Strategi Metakoknitif Simpulan
Diunggah oleh
Endiah Dwi Rahayu Astuti0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
33 tayangan10 halamanstrategi belajar metakoknitif
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inistrategi belajar metakoknitif
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
33 tayangan10 halamanStrategi Metakoknitif Simpulan
Diunggah oleh
Endiah Dwi Rahayu Astutistrategi belajar metakoknitif
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 10
METACOGNITIVE READING STRATEGY
ENHANCING ENGLISH READING
COMPREHENSION
WARDAH
Penulis adalah Pengajar IAIN Pontianak,
Fakultas Tarbiyah & Ilmu Keguruan, Jurusan Pendidikan Agama Islam
ABSTRACT
Strategi metakognitif peserta didik dapat mengatur, merencanakan, dan mengevaluasi
pembelajaran mereka sendiri. Strategi metakognitif yang digunakan untuk mengkoordinasikan
proses pembelajaran. Strategi juga melibatkan berpikir tentang belajar, memantau pemikiran,
dan mengevaluasi pemahaman dalam membaca. Dalam jurnal ini membahas tentang prosedur
Strategi Metakognitif dalam Membaca untuk memahami bacaan. Strategi metakognitif
meningkatkan konstruksi makna bacaan pembaca, memantau teks dan pemahaman bacaan,
dan kemampuan mereka untuk mengevaluasi teks yang mereka baca. Kerangka membaca
metakognitif ini harus akrab bagi pengajar yang mengintegrasikan proses sebelum membaca,
pada saat membaca, dan setelah membaca pada proses ketika mengajar peserta didik strategi
pemahaman yang efektif. Strategi Metakognitif dalam membaca membantu peserta didik
untuk memantau pemikiran mereka saat membaca. Strategi Metakognitif membantu peserta
didik untuk menjadi pembelajar mandiri. Pengajar secara teratur menggunakan strategi
membaca metakognitif dengan peserta didik mereka, dan berharap mereka untuk juga
menggunakannya secara independen. Pengajar didorong untuk menggunakan model strategi
metakognitif, mendukung siswa karena mereka belajar bagaimana menggunakannya, dan
kemudian mendukung peserta didik belajar bagaimana menggunakannya secara mandiri.
Dalam makalah ini menunjukkan bahwa strategi metakognitif membantu peserta didik untuk
menggunakan strategi yang tepat dalam memecahkan masalah dalam membaca. Strategi
metakognitif membantu siswa untuk menghentikan ketergantungan mereka menggunakan
kamus. Strategi ini membantu peserta didik untuk menemukan gagasan utama, informasi
tersirat, informasi tersurat, referensi, dan makna kata-kata.
Kata kunci: strategi metakognitif, membaca, peserta didik
_____________________________
INTRODUCTION Reading can be used by the English teacher
Reading as an activity that involves as a media to teach other language skills
the reader, the text, to get information such as listening, speaking, and writing and
through written text, and build the meaning also language elements such as vocabulary,
based on the reader’s prior knowledge is pronunciation, and grammar. According to
important to be learned and mastered by Nunan (2003: 68), reading is a fluent
every learner. Reading is important skill for process of readers combining information
students, because the students must able to from a text and their own background
read and understand an English text. knowledge to build meaning. Meaning does
not rest in the reader nor does it rest in text. students what to do. Teachers need more
The reader’s background knowledge than classroom and techniques to be success
integrates with the text to create the in reading class. Furthermore, Aebersold
meaning. Furthermore, Nunan (2003: 68) and Field (1997: 95) explain that becoming
defines reading as being composed of four better readers, students need to become
elements; those are the text, the reader, aware of how they are reading and what
fluency, and strategies. Meanwhile, they could do to improve comprehension.
