6 3.6 // 3.0 cm (with unit)
1M
1 d (ii)
3.0 / 5 (accept ecf d(i) ) ......................1
= 0.6 cm (with unit) ............................. 1
2M
Diagram 5.3
1M
1e
TOTAL MARK
2a
1M
8M
The energy produce due to the lost of mass (mass defect)
during the radioactivity process
1M
Size of nucleuses of the nuclear fission is bigger before
reaction and size of nucleuses of the nuclear fusion is smaller
before reaction // vice versa
1M
2 b(ii)
For both reaction, the total atomic mass is decreasing after
reaction
1M
2 b(iii)
Nuclear Fission produce more neutrons // Nuclear fission
produce 2 neutrons and Nuclear fusion produce 1 neutron
1M
2c
When the size of nucleus is big and number of neutron
produced is big, the energy released is big // vice versa
1M
2d
Mass defect during reaction is change to energy // E = mc2 ...1
Energy released is directly proportional to mass defect ...........1
Einsteins theory / or statements
2 b(i)
2e
TOTAL MARK
3a
3b
Net force is zero
{ WRONG CONCEPT : no net force )
W = mg = 60 x 10 // 600 N
{ WRONG CONCEPT : 60 kg = 600 N )
Segitiga
4531/2 @SET 2
2M
1M
8M
1M
1M
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
29
PAPER 2 / SET 2
betul .................. 1
Jawapan betul ................. 1
3 c (i)
Julat jawapan : 330 N - 350 N
2M
3 c(ii)
2T2 = W // 2T2 = 600 ............................. 1
T2 = 300 N ( with unit ) .............................. 1
2M
3d(i)
Method in Diagram 7.2 ,
1M
3 d(ii)
tension is lower
1M
3e
mv2 = mgh
V2 = 2 gh
= 2 x 10 x 2 ............................................... 1
= 40
V = 6.32 ms-1 .............................................. 1
2M
TOTAL MARK
4 a(i)
A transformer is a device that steps up or steps down the voltage of
an alternating current.
4a(ii)
Transformer Q
1M
..................................................... 1
2M
Ns > Np ................................................................
4 b (i)
Vs = Ns Vp =
Np
4b (ii)
Vs =
4 c (i)
10 M
500 x 240 // 60 V
2000
1000 x 110
500
//
220 V
Low resistivity .......................................... 1
To reduce heat loss in the cables ................ 1
4531/2 @SET 2
1M
1M
2M
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
30
PAPER 2 / SET 2
4 c (ii)
Low density
................................... 1
The cables will be lighter // easy to carry ................. 1
4 c (iii)
Low rate of thermal expansion .............................. 1
The cables will not expand under hot weather ....... 1
Cable Q
4d
TOTAL MARK
2M
2M
1M
12 M
SECTION B
5(a)
(i)
(ii)
Angle between incident ray and normal line
(b)
Increase the angle of incidence,i, then angle of
refraction,r will also increase
Keep on increasing the angle of incidence until
angle of refraction is 90
The angle of incidence is called critical angle
Increase the angle of of incidence more than the
critical angle
The ray will be reflected.
Suggestion
Explanation
Userefractive
index
of
outer
So that
total internal
Density diagram 5.2 < density
diagram
5.3
layer is less than the
reflection can happen in the
Refractive index 5.2 < Refractive index 5.3
refractive index of outer
fiber optic.
Angle
of
refraction
in
diagram
5.2 > angle of
layer
refraction
in diagram
Use high
flexibility
material5.3 so that it can be bend
The higher
the density thedo
smaller
the angle
Usestrong
material
not break
easily of
refraction
Use thin material
Lighter // can be use in
The higher the refractive index
small the
areasmaller the angle
of refraction.
Low density
material
Lighter
1
1
1
1
1
1
4/5
1
1
1
1
1
(c)
10
6(a)
4531/2 @SET 2
Total
A resultant field due to the combination of the magnetic
field due to the current in the conductor and external
20
1
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
31
PAPER 2 / SET 2
magnetic field // Diagram
(b)
M1
M2
Number of turns in D6.2 is bigger
angle of deflection of the ammeter indicator in D6.2
is bigger
the reading of spring balance in D6.2 is smaller
as current flows is bigger, force acting upwards is
bigger
the reading of spring balance is smaller as ,the force
upwards that act on the coils is bigger
1
1
M1
M2
M1
M2
Force acting on the cooper rod
moved the cooper rod towards the magnet
the cooper rod vibrates
as current change direction
1
1
1
1
M1
When the current flow into the coil, magnetic field
is produced.
And forces are produced
Catapult field is produced
The forces are in the opposite direction
These pair of forces produce the turning effect on
the coil.
