Serumen Prop
Diunggah oleh
dedefreddyDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Serumen Prop
Diunggah oleh
dedefreddyHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Serumen Prop
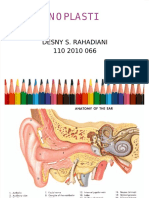
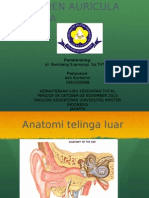
Defenisi Serumen
Serumen adalah hasil produksi kelenjar sebasea, kelenjar seruminosa, epitel kulit yang
terlepas dan partikel debu.
Dalam Keadaan normal serumen terdapat di sepertiga luar linag telinga karena
kelenjar tersebut banyak terdapat pada daerah ini.
Konsistensinya biasa ludang tetapi terkadang kering dan dipengaruhi oleh faktor
keturunan, iklim, usia, dan keadaan lingkungan.
Serumen dapat keluar sendiri dari liang telinga akibat migrasi epitel kulit yang
bergerak dari arah membran timpani menuju ke luar serta dibantu oleh gerakan rahang
sewaktu mengunyah.
Fungsi Serumen :
Sebagai proteksi yaitu dengan mengikat kotoran, menyebarkan aroma yang
tidak disenangi serangga sehingga serangga tidak masuk ke liang telinga.
sarana pengangkut debris epitel dan komtaminan untuk dikelurkan dari
membran timpani.
Pelumas dan mencegah kekeringan dan pembentukan fisura pada epidermis.
Faktor-faktor yang dapat menyebabkan serumen terkumpul dan mengeras
diliang telinga :
1. Dermatitis kronik liang telinga luar
!. "iang telinga sempit
#. Produksi serumen banyak dan kental
$. %danya benda asing di liang telinga
&. %danya eksostosis liang telinga
'. Serumen terdorong oleh jari tangan atau ujung handuk setelah mandi atau
kebiasaan mengorek telinga
Serumen dapat dibersihkan dengan konsistensinya.
Serumen "embek dapat menggunakan kapas yang dililitkan pada pelilit kapas.
Serumen yang keras dapat dikeluarkan dengan pengait atau kuret.
%pabila kedua cara ini tidak dapat mengeluarkan serumen maka dapat
dilunakkan lebih dahulu menggunakan tetes karbolgliserin 1() selama # hari.
Serumen yang sudah terlalu jauh terdorong ke dalam liang telinga dapat
dikeluarkan dengan mengalirkan air hangat sesuai suhu tubuh.
Indications
*erumen in the e+ternal ear canal is physiological. ,ndications to address the cerumen
include the following-$. :
Difficulty in e+amining the full tympanic membrane
/titis e+terna
0a+ occlusion of the e+ternal ear canal
%s part of the workup for conducti1e hearing loss
Prior to taking the impression for hearing aid fitting
Suspected e+ternal ear canal or middle ear cholesteatoma
Suspected e+ternal ear canal pathology such as s2uamous cell carcinoma or
ec3ema
%s part of the follow4up to canal wall down mastoidectomy
%s part of grommet insertion or middle ear surgery 5preoperati1ely or
perioperati1ely
Patient re2uest
Contraindications
Specific contraindications e+ist for each specific procedure. ,ndi1idual assessment
should dictate which techni2ue is the most appropriate.
*ontraindications to irrigation include the presence or history of a perforated
tympanic membrane, pre1ious pain on irrigation, or pre1ious surgery to the
middle ear.
% relati1e contraindication to probing is the inability to 1isuali3e the ear canal.
6elati1e contraindications to microsuction are se1ere pre1ious e+acerbation of
tinnitus, 1ery hard cerumen, and an uncooperati1e patient.
7+ceptional caution has to be used when clearing cerumen in patients who
ha1e undergone a mastoidectomy in the past, during which sensiti1e
anatomical structures like the facial ner1e and semicircular canals may ha1e
been e+posed.
Preparation and visual assessment
%ssemble and prepare all necessary e2uipment.
8ake time to e+plain the procedure to the patient and obtain consent.
*onnect suction tip and turn on the suction machine and microscope light.
Position the patient9s head facing away from the operator, the neck fle+ed
laterally and the shoulder pulled down.
7+amine the pinna, outer portions of the e+ternal canal, and the adjacent scalp
for any e1idence of pre1ious surgery incision scars, signs of infection, or
discharge.
,nspect the outer ear canal opening, using the appropriate aural
o 8he speculum should be the largest si3e that fits. ,t should be placed
deep enough to clear the hair4bearing skin but not deeper, as
unnecessary pain may result.
o 8he speculum should be held with the first and second fingers. :se the
other fingers to retract the pinna up and backward in an adult 5retract
the pinna up and downward in a child.