Aebersold and Field (1997: 15) say that They need to develop their level of
reading is what happens when people look metacognitive awareness. According to
at a text and assign meaning to the written them, the term metacognitive comes from
symbols in that text. It not only deals with the field of cognitive psychology and it is
word interpretation, but also how reader increasingly used in language teaching and
interprets the intended meaning. In addition, learning.
reading as a process of readers combining Meta means after or behind, and
information from a text and their own cognition means the act or process of
background knowledge to building knowing perception. Metacognition is the
meaning. understanding what is behind, what
Reading is receptive skill which supports or informs, readers’ knowledge
means it involves responding to text, rather and perception. As teachers, the have to
than producing it. It involves making sense help their students use every possible
of text by understanding the language of the strategy and ability available to them during
text (at word level, sentence level, and the act of reading. In order to do that,
whole text level), and connecting the teachers need to understand reading
message of the text to background behavior as thoroughly as possible.
knowledge. Understanding the language of Teachers observe and encourage the process
the text will lead reader to understand the of students’ learning as it occurs during
connections between sentences (coherence class time, and the teachers evaluate
and cohesion) in different text types simultaneously the products of students’
depending on what is read and for what learning when students speak and respond.
reason. Furthermore, reading is a mental, or In achieving the standard of
cognitive, process which involves a reader competency in reading skill, teachers and
in trying to follow and respond to a students should involve the teaching and
message from a writer who is distant in learning process. The aim of teaching
space and time. In summary, reading is a reading is developing the students’ reading
thinking process that enables reader to skill so that they can read English text
comprehend the meaning of a text trough comprehensibly, efficiently, and effectively.
connecting to background knowledge, From the principles and teaching reading
understanding the connections between above, it can be concluded that both
sentences (coherence and cohesion), teachers and students should develop
understanding different text types, and reading instructional activities which
applying the appropriate reading skill. accommodate the students’ activities when
The quality of the individual reading independently. In other reason, the
teacher is integral to success of foreign goal of reading is comprehension.
language readers. Reading teacher need to Comprehension is ability to
be passionate about their work. They should understand/generate meaning of text or to
view themselves as facilitators, helping connect the message of the text to
each reader discover what works best. The background knowledge. Comprehension is
good reading teacher actively teaches the reason for reading, and vocabulary
plays a significant role in comprehension. your brain is actively building connections
To be able to comprehend a text, reader between the words and meaning of the
must use appropriate reading skills. passage or text. According to Anderson
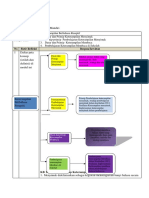
According to Snow (2002: 11), he defines (2002:365), metacognition combines
reading comprehension as the process of various attended thinking and reflective
simultaneously extracting and constructing processes. His division has five primary
meaning through interaction and components: (1) preparing and planning for
involvement with written language. It can learning; (2) selecting and using learning
be used the words extracting and strategies; (3) monitoring strategy use; (4)
constructing to emphasize both the orchestrating various strategies; (5)
importance and the insufficiency of the text evaluating strategy use and learning. It
as a determinant of reading comprehension. shows in the following figure:
She says that there are three elements taking
a part in the process; the reader who is Figure 1. Anderson’s Concept of
doing the comprehension, the text is to be Metacognition
comprehended, and the activity in which
comprehension is a part.
Furthermore, reading Preparing Selecting Monitoring Orchestra Evaluating
Strategy use:
comprehension means extracting the and
Planning
and Using
Learning
Strategy
Use
ting
Strategies Is there
required information from a written text as for
Learning
Strategies comprehension
?
efficiently as possible, rejecting irrelevant
information and finding what we are
looking for, quickly. She establishes that
there are two main reasons for us to read, Adult learning theory emphasizes the
first one is for pleasure and the second one importance of connecting new information
is for information. This is the fact that to the existing knowledge base, so this is an
working with a text as if it was a series of important aspect in discussing
independent units would only lead students metacognition in adults. Similar to Flavell,
to feel the need of understanding every Paris and Parecki segment metacognition
single sentence, which is not necessary in into self-appraisal and self-management.
order to fulfill the purpose of understanding Self-appraisal of the cognitive process
the text and to be reluctant to infer includes three types of knowledge:
meanings of sentences from what comes declarative knowledge or what affects the
before or after them. So, in this paper will learning; procedural knowledge, or how the
elaborate about metacognitive reading strategies operate; and conditional
strategy enhancing English reading knowledge, which is the understanding of
comprehension. why and when to use strategies. Their self-
management is similar to Anderson’s,
CONTENT incorporating planning, evaluation and
In this part of paper explains about regulation.