Increase the strength of magnet / add more magnet
increase the strength of magnetic field
Increase the number of turns in the coils
to increase the magnitude of force
Increase the magnitude of current
to increase the magnitude of force / increase the
strength of magnetic field
1
1
1
1
1
1
M3
M4
M5
(c)
(i)
(ii)
(d)
(i)
M2
M3
M4
(ii)
M1
M2
M3
M4
M5
M6
Total
1
1
1
20
SECTION C
4531/2 @SET 2
1
1
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
No.
PAPER 2 / SET 2
Marking Criteria/Answers
11.(a)
(i)
(ii)
32
An upwards force on an object placed in a liquid which comes from
the liquid itself and makes the object appear to lose weight.
P = hg
The pressure
difference in the
fluid = P2 - P1 =
h2g - h1g
P = F/A, A =
area of the object (bottom and top)
The difference between the two forces (at bottom and top)
=
P2A - P1A
=
A(P2 - P1)
=
A g(h2 - h1)
Buoyant force
=
V g
=
mg = weight of the fluid displaced
(m = V; volume of the object = volume of the liquid displaced)
Marks
1
1
1
1
PARACHUTE CONSTRUCT FROM NYLON
(b)
Lightweight material //
Reduce the total weight of the balloon. Resultant force is bigger. Lift up
the balloon higher //
Strong, not easily torn, can withstand the strong winds which could
easily wreck the balloon.
Mana-mana satu
1
BALLOON SHOULD BE LARGE SIZE
1
Displace more volume of air //
Weight of air displaced is greater //
To create sufficient buoyant force. Lift up the balloon higher.
Mana-mana satu
USE TWO BURNERS
To warm up the air in the balloon quickly //
4531/2 @SET 2
1
1
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
33
PAPER 2 / SET 2
To keep the balloon rising
Mana-mana satu
1
THE BASKET MUST BE MADE OF RATTAN
1
Light and flexible/safe material //
To stop the balloon gradually AND minimizing the impact //
Prolong the collision time between basket and ground// reduce
impulsive force when basket hits the ground
Mana-mana satu
S
Material of envelope is nylon, large size of the envelope, use two burners and
the basket is made of rattan
1
1
1
1
W air
= 0.8 X 1200 X 10 = 9600 N
c) Total weight =
9600 + 4000 = 13 600 N
(i)
Buoyant force =
Net force
1.3 X 1200 X 10
= 15 600 N
= 15 600 N - 13 600 N = 2000 N
1
1
1, 1
1
20
(a)
(i)
(ii)
(b)
4531/2 @SET 2
(i)
240 V, 80 W means the bulb transforms energy of 80 J/s if
connected to 240 V power supply.
1M
M1 : the resistance of metal Z is constant / The resistance of
metal Y is increasing
M2
The suitable material to be used as filament of the bulb is
metal Y
M3
resistance increases as the temperature increases
M4
the higher the resistance the brighter the bulb.
4M
M1 :
M2
M3
M4
M5
M6
M7
M8
The cross-sectional area is small
because it can release more heat/ resistance is higher
Melting point is high
so it cannot be melt easily at high temperature.
the specific heat capacity is low
so it can release heat in a shorter time
length of the heating element is long
it can be shaped as a coil and release more heat.
8M
Modul Cakna Akademik Kelantan
(b)
(c )
(ii)
M1
M2
34
PAPER 2 / SET 2
The best heating element is L
It has a small cross-sectional area, high melting point, low
specific heat capacity and long.