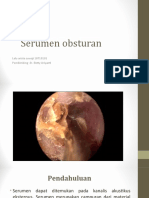
%ssess the cerumen. ;ently probe with a blunt instrument such as <obson
=orne curette to determine whether the cerumen is soft, hard, or bony hard.
%ssess whether tympanic membrane is 1isible. "ook for any air spaces around
the cerumen.
>efore beginning the cerumen remo1al, ensure that the microscope and
operator are optimally positioned. 8he microscope should be positioned to
pro1ide the optimal 1iew of the ear canal, and the operator should be sitting
comfortably and with a straight back.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Laporan Kasus THTDokumen37 halamanLaporan Kasus THTYudi HandokoBelum ada peringkat
- SOP Pemeriksaan Fisik TelingaDokumen5 halamanSOP Pemeriksaan Fisik TelingaOndi SupriadiBelum ada peringkat
- Kelainan Liang TelingaDokumen12 halamanKelainan Liang TelingahandayaniarifinBelum ada peringkat
- Refleksi Kasus THTDokumen12 halamanRefleksi Kasus THTRaafika Studiviani Dwi BinukoBelum ada peringkat
- Ekstraksi Serumen Dan Corpal NewDokumen12 halamanEkstraksi Serumen Dan Corpal NewismailyBelum ada peringkat
- Penatalaksanaan SerumenDokumen20 halamanPenatalaksanaan SerumenSebastian AoBelum ada peringkat
- Serumen BpjsDokumen20 halamanSerumen BpjsnovritasariBelum ada peringkat
- SerumenDokumen20 halamanSerumenAvee K-tsukiBelum ada peringkat
- CRS Arif Serumen PropDokumen18 halamanCRS Arif Serumen PropdokterbotakBelum ada peringkat
- Pemeriksaan Membran TimpaniDokumen3 halamanPemeriksaan Membran TimpaniAnita Purnama SariBelum ada peringkat
- THT KLDokumen112 halamanTHT KLErliana Tantri HarsonoBelum ada peringkat
- Reinhart Fikram Imam AkbarDokumen28 halamanReinhart Fikram Imam AkbarFikram Imam AkbarBelum ada peringkat
- Serumen Obsturan & Benda Asing Di TelingaDokumen18 halamanSerumen Obsturan & Benda Asing Di Telingapithoweety86Belum ada peringkat
- PF THTDokumen33 halamanPF THTEvita ZevanyaBelum ada peringkat
- TimpanoplastiDokumen25 halamanTimpanoplastiArdian PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Irigasi TelingaDokumen11 halamanIrigasi TelingaNovia SafitriBelum ada peringkat
- LP Poli THT - Serumen ObturansDokumen10 halamanLP Poli THT - Serumen ObturansGyta ApriatiBelum ada peringkat
- LP Corpal MaeDokumen13 halamanLP Corpal MaeWinda ShifaAkindaBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Ekstraksi SerumenDokumen4 halamanTugas Ekstraksi SerumenSibang HoreBelum ada peringkat
- SkillDokumen56 halamanSkillnia krisnaBelum ada peringkat
- Refleksi Kasus THTDokumen15 halamanRefleksi Kasus THTShafira VidiastriBelum ada peringkat
- LP Impaksi SerumenDokumen8 halamanLP Impaksi Serumenviny dwi wahyuniBelum ada peringkat
- Serumen Auricula Dextra (Case Report)Dokumen38 halamanSerumen Auricula Dextra (Case Report)Adli NurfakhriBelum ada peringkat
- Limfadenopati Leher Level 2Dokumen28 halamanLimfadenopati Leher Level 2Lia PraBelum ada peringkat
- 02 MODUL PRAKTIKUM Flebotomi Dan Pengelolaan Spesimen (Gaby)Dokumen6 halaman02 MODUL PRAKTIKUM Flebotomi Dan Pengelolaan Spesimen (Gaby)Restu KristianzegaBelum ada peringkat
- Timpanoplasti PPT Referat DesnyDokumen25 halamanTimpanoplasti PPT Referat DesnyYazAuliaBelum ada peringkat
- Patofisiologi Telinga EKADokumen61 halamanPatofisiologi Telinga EKAfauziacitraBelum ada peringkat
- Arifaa Thalita Zuleikha - PENGELUARAN BENDA ASING HIDUNG DAN TELINGADokumen14 halamanArifaa Thalita Zuleikha - PENGELUARAN BENDA ASING HIDUNG DAN TELINGAPIXLS idBelum ada peringkat
- Serumen PropDokumen4 halamanSerumen PropSyaffira SalsabilaBelum ada peringkat