the concept of metacognition and Metacognition plays an important
metacognitive reading strategy in reading role in reading comprehension. Research on
comprehension. metacognition has revealed that less
a. The Concept of Metacognition proficient learners do not recognize the
Metacognition is actively thinking purpose of reading and tend to focus on
about what you are reading, as you are word-byword reading rather than reading
reading. Or another way to look at it is that for meaning. Poor readers often finish
as you are reading something mechanically, reading passages without even knowing that
they have not understood them. Also, poor b. Metacognitive Reading Strategy in
readers are less able to adjust their reading Reading Comprehension
rate to suit the purpose of reading. When Metacognitive is a key for success
they fail to comprehend the test, poor in reading. The purpose of metacognitive
readers are not as flexible as good readers instruction is to help readers become more
in utilizing different strategies to solve the aware of their own thinking during the
problem. Poor readers are less efficient in reading process. During instruction,
monitoring their understanding of the teachers provide explicit instruction on the
material read or are deficient in use of metacognitive reading strategies that
metacognitive skills. Furthermore, by students can employ while reading. Explicit
contrast, Pressley (2006:245) highlighted teaching of comprehension strategies begins
that good readers automatically employ with a teacher clearly explaining and
metacognitive strategies to focus their modeling the strategies, followed by
attention. It concluded that since discussion about when and how a reader
metacognitive strategies are potentially should apply the strategy while reading, and
conscious and potentially controllable, finally moving to provide scaffolded
learners with good metacognition are able student practice of the strategies during
to monitor and direct their own learning reading. Modeling strategies often occurs
processes quite efficiently, to derive through teacher think- aloud methods.
meaning, and to make adjustments when Through this instructional cycle, gradual
something goes wrong. transfer or release of responsibility from
Readers who have higher teacher to student is possible. Over time,
metacognitive skills are able to check for students gradually become able to
confusion or inconsistency, undertake a independently initiate and utilize that
corrective strategy, such as rereading, particular strategy. The cycle repeats with
relating different parts of the passage to one another strategy.
another, look for topic sentences or Theoretically, the strategies
summary paragraphs, and relating the specific to reading can be classified in the
current information to their past knowledge. following three clusters of metacognition:
The readers do not label these skills while (1) planning; (2) monitoring; and (3)
performing them but if asked, they can evaluating strategies (Israel, 2007:436).
describe their metacognitive processes Planning strategies are used before reading;
accurately. They have a conscious activating learners’ background knowledge
awareness of their own knowledge and the to get prepared for reading is an example of
conscious ability to understand, control, and planning strategies. Also, previewing a title,
manipulate their own cognitive processes. picture, illustration, heading, or subheading
One of the researches was conducted by can help readers grasp the overview of the
Duffy (2009:691) concerned with the text. Readers may also preview the general
findings. He looked for alternatives to the information in the text and its structure.
directed reading lesson that would afford Learners may check whether their reading
greater opportunities for students to develop material has a certain text structure, such as
independent reading comprehension cause and effect, question and answer, and
abilities. The result of this research compare and contrast. Further, setting the
identified metacognition as a way to purpose for reading can also be categorized
understand reading comprehension and as as a planning strategy.
an approach to comprehension instruction. Monitoring strategies occur during
reading. Some examples of monitoring
strategies are comprehension of vocabulary,
self-questioning (reflecting on whether they knowledge/understanding of the subject; (5)
understood what they have read so far), searching according to the goals: I search
summarizing, and inferring the main idea of out information relevant to my reading
each paragraph (Israel, 2007:450). Readers goals;(6) reading goals: I evaluate whether
may also identify and focus on key what I am reading is relevant to my reading
information or key words, including: (1) goals; (7) distinguishing: As I am reading, I
but; (2) however; (3) on the other hand; (4) distinguish between information that I
in addition; (5) also; and (6) in conclusion. already know and new information; (8)
Determining which part of the passage can deciding on the difficulty: I note how hard
be emphasized or ignored based on the or easy a text is to read; (9) revising: While
purpose of the task is another monitoring I am reading, I reconsider and revise my
strategy. prior questions about the topic, based on the
Evaluating strategies are employed text’s content; (10) guessing the later
after reading. For example, after reading a topics: I anticipate information that will be
text, learners may think about how to apply presented later in the text.