2M
1
1
1
1
1
TOTAL 20
4531/2 @SET 2
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Analisa UPKK SirahDokumen4 halamanAnalisa UPKK Sirahcikguwanismktsl75% (8)
- Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun Sains Tingkatan 2Dokumen14 halamanPeperiksaan Akhir Tahun Sains Tingkatan 2Nurhuda Mitie44% (9)
- Kertas Kerja Penetapan Target Dan Akujanji 2020Dokumen4 halamanKertas Kerja Penetapan Target Dan Akujanji 2020cikguwanismktsl100% (1)
- Kertas Biologi 2Dokumen19 halamanKertas Biologi 2Azilani Bin IshakBelum ada peringkat
- Trial SPM Physics (P2) (Zon Sri Aman, Sarawak)Dokumen32 halamanTrial SPM Physics (P2) (Zon Sri Aman, Sarawak)Ajwad Ghali100% (1)
- P 2 FizikDokumen26 halamanP 2 FizikzaliniBelum ada peringkat
- Elektrik SoalanDokumen25 halamanElektrik SoalanRameshLoganathanBelum ada peringkat
- Fiz 2Dokumen0 halamanFiz 2Balan KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 08 - ElektromagnetDokumen52 halamanBab 08 - ElektromagnetAl Nazuris33% (3)
- Bab 03 Daya TekananDokumen50 halamanBab 03 Daya TekananA. SuhaimiBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 02 - Daya & GerakanDokumen36 halamanBab 02 - Daya & GerakanAl Nazuris100% (4)
- Bab 05 - CahayaDokumen47 halamanBab 05 - CahayaAl Nazuris100% (1)
- Penilaian Kurikulum 1Dokumen13 halamanPenilaian Kurikulum 1Julia AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- KERTAS 2 Percubaan SPM Sains Limbang SarawakDokumen17 halamanKERTAS 2 Percubaan SPM Sains Limbang SarawakNurul Syahira RaduanBelum ada peringkat
- Sains tg5Dokumen20 halamanSains tg5cikguana79Belum ada peringkat
- Kertas Peperiksaan Fizik Pertengahan Tahun Tingkatan 4 2013Dokumen19 halamanKertas Peperiksaan Fizik Pertengahan Tahun Tingkatan 4 2013suzanaliza101Belum ada peringkat
- Kertas 2 Set 2 Soalan Kbat Kinta SelatanDokumen15 halamanKertas 2 Set 2 Soalan Kbat Kinta SelatanYvonne ChuaBelum ada peringkat
- Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun SBP 2011 Ting 4 Chemistry Paper 2 - QuestionsDokumen22 halamanPeperiksaan Akhir Tahun SBP 2011 Ting 4 Chemistry Paper 2 - Questionsnurul atiqah100% (1)
- Kertas 2Dokumen26 halamanKertas 2hidayah170% (1)
- Pat F4 P2 2018Dokumen27 halamanPat F4 P2 2018Jue MayaBelum ada peringkat
- Percubaan SPM FizikDokumen32 halamanPercubaan SPM Fizikhahilsum0% (2)
- Module PhysicsDokumen16 halamanModule PhysicszaliniBelum ada peringkat
- Section ADokumen19 halamanSection ANOR JAMALIAH BINTI MOHAMAD TARMIZI MoeBelum ada peringkat
- Mbahagian ADokumen19 halamanMbahagian ANOR JAMALIAH BINTI MOHAMAD TARMIZI MoeBelum ada peringkat
- PPTK 2 BioDokumen17 halamanPPTK 2 Biocikguana79Belum ada peringkat
- Bab 02 - Daya & GerakanDokumen46 halamanBab 02 - Daya & GerakanAl Nazuris100% (4)
- Daya-Tekanan Edit PelajarDokumen36 halamanDaya-Tekanan Edit PelajarA. SuhaimiBelum ada peringkat
- Physics A+ ScorerDokumen42 halamanPhysics A+ ScorerKhairun AfrihahBelum ada peringkat
- Keradioaktifan SoalanDokumen19 halamanKeradioaktifan SoalanIlya IsmailBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Paper 2 SPM Perak 2011Dokumen26 halamanPhysics Paper 2 SPM Perak 2011Raymond Cheang Chee-CheongBelum ada peringkat
- 5 459822407050330116Dokumen24 halaman5 459822407050330116puvanesvaranBelum ada peringkat
- Daya Dan Gerakan - SoalanDokumen16 halamanDaya Dan Gerakan - SoalanFaezah Shamsudin100% (2)
- Bab 03 Daya Tekanan Edit PelajarDokumen38 halamanBab 03 Daya Tekanan Edit PelajarA. SuhaimiBelum ada peringkat
- Peperiksaan Pertengahan TahunDokumen9 halamanPeperiksaan Pertengahan TahunNorazah Zainal AbidinBelum ada peringkat
- F4 Physics Final Exam Paper 2 2013Dokumen30 halamanF4 Physics Final Exam Paper 2 2013MadAm JaJaBelum ada peringkat