- TIMPANOPLASTIDokumen14 halamanTIMPANOPLASTIwhy1328Belum ada peringkat
- Cerumen ImpactDokumen24 halamanCerumen ImpactTiti PrAtiwiBelum ada peringkat
- Pengeluaran Benda Asing Di TelingaDokumen10 halamanPengeluaran Benda Asing Di TelingaMuhamad IkhsanBelum ada peringkat
- Cara Membersihkan SerumenDokumen16 halamanCara Membersihkan SerumenNely M. RosyidiBelum ada peringkat
- Kelainan Telinga LuarDokumen32 halamanKelainan Telinga LuarMuhamad AgungBelum ada peringkat
- Sop Irigasi TelingaDokumen4 halamanSop Irigasi TelingaDa Si OBelum ada peringkat
- Presus Serumen SuryaDokumen8 halamanPresus Serumen SuryaHermawan Surya DharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Aural Hematoma (Othematoma) Pada Anjing A5Dokumen13 halamanAural Hematoma (Othematoma) Pada Anjing A5Chandra Kefi AmtiranBelum ada peringkat
- Serumen Imfaksi ArmanDokumen2 halamanSerumen Imfaksi Armanrisfa indrisefaniBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Serumen Prop SusanDokumen3 halaman1 Serumen Prop SusansusanBelum ada peringkat
- InterpretasiDokumen5 halamanInterpretasicaplangcloudBelum ada peringkat
- 3.2.1 SOP Pemeriksaan Fisik TelingaDokumen4 halaman3.2.1 SOP Pemeriksaan Fisik TelingaYulia AyaBelum ada peringkat
- Irigasi TelingaDokumen3 halamanIrigasi TelingaagusBelum ada peringkat
- CerumenDokumen2 halamanCerumenadityaBelum ada peringkat
- Presentasi Serumen ObsturanDokumen31 halamanPresentasi Serumen Obsturanarista suwajiBelum ada peringkat
- LP Irigasi TelingaDokumen8 halamanLP Irigasi TelingaNurulBelum ada peringkat
- Sop Hiygine TelingaDokumen4 halamanSop Hiygine Telingaweniandryani100% (1)
- Laporan Pendahuluan Impaksi SerumenDokumen7 halamanLaporan Pendahuluan Impaksi SerumenRirind100% (1)
- Penyakit Pada TelingaDokumen23 halamanPenyakit Pada TelingaBhismo PrasetyoBelum ada peringkat
- Sop TelingaDokumen3 halamanSop TelingaVeraNitaBelum ada peringkat
- Serumen PropDokumen6 halamanSerumen PropCarolina Sidabutar100% (1)
- Trauma TelingaDokumen10 halamanTrauma TelingaCut Risna WatiBelum ada peringkat
- Pemeriksaan Fisik THTDokumen11 halamanPemeriksaan Fisik THTNurul HidayahBelum ada peringkat
- Kuliah THTDokumen58 halamanKuliah THTTuan Muda TunggulBelum ada peringkat
- Case Otitis Eksterna - UtiDokumen19 halamanCase Otitis Eksterna - UtiAyu AndrianBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Gigi FINALDokumen109 halamanTugas Gigi FINALdedefreddyBelum ada peringkat
- Polip HidungDokumen6 halamanPolip HidungdedefreddyBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Kasus BronkopneumoniaDokumen12 halamanLaporan Kasus BronkopneumoniadedefreddyBelum ada peringkat
- Demam RuamDokumen2 halamanDemam RuamdedefreddyBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Kasus DengueDokumen14 halamanLaporan Kasus DenguededefreddyBelum ada peringkat
- LabirinitisDokumen6 halamanLabirinitisdedefreddyBelum ada peringkat
- LabirinitisDokumen6 halamanLabirinitisdedefreddyBelum ada peringkat
- Katarak SenilisDokumen18 halamanKatarak SenilisifahafniBelum ada peringkat
- Katarak SenilisDokumen18 halamanKatarak SenilisifahafniBelum ada peringkat
- Serumen PropDokumen4 halamanSerumen Propdedefreddy100% (1)
- PEDIKULOSIS Kapitis, Korporis, PubisDokumen17 halamanPEDIKULOSIS Kapitis, Korporis, PubisdedefreddyBelum ada peringkat
- Pedikulosis PubisDokumen11 halamanPedikulosis PubisdedefreddyBelum ada peringkat
- Kriteria Pasien Masuk ICUDokumen32 halamanKriteria Pasien Masuk ICUdedefreddyBelum ada peringkat