what they have read to other situations. Metacognitive strategies increase
They may identify with the author, a readers’ meaning construction, monitoring
narrative, or main character, and may have of text and reading comprehension, and
a better perspective of the situation in the their ability to evaluate the text they are
book than they did at first. Besides, reading. This metacognitive reading
Metacognitive reading strategies consisted framework should be familiar to teachers
of the following: (1) setting goals for who integrate before, during, and after
reading; (2) previewing a book before reading processes when teaching students
reading; (3) monitoring the appropriateness effective comprehension strategies
of the textbook for the purpose; (4) (Pressley, 2006:564). In summary,
identifying text structure; (5) determining metacognitive reading strategies are
important information in the textbook; (6) classified into three groups of planning
utilizing supplemental features (such as (pre-reading), monitoring (during reading),
tables); (7) using cue words and and evaluating (post-reading) strategies, and
typographical support (e.g., italics); (8) each group has a variety of strategies that
inferring; and (9) confirming predictions. require readers’ metacognitive processing.
Metacognitive strategy is the strategies
which were taught are: (1) using strengths: 1) Planning Strategies
While reading, I exploit my personal Planning strategies are
strengths in order to better understand the metacognitive strategies that the reader does
text. If I am a good reader, I focus on the early on in the reading process (before
text; if I am good at figures and diagrams, I reading) to increase reading comprehension.
focus on that information; (2) inferring The following planning strategies are
meaning (through word analysis or other utilized by metacognitive readers before
strategies): While I am reading, I try to reading: (1) activating prior knowledge; (2)
determine the meaning of unknown words overviewing information in the text; (3)
that seem critical to the meaning of the text. relating text to text; and (4) relating text to
(3) using background information: While I self.
am reading, I reconsider and revise my 2) Monitoring Strategies
background knowledge about the topic, Monitoring strategies—usually
based on the text’s content; (4) evaluating: occurring during the reading of a text help
As I am reading, I evaluate the text to the reader pay attention to meaning
determine whether it contributes to my construction as well as correct breakdowns
in comprehension. The following Oriented Reading Instruction, there is phase
monitoring strategies are utilized by 1. First, the teacher introduced about
metacognitive readers during reading: (1) Metacognitive Reading Strategy. After
determining word meaning; (2) questioning; being first introduced to a strategy, students
(3) reflecting, (4) monitoring; are not yet able to use it spontaneously.
(5) summarizing; and (6) looking for Second, the teacher repeated modeling of
important information. strategy for students through think aloud for
3) Evaluating Strategies example. One way to teach metacognition is
Evaluation strategies used after through teacher modeling using a think-
reading that allow the reader to think aloud process. The teacher reads the
critically about the text and make a passage and simultaneously verbalizes the
cognitive or affective judgment. The thinking process occurring. The helps the
following evaluating strategies are utilized students see that there are certain
by metacognitive readers after reading: (1) considerations that all readers need to make
thinking like the author; (2) evaluating the during the reading process. After modeling,
text; (3) anticipating use of knowledge; (4) students can be given a passage to read, but
monitoring for meaning, knowing when you with the task of thinking about the strategies
know, knowing when you don’t know; they are using to understand its content. A
(5) using and creating schema, making class discussion could follow where
connections between the new and the students share their own techniques and
known, building and activating background discoveries. This debriefing of the thinking
knowledge; (6) asking questions, generating process can regularly be incorporated into
questions before, during, and after reading the activities around the reading lesson.
that lead you deeper into the text; (7) Beyond helping the students
determining importance, deciding what practice thinking about their thinking, it can
matters most, what is worth remembering; assist the teacher on a diagnostic level
(8) inferring, combining background regarding problematic areas for individual
knowledge with information from the text students. Teaching how to think is very
to predict, conclude, make judgments, different that teaching students what to
interpret; (9) using sensory and emotional think. There are a variety of techniques that
images, creating mental images to deepen can help. One is to give the students a
and stretch meaning; and (10) synthesizing- variety of questioning techniques prior to
creating an evolution of meaning by the reading to set purpose as well as to
combining understanding with knowledge assess comprehension afterwards.
from other texts/sources. Questions like: (1) what is the main idea of
Metacognitive strategies learners this selection?; (2) how many supporting
can organize, plan, and evaluate their own details are there?; (3) what are the
learning. Metacognitive strategies are used supporting details; and (4) are there
to coordinate the learning process. examples to help clarify the main idea?.
