Pengantar Kristalografi
Diunggah oleh
Putri Rafika DewiHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Pengantar Kristalografi
Diunggah oleh
Putri Rafika DewiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
I.
Pengantar Kristalografi
Lattice kisi kristal
Motif
Crystal structure struktur kristal
Unit cell
Fractional coordinates fraksi
koordinat
Coordination number bilangan
koordinasi
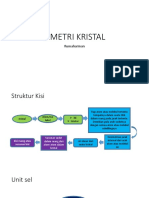
Kisi dan Unit sel
Setiap kristal diturunkan dari building
block dasar yang berulang ke segala
arah
Building block ini dikenal sebagai
unit sel.
Garis dari disebut lattice / kisi dan setiap lattice point ( )
harus dikelilingi oleh sistem yang identik motif
Dimensi Unit sel
a, b dan c : panjang dari sisi unit sel
, and : sudut antara 2 sisi (a dengan
b, a dengan b, b dengan c, dll....)
Fraksi koordinat atomik
Posisi satu atom dalam unit sel biasanya digambarkan
dengan fraksi koordinat
x x a paralel a
y x b paralel b
z x c paralel c
Fraksi koordinat (x, y, z).
2D LATTICES
contoh pola heksagonal dari lapisan tunggal pda GRAFIT
1926: Goldschmidt mengusulkan atom-atom dapat
dianggap terususun dalam padatan itu sebagai bola-bola
Close packing of Spheres
Close packing of Spheres
Menghitung atom dalam unit sel 3D
FRAKSI ATOM YANG MENEMPATI SATU UNIT SEL
UNTUK BEBERAPA POSISI DALAM UNIT SEL
(PUSAT)
(MUKA)
(TEPI)
(SUDUT)
Menghitung atom dalam unit sel 3D
Tipe penyusunan atom pada
logam-logam
II. Pengantar ion koordinasi
Bilangan Koordinasi (CN): Jumlah ion atau atom yang
langsung mengelilingi atom pusat
bergantung pada ukuran relatif dari sutu ion.
Bilangan koordinasi pada struktur padat terjejal (Close
Packed structures)
hcp 12
ccp 12
bcc 8
sc / pc 6
CN
Ion koordinasi
Bilangan koordinasi (C.N) bergantung pada ukuran relatif
ion. Bila semua atom dalam suatu kirstal berukuran sama,
maka terdapat 2 cara untuk menyusun atom-atom dalam
struktur kristal. Dalam hal ini, jumlah atom maksimum yang
terkoordinasi pada setiap atom adalah 12, sehingga disebut
koordinasi kelipatan-12.
Terdapat 2 cara atom-atom disusun dalam koordinasi-12. :
heksagonal terjejal dan kubus terjejal.
Rule 1
Around every cation, a coordination polyhedron of anions forms, in which
the cation-anion distance is determined by the radius sums and the
coordination number is determined by the radius ratio.
Rule 2, The Electrostatic Valency Principle
An ionic structure will be stable to the extent that the sum of the strengths
of the electrostatic bonds that reach an ion equal the charge on that ion.
In order to understand this rule we must first define electrostatic valency, e.v.
e.v = Charge on the ion/C.N.
Rule 3
Shared edges, and particularly faces of two anion polyhedra in a crystal
structure decreases its stability.
Rule 4
In a crystal structure containing several cations, those of high valency
and small coordination number tend not to share polyhedral elements
Rule 5, The Principle of Parsimony
The number of different kinds of constituents in a crystal tends to be
small.
Paulings Rules
A
A
B
A
B
A
B
C
CN = 8, 8-fold, kubus
CN=6, 6-fold, OKTAHEDRAL
CN = 4, 4-fold, TETRAHEDRAL
Hukum Pauling
1. Lingkungan di sekitar polihedron dipengaruhi oleh jarak ikatan
kation-anion dan CN
2. Hubungan antara ikatan valensi dan bilangan oksidasi
Struktur ionik akan stabil sampai batas di mana jumlah dri
kekutan ikatan elektrostatik yang mencapai ion setara dengan
muatan dari ion tersebut
Untuk itu kita harus memahami: valensi elektrostatis (e.v.)