- PAPER 2-Sc F4 (Final Exam)Dokumen17 halamanPAPER 2-Sc F4 (Final Exam)Yatie JaafarBelum ada peringkat
- Sains Paper 2 Form 5Dokumen19 halamanSains Paper 2 Form 5Bbiesoth AJBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 03 - Daya & TekananDokumen51 halamanBab 03 - Daya & TekananAl Nazuris67% (3)
- Daya Dan Gerakan - SoalanDokumen16 halamanDaya Dan Gerakan - SoalanzhuzaiBelum ada peringkat
- Mid Term-Paper 2Dokumen17 halamanMid Term-Paper 2Siti MaisarahBelum ada peringkat
- Paper2 PPT FZK Smks7Dokumen25 halamanPaper2 PPT FZK Smks7Azzu Adni AzaharuddinBelum ada peringkat
- TRIAL2Dokumen21 halamanTRIAL2Palidah BasinauBelum ada peringkat
- Lapkhir Parabola Revisi 2Dokumen27 halamanLapkhir Parabola Revisi 2aldyhidayahh46Belum ada peringkat
- Ujian Sains Januari 2022Dokumen15 halamanUjian Sains Januari 2022Subba KanesenBelum ada peringkat
- 15 Kelantan p2Dokumen31 halaman15 Kelantan p2Nadia Saidon50% (2)
- Section 1Dokumen9 halamanSection 1Ir Fik TBelum ada peringkat
- BAHAGIAN B-Tov 1Dokumen6 halamanBAHAGIAN B-Tov 1Mohammad Haidil MisiranBelum ada peringkat
- Daya Dan Gerakan - SoalanDokumen8 halamanDaya Dan Gerakan - SoalanChrise RajBelum ada peringkat
- Kertas 2Dokumen19 halamanKertas 2pinkyoya86Belum ada peringkat
- Percubaan Biologi 2016 (k2) - 1Dokumen19 halamanPercubaan Biologi 2016 (k2) - 1Ferguson TehBelum ada peringkat
- Teknik Menjawab Kertas 2 Kimia SPMDokumen23 halamanTeknik Menjawab Kertas 2 Kimia SPMAzie Nurul AkhtarBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 04 Haba PDFDokumen26 halamanBab 04 Haba PDFDequeNo Mohd NoorBelum ada peringkat
- Sumatif Sains f2Dokumen10 halamanSumatif Sains f2Shazlynn Taib100% (1)
- Percubaan SPM 2013Dokumen19 halamanPercubaan SPM 2013AqishAthiraBelum ada peringkat
- Kertas 3 Pep Pertengahan Tahun MPP2 Terengganu 2020 - Soalan-1Dokumen15 halamanKertas 3 Pep Pertengahan Tahun MPP2 Terengganu 2020 - Soalan-1ARIF AHMAD BIN SIDIK KPM-GuruBelum ada peringkat
- Soalan Struktur Spring Dan ElektronikDokumen5 halamanSoalan Struktur Spring Dan Elektronikleelee1127Belum ada peringkat
- Laporan PKLI AndreDokumen53 halamanLaporan PKLI AndreandreBelum ada peringkat
- Soalan Kertas 2Dokumen25 halamanSoalan Kertas 2Khalil AzizBelum ada peringkat
- Fizik Kertas 2 KBAT 2016Dokumen25 halamanFizik Kertas 2 KBAT 2016Tan Teik SoonBelum ada peringkat
- Sains SPM Latihan AsasDokumen14 halamanSains SPM Latihan AsascikguwanismktslBelum ada peringkat
- MINGGU 29 Ujian OnlineDokumen3 halamanMINGGU 29 Ujian OnlinecikguwanismktslBelum ada peringkat
- Perancangan Program Panitia Perniagaan 2019Dokumen1 halamanPerancangan Program Panitia Perniagaan 2019cikguwanismktsl100% (4)
- Teknik Menjawab Sains SPMDokumen41 halamanTeknik Menjawab Sains SPMcikguwanismktslBelum ada peringkat
- Sijil Penghargaan AJK PIBGDokumen1 halamanSijil Penghargaan AJK PIBGcikguwanismktslBelum ada peringkat
- Pk06 1 Laporan Semakan Hasil Kerja MuridDokumen1 halamanPk06 1 Laporan Semakan Hasil Kerja MuridcikguwanismktslBelum ada peringkat
- SubjektifDokumen9 halamanSubjektifcikguwanismktslBelum ada peringkat
- Langkah - Langkah Eksperimen Ujian KanjiDokumen6 halamanLangkah - Langkah Eksperimen Ujian KanjicikguwanismktslBelum ada peringkat
- Ekonomi AsasDokumen17 halamanEkonomi AsascikguwanismktslBelum ada peringkat
- Latihan Eksperimen Ujian Kehadiran KanjiDokumen1 halamanLatihan Eksperimen Ujian Kehadiran Kanjicikguwanismktsl100% (2)
- Documents - Tips Soalan Ujian PJK Tingkatan 1Dokumen10 halamanDocuments - Tips Soalan Ujian PJK Tingkatan 1cikguwanismktslBelum ada peringkat
- Pk03 1 Borangpenghantaran Buku Persediaan MengajarDokumen1 halamanPk03 1 Borangpenghantaran Buku Persediaan MengajarcikguwanismktslBelum ada peringkat