Strategies also involve thinking about Before having a pre test, the teacher gave a
learning, monitoring one’s own production, questionnaire from the expert about
and evaluating comprehension. In this cognitive and metacognitive strategy to
research the researcher focused on the reveal students’ metacognitive awareness.
procedure of MRS for reading After having pre test, the students review
comprehension. The procedure of their reading strategies by answering some
Metacognitive Reading Strategy happened questions, such as:
in the class to overcome the problem
indicators. In the phase of Metacognitively
1. What sort of strategy that you have 1. Do I think about what I am reading?
used to understand the reading 2. Do I pause or stop sometimes and ask
passage? myself whether I understand the
2. How can you grasp the main idea in reading or not what I have read about
reading passage? so far? Do I picture in my mind the
3. What do you do well as a reader in people, places, and events I am reading
comprehending reading passage? about?
4. Do you have sort of specific strategy 3. Do I imagine that I am talking with the
in comprehending reading? author while I am reading?
5. What do you do before start 4. Do I consider some options when I am
reading? trying to answer the questions that I
6. What do you do while you are have asked before reading?
reading to get more idea of 5. Do I need to review what I have read
understanding reading? in order to understand the reading?
7. What do you do when you come to a 6. Do I analyze the content of reading
word you don’t understand? already?
8. When you come to a part of the text 7. Do I translate the information that I
that is confusing, what do you do? have read in my own words?
9. After you finish reading, what do 8. Do I still keep myself on the track the
you do? reading?
In the process of metacognitive 9. Do I look for clues and try to figure it
reading strategy, teacher asked students to out?
share what they recall from the lessons on 10. Do I use a glossary or dictionary if I
background knowledge presented during the do not know the words, sentence, or
reading. There are 3 steps of MRS, such as passage?
Planning, Monitoring and Evaluating. The In the last strategy, students
process of planning, monitoring and generate some questions in order to do
evaluating assesses by using metacognitive evaluating and reviewing reading
awareness. In planning, students implement comprehension, such as:
monitoring metacognitive strategies by 1. Do I read the text again?
generating some questions to monitor their 2. Do I just keep reading?
understanding while reading by asking 3. Do I try to get help from pictures or
herself some questions, such as: drawings?
1. Do I read the title and headings? 4. Do I think about what I have read?
2. Do I look at the pictures? 5. Do I do something with the
3. Do I predict what the passage might be information that I have learned?
about? 6. Do I compare what I have just read
4. Do I ask myself what I already know with what I already knew?
about the topic?
5. Do I need to read this reading passage? Table 1. List of Activities to use
6. Do I need to use organizational structure MRS to enhance students’ reading
of text to help me understand this reading comprehension
passage? Activity Objectives
After planning strategy, students
1. Students To enrich their
generate some questions in order to do
were asked
evaluating and reviewing reading knowledge about the
to use prior
comprehension in monitoring strategy, such text
knowledge
as : Motivating students
to think
about the to read the text analyze the text easily
topic thoroughly main points
2. Students in each
read silently Helping students to paragraph.