e.v = Charge on the ion/C.N
3. Sudut (corner), sisi (edge) dan muka (face) sharing polyhedra
Sharing polyhedra dengan sisi dan muka akan menurunkan
kestabilan dari kristal gaya tolakan M
n+
M
n+
4. Kation dengan valensi yang besar dan CN yang kecil cenderung
untuk tidak berbagi polihedra
5. Rule of parsimony
Jumlah dri konstituen yang berbeda dalam satu kristal
cenderung kecil/sedikit
e.v = Charge on the ion/C.N
RULE 3
RULE 2
OKTAHEDRAL dalam CP
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- StrukturKristalDokumen78 halamanStrukturKristalYur NalisBelum ada peringkat
- Topik2-Konsep Dasar-2020Dokumen36 halamanTopik2-Konsep Dasar-2020hafidatul wahidahBelum ada peringkat
- Zat PadatDokumen26 halamanZat PadatwandadwilestariBelum ada peringkat
- PPT Kimia Zat PadatDokumen58 halamanPPT Kimia Zat PadatWidi KurniaBelum ada peringkat
- Kimia Zat PadatDokumen6 halamanKimia Zat PadatsaripurwantiBelum ada peringkat
- Kelompok 1Dokumen13 halamanKelompok 1Endang AldillaBelum ada peringkat
- PADATANDokumen27 halamanPADATANI Putu Adi Surya MahardikaBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Pert 4 Fisika Zat Padat - Mitra GeaDokumen7 halamanTugas Pert 4 Fisika Zat Padat - Mitra GeaMitra geaBelum ada peringkat
- STRUKTUR KRISTALDokumen30 halamanSTRUKTUR KRISTALSuci Aulia RahmiBelum ada peringkat
- Rangkuman FZPDokumen9 halamanRangkuman FZPDhea aura nabithaBelum ada peringkat
- Sifat Fis Mol ObatDokumen88 halamanSifat Fis Mol ObatHartini HamsuriBelum ada peringkat
- Zatpadatdanstrukturkristal 091024215227 Phpapp01Dokumen36 halamanZatpadatdanstrukturkristal 091024215227 Phpapp01Ccieychanty TjahmoehiessedjatyBelum ada peringkat
- K1 Struktur KristalDokumen34 halamanK1 Struktur KristalmutiaBelum ada peringkat
- Structure of Metals and AlloysDokumen44 halamanStructure of Metals and AlloysAbuyazid RaisalBelum ada peringkat
- BKPK Pertemuan Ke 5Dokumen37 halamanBKPK Pertemuan Ke 5AufalBelum ada peringkat
- Struktur Krisatal LogamDokumen11 halamanStruktur Krisatal LogamLanBelum ada peringkat
- 00-Silabus Dan PengantarDokumen30 halaman00-Silabus Dan PengantarhaifaniaBelum ada peringkat
- RESUME 1 - Denisa Rizka Maulia - 19033014Dokumen31 halamanRESUME 1 - Denisa Rizka Maulia - 19033014DenisaBelum ada peringkat
- OPTIMALKAN STRUKTUR KRISTALDokumen7 halamanOPTIMALKAN STRUKTUR KRISTALAndrian RianBelum ada peringkat
- Kimia Zat PadatDokumen7 halamanKimia Zat PadatWahidin 'Ibhoot' 'Idin' NuayiBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas 1 RingkasanDokumen10 halamanTugas 1 RingkasanINFONIX infounixBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Struktur Kristal Padat LazuardyDokumen39 halaman2 Struktur Kristal Padat LazuardyPeter Hadirat WaruwuBelum ada peringkat
- Astrid Alfira Noermawati - 20030234024 - Tugas Kimfis LKM MOTDokumen19 halamanAstrid Alfira Noermawati - 20030234024 - Tugas Kimfis LKM MOTAstrid AlfiraBelum ada peringkat
- STRUKTUR DAN BENTUK KRISTALDokumen13 halamanSTRUKTUR DAN BENTUK KRISTALDarisman BaehakiBelum ada peringkat
- Struktur Atom Dan KristalDokumen28 halamanStruktur Atom Dan KristalYohan DesraBelum ada peringkat
- Struktur Kristal PadatDokumen80 halamanStruktur Kristal PadatFatia RahmaniaBelum ada peringkat
- Ikatan RosdaDokumen31 halamanIkatan RosdaAsri Aphil Taiga CholapBelum ada peringkat
- Kristal Ilmu BahanDokumen10 halamanKristal Ilmu BahanAmbar AmKaBelum ada peringkat
- Bab IiiDokumen34 halamanBab IiiRoby SambeyanoBelum ada peringkat
- Kelompok 5 - Struktur KristalDokumen32 halamanKelompok 5 - Struktur KristalriswanBelum ada peringkat
- Amelia Saraswati - 1710121120001 - Kelas A - Tugas Pendahuluan Fisika Zat Padat 2Dokumen20 halamanAmelia Saraswati - 1710121120001 - Kelas A - Tugas Pendahuluan Fisika Zat Padat 2AnggitaBelum ada peringkat
- Struktur KristalDokumen20 halamanStruktur KristalSastra Milanisti E'Md100% (1)
- P1 Struktur KristalDokumen34 halamanP1 Struktur KristalRiri MurniatiBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Rutin Pertemuan 4 - Yuniar Lestari Rangkuti - Pendahuluan Fisika Zat PadatDokumen15 halamanTugas Rutin Pertemuan 4 - Yuniar Lestari Rangkuti - Pendahuluan Fisika Zat PadatYuniar LestariBelum ada peringkat
- F.Zat Padat 3Dokumen40 halamanF.Zat Padat 3Erwan RahmadiBelum ada peringkat