and make 11. Students
keep concentration
notes about asking
in reading the text themselves
mind
Helping students to how this To get specific
pictures that
visualize what they information information from the
emerge from
read relates to the text
the words in
the texts information
3. Students use that came
clues to find Helping students to before
the main find main idea easily 12. Students
idea look for To get better
4. Students supporting understanding about
ideas and the text
scan the
details
familiar Helping students to
passage to 13. Students
understand the identify and To comprehend the
identify
passage record text organization
highlighted
words and signal words
phrases. 14. Students use
the signal
5. Students To note the main To comprehend the
underline words as
information from the clues to find text organization
and make
text the meaning
highlighting
of the text
6. Students To find specific
15. Students
note key words for better
identify key
words from understanding in
words To find specific
the text reading the text
(nouns and information from the
7. Students verbs) found
guess To find specific text
within a
unknown words single
words sentence
8. Students use 16. Students
titles to infer To get main point identify key
what words To find specific
from the text
information (nouns, information from the
might follow verbs, and text
9. Students adjectives)
analyze the in a single
key words in To get the main paragraph
the first 17. Students
topic of the text To comprehend the
sentences of recall what
the they already text
paragraphs know about
10. Students To understand the
the topic or reading. This metacognitive reading
concept framework should be familiar to teachers
18. Students To get better who integrate before-, during-, and after
reread for understanding about reading processes when teaching students
getting the text effective comprehension strategies. MRS
meaning helps students to monitor their thinking
19. Students use To get better while reading. MRS helps students to be
context and understanding about independent learner. Teachers regularly use
clues for the text metacognitive reading strategies with their
hints students, expecting students to also use
them independently, which may or may not
The table above states that the be the case. Teachers are encouraged to
example of list the activities to use model metacognitive strategies, supporting
metacognitive reading strategy to enhance students as they learn how to use them, and
students’ reading comprehension. then reducing that support as students learn
how to use them independently. In this
CONCLUSION research showed that MRS helps the
In conclusion, it is important for students to use appropriate strategies in
teachers to understand the suitable method solving their reading problems. MRS helps
to improve the students’ motivation in students to stop their dependency of using
learning reading because it is the key of dictionary. MRS helps students to find main
success in teaching learning process. The idea, implicit information, explicit
use of MRS has proven to be an appropriate information, reference, and meaning of
strategy in teaching learning reading words.
comprehension.. So teachers can use this
strategy in their class. Before implementing BIBLIOGRAPHY
the strategy, teachers should explain how to Aebersold, J. & Field M. (1997). From
do the steps clearly. The teachers must Reader to Reading Teacher.
guide the students patiently. Explain one by Cambridge: Cambridge University
one the steps and the activities that can help Press.
students to find main idea, explicit
information, implicit information, reference Anderson, N. J. (2002). The role of
and meaning of words. The students should metacognition in second language
have a great motivation in learning English. teaching and learning. ERIC
They must change their mind that reading
comprehension is not difficult. Students Duffy, Gerald G. (2009). Explaining
have to realize that understanding reading Reading: A Resource Four Teaching
text needs a good and appropriate strategy. Concepts, Skills, and Strategies.
When the students apply a good and New York:The Guildford Press.
appropriate strategy, the process of
understanding the reading text will be Israel, S. E. (2007). Using metacognitive
easier. The students can use MRS as a assessments to create individualized
strategy that can be applied to comprehend reading instruction. Newark, DE:
reading comprehension. International Reading Association.
Metacognitive strategies increase
readers’ meaning construction, monitoring Nunan, David. (2003). Language Teaching
of text and reading comprehension, and Methodology. London: Prentice Hall
their ability to evaluate the text they are International.
Pressley, M. (2006). Reading Instruction
That Works: The Case for Balanced
Teaching. New York: Guilford.
Snow, Catherine. (2002).
Reading for
Understanding: Toward an R&D
Program in Reading
Comprehension. Los Angeles:
RAND
Bodrova, E. & Leong, L. J. Tools of the
Mind: A Vygotskian approach to
earlychildhood education.
Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Merrill
Publishing Company. 1996
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Buku Pedoman Guru SMK Bahasa InggrisDokumen31 halamanBuku Pedoman Guru SMK Bahasa InggrisMia Asmiati100% (3)
- Metacognitive Reading Strategy Enhancing English Reading ComprehensionDokumen10 halamanMetacognitive Reading Strategy Enhancing English Reading ComprehensionBuhariBelum ada peringkat
- Kemampuan Efektif MembacaDokumen10 halamanKemampuan Efektif MembacaasriwperBelum ada peringkat
- Rangkuman Materi Literasi Bahasa Dan Sastra IndonesiaDokumen17 halamanRangkuman Materi Literasi Bahasa Dan Sastra Indonesiairma yani100% (1)
- Penerapan Cognitive Strategy Pada Pembelajaran Bahasa InggrisDokumen4 halamanPenerapan Cognitive Strategy Pada Pembelajaran Bahasa InggrisernaBelum ada peringkat
- S - BHS A - KDSERANG - 1103957 - Chapter2Dokumen13 halamanS - BHS A - KDSERANG - 1103957 - Chapter2Helmi Tri RahmawatiBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Strategi Pembalajaran Bahasa IndonesiaDokumen9 halamanMakalah Strategi Pembalajaran Bahasa Indonesiazahra KhumayraBelum ada peringkat
- Kelompok 4 - CJR PbsiDokumen22 halamanKelompok 4 - CJR PbsiKristin DeviBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 6 (Bacaan Intensif Dan Berfokus)Dokumen9 halamanUnit 6 (Bacaan Intensif Dan Berfokus)Emy ShafinazBelum ada peringkat
- Dian Bahasa 2Dokumen16 halamanDian Bahasa 2fadly021284Belum ada peringkat
- 2018 Mochlis Keterampilan Membaca 3Dokumen8 halaman2018 Mochlis Keterampilan Membaca 3Dwi Maharani PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan KemajuanDokumen11 halamanLaporan Kemajuanrini trinovitaBelum ada peringkat
- Phreaking Mass DelopDokumen11 halamanPhreaking Mass DelopWitya Chairinda SitorusBelum ada peringkat
- Keterampilan Membaca Kelompok 4Dokumen11 halamanKeterampilan Membaca Kelompok 4lusti lestariBelum ada peringkat
- Rangkuman Materi Pendekatan Pembelajaran Bahasa Indonesia SDDokumen4 halamanRangkuman Materi Pendekatan Pembelajaran Bahasa Indonesia SDririnBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas PPT Bahasa IndonesiaDokumen13 halamanTugas PPT Bahasa IndonesiaAlisa MaharaniBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 1-5Dokumen65 halamanBab 1-5Tri AdiBelum ada peringkat
- Strategi PembelajaranDokumen11 halamanStrategi PembelajaranSemester1BSararateoli telaumabanuaBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Bahasa IndonesiaDokumen17 halamanMakalah Bahasa IndonesiaSulfina SufyaBelum ada peringkat
- Strategi Pembelajaran Bahasa Indonesia Di Erakurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP)Dokumen7 halamanStrategi Pembelajaran Bahasa Indonesia Di Erakurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP)Rotua TambunanBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal ThievesDokumen6 halamanJurnal ThievesFarikha UlyBelum ada peringkat
- Strategi Pembelajaran BahasaDokumen8 halamanStrategi Pembelajaran BahasaSabita QomariaBelum ada peringkat
- Upload Proposal PDP 2020Dokumen9 halamanUpload Proposal PDP 2020miptakohlBelum ada peringkat
- 193-Article Text-468-1-10-20220930Dokumen12 halaman193-Article Text-468-1-10-20220930kaitani RikuBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Strategi Dan Metode PBIDokumen17 halamanMakalah Strategi Dan Metode PBIRidwan AnasBelum ada peringkat
- Subunit 2 Pembelajaran Berbahasa TulisDokumen7 halamanSubunit 2 Pembelajaran Berbahasa TulisEkhy XboyzBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah B.Indo IIDokumen10 halamanMakalah B.Indo IINuri IsmailBelum ada peringkat
- 37146-Article Text-54157-1-10-20210212Dokumen8 halaman37146-Article Text-54157-1-10-20210212Nada NadiaBelum ada peringkat
- 77 153 1 SMDokumen17 halaman77 153 1 SMSurita UngalesiBelum ada peringkat