- Fisika Zat PadatDokumen19 halamanFisika Zat PadatSinta Ritari MBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas 1 Struktur Kristal (Asmi Putri)Dokumen25 halamanTugas 1 Struktur Kristal (Asmi Putri)Asmi PutryBelum ada peringkat
- A. KristalografiDokumen60 halamanA. KristalografiLuh Desi Ari SandiBelum ada peringkat
- Struktur KristalDokumen26 halamanStruktur KristalNengah NitrianiBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 1 - Struktur Kristal (Revisi)Dokumen35 halamanBab 1 - Struktur Kristal (Revisi)Shofa UlyanaBelum ada peringkat
- Kelompok 1.PSF 19 A.Fisika Keramik - Makalah 01.struktur Kristal Dan Non-KristalDokumen14 halamanKelompok 1.PSF 19 A.Fisika Keramik - Makalah 01.struktur Kristal Dan Non-KristalJevri Ananda BarusBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Struktur KristalDokumen12 halamanMakalah Struktur KristalMaRiaFaothBelum ada peringkat
- Fis PadatDokumen3 halamanFis PadatWelsy097Belum ada peringkat
- Struktur Kristal 1Dokumen17 halamanStruktur Kristal 1Dedo Prima PutraBelum ada peringkat
- Material TeknikDokumen16 halamanMaterial TeknikFikry ZulfikarBelum ada peringkat
- 5.pertemuan Ke 5kimia Fisika 21Dokumen19 halaman5.pertemuan Ke 5kimia Fisika 21Mansur FirmansahBelum ada peringkat
- Struktur Kristal Dan NonkristalDokumen36 halamanStruktur Kristal Dan NonkristalInayah HaqqiBelum ada peringkat
- IONIK SENYAWADokumen11 halamanIONIK SENYAWASyifaBelum ada peringkat
- Simetri KristalDokumen19 halamanSimetri KristalRumaharman RumaharmanBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 2 - 08306144007Dokumen48 halamanBab 2 - 08306144007ritong_aBelum ada peringkat
- STRUKTUR KRISTALDokumen10 halamanSTRUKTUR KRISTALEndang AldillaBelum ada peringkat
- Struktur KristalDokumen25 halamanStruktur KristalSella sembiringBelum ada peringkat
- Diktat Kristal Zat PadatDokumen11 halamanDiktat Kristal Zat PadatRouli MuntheBelum ada peringkat
- Rangkuman Materi Atomic Bonding (IBE) Ahmad Naufal WaliyyuddinDokumen16 halamanRangkuman Materi Atomic Bonding (IBE) Ahmad Naufal WaliyyuddinAhmad NaufalBelum ada peringkat
- Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)Dokumen21 halamanDiscrete Fourier Transform (DFT)Putri Rafika Dewi50% (2)
- GEOPHONE ALAT PENDETEKSIDokumen2 halamanGEOPHONE ALAT PENDETEKSIPutri Rafika DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Teori SeisfrakDokumen17 halamanTeori SeisfrakPutri Rafika DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem Panas Bumi P. KasbaniDokumen10 halamanSistem Panas Bumi P. KasbanialfirafresdiBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas 2 Jenis Eror, Angka Penting, Akuisisi PresisiDokumen5 halamanTugas 2 Jenis Eror, Angka Penting, Akuisisi PresisiPutri Rafika DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Batuan SedimenDokumen42 halamanBatuan SedimenNovi Maha PutraBelum ada peringkat
- Umur HidrotermalDokumen3 halamanUmur HidrotermalPutri Rafika DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas 1 Bahasa PemrogramanDokumen9 halamanTugas 1 Bahasa PemrogramanPutri Rafika DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Modul 1 (Rangkaian Setara Thevenin-Norton Dan Tapis (Filter) )Dokumen9 halamanModul 1 (Rangkaian Setara Thevenin-Norton Dan Tapis (Filter) )Putri Rafika DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Latihan Petrologi 2012Dokumen1 halamanLatihan Petrologi 2012Hasan Arif EfendiBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan MODUL 2Dokumen5 halamanLaporan MODUL 2Putri Rafika DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Metode GeofisikaDokumen4 halamanMetode GeofisikaGilang Norman RizesaBelum ada peringkat
- BatuanDokumen57 halamanBatuanPutri Rafika DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Tekstur BatuanDokumen3 halamanTekstur BatuanPutri Rafika DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Mineral OgiDokumen11 halamanMineral OgiPutri Rafika DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Lirik LaguDokumen4 halamanLirik LaguPutri Rafika DewiBelum ada peringkat
- SESARDokumen14 halamanSESARPutri Rafika DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Fraksi Minyak BumiDokumen11 halamanFraksi Minyak BumiFanny NoviaBelum ada peringkat
- Kamus MeteorologiDokumen92 halamanKamus MeteorologiPutri Rafika Dewi100% (1)