- BAB II Poster Comment REVISIIDokumen28 halamanBAB II Poster Comment REVISIISitimaemunahazahra MaemunahazahraBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Tentang Strategi Pembelajaran Membaca Di Kelas TinggiDokumen20 halamanMakalah Tentang Strategi Pembelajaran Membaca Di Kelas TinggiHANAFI ARYONOBelum ada peringkat
- 1 PBDokumen8 halaman1 PBalimsumarnoBelum ada peringkat
- PENDIDIKAN DASAR K12 Psikologi PendidikanDokumen15 halamanPENDIDIKAN DASAR K12 Psikologi Pendidikanlanisaf ieBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Writing by Using Ripple Writing Strategy On Students Writing AchievementDokumen5 halamanTeaching Writing by Using Ripple Writing Strategy On Students Writing AchievementAsmaaBelum ada peringkat
- Bab 1 - 2 KooperatifDokumen22 halamanBab 1 - 2 KooperatifOff JumpolBelum ada peringkat
- UTS Lintas Literasi Dalam Lintas Mata Pelajaran Ivon Bella SukmaDokumen17 halamanUTS Lintas Literasi Dalam Lintas Mata Pelajaran Ivon Bella SukmaIvon Bella Sukma S.S.Belum ada peringkat
- PEMBELAJARANDokumen17 halamanPEMBELAJARANWiguna Putrasimpang GunawanBelum ada peringkat
- Literasi MapelDokumen15 halamanLiterasi MapelWahdiatin FirdaBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Kampus - MAKALAH STRATEGI PEMBELAJARAN HADIST153856Dokumen16 halamanMakalah Kampus - MAKALAH STRATEGI PEMBELAJARAN HADIST153856Azwa zuna ShalihaBelum ada peringkat
- Materi Modul 1 Hakikat Bahasa Dan PembelajaranDokumen10 halamanMateri Modul 1 Hakikat Bahasa Dan PembelajaranmastariBelum ada peringkat
- Ratna Sari Dewi-FitkDokumen9 halamanRatna Sari Dewi-FitkYulanda Mila Marcella PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal 3 PDFDokumen6 halamanJurnal 3 PDFAnnisa DielavyBelum ada peringkat
- Modul 4Dokumen5 halamanModul 4Anggun SetianaBelum ada peringkat
- Artikel Jurnal Metode SkimmingDokumen10 halamanArtikel Jurnal Metode SkimmingEkanita RakhmahBelum ada peringkat
- Literasi Lintas Mata Pelajaran - Jurnal Refleksi - Lintang Mutiara PutriDokumen5 halamanLiterasi Lintas Mata Pelajaran - Jurnal Refleksi - Lintang Mutiara PutriLintang Mutiara PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Strategi Membaca Text Bahasa KeduaDokumen130 halamanStrategi Membaca Text Bahasa KeduaDedi JasrialBelum ada peringkat
- 06tugas Aplikom Daffa HusniDokumen7 halaman06tugas Aplikom Daffa HusniRoni SabirinBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Strategi Pembelajaran PAIDokumen7 halamanMakalah Strategi Pembelajaran PAIzulfikrriiBelum ada peringkat
- 3155 8002 2 PBDokumen8 halaman3155 8002 2 PBLia Lia SafitriBelum ada peringkat
- Baiq Faizatul Rodiah - 190102039Dokumen26 halamanBaiq Faizatul Rodiah - 190102039Rosmiatun ApriliaBelum ada peringkat
- CLEDokumen10 halamanCLENana SuraiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Peningkatan Ket. Bhs TulisDokumen15 halamanPeningkatan Ket. Bhs TulisNurmin Sari Aminah 062Belum ada peringkat
- Keterampilan Berbahasa Indonesia Kode pdgk4101 Modul 8Dokumen5 halamanKeterampilan Berbahasa Indonesia Kode pdgk4101 Modul 8Arlia Septiani MutiaBelum ada peringkat
- LK - SDN 104201 KolamDokumen12 halamanLK - SDN 104201 KolamEVA LEVIABelum ada peringkat
- Strategi Pembelajaran MembacaDokumen3 halamanStrategi Pembelajaran MembacaAduh HaayBelum ada peringkat
- Proposal PTKDokumen21 halamanProposal PTKDina Ahsanta PuriBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Pengertian Strategi, Model, Pendekatan, Metode, Dan TeknikDokumen22 halamanMakalah Pengertian Strategi, Model, Pendekatan, Metode, Dan TeknikAmelia MaweikereBelum ada peringkat
- PSIKOLOGI PERKEMBANGAN ANAK DAN DISTURBILITAS PADA USIA EVOLUTIF: Apa itu dan bagaimana cara kerjanyaDari EverandPSIKOLOGI PERKEMBANGAN ANAK DAN DISTURBILITAS PADA USIA EVOLUTIF: Apa itu dan bagaimana cara kerjanyaBelum ada peringkat
- PSIKOLOGI, DEPRESI DAN DISTURBILITAS HUMOR: Memahami mekanisme dasarDari EverandPSIKOLOGI, DEPRESI DAN DISTURBILITAS HUMOR: Memahami mekanisme dasarPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